Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table of Laplace and Z Transforms
Uploaded by
Suvra PattanayakCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of Laplace and Z Transforms
Uploaded by
Suvra PattanayakCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of Laplace and Z Transforms
http://lpsa.swarthmore.edu/LaplaceZTable/LaplaceZFuncTable.html
Table of Laplace and Z Transforms
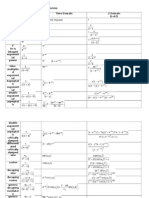
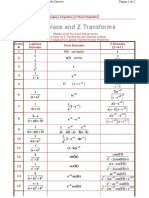
Laplace and Z Transforms Laplace Properties Z Xform Properties
Using this table for Z Transforms with Discrete Indices Shortened 2-page pdf of Laplace Transforms and Properties Shortened 2-page pdf of Z Transforms and Properties
All time domain functions are implicitly=0 for t<0 (i.e. they are multiplied by unit step).
Entry unit impulse unit step Laplace Domain Time Domain (note) Z Domain (t=kT)
unit impulse (note)
ramp
parabola
tn (n is integer)
exponential
power
time multiplied exponential
Asymptotic exponential
double exponential
asymptotic double exponential asymptotic critically damped differentiated critically damped
sine
cosine
decaying sine
decaying cosine
generic decaying oscillatory
generic decaying oscillatory (alternate)
(note)
Z-domain generic decaying oscillatory
1 of 2
2/2/2013 11:45 AM
Table of Laplace and Z Transforms
http://lpsa.swarthmore.edu/LaplaceZTable/LaplaceZFuncTable.html
(note)
Prototype Second Order System (<1, underdampded) Prototype 2nd order lowpass step response
Prototype 2nd order lowpass impulse response
Prototype 2nd order bandpass impulse response
Using this table for Z Transforms with discrete indices
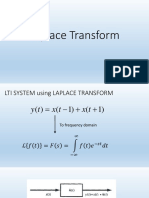
Commonly the "time domain" function is given in terms of a discrete index, k, rather than time. This is easily accommodated by the table. For example if you are given a function:
Since t=kT, simply replace k in the function definition by k=t/T. So, in this case,
and we can use the table entry for the ramp
The answer is then easily obtained
References
Copyright 2005-2013 Erik Cheever This page may be freely used for educational purposes. Comments? Questions? Suggestions? Corrections? Erik Cheever Department of Engineering Swarthmore College
2 of 2
2/2/2013 11:45 AM
You might also like
- Table of Laplace and Z TransformsDocument3 pagesTable of Laplace and Z TransformsfreonxzNo ratings yet
- Table of Laplace and Z TransformsDocument2 pagesTable of Laplace and Z Transformsvenkat0% (1)
- Table of Laplace and Z TransformsDocument4 pagesTable of Laplace and Z TransformsChristian BausoNo ratings yet
- Unit Impulse (Note) : Entry Laplace Domain Time Domain Z DomainDocument3 pagesUnit Impulse (Note) : Entry Laplace Domain Time Domain Z DomainEdgar LandryNo ratings yet
- Laplace ZTableDocument2 pagesLaplace ZTableomyssNo ratings yet
- App IIIcha 3Document123 pagesApp IIIcha 3Sena MekoninNo ratings yet
- Discrete Time DomainDocument28 pagesDiscrete Time DomainfurqanNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument9 pagesZ TransformKiran Googly JadhavNo ratings yet
- EEE321 - Digital Signal Processing - LAB 5Document6 pagesEEE321 - Digital Signal Processing - LAB 5Tâm NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Multi-Resolution Analysis (MRA)Document46 pagesMulti-Resolution Analysis (MRA)meenatchi5590No ratings yet
- DSP Unit 2Document14 pagesDSP Unit 2KARTHIGA MNo ratings yet
- Realization of Digital Filters: Z-TransformDocument8 pagesRealization of Digital Filters: Z-TransformsantoshNo ratings yet
- Lab 05-The Z Transform: Objectives: Time Required: 3 Hrs Programming Language: MATLAB Software RequiredDocument5 pagesLab 05-The Z Transform: Objectives: Time Required: 3 Hrs Programming Language: MATLAB Software RequiredAleena QureshiNo ratings yet
- Wavelets and MRADocument53 pagesWavelets and MRAkusuma nadimintiNo ratings yet
- PGT 205 Signals and SystemsDocument12 pagesPGT 205 Signals and SystemsioioiiNo ratings yet
- LT, DTFT, ZT (SC)Document21 pagesLT, DTFT, ZT (SC)Col. Jerome Carlo Magmanlac, ACPNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transforms - : ApplicationsDocument11 pagesLaplace Transforms - : ApplicationsgkuttamaNo ratings yet
- Signal and System Lecture 18Document18 pagesSignal and System Lecture 18ali_rehman87No ratings yet
- EEE443 Lect 7Document10 pagesEEE443 Lect 7Mikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document7 pagesLab 4shahzaibNo ratings yet
- Lab Report#5: Digital Signal Processing EEE-324Document11 pagesLab Report#5: Digital Signal Processing EEE-324Abdul BasitNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Transformasi-Z - TPID - 2022-UnlockedDocument23 pagesTopic 7 - Transformasi-Z - TPID - 2022-UnlockedWizdan DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Dynamic ResponseDocument78 pagesChapter 3: Dynamic ResponseAhmedSalahNo ratings yet
- U18EET5005-Digital Signal Processing Unit 2: Z-Transform: Course Faculty: R.KavithaDocument32 pagesU18EET5005-Digital Signal Processing Unit 2: Z-Transform: Course Faculty: R.KavitharoopikaNo ratings yet
- Prototype Analog Low Pass Filters: Cut-ODocument3 pagesPrototype Analog Low Pass Filters: Cut-OMinh Hung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Inverse Z TransformDocument16 pagesInverse Z TransformMd Shariful IslamNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transforms1Document81 pagesLaplace Transforms1arunkumar SNo ratings yet
- Installation: Distributed - Files, and Send Kerno.89Z To Calc. If Your Calculator IsDocument9 pagesInstallation: Distributed - Files, and Send Kerno.89Z To Calc. If Your Calculator IsarmandoNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformsDocument81 pagesLaplace TransformsChristopher OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Appndx D Mae175Document26 pagesAppndx D Mae175JAyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Laplace TransformsDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Laplace TransformsTalha MazharNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transforms1Document81 pagesLaplace Transforms1MoslemaWaftakherNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital Signal Processing (DSP) : Part 3 of 4 ("Implementing Discrete Filters")Document18 pagesIntroduction To Digital Signal Processing (DSP) : Part 3 of 4 ("Implementing Discrete Filters")William's Limonchi SandovalNo ratings yet
- Debmalya Dash - Ca1 - Ec504Document10 pagesDebmalya Dash - Ca1 - Ec504Debmalya DashNo ratings yet
- Laplace Tansform & The InverseDocument24 pagesLaplace Tansform & The InverseFiga Aghani RosyidNo ratings yet
- CA 452 MUX Sequential CKTDocument44 pagesCA 452 MUX Sequential CKTanamNo ratings yet
- NTF - Design - For - Coeffiecents - in Practical - OTA - Systematic - Design - Centering - of - Continuous - Time - Oversampling - ConvertersDocument5 pagesNTF - Design - For - Coeffiecents - in Practical - OTA - Systematic - Design - Centering - of - Continuous - Time - Oversampling - Convertersbhargav nagarajuNo ratings yet
- EE 3411 Experiment11Document6 pagesEE 3411 Experiment11souaid.hussen161anNo ratings yet
- The Inverse Z-TransformDocument16 pagesThe Inverse Z-Transformud54No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - IIDocument12 pagesLecture 2 - IIgks5kc8bhdNo ratings yet
- Laplace, Z Transform and Frequency Response: Experiment 10Document7 pagesLaplace, Z Transform and Frequency Response: Experiment 10Engr Haseena JabbarNo ratings yet
- Z-Transform and ConvolutionDocument9 pagesZ-Transform and ConvolutionMichelle MachimbiraNo ratings yet
- Kreatryx Control SystemDocument33 pagesKreatryx Control SystemNitin MauryaNo ratings yet
- EE331 - L10 - Signals & SystemsDocument37 pagesEE331 - L10 - Signals & Systemsahmetyasinbulut99No ratings yet
- Iir Filter PythonDocument11 pagesIir Filter Pythongosaitse seaseoleNo ratings yet
- E. Ambikairajah Australia: Introduction To Z-TransformDocument71 pagesE. Ambikairajah Australia: Introduction To Z-TransformTahir KhAnNo ratings yet
- Rotational Mechanical Systems Extra Notes NiseDocument6 pagesRotational Mechanical Systems Extra Notes NiseCristian Nino JargueNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of IIR FilterDocument45 pagesDesign and Implementation of IIR FilterSaurabh Shukla67% (3)
- Z TransformDocument56 pagesZ Transformcrux_123No ratings yet
- Laplace Transforms: M. Awais YaqoobDocument81 pagesLaplace Transforms: M. Awais YaqoobDewala KutaNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformsDocument81 pagesLaplace TransformsDewala KutaNo ratings yet
- ME 3001-Lecture 2 - Laplace Transform - 2017 - 18Document17 pagesME 3001-Lecture 2 - Laplace Transform - 2017 - 18vahitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Modern Network TheoryDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Modern Network TheoryOscar PachecoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - 5Document78 pagesLecture 4 - 5rachit guptaNo ratings yet
- The Z TransformDocument37 pagesThe Z TransformNikhil HosurNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Laplace Transform PDFDocument21 pages3.1 Laplace Transform PDFjwdaliNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Linear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandLinear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Power System Dynamics Simulation Tutorial 1Document9 pagesPower System Dynamics Simulation Tutorial 1Suvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Synchronous AlternatorDocument228 pagesSynchronous AlternatorSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Notes - Indefinite Integrals - AglaSem SchoolsDocument15 pagesCBSE Class 12 Maths Notes - Indefinite Integrals - AglaSem SchoolsSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- 1st Stage CBT (Common For All Notified Posts of This CEN) : Duration: 90 Minutes No of Questions: 100Document2 pages1st Stage CBT (Common For All Notified Posts of This CEN) : Duration: 90 Minutes No of Questions: 100Suvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument14 pagesSingle Phase Induction MotorSuvra Pattanayak100% (1)
- Registration Form: National Institute of Technology RourkelaDocument3 pagesRegistration Form: National Institute of Technology RourkelaSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- To The Principal, Industrial Training Institute Jhargram P O: Jhargram Dist: Paschim MedinipurDocument1 pageTo The Principal, Industrial Training Institute Jhargram P O: Jhargram Dist: Paschim MedinipurSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Information BrochureDocument28 pagesPh.D. Information BrochureSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine SyllabusDocument3 pagesElectrical Machine SyllabusSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Airtel Hack For Free InternetDocument11 pagesAirtel Hack For Free InternetSuvra Pattanayak100% (1)
- Ceramic MaterialsDocument236 pagesCeramic Materialsccc2006No ratings yet
- 4 Ways To Tie A Tie - Wikihow PDFDocument6 pages4 Ways To Tie A Tie - Wikihow PDFSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Availability Based Tariff (ABT)Document5 pagesAvailability Based Tariff (ABT)Suvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- T3DC Productinfo 20150601 en LresDocument1 pageT3DC Productinfo 20150601 en LresSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- G Frflio ? : Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesG Frflio ? : Electrical EngineeringSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet