Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cefuroxime
Uploaded by
hahahahaaaaaaaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cefuroxime
Uploaded by
hahahahaaaaaaaCopyright:
Available Formats
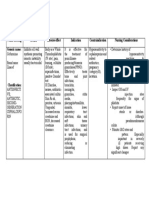
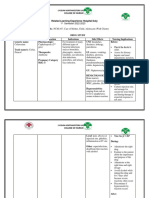
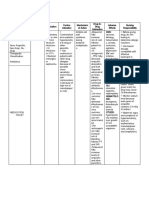
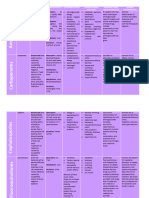
Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities
Generic Name: Bind to bacterial cell wall Treatment of It is effective Hypersensitivity to GI: Before:
Cefuroxime membrane, causing cell for the treatment of cephalosporins and related Diarrhea,
death penicillinase-producing antibiotics; pregnancy nausea, antibiotic- • Determine history of hypersensitivity reactions
Brand Name: Neisseria gonorrhoea. (category B), lactation. associated colitis. to cephalosporins, penicillins, and history of
Ceftin Therapeutic Effects: Effectively treats bone and allergies, particularly to drugs, before therapy
Bactericidal action joint infections, bronchitis, Skin: is initiated.
Classification of Drug: meningitis, gonorrhea, otitis Rash, pruritus, • Lab tests: Perform culture and sensitivity tests
media, pharyngitis/tonsillitis, urticaria. before initiation of therapy and periodically
Therapeutic: sinusitis, lower respiratory during therapy if indicated. Therapy may be
Anti-infectives tract infections, skin and soft Urogenital: instituted pending test results. Monitor
tissue infections, urinary tract Increased serum periodically BUN and creatinine clearance.
Pharmacologic: infections, and creatinine and
Second generation is used for surgical BUN, decreased
Cephalosporins prophylaxis, reducing or creatinine During:
eliminating infection. clearance.
Pregnancy Catergory B • Inspect IM and IV injection sites frequently for
Hema: signs of phlebitis.
Tablets: 125mg, 250mg, Hemolytic anemia • Monitor for manifestations of hypersensitivity.
500mg Discontinue drug and report their appearance
Powder for injection: MISC: promptly.
750mg, 1.5g, 7.5g Anaphylaxis • Monitor I&O rates and pattern: Especially
Premixed containers: 750 important in severely ill patients receiving high
mg/50ml, 1.5g/50ml doses.
• Report any significant changes.
• Report onset of loose stools or diarrhea.
Although pseudomembranous colitis rarely
occurs, this potentially life-threatening
complication should be ruled out as the cause
of diarrhea during and after antibiotic therapy.
After:
• Instruct patient to take medication around the
clock at evenly spaced times and to finish the
medication completely, even if feeling better
• Advise patient to report signs of superinfection
and allergy
• Instruct patient to notify health professional if
fever and diarrhea develop
You might also like
- The Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxomine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCefuroxomine Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NicoleDocument6 pagesDrug Study NicoleFrancheska Nicole Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- NCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!From EverandNCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentPRECIOUS LOVE LAGRIMASNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineFrom EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument1 pageDrug Study CefuroximeDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.No ratings yet
- Drug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, CefuroximeDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, Cefuroximeapi-3701489100% (12)
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeCia TriiNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug AlgeDocument1 pageName of Drug Algealgerich_delacuestaNo ratings yet
- Drug action, indication, adverse reactionsDocument11 pagesDrug action, indication, adverse reactionsAlphagene FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion Case PresentationDocument16 pagesPleural Effusion Case PresentationDhindee OmahoyNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanDocument5 pagesCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Axetil (IV)Document2 pagesCefuroxime Axetil (IV)STORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!Document3 pagesDrug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!shasheeeeyNo ratings yet
- Cefixime and Azithromycin Drug GuideDocument3 pagesCefixime and Azithromycin Drug GuideArianne Joy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument2 pagesDrug Study FormJessa Mae PagoboNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug Study Rosemarie Llanillo BSN Ii eDocument3 pagesCefuroxime Drug Study Rosemarie Llanillo BSN Ii eFernandez, Florence NicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoseph Angelo Fortuna CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsmelody_loki1464No ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Dosage and effects of ampicillinDocument1 pageDosage and effects of ampicillinkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Classification Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrugs Classification Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesAiramCeszDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCefuroxime Drug StudyJC LumayaNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Axetil (Oral)Document2 pagesCefuroxime Axetil (Oral)STORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- F. Drug Study: Drug Dosage Action Indication/ Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesF. Drug Study: Drug Dosage Action Indication/ Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTracy Megan RusillonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- Pharma SheetDocument2 pagesPharma SheetcdctinNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Amikacin SulfateDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Amikacin Sulfateichiro017100% (7)
- DS - Format - MedDocument3 pagesDS - Format - MedChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyGenovee Angela FayeNo ratings yet
- DS CSDocument2 pagesDS CSTracy Megan RusillonNo ratings yet
- Table of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesTable of AntibioticsBerenese DianneNo ratings yet
- CHLAMYDIA-Abubakar-IsmaelDocument10 pagesCHLAMYDIA-Abubakar-Ismaelaisa baladjiNo ratings yet
- KlindexDocument2 pagesKlindexPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Cefu, Metro, KetoDocument4 pagesCefu, Metro, KetoSethlyn_Gomez_5337No ratings yet
- Cefoxitin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- EthambutolDocument1 pageEthambutolSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Ceftriaxone (Forgram)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Ceftriaxone (Forgram)julesubayubay5428100% (8)
- PIPTAZDocument2 pagesPIPTAZMacmac GalabacNo ratings yet
- Drug Tab Ms (SBGH)Document4 pagesDrug Tab Ms (SBGH)tinaydelossantos2001No ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximeMarjorie EragNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - AmoxicillinVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument6 pagesCefuroximeJoyce Joyx Joycee SalonoiNo ratings yet
- Name of The Drug Route, Dosage AND Frequenc Y Mechanism of Action Indicatio N Contraindicat ION Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesName of The Drug Route, Dosage AND Frequenc Y Mechanism of Action Indicatio N Contraindicat ION Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoshua DavantesNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime drug overview: indications, side effects and nursing implicationsDocument1 pageCefuroxime drug overview: indications, side effects and nursing implicationsEkusu Yu ShunNo ratings yet
- Drug study nursing considerationsDocument4 pagesDrug study nursing considerationsMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- AsncudDocument2 pagesAsncudJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime drug study titleDocument2 pagesCefuroxime drug study titleDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Cefuroxime, Azithromycin, Hydrocortisone, IpratropiumDocument7 pagesDrug Study: Cefuroxime, Azithromycin, Hydrocortisone, IpratropiumAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNo ratings yet
- Home Visit and Bag Technique AlliedDocument36 pagesHome Visit and Bag Technique AlliedEdrick ValentinoNo ratings yet
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- Drug mechanism indication contraindication side effects nursingDocument1 pageDrug mechanism indication contraindication side effects nursinghahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- 11111a - BetamethasoneDocument2 pages11111a - BetamethasonehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Roey NCPDocument1 pageRoey NCPEdrick ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Ipratropium Bromide Plus SalbutamolDocument3 pagesIpratropium Bromide Plus SalbutamolA sison100% (1)
- Oral: PO 50mg/day Alone Or: ND RDDocument2 pagesOral: PO 50mg/day Alone Or: ND RDhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement ReceiptDocument1 pageAcknowledgement ReceipthahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Balance, Posture and Body AlignmentDocument6 pagesBalance, Posture and Body AlignmenthahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- FOGLIFE VAPOR CO. Est. 2015: Steeped Bread E-Juice Salt Nic & FreebaseDocument1 pageFOGLIFE VAPOR CO. Est. 2015: Steeped Bread E-Juice Salt Nic & FreebasehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Drug ListDocument2 pagesDrug ListhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Guinea Pig Farm (Out)Document3 pagesGuinea Pig Farm (Out)hahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement ReceiptDocument1 pageAcknowledgement ReceipthahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement ReceiptDocument1 pageAcknowledgement ReceipthahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Apparels and LinensDocument1 pageApparels and LinenshahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- 300 Pcs 302 Pcs 406 PCS: Flavor 75 Pcs 77 Pcs 100 Pcs 75 Pcs 102 Pcs 75 Pcs 102 Pcs 75 Pcs 75 Pcs 102 PcsDocument1 page300 Pcs 302 Pcs 406 PCS: Flavor 75 Pcs 77 Pcs 100 Pcs 75 Pcs 102 Pcs 75 Pcs 102 Pcs 75 Pcs 75 Pcs 102 PcshahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Zamboanga Del Sur General Hospital: Staff Nurse Performance Evaluation SheetDocument5 pagesZamboanga Del Sur General Hospital: Staff Nurse Performance Evaluation SheethahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Biodata and AnaphyDocument3 pagesBiodata and AnaphyhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Quiz With AnswersDocument1 pageQuiz With AnswershahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Budgeting: - Construction Materials - Construction Team and Workers - ElectricianDocument11 pagesHospital Budgeting: - Construction Materials - Construction Team and Workers - ElectricianhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Biodata and AnaphyDocument3 pagesBiodata and AnaphyhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Journal Headnusring 4CDocument1 pageJournal Headnusring 4ChahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- 4c Drug StudyDocument6 pages4c Drug StudyhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- FilariasisDocument11 pagesFilariasishahahahaaaaaaa100% (1)
- FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES: MAINTAINING BALANCEDocument13 pagesFLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES: MAINTAINING BALANCEhahahahaaaaaaa100% (1)
- Composition Qualifications and Terms of HRDocument2 pagesComposition Qualifications and Terms of HRhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Drug TableDocument1 pageDrug TablehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Escavape Cloud RoomDocument2 pagesEscavape Cloud RoomhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Public Health SpecialistpptBSN2BDocument29 pagesPublic Health SpecialistpptBSN2BhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- IOA Annual Report 2005Document18 pagesIOA Annual Report 2005matt30911No ratings yet
- Shantappa B K FinalDocument32 pagesShantappa B K Finalasmita patilNo ratings yet
- HTTP Sleekfreak Ath CX 81 3wdev CD3WD METALWRK GTZ075CE B65 7 HTMDocument14 pagesHTTP Sleekfreak Ath CX 81 3wdev CD3WD METALWRK GTZ075CE B65 7 HTMPavan SripadaNo ratings yet
- The State of Madflya Pradesh: Chaptee SeconDocument38 pagesThe State of Madflya Pradesh: Chaptee Seconnavdeep tiwariNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 9 Incropera 4 EdDocument16 pagesCapitulo 9 Incropera 4 EdDaxon RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Reservoir SedimentationDocument20 pagesReservoir SedimentationKathlienNo ratings yet
- Steel Code Check Theory EnuDocument341 pagesSteel Code Check Theory Enupopaciprian27No ratings yet
- FM 4 Fluid Kinematics CompleteDocument48 pagesFM 4 Fluid Kinematics Completeالياس يونس مرغلانيNo ratings yet
- 1 Scalars and Vectors Exam Qs and MsDocument81 pages1 Scalars and Vectors Exam Qs and MsAnh TranNo ratings yet
- Cengel FTFS 6e ISM CH 13Document83 pagesCengel FTFS 6e ISM CH 13Duck FernandoNo ratings yet
- Ce6101 Problem Sheet 3Document4 pagesCe6101 Problem Sheet 3HT BinhNo ratings yet
- Mineral Resources: Earth ScienceDocument20 pagesMineral Resources: Earth ScienceRegina Mae Narciso NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Citroen c3Document3 pagesCitroen c3yoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Kangaroo Mother CareDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Kangaroo Mother CareafdtuwxrbNo ratings yet
- Rice Today Vol. 13, No. 3 One Rice, Thousand GoldDocument2 pagesRice Today Vol. 13, No. 3 One Rice, Thousand GoldRice TodayNo ratings yet
- STK6712BMK4: Unipolar Fixed-Current Chopper-Type 4-Phase Stepping Motor DriverDocument11 pagesSTK6712BMK4: Unipolar Fixed-Current Chopper-Type 4-Phase Stepping Motor DriverGerardo WarmerdamNo ratings yet
- Game Theory Behavioral FinanceDocument5 pagesGame Theory Behavioral Financeplato363No ratings yet
- The Girls Center: 2023 Workout CalendarDocument17 pagesThe Girls Center: 2023 Workout Calendark4270621No ratings yet
- Etoricoxib Decreases Subchondrial Bone MassDocument9 pagesEtoricoxib Decreases Subchondrial Bone MassQuímica y FarmaciaNo ratings yet
- Quickspecs: HP Z840 WorkstationDocument108 pagesQuickspecs: HP Z840 WorkstationAbraham Leon GuardalesNo ratings yet
- Quality Testing of Honey StandardsDocument33 pagesQuality Testing of Honey StandardsK. N RaoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of An Ohmic Heater Applied To Mango Pulp Through CFD in Ansys ApdlDocument11 pagesThermal Analysis of An Ohmic Heater Applied To Mango Pulp Through CFD in Ansys ApdlOLANIYINo ratings yet
- Basic Discrete Structure:: FunctionDocument56 pagesBasic Discrete Structure:: FunctionSamratNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 11-Oct-2022Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 11-Oct-2022onkarkumarsolankiNo ratings yet
- A 3-Channel Monopulse Tracking Receiver System Using Commercial Off-The-Shelf EquipmentDocument9 pagesA 3-Channel Monopulse Tracking Receiver System Using Commercial Off-The-Shelf EquipmentJean-Hubert DelassaleNo ratings yet
- Aronne Armanini (Auth.) - Principles of River Hydraulics-Springer International Publishing (2018)Document230 pagesAronne Armanini (Auth.) - Principles of River Hydraulics-Springer International Publishing (2018)Matija LozicNo ratings yet
- Pelton WheelDocument5 pagesPelton WheelMuhammedShafiNo ratings yet
- Bittersweet Tragedy - Melanie Martinez - LETRASDocument2 pagesBittersweet Tragedy - Melanie Martinez - LETRASFlávia FernandesNo ratings yet
- Class Guide - Soldier Wheelman PDFDocument105 pagesClass Guide - Soldier Wheelman PDFRalph VasquezNo ratings yet
- Bar Code Label Requirements, Compatibility, and UsageDocument22 pagesBar Code Label Requirements, Compatibility, and Usagelarrylegend33No ratings yet