Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid Cefuroxime
Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid Cefuroxime
Uploaded by
Sherlyn KirisakiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid Cefuroxime
Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid Cefuroxime
Uploaded by
Sherlyn KirisakiCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Name of Drug
Classification
Adverse effect
Indication
Contraindication
Nursing Considerations
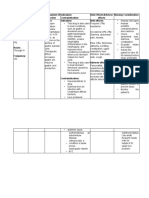
Cefuroxime IV 50mg q6
ANTIINFECTIVE; ANTIBIOTIC; SECONDGENERATION CEPHALOSPORIN
Body as a Whole: Thrombophlebitis (IV site); pain, burning, cellulitis (IM site); superinfections, positive Coombs' test. GI: Diarrhea, nausea, antibioticassociated colitis. Skin: Rash, pruritus, urticaria. Urogenital: Increased serum creatinine and BUN, decreased creatinine clearance.
It is effective for the treatment of penicillinaseproducing Neisseria gonorrhoea (PPNG). Effectively treats bone and joint infections, bronchitis, meningitis, gonorrhea, otitis media, pharyngitis/tonsilliti s, sinusitis, lower respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and is used for surgical prophylaxis, reducing or eliminating infection.
Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins and related antibiotics; pregnancy (category B), lactation.
Determine history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins, and history of allergies, particularly to drugs, before therapy is initiated. Inspect IM and IV injection sites frequently for signs of phlebitis. Report onset of loose stools or diarrhea. Although pseudomembranous colitis. Monitor I&O rates and pattern: Especially important in severely ill patients receiving high doses. Report any significant changes.
Classification Name of Drug
Adverse effect
Indication
Contraindication
Nursing Consideration
GI: Nausea, Ascorbic acid 0.5 bid Vitamins vomiting, heartburn, diarrhea. Hematologic: Acute hemolytic anemia (patients with deficiency of G6PD); sickle cell crisis. CNS: Headache (high doses). Urogenital: Urethritis, dysuria, crystalluria (high doses). Other: Mild soreness at injection site; dizziness and temporary faintness with rapid IV administration.
Proph ylaxis and treatment of scurvy and as a dietary supplement. Increases protection mechanism of the immune system, thus supporting wound healing. Necessary for wound healing and resistance to infection.
Assessment & Drug Effects Use of sodium ascorbate in patients on sodium restriction; use of calcium ascorbate in patients receiving digitalis. Safety during pregnancy (category C) or lactation is not established.
Lab tests: Periodic Hct & Hgb, serum electrolytes. Monitor for S&S of acute hemolytic anemia, sickle cell crisis.
Patient & Family Education Take large doses of vitamin C in divided amounts because the body uses only what is needed at a particular time and excretes the rest in urine.
Megadoses can interfere with absorption of vitamin B12.
Note: Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron when taken at the same time as iron-rich foods.
Name of Drug
Classification
Adverse effect
Indication
Contraindication
Nursing Consideration
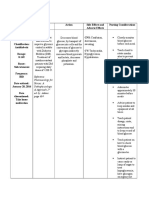
Assessment & Drug Effects Paracetamol drops 60mg/ml 1.5ml q4 Non-opioid analgesic Side effects are rare with paracetamol when it is taken at the recommended doses. Skin rashes, blood disorders and acute inflammation of the pancreas have occasionally occurred in people taking the drug on a regular basis for a long time. One advantage of paracetamol over aspirin and NSAIDs is that it doesn't irritate the stomach or causing it to bleed, potential Side effects of aspirin and NSAIDs. To relieve mild to moderate pain due to things such as headache, muscle and joint pain, backache and period pains. It is also used to bring down a high temperature. For this reason, paracetamol can be given to children after vaccinations to prevent postimmunisation pyrexia (high temperature). Paracetamol is often included in cough, cold and flu remedies. Hypersensitivity to acetaminophen or phenacetin; use with alcohol.
Monitor for S&S of: hepatotoxicity, even with moderate acetaminophen doses, especially in individuals with poor nutrition.
Patient & Family Education Do not take other medications (e.g., cold preparations) containing acetaminophen without medical advice; overdosing and chronic use can cause liver damage and other toxic effects.
Do not self-medicate children for pain more than 5 d without consulting a physician. Do not use for fever persisting longer than 3 d, fever over 39.5 C (103 F), or recurrent fever. Do not give children more than 5 doses in 24 h unless prescribed by physician.
Classification Name of Drug
Adverse effect
Indication
Contraindication
Nursing Consideration
Ambroxol 0.5m tid
Mucolytic
Occasional gastrointestinal side effects may occur but these are almost invariably mild.
Adjuvant therapy in patients with abnormal, viscid, or inspissated mucous secretions in acute and chronic bronchopulmonary diseases, and in pulmonary complications of cystic fibrosis and surgery, tracheostomy, and atelectasis. Also used in diagnostic bronchial studies and as an antidote for acute acetaminophen poisoning.
There are no absolute contraindication but in patients with gastric ulceration relative caution should be observed.
Assessment & Drug Effects Monitor for S&S of aspiration of excess secretions, and for bronchospasm (unpredictable); withhold drug and notify physician immediately if either occur. Lab tests: Monitor ABGs, pulmonary functions and pulse oximetry as indicated. Have suction apparatus immediately available. Increased volume of respiratory tract fluid may be liberated; suction or endotracheal aspiration may be necessary to establish and maintain an open airway. Patient & Family Education Report difficulty with clearing the airway or any other respiratory distress.
You might also like
- Nursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)Document24 pagesNursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)api-370148995% (19)
- Irbesartan (Avapro)Document1 pageIrbesartan (Avapro)ENo ratings yet
- DRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinDocument1 pageDRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinRadicalRay100% (3)
- Mupirocin Drug StudyDocument1 pageMupirocin Drug StudyArthur Christopher Corpuz0% (1)
- Imbalanced Nutrition NCPDocument3 pagesImbalanced Nutrition NCPapi-3701489100% (6)
- Fluid & Electrolytes and Acid Base BalanceDocument108 pagesFluid & Electrolytes and Acid Base Balanceapi-3701489100% (12)
- Paracetamol PODocument3 pagesParacetamol POSheena GallardoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Ambroxol, AmpicillinDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Ambroxol, AmpicillinPaul John RutaquioNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHNo ratings yet
- DS - ColchicineDocument2 pagesDS - ColchicineMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexDocument3 pagesDrug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexMichelle Manibale R.N100% (4)
- Drug Study Celecoxib NubainDocument4 pagesDrug Study Celecoxib NubainMaiko TyNo ratings yet
- Acetylcysteine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetylcysteine Drug StudyArabelle GONo ratings yet
- Meropenem Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMeropenem Drug StudyKullin RainNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolDocument3 pagesDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128No ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductDocument3 pagesMyasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument5 pagesOB Drug Studyvanni213No ratings yet
- Drug Study MgSO4Document1 pageDrug Study MgSO4Brigette Quirante100% (1)
- CefoxitinDocument1 pageCefoxitinDaryl PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFUROXIMEMelvz BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAbdullah Mascardo BarabagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IbuprofenDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ibuprofendawnscribd80% (5)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDsquared100% (1)
- Senna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeDocument2 pagesSenna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeTempoNo ratings yet
- PhytomenadioneDocument3 pagesPhytomenadioneanareads100% (1)
- DRug StudyDocument6 pagesDRug StudyRochell Torres ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac DRUG STUDYDocument3 pagesKetorolac DRUG STUDYA.No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Nursing Departmentrica sebabillones100% (1)
- Drug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneDocument4 pagesDrug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneJohn Kristoffer JisonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJonica CamposNo ratings yet
- Balido, John Emmanuel A. BSN223/Grp89 Drug Study: 8 G/dayDocument1 pageBalido, John Emmanuel A. BSN223/Grp89 Drug Study: 8 G/dayEmman BalidoNo ratings yet
- Rabies PJ NCPDocument3 pagesRabies PJ NCPFredrick PaderangaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument1 pageOmeprazoleLili Ann PentonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Omeprazole CompressDocument2 pagesDrug Study Omeprazole CompressAngelica TolledoNo ratings yet
- PantoprazoleDocument1 pagePantoprazolehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Drug Stidy TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Document1 pageNursing Care Plan (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Michael Vincent DuroNo ratings yet
- Sultamicillin, Hydroxyurea, Paracetamol, NystatinDocument4 pagesSultamicillin, Hydroxyurea, Paracetamol, NystatinLeodel Tolentino Barrio100% (1)
- Augmentin - CoamoxiclavDocument1 pageAugmentin - CoamoxiclavRoch OconerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Vergara, Valerie G. Drug Study (Ma'Am Dean)Document3 pagesVergara, Valerie G. Drug Study (Ma'Am Dean)Valerie VergaraNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeCia TriiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoseph Angelo Fortuna CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug AlgeDocument1 pageName of Drug Algealgerich_delacuestaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxomine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCefuroxomine Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilityjenny_lopez_48No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoshua DavantesNo ratings yet
- Drugn Study 2 0Document15 pagesDrugn Study 2 0Ken ChavezNo ratings yet
- Ce Fur OximeDocument2 pagesCe Fur OximeDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- F. Drug Study: Drug Dosage Action Indication/ Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesF. Drug Study: Drug Dosage Action Indication/ Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTracy Megan RusillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Urdaneta City University College of NursingDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Urdaneta City University College of NursingChris Tine CaccamNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY CefuroximeParado Cabañal Skyliegh50% (2)
- Medical WardDocument15 pagesMedical WardMon Revez LiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MugnaDocument7 pagesDrug Study Mugnakint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension - Nursing Diagnosis (NANDA)Document12 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension - Nursing Diagnosis (NANDA)api-370148988% (43)
- Postpartum NCPDocument20 pagesPostpartum NCPapi-370148988% (34)
- Thesis Cover Page and AcknowledgementDocument4 pagesThesis Cover Page and Acknowledgementapi-3701489100% (10)
- ICD 11 ExercisesDocument30 pagesICD 11 Exerciseszawiyah GhaniNo ratings yet
- DSM 5 CriteriaDocument6 pagesDSM 5 CriteriaCarmela ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Ed 2020 1Document25 pagesEd 2020 1Alejandra Loyo MonsalveNo ratings yet
- DISEASE: - Malaria - : CAUSATIVE AGENTDocument3 pagesDISEASE: - Malaria - : CAUSATIVE AGENTDiamante MhayaleneNo ratings yet
- Smallpox Was AnDocument41 pagesSmallpox Was AnClars storyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For GDMDocument7 pagesDrug Study For GDMFuture RNNo ratings yet
- Apache ScoreDocument36 pagesApache ScoreSugianto Parulian SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- GB 20Document2 pagesGB 20cofoneNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Serum Creatinine Level Treatment - Why It Is NecessaryDocument4 pagesAyurvedic Serum Creatinine Level Treatment - Why It Is NecessaryAnonymous vfzbbCKaENo ratings yet
- Fraktur Dan DislokasiDocument77 pagesFraktur Dan DislokasiRicky Jawwa0% (1)
- HCC Surveillance in An Era of BiomarkersDocument48 pagesHCC Surveillance in An Era of BiomarkersRobert G. Gish, MDNo ratings yet
- Care For Elderly - TAGALOGDocument29 pagesCare For Elderly - TAGALOGKarl Kevin MarbellaNo ratings yet
- NCM 118Document8 pagesNCM 118Zanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Disaster Triage: Learning ObjectivesDocument17 pagesDisaster Triage: Learning ObjectivesFANER CIENAH MARIENo ratings yet
- ConjunctivitisDocument9 pagesConjunctivitisSaranya DeviNo ratings yet
- Glossary Medical TermsDocument18 pagesGlossary Medical Termssazmeeta pantaNo ratings yet
- What Are The New 2014 Regulations DOT PhysicalDocument18 pagesWhat Are The New 2014 Regulations DOT PhysicalMatias DestefanoNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life of Patients On Peritoneal Dialysis and Its Impact On The Social DimensionDocument7 pagesQuality of Life of Patients On Peritoneal Dialysis and Its Impact On The Social DimensionRUDVAL SOUZANo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument41 pagesUntitledgladyannNo ratings yet
- Learning Issue 1 BAB 2 LaporanDocument32 pagesLearning Issue 1 BAB 2 LaporanHelmiNo ratings yet
- S1 Guidelines "Lumbar Puncture and Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis"Document28 pagesS1 Guidelines "Lumbar Puncture and Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis"alejandro montesNo ratings yet
- Sepsis 2021Document50 pagesSepsis 2021Dhitiwat ChangNo ratings yet
- Alice in Chains - DirtDocument7 pagesAlice in Chains - Dirtcajun28No ratings yet
- Flavonoids Analgesic AgentDocument17 pagesFlavonoids Analgesic AgentStella AguirreNo ratings yet
- Legal EthicsDocument46 pagesLegal EthicsNia SinghNo ratings yet
- "CPSP Questions": Question No. 01Document39 pages"CPSP Questions": Question No. 01Moin AshrafNo ratings yet
- Pandemia y Salud Mental Global InglesDocument5 pagesPandemia y Salud Mental Global InglesPaito AlcivarNo ratings yet
- T C AnkrahDocument198 pagesT C AnkrahDeep Sleep100% (8)
- Chemistry Soyabean MilkDocument14 pagesChemistry Soyabean MilkAyush MallickNo ratings yet
- Takayasu's ArteritisDocument2 pagesTakayasu's ArteritisJuan Pablo Zuluaga CastañoNo ratings yet