Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rats liver experiment over time
Uploaded by
aset999Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rats liver experiment over time
Uploaded by
aset999Copyright:
Available Formats
QUEEN MARY, UNIVERSITY OF LONDON MTH6116
Assignment 6
Design of Experiments
For discussion on 2nd March 2012
Work on your solutions beforehand so you can participate in the discussion. 1 In a toxicology experiment, the toxin bromobenzene is administered to rats. The toxicologist is interested in how the body deals with the toxin over time. For example, if the toxin aects normal liver function, does the liver ever return to normal? If so, when? (a) Three doses (low, medium and high) of the toxin are each diluted in a standard quantity of corn oil. Nine rats are fed each dose. Nine further rats are fed the same quantity of corn oil, with no added bromobenzene, and nine more have no addition to their normal diet. Six hours after administration of the corn oil (or nothing), three rats are randomly chosen from each group of nine: they are sacriced, and their liver extracted and measured. Same thing happens at 24 and 48 hours after administration. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) What are the experimental units? What are the observational units? What are the treatments? Explain why some corn oil is used without bromobenzene.
(b) Another scientist suggests that measurements on the rats urine can provide just as much information as measurements on their livers. Then there is no need to sacrice rats. Moreover, the experiment can be run using only fteen rats, three for each of the ve diets. A sample of urine will be taken from each rat at six, 24 and 48 hours after administration. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) What are the experimental units? What are the observational units? What are the treatments? What are the advantages and disadvantages of this design compared to the design in part (a).
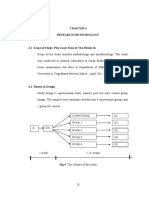
2 In an agricultural eld experiment, ve fertiliser treatments were tested in a randomised block design with three replicate blocks. The experiment yielded the following data (recorded in non-standard units of measurement):
Treatment
I A 10 B 17 C 10 D 13 E 20
Block II III 13 13 15 16 15 14 * 17 17 20
(a) Outline at least three methods for estimating the missing value (denoted by an asterisk). (b) Use one of your methods, estimate the missing value and then perform an analysis of variance by a method that is in general, approximate.
You might also like
- C. True Experimental: Nres 1 Semi-Final ExamDocument17 pagesC. True Experimental: Nres 1 Semi-Final ExamXenita Vera0% (1)
- 9 Types of Mnemonics For Better MemoryDocument13 pages9 Types of Mnemonics For Better Memoryaset999No ratings yet
- Statistical Principles of Experimental Design: Dov StekelDocument58 pagesStatistical Principles of Experimental Design: Dov StekelAtif HussainNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics AssignmentDocument3 pagesBiostatistics AssignmentKonjit MitikuNo ratings yet
- Ccras and NinDocument9 pagesCcras and NinPRAKASH DESHPANDENo ratings yet
- Ex - Diuretics On RatsDocument5 pagesEx - Diuretics On RatsAryan PisatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 AP ProblemsDocument3 pagesChapter 13 AP ProblemsVera PandeNo ratings yet
- 11 Culture, Microscopic and SamplingDocument24 pages11 Culture, Microscopic and SamplingEdwar JpNo ratings yet
- Living Environment - Break PacketDocument4 pagesLiving Environment - Break PacketKIPPNYCDocsNo ratings yet
- Transported Within 2 Hours of Collected Leak-Proof Plastic Bags With A Permanent SealDocument5 pagesTransported Within 2 Hours of Collected Leak-Proof Plastic Bags With A Permanent SealMarlonZunigaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Toxicity/safety Profile Evaluation of Ayurved & Siddha, Plant DrugsDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Toxicity/safety Profile Evaluation of Ayurved & Siddha, Plant DrugsPRAKASH DESHPANDENo ratings yet
- Warm Autoadsorption-Are We Wasting Our TimeDocument13 pagesWarm Autoadsorption-Are We Wasting Our TimeMohamed ElmasryNo ratings yet
- DESAIN PENELITIAN HEWAN COBA BIOMOLEKULER & IMUNOLOGIDocument56 pagesDESAIN PENELITIAN HEWAN COBA BIOMOLEKULER & IMUNOLOGIFarizka Dwinda HNo ratings yet
- Cc217612-HSCI3003 Assignment 4 Questions 2023Document5 pagesCc217612-HSCI3003 Assignment 4 Questions 2023jl18904lamNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Pharmacology 2016Document6 pagesVeterinary Pharmacology 2016Stephan StephanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No.1Document1 pageLaboratory Exercise No.1Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. - MicrobiologyDocument27 pagesM.Sc. - MicrobiologyDolly ChhajedNo ratings yet
- Biology Question Answer Book Name: Class: SECTION B. Structural Questions (54 Marks)Document6 pagesBiology Question Answer Book Name: Class: SECTION B. Structural Questions (54 Marks)Chun Kit LauNo ratings yet
- Anti InflamasiDocument27 pagesAnti InflamasiAuLia DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper0808pkn100% (1)
- Internship: Visit To Pathology Lab - Khyati Kansagra - SNKDocument16 pagesInternship: Visit To Pathology Lab - Khyati Kansagra - SNKapi-174466857No ratings yet
- Statistic Final AssignmentDocument2 pagesStatistic Final AssignmentJulio PutraNo ratings yet
- Mpharmacy 1 Sem Advanced Pharmacology Preclinical Evaluation of Drugs p3970Document1 pageMpharmacy 1 Sem Advanced Pharmacology Preclinical Evaluation of Drugs p3970Prince PatilNo ratings yet
- Biological Testing of BiomaterialsDocument92 pagesBiological Testing of BiomaterialsShazia Rehman100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Evaluation by FUENTES, THEA JYDEE 9 STE ADocument4 pagesChapter 5 Evaluation by FUENTES, THEA JYDEE 9 STE AThea Jydee FuentesNo ratings yet
- ChE 170 Homework #2 ATP, cAMP Structures and Energy StorageDocument3 pagesChE 170 Homework #2 ATP, cAMP Structures and Energy StorageTimothy HillNo ratings yet
- Castor OilDocument6 pagesCastor OiltonerangerNo ratings yet
- 4.7.22 Class 10 Bio WSDocument1 page4.7.22 Class 10 Bio WSSubha VijayNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument35 pages1 Introductionelsayed.mohamed488thmnNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological and Toxicological Screening Methods-I CBCS Question Paper 2018 - Mizoram University PDFDocument8 pagesPharmacological and Toxicological Screening Methods-I CBCS Question Paper 2018 - Mizoram University PDFPrashant DhakadNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 8 Enumeration: E. Coli Using Three Different Methods: Optical Density, Direct Counts and Plate Counts. YouDocument6 pagesLaboratory 8 Enumeration: E. Coli Using Three Different Methods: Optical Density, Direct Counts and Plate Counts. YouskgohNo ratings yet
- Fst556 - Introduction, Sampling and Data AnalysisDocument80 pagesFst556 - Introduction, Sampling and Data AnalysisNurSyazaHaniNo ratings yet
- Biological Science Model Questions Paper for Class X Summative AssessmentDocument4 pagesBiological Science Model Questions Paper for Class X Summative AssessmentAbcxyz XyzabcNo ratings yet
- IEStat2 - Laboratory 4 Design and Analysis of Single-Factor ExperimentsDocument5 pagesIEStat2 - Laboratory 4 Design and Analysis of Single-Factor ExperimentsChristienne Simone De JesusNo ratings yet
- Pig D Lab ReportDocument8 pagesPig D Lab ReportabdallaaNo ratings yet
- Manual Lab Act Clinical Pathology-GUS-2021 FOR STUDENT 2122Document9 pagesManual Lab Act Clinical Pathology-GUS-2021 FOR STUDENT 2122EgieAprianNo ratings yet
- Jan14 SciMethod HelicobacDocument45 pagesJan14 SciMethod HelicobacMarcel Troy SabadjaNo ratings yet
- ANOVADocument8 pagesANOVAMAHESH.RNo ratings yet
- AnovaDocument8 pagesAnovaMAHESH.RNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab 1Document8 pagesBio Lab 1Adriana Isabel PeñaNo ratings yet
- Experimental DesignDocument11 pagesExperimental DesignSarita RathiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for toxicity evaluation of Bhasma / Rasa kalpasDocument4 pagesGuidelines for toxicity evaluation of Bhasma / Rasa kalpasPRAKASH DESHPANDENo ratings yet
- Tmp32e0 TMPDocument8 pagesTmp32e0 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Biological MoleculesDocument6 pagesLab 1 - Biological Moleculesapi-535279488No ratings yet
- Idm Group Screening enDocument5 pagesIdm Group Screening enMikaela RoblesNo ratings yet
- World Health Organization, Genel A, Switzerland: PurposesDocument12 pagesWorld Health Organization, Genel A, Switzerland: PurposesKhaled MohamedNo ratings yet
- 3.5.2 Respiration Pack 1Document91 pages3.5.2 Respiration Pack 1tomtinoy2019No ratings yet
- 2GG - Antibody Screening ProcessDocument20 pages2GG - Antibody Screening ProcessAdeNujuKumprungNo ratings yet
- Live Cell Assays: From Research to Regulatory ApplicationsFrom EverandLive Cell Assays: From Research to Regulatory ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Fall Research Final PresentationDocument20 pagesFall Research Final PresentationSam BolandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document9 pagesChapter 4Lejanni Chiel BaldozNo ratings yet
- Standard 10Document12 pagesStandard 10api-312341089No ratings yet
- The Effect of Confinement Stress On The Immune System An Endocrinology Laboratory Exercise DemonstratingDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Confinement Stress On The Immune System An Endocrinology Laboratory Exercise DemonstratingArun Kumar N SNo ratings yet
- Chicken Ileum For Experiments PDFDocument4 pagesChicken Ileum For Experiments PDFShardendu MishraNo ratings yet
- Koch's Postulate in Reproduction of Broiler Coccidiosis by Co-Infection With Eight Most CommonDocument13 pagesKoch's Postulate in Reproduction of Broiler Coccidiosis by Co-Infection With Eight Most CommonDanielle AyyashNo ratings yet
- Science Class 8 Monthly Test-1Document1 pageScience Class 8 Monthly Test-1Swostik RoutNo ratings yet
- Animal Research and Alternatives LessonDocument17 pagesAnimal Research and Alternatives LessonVivekanandhan RNo ratings yet
- Cultivation Methods & Sterilization StreakingDocument6 pagesCultivation Methods & Sterilization StreakingYazeed AsrawiNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Microbiology Test 2Document2 pagesPractice Questions For Microbiology Test 2Lia RoseNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Method of Three Dimensional Technique For The Detection of AmpC Beta-LactamasesDocument7 pagesA Simplified Method of Three Dimensional Technique For The Detection of AmpC Beta-LactamasesInternational Medical PublisherNo ratings yet
- STAT 113 Week 4 Work SheetDocument4 pagesSTAT 113 Week 4 Work Sheetcaleb castilloNo ratings yet
- David IckeDocument10 pagesDavid Ickeaset999No ratings yet
- Zoroastrian Is MDocument12 pagesZoroastrian Is Maset999No ratings yet
- TutankhamunDocument16 pagesTutankhamunaset999No ratings yet
- EssenesDocument4 pagesEssenesaset999No ratings yet
- Dinka PeopleDocument3 pagesDinka Peopleaset999No ratings yet
- Church of ScientologyDocument19 pagesChurch of Scientologyaset999No ratings yet
- ConstellationDocument4 pagesConstellationaset999No ratings yet
- Farouk of EgyptDocument5 pagesFarouk of Egyptaset999No ratings yet
- Dagon, Babylonian DeityDocument5 pagesDagon, Babylonian Deityaset999No ratings yet
- Church of ScientologyDocument19 pagesChurch of Scientologyaset999No ratings yet
- Darfur ConflictDocument7 pagesDarfur Conflictaset999No ratings yet
- Church of Scientology in France Accused of FraudDocument2 pagesChurch of Scientology in France Accused of Fraudaset999100% (1)
- Carbon Cycle: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesCarbon Cycle: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaaset999No ratings yet
- Carbon Dating (Simplified)Document3 pagesCarbon Dating (Simplified)aset999No ratings yet
- Ancient RomeDocument15 pagesAncient Romeaset999No ratings yet
- Amha Selassie of EthiopiaDocument3 pagesAmha Selassie of Ethiopiaaset999No ratings yet
- ConstellationDocument4 pagesConstellationaset999No ratings yet
- Balfour Declaration of 1926Document1 pageBalfour Declaration of 1926aset999No ratings yet
- Balfour Declaration of 1917Document7 pagesBalfour Declaration of 1917aset999No ratings yet
- Yasser ArafatDocument14 pagesYasser Arafataset999No ratings yet
- American RevolutionDocument11 pagesAmerican Revolutionaset999No ratings yet
- Ashkenazi JewsDocument12 pagesAshkenazi Jewsaset999100% (2)
- Amha Selassie of EthiopiaDocument3 pagesAmha Selassie of Ethiopiaaset999No ratings yet
- Akkadian EmpireDocument9 pagesAkkadian Empireaset999No ratings yet
- Ancient RomeDocument15 pagesAncient Romeaset999No ratings yet
- AztecDocument12 pagesAztecaset999No ratings yet
- Allāt, the pre-Islamic Arabian goddessDocument1 pageAllāt, the pre-Islamic Arabian goddessaset999No ratings yet
- Alexander The GreatDocument15 pagesAlexander The Greataset999No ratings yet
- Zoroastrian Is MDocument12 pagesZoroastrian Is Maset999No ratings yet