Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Bonding 2 Answers
Uploaded by
satya176Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Bonding 2 Answers
Uploaded by
satya176Copyright:
Available Formats
CBSE TEST PAPER-02 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure) Topic: - Ionic Bonding (ANSWERS)
Ans1.
An ionic bond (or electrovalent bond) is formed by a complete transfer of one of outer most electrons from the atom of a metal to that of a non metal.
Ans2.
Due to the electron transfer the following changes occurs (i) (ii) (iii) Both the atoms acquire stable noble gas configuration. The atom that loses electrons becomes +vely charged called cation whereas that gains electrons becomes vely charged called anion. Cation and anion are held together by the coulombic forces of attraction to form an ionic bond.
Ans3.
Ionic bond formation mainly depends upon three factors (i) (ii) (iii) Low ionization energy elements with low ionization enthalpy have greater tendency to form an ionic bonds. High electron gain enthalpy high negative value of electron gain enthalpy favours ionic bond. Lattice energy high lattice energy value favours ionic bond formation.
Ans4. Ans5. Ans6.
N2 has the highest bond order. Bond order is defined as number of bonds between two atoms in a molecule. In H2- ion, one electron is present in anti bonding orbital due to which destabilizing effect is more and thus the stability is less than that of H2+ ion.
Ans7. Ans8. Ans9. Ans10.
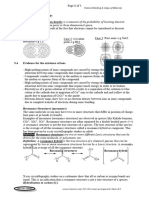
The order of bond lengths in C2 , C2- and C22- is C2 > C2- > C22-. Electrovalent or ionic bond. Covalent bond. The covalent radius is measured approximately as the radius of an atoms core which is in contact with the core of an adjacent atom in a bonded situation.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Narayana PDFDocument35 pagesChemical Bonding Narayana PDFggk201390% (10)
- Chemical Bonding - Study NotesDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding - Study NotesTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument44 pagesChemical Bondingjas_ong_man_ling1996No ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond Typesapi-287081563No ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Handout Chapter 4Document17 pages11 Chemistry Handout Chapter 4Erreneo100% (1)
- Bonding Ionic CovalentDocument30 pagesBonding Ionic CovalentRaul MejiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding theories-SectionH-S Chatterjee PDFDocument110 pagesChemical Bonding theories-SectionH-S Chatterjee PDFAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondingDocument80 pagesAtomic BondingChan Chan M100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFDocument56 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFAbhishek AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4Document33 pagesChemistry 4Ridwan MugdhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE - 033838Document26 pagesUnit 4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE - 033838Gautam SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Hemical Onding: Saman Kotigala BSC MSCDocument24 pagesHemical Onding: Saman Kotigala BSC MSCSaman Bharatha Kotigala100% (1)
- Chemistry: The Central Science: 8.S: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding (Summary)Document6 pagesChemistry: The Central Science: 8.S: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding (Summary)Harshal BandkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- Q2 W4 Ionic BondingDocument30 pagesQ2 W4 Ionic BondingMARY JOY PIOSCANo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING - NotesDocument30 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING - NotesP YNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument26 pagesChemical BondingShannelle Anne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument132 pagesChemical BondingKowser mahmud100% (1)
- Bonding and Structure PDFDocument14 pagesBonding and Structure PDFWandaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Chapt 2 Part 2&3 cmt352Document20 pagesChapt 2 Part 2&3 cmt352Siti Zulaika Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Ib PPT 4 SL PDFDocument103 pagesIb PPT 4 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument81 pagesChemical BondingkhushiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Document9 pagesEngineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Nivetha ENo ratings yet
- PHSC GR 11 REVISION DOCUMENT APRIL 2022 Collated Final Final PDFDocument66 pagesPHSC GR 11 REVISION DOCUMENT APRIL 2022 Collated Final Final PDFPhilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Chemical BondingDe AktivedNo ratings yet
- CB 1Document4 pagesCB 1Mahmudur Rahman27No ratings yet
- downloadChemistryA levelNotesEdexcel IALUnit 1Detailed3.20Bonding20and20StructureDocument14 pagesdownloadChemistryA levelNotesEdexcel IALUnit 1Detailed3.20Bonding20and20Structurelaksandy360No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: (A Step Towards Smart Education)Document33 pagesChemical Bonding: (A Step Towards Smart Education)RANJEET SHARMANo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument20 pagesChemical BondsAnbarin ParisaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument46 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingHendri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Che101 - Module I - Part 1Document14 pagesChe101 - Module I - Part 1Gautam SangeethNo ratings yet
- Chap2 2012Document26 pagesChap2 2012Roh KyoungjunNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document36 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?aditya_2013No ratings yet
- XI CH 4 Chemistry Notes by AkDocument19 pagesXI CH 4 Chemistry Notes by AkappugmenonNo ratings yet
- C15 Notes CH4 Chemical BondsDocument16 pagesC15 Notes CH4 Chemical BondsArnieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Atomic Structure and Inter-Atomic Bonding BiomaterialsDocument24 pagesLecture 02 Atomic Structure and Inter-Atomic Bonding BiomaterialsAbdallah ShaatNo ratings yet
- CHM 112 Aspect Note-Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesCHM 112 Aspect Note-Chemical BondingOluwatosin KoyejoNo ratings yet
- 1.3. BondingDocument10 pages1.3. BondingdodoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Class11th by PS Sir IIT JEEDocument44 pagesChemical Bonding Class11th by PS Sir IIT JEEMahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentDocument131 pages2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentanathinothandoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Document70 pagesEngineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Abdul Rauf ChNo ratings yet
- Bonding & Shapes of Mol - CN - STDT2Document3 pagesBonding & Shapes of Mol - CN - STDT2NkemziNo ratings yet
- Unit IV PPT - Chemical BondingDocument68 pagesUnit IV PPT - Chemical BondingYash TajaneNo ratings yet
- Article (Bonding&Structure)Document3 pagesArticle (Bonding&Structure)Fawzan Fahad MDNo ratings yet
- Review of IB Chem Topics 4 and 14Document10 pagesReview of IB Chem Topics 4 and 14coolpianocatNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument18 pagesChemical BondingJade GumonayNo ratings yet
- Q and A MetalsDocument3 pagesQ and A Metalsysaaa. rbNo ratings yet
- Islamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesIslamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyRayhanuzzaman ShazibNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 11 Unit 3: By: Addis Ababa Education Bureau APRIL 2020Document22 pagesChemistry Grade 11 Unit 3: By: Addis Ababa Education Bureau APRIL 2020Abdi sunNo ratings yet
- W2 - SE1 - Energy Bands and Charge CarriersDocument46 pagesW2 - SE1 - Energy Bands and Charge Carrierswjsdnwjd9219No ratings yet
- MSE 250: Structure and Properties of Materials: 2. Atomic Structure & Atomic BondingDocument25 pagesMSE 250: Structure and Properties of Materials: 2. Atomic Structure & Atomic BondingdubdubNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocument11 pagesPeriodic Table and Periodicityakeemoluwadamilare623No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument52 pagesChemical BondingMohammed ZakeeNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Notes-Anil-Ch-4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Notes-Anil-Ch-4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRihab ShehzeenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 06Document2 pages11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 06satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Test 03Document1 page11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Test 03satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 04Document2 pages11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 04satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Test 06Document1 page11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Test 06satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 05Document2 pages11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 05satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Test 04Document1 page11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Test 04satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 01Document2 pages11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 01satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Matter Test 04Document1 page11th Chemistry Matter Test 04satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 02Document2 pages11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Answer 02satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Test 02Document1 page11th Chemistry Atom Structure-Test 02satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Matter Test 05Document1 page11th Chemistry Matter Test 05satya176No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (States of Matter: Gases and Liquids) Topic: - Ideal Gas Equation (ANSWERS)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (States of Matter: Gases and Liquids) Topic: - Ideal Gas Equation (ANSWERS)satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Matter Answer 05Document1 page11th Chemistry Matter Answer 05satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Matter Test 01Document1 page11th Chemistry Matter Test 01satya176No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (States of Matter: Gases and Liquids) Topic: - Ideal Gas EquationDocument1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (States of Matter: Gases and Liquids) Topic: - Ideal Gas Equationsatya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Matter Answer 01Document1 page11th Chemistry Matter Answer 01satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Matter Answer 02Document2 pages11th Chemistry Matter Answer 02satya176No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties) Topic: - Miscellaneous QuestionsDocument1 pageCbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties) Topic: - Miscellaneous Questionssatya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Matter Test 02Document1 page11th Chemistry Matter Test 02satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Elements Test 04Document1 page11th Chemistry Elements Test 04satya176No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties) Topic: - Chemical Properties of Element (ANSWERS)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties) Topic: - Chemical Properties of Element (ANSWERS)satya176No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties) Topic: - Miscellaneous QuestionsDocument1 pageCbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties) Topic: - Miscellaneous Questionssatya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Elements Answer 01Document1 page11th Chemistry Elements Answer 01satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Elements Answer 02Document2 pages11th Chemistry Elements Answer 02satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Elements Classification Test 01Document1 page11th Chemistry Elements Classification Test 01satya176No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Elements Test 02Document1 page11th Chemistry Elements Test 02satya176No ratings yet