Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Salt Analysis Chart
Salt Analysis Chart
Uploaded by
Nayan GuptaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Salt Analysis Chart
Salt Analysis Chart
Uploaded by
Nayan GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
SEMI MICRO QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF SIMPLE INORGANIC SALT _______________________________________________________________
CATIONS: Pb2+ ,Hg2+ ,Cu2+ ,Cd2+ , Ag+ , Fe2+ , Fe3+ , Al3+ , Zn2+ , Mn2+ , Co2+ , Sr2+ , Ba2+ , Mg2+ , NH4+ ANIONS: CO32- , S2- , SO32- , SO42- , NO2- , NO3- , Cl- , Br2- , PO43- , CH3COO-
_______________________________________________________________
PRELIMINARY TESTS
1. Note the state (amorphous or crystalline) and colour of salt. 2. Test the solubility of the salt in the following solutions: i. Water (cold and hot) ii. Dilute HCl (cold and hot) iii. Dilute HNO3 (cold and hot)
_______________________________________________________________
IDENTIFICATION OF ACID RADICALS (ANIONS)
This part is the classified into three groups:
FIRST GROUP OF ACID RADICALS
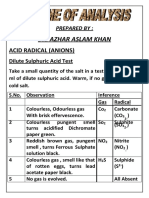
The acid radicals involved in this group are carbonate(CO32-), Sulphide(S2-), Sulphite(SO32-), Thiosulphate(S2O32-) and nitrate(NO2-). The group reagent is dilute hydrochloric acid. EXPERIMENT Salt + dil. HCl OBSERVATION Effervescence or evolution of gases (a) Colourless, odourless gas turns lime water milky (b) Colourless with rotten eggs smell and turns lead acetate paper black. (c) Colourless gas with suffocating smell. Heat and pass the gas through acidified K2Cr2O7 solution. The solution turns green (d) Colourless gas with suffocating smell with a yellow ppt. of sulphur in the test tube. Heat and pass the gas through acidified K2Cr2O7 solution. The solution turns dark blackish green. (e) Colourless gas followed by brown gas and it turns starch iodide paper blue. (f) Colourless gas with the smell of vinegar. INFERENCE 1st group of acid radicals is present. The acid radical may be CO32- or HCO3Sulphide(S2-) is confirmed.
SO32- is confirmed.
S2O32- is confirmed.
NO2- is confirmed. The acid radical may be CH3COO-
-1-
Tests to distinguish between CO32- and HCO3EXPERIMENT Salt + water, boil and pass the gas through lime water OBSERVATION (a) Lime water does not turn milky. (b) Lime water turns milky. Confirmation test for Acetate EXPERIMENT Salt solution + Neutral FeCl3 sol. OBSERVATION Appearance of blood red colour. INFERENCE Acetate is confirmed INFERENCE CO32- is confirmed. HCO3- is confirmed.
The acid radicals involved in this group are Cl-, Br- and NO3- . The group reagent is concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4). EXPERIMENT OBSERVATION Effervescence with colourless or coloured gases (a) Colourless gas with a pungent smell and gives dense white fumes when a glass rod dipped in ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) is exposed. (b) Brown gas and the solution is not blue. (c) Light brown gas and brown gas with pieces of copper turnings and the solution turns blue in the test tube. Confirmation test for Chloride EXPERIMENT (a) Chromyl Chloride test: Salt + few K2Cr2O7 crystals + conc. H2SO4 and heat Pass the vapours through the test tube which contains NaOH solution. To this yellow solution, add dilute CH3COOH and lead acetate solution. OBSERVATION Red vapours are obtained. The solution turns yellow. Yellow ppt. is formed Chloride is confirmed. INFERENCE INFERENCE 2nd group Acid radical is present The Acid radical may be Cl-
SECOND GROUP OF ACID RADICALS
Salt + Concentrated H2SO4 and heat if necessary.
The acid radical may be BrThe Acid radical may be NO3-
(b) Silver Nitrate test: Salt solution + AgNO3 solution + dilute HNO3
White ppt. is formed which is soluble in NH4OH.
Chloride is confirmed.
-2-
Confirmation test for Bromide
EXPERIMENT
(a) Globule Test: Aqueous solution of salt + two drops of CCl4 + 1ml chlorine water and shake well. (b)Silver Nitrate test: Salt solution + AgNO3 solution + dilute HNO3
OBSERVATION
An orange-red globule is obtained A pale yellow ppt. slightly soluble in NH4OH is obtained.
INFERENCE
Bromide is confirmed.
Bromide is confirmed.
Confirmation test for Nitrate
EXPERIMENT
Brown ring test: Strong solution of the substance + 2 or 3 drops of conc. H2SO4, and cool. Add freshly prepared FeSO4 solution on the sides of the test tube.
OBSERVATION
A brown ring is formed at the junction of two liquids.
INFERENCE
Nitrate is confirmed.
THIRD GROUP OF ACID RADICALS
The basic radicals involved in this group are SO42- and PO43- .
EXPERIMENT
Test for Sulphate: Aqueous solution of salt + dilute HCl + BaCl2 solution. Ammonium Molybdate Test: 2ml of soda extract 1 + dilute HNO3 + Ammonium Molybdate solution.
OBSERVATION
A white ppt. insoluble in dilute HCl is obtained A canary yellow precipitate is obtained.
INFERENCE
Sulphate (SO42-) is confirmed. Phosphate (PO43-) is confirmed.
Soda extract to be prepared if the given salt is partially soluble in water.
-3-
ANALYSIS OF BASIC RADICALS OR CATIONS
This is classified into 6 groups. They are mentioned as below:
GROUP
I II III IV V VI Pb
2+
RADICALS
Pb2+ ,Ag+ ,Hg
2+
GROUP REAGENTS
Dilute Hydrochloric acid(HCl)
2+
,Cu
2+
,Cd ,Ni
+
Dilute HCl + H2S gas. NH4Cl(s) + NH4OH NH4Cl(s) + NH4OH + H2S gas NH4Cl(s) + NH4OH + (NH4) 2CO3 -Nil-
Al3+ ,Fe2+ , Fe3+ Zn
2+
,Mn Mg
2+
,Co
2+
2+
Ca2+ ,Sr2+ ,Ba2+
2+
, NH4
Preparation of Original solution: A suitable solvent is found for the salt as given in the preliminary test. A few drops are used as solution. Test for NH4+ Radicals: This test is carried out before starting the analysis for the basic radicals.
EXPERIMENT
(a) Salt + NaOH solution and heat it. Expose a glass rod dipped in conc. HCl to the gas and moist red litmus paper. (b) Original solution + Nesselers reagent.
OBSERVATION
Colourless gas with a pungent smell is obtained. Dense white fumes and moist red litmus paper turns blue Brown solution or ppt. is obtained
INFERENCE
NH4+ may be present in the salt
NH4+ is confirmed.
FIRST GROUP OF BASIC RADICALS
The basic radicals of this group are Pb2+ & Ag+ .The group reagent is dilute HCl.
EXPERIMENT
(1) Original solution + Dilute HCl Filter and add water to ppt. and heat
OBSERVATION White ppt. is formed. (a) ppt. dissolves in hot water. (b) ppt. is insoluble in water.
INFERENCE May be Pb2+ & Ag+ May be Pb2+ May be Ag+
-4-
(2) Original solution + Potassium Chromate solution. (3) Original solution + KCl sol.
(a) A yellow ppt. is formed. (b) A brick red ppt. is formed. A yellow ppt. soluble in hot water, on cooling reappears as golden yellow spangles. The yellow ppt. is insoluble in hot water.
Pb2+ is confirmed. Ag+ is confirmed.
ppt. obtained + water and heat it.
Pb2+ is confirmed.
SECOND GROUP OF BASIC RADICALS
The basic radicals of this group are Pb2+, Hg2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+.The group reagent is Dilute HCl + H2S gas.
EXPERIMENT
Original solution + Dilute HCl + H2S gas.
OBSERVATION
(a)A Black ppt. is observed. (b)A yellow ppt. is observed.
INFERENCE
May be Pb2+ Hg2+ & Cu2+ May be Cd2+
The identification of Pb2+, Hg2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ are as follows:
EXPERIMENT
(a) Original solution + Potassium Chromate. (b)Original solution + NH4OH (c) Original solution + dil. acetic acid + potassium Ferro cyanide sol. (d) Dissolve the black ppt. in aqua regia 2 + 1ml of distilled water, heat & add 2 drops of SnCl2 (e) Original solution + dilute acetic acid + H2S gas.
OBSERVATION
A yellow ppt. is observed. A bluish white ppt. soluble in excess of NH4OH is observed which gives rise to a deep blue solution. A chocolate red ppt. is observed. A white ppt. is observed which turns grey. A yellow ppt. is formed.
INFERENCE
Pb2+ is confirmed. May be Cu2+ Cu2+ is confirmed. Hg2+ is confirmed.
Cd2+ is confirmed.
Aqua regia is mixture of 3 drops of HCl + 1 drop of HNO3
-5-
THIRD GROUP OF BASIC RADICALS
The basic radicals of this group are Al3+, Fe2+ and Fe3+ .The group reagent is NH4Cl + NH4OH
EXPERIMENT
(1) Original solution + NH4Cl(s) + NH4OH in excess
OBSERVATION
(a) A white gelatinous ppt. is obtained. (b) A dirty green ppt. is obtained (c) A reddish brown ppt. is obtained (a) White gelatinous ppt. soluble in excess of NaOH is obtained which gives a colourless sol.
INFERENCE
May be Al3+ May be Fe2+ May be Fe3+ The basic radical is Al3+ The basic radical is Fe2+ The basic radical is Fe3+ Al3+ is confirmed.
(2) Original solution + NaOH solution
(b) Dirty green ppt. insoluble in excess of NaOH (c) Reddish brown ppt. insoluble in excess of NaOH
(3) Clear solution of 2(a) + solid NH4Cl and heat (4) Original solution + acidified KMnO4 solution which is added drop wise.
The white gelatinous ppt. reappears.
(a) The pink colour of KMnO4 is not discharged.
Fe3+ is confirmed.
FOURTH GROUP OF BASIC RADICALS
The basic radicals of this group are Zn2+, Mn2+, Co2+ & Ni2+.The group reagent is NH4Cl + NH4OH And H2S(g). EXPERIMENT (1) Original solution + NH4Cl(s) + NH4OH in excess + H2S(g) OBSERVATION (a) a white ppt. is obtained (b) Buff or pale pink or flash coloured ppt. soluble in dilute HCl is obtained. (a) The white ppt. is soluble in excess of NaOH giving a colourless solution. (b) The white ppt. insoluble in excess of NaOH but turns brown. INFERENCE May be Zn2+, Mn2+ or Co2+ May be Mn2+ Zn2+ is confirmed Mn2+ is confirmed
(2) Original solution + NaOH solution+.
-6-
(3) Dissolve the 1(a) in aqua regia, evaporate to Dryness, add 1ml of distilled water and divide the resultant product into two parts. Part (1) + 1 ml of amyl alcohol + 100 mg of solid NH4SCN and stir it. Part (2) + 5 drops of dimethyl glyaxime reagent + NH4OH. A Blue colour in the alcohol layer is obtained. A pink ppt. is obtained. Co2+ is confirmed
Ni2+ is confirmed.
FIFTH GROUP OF BASIC RADICALS
The basic radicals of this group are Ca2+, Sr2+ & Ba2+ .The group reagent is NH4Cl(s) + NH4OH and (NH4)2 CO3.
EXPERIMENT (1) Original solution + NH4Cl(s) + NH4OH in excess + (NH4)2 CO3 solution. (2) Dissolve the white ppt. obtained in small amounts of dilute acetic acid. Divide the solution in three parts. Part (1) + Potassium chromate solution. Part (2) + Calcium Sulphate Sol. and heat. Part (3) + Ammonium exalate solution. (3)Flame tests: Make a paste of the given salt with few drops of Conc. HCl in a watch glass. Heat a Pt. wire in non luminous flame till no colour is imparted to the flame. Dip the Pt. wire in the paste and hold it in the flame.
OBSERVATION (a) A white ppt. is obtained.
INFERENCE May be Ca2+, Sr2+ or Ba2+
A yellow ppt. is obtained. A thin white ppt. is obtained. A white ppt. is obtained. (a) Apple green coloured flame is obtained. (b) Crimson red coloured flame is obtained. (c) Brick red coloured flame is obtained,
May be Ba2+ . May be Sr2+ . May be Ca2+ . Ba2+ is confirmed. Sr2+ is confirmed. Ca2+ is confirmed.
SIXTH GROUP OF BASIC RADICALS
EXPERIMENT (1) Original solution + excess of NH4OH + Ammonium Hydrogen Phosphate. OBSERVATION A white ppt. is obtained. INFERENCE Mg2+ is confirmed.
______________________________________________________________ *****THE END*****
-7-
You might also like
- Refining Linseed OilDocument11 pagesRefining Linseed OilPeti SzalaiNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Salt Analysis Calcium Chloride 2223Document2 pagesExperiment - Salt Analysis Calcium Chloride 2223ARYAN GOEL100% (1)
- Ammonium Chloride Salt Analysis TestDocument2 pagesAmmonium Chloride Salt Analysis TestSantosh Kumar Sahu100% (1)
- Salt Analysis With EquationsDocument12 pagesSalt Analysis With Equationsabhikhya arya0% (1)
- Salt Analysis I: Experiment Observations Inference Preliminary TestsDocument19 pagesSalt Analysis I: Experiment Observations Inference Preliminary TestsPreetam Kalyaan100% (1)
- Experiment Salt Analysis Ammonium Chloride 2223Document2 pagesExperiment Salt Analysis Ammonium Chloride 2223ARYAN GOELNo ratings yet
- Strontium ChlorideDocument5 pagesStrontium ChlorideAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Salt AnalysisDocument8 pagesScheme of Salt AnalysisAz Ahmed100% (1)
- Salt AnalysisDocument12 pagesSalt AnalysisAditya Verma50% (4)
- Salt Analysis-Calcium ChlorideDocument3 pagesSalt Analysis-Calcium ChlorideAmythNo ratings yet
- Experiment Salt Analysis Ammonium Bromide 2223Document2 pagesExperiment Salt Analysis Ammonium Bromide 2223ARYAN GOELNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical Procedure Systematic Analysis of Salt STD: Xi & XiiDocument9 pagesChemistry Practical Procedure Systematic Analysis of Salt STD: Xi & XiivarshiniNo ratings yet
- Lead Nitrate Chemistry Cbse 12 AnalysisDocument8 pagesLead Nitrate Chemistry Cbse 12 AnalysisA.n. Surya50% (12)
- 6 CaCO3Document3 pages6 CaCO3Abhi Suresh100% (3)
- Salt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2Document7 pagesSalt Analysis of PB (NO3) 2piyush rajputNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetDocument4 pagesChemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetSumit Dhall74% (50)
- Analysis of Simple Salt-II-magnesium Nitrate For Record and ReferenceDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Simple Salt-II-magnesium Nitrate For Record and Referencenikil saibaba100% (1)
- Coin Investigatory)Document19 pagesCoin Investigatory)Saumya Kharya70% (10)
- Zinc AcetateDocument4 pagesZinc AcetateAbinaya chettiappanNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Chemistry Salt Analysis 12th CBSEDocument5 pagesCheat Sheet Chemistry Salt Analysis 12th CBSETammanurRaviNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument23 pagesSalt AnalysisflippodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - Xii PDFDocument9 pagesSalt Analysis - Xii PDFहर्ष सैनी. कक्षा::बारहवीं 'द'No ratings yet
- Analysis of Simple Salt - (Copper Nitrate) : Dry TestsDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Simple Salt - (Copper Nitrate) : Dry TestsSarvan SankaranNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions-1Document8 pagesViva Questions-1Anindya Acharya100% (1)
- Chemistry Salt ChartDocument3 pagesChemistry Salt ChartAnup NavaleNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions Class 12 ChemistryDocument17 pagesViva Questions Class 12 ChemistrymrinalinimalavigaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Bromide Salt AnalysisDocument3 pagesAluminium Bromide Salt AnalysisShanmuganathan100% (1)
- Ammonium CarbonateDocument1 pageAmmonium CarbonateSophieNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Sulphate Salt Analysis TestDocument2 pagesAmmonium Sulphate Salt Analysis TestSantosh Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateShreeNo ratings yet
- 3.SALT ANALYSIS Cobalt NitrateDocument4 pages3.SALT ANALYSIS Cobalt Nitratemohnish100% (1)
- Salt Analysis - Barium NitrateDocument2 pagesSalt Analysis - Barium NitrateSwarnabha Bhattacharyya100% (2)
- Lead Nitrate Salt AnalysisDocument2 pagesLead Nitrate Salt AnalysisSantosh Kumar Sahu0% (1)
- Aluminium Sulphate (Al2 (SO4) 3)Document3 pagesAluminium Sulphate (Al2 (SO4) 3)Rajesh MishraNo ratings yet
- 1 Salt Analysis Lead AcetateDocument2 pages1 Salt Analysis Lead AcetateSuman PandeyNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - Viva QuestionsDocument7 pagesSalt Analysis - Viva Questionsnoora100% (1)
- Identification of Acid Radicals (Anions) : Prepared by R.K. Malik'S Newton Classes, RanchiDocument7 pagesIdentification of Acid Radicals (Anions) : Prepared by R.K. Malik'S Newton Classes, RanchiAadarsh YadavNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis ChartDocument8 pagesSalt Analysis Chartrajeev tomarNo ratings yet
- Systematic Analysis of Simple Inorganic SaltsDocument6 pagesSystematic Analysis of Simple Inorganic Saltspavan AckermanNo ratings yet
- 1-Salt Analysis General ProcedureDocument9 pages1-Salt Analysis General ProcedureGovind Singh KhatiyanNo ratings yet
- Salt ChartDocument9 pagesSalt ChartSohum VenkatadriNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 3Document4 pagesSalt Analysis 3snehanp2005No ratings yet
- Systematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple Inorganic Salt PDFDocument11 pagesSystematic Qualitative Analysis of Simple Inorganic Salt PDFThriambakeshwar ShramaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Nitrate PDFDocument4 pagesAluminium Nitrate PDFiitbombayjivitheshNo ratings yet
- Barium Chloride PDFDocument3 pagesBarium Chloride PDFiitbombayjivitheshNo ratings yet
- 15.salt Lead Nitrate 1Document2 pages15.salt Lead Nitrate 1Sarthika GaulkarNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride PDFDocument3 pagesCalcium Chloride PDFiitbombayjivitheshNo ratings yet
- Notefile 1 1704350572Document59 pagesNotefile 1 1704350572tteokbbokki.395No ratings yet
- Acid & Basic Radicals Xi - 1Document16 pagesAcid & Basic Radicals Xi - 1jayeshNo ratings yet
- Class X Chem Practical 6 To 10Document6 pagesClass X Chem Practical 6 To 10AnanyaNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Salt Analysis 12Document9 pagesExperiment - Salt Analysis 12Ayush MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Ammonium BromideDocument2 pagesAmmonium BromideA KNo ratings yet
- Scheme For Qualitative Inorganic AnalysisDocument4 pagesScheme For Qualitative Inorganic Analysisgamingbrothers201510No ratings yet
- Updated 2Document15 pagesUpdated 2Balaji BNo ratings yet
- Test of Cation and Anions-1Document19 pagesTest of Cation and Anions-1HARDIK MISHRANo ratings yet
- General Salt Analysis ProcedureDocument10 pagesGeneral Salt Analysis ProcedureAkshat KashyapNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument20 pagesSalt AnalysisPriyansh VermaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Sample 8Document2 pagesInorganic Sample 8fix my styleNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis, ClassxiiDocument11 pagesSalt Analysis, ClassxiiDhairya KumarNo ratings yet
- 28 Salt Analysis Revision Notes QuizrrDocument46 pages28 Salt Analysis Revision Notes Quizrrprince thakur100% (2)
- Mangnese ChlorideDocument3 pagesMangnese ChloridenishchayNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Zinc Ltd. - Summer Internship - July2009 - HZL - Internship Project - Revised 2 August 2009Document167 pagesHindustan Zinc Ltd. - Summer Internship - July2009 - HZL - Internship Project - Revised 2 August 2009Zulfiquar Hadi0% (1)
- SRS of ATMDocument7 pagesSRS of ATMZulfiquar Hadi80% (44)
- Saudi Arabian AirlinesDocument4 pagesSaudi Arabian AirlinesZulfiquar Hadi100% (3)
- The Indian Chocolate Packaging Industry - Revised 26th July 2008Document43 pagesThe Indian Chocolate Packaging Industry - Revised 26th July 2008Zulfiquar Hadi93% (29)
- Lecture6 PDFDocument27 pagesLecture6 PDFAnkita RoyNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Previous Year Question Paper 2015Document7 pagesICSE Class 10 Chemistry Previous Year Question Paper 2015Study in an easy wayNo ratings yet
- Kation Bahasa InggrisDocument14 pagesKation Bahasa InggrisFina Rika WardaniNo ratings yet
- European Patent Specification C23F 11/10, C02F 5/12: Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)Document11 pagesEuropean Patent Specification C23F 11/10, C02F 5/12: Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)mini2018No ratings yet
- Anthony Hower, Julia Kim, and Stan Kim - Lab 9Document8 pagesAnthony Hower, Julia Kim, and Stan Kim - Lab 9Anthony HowerNo ratings yet
- Expt 4-Ionic EquilibriaDocument42 pagesExpt 4-Ionic EquilibriatwinkledreampoppiesNo ratings yet
- Articulo Fundentes de AliminioDocument10 pagesArticulo Fundentes de AliminioMontserrat MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ques1 218abc1mcDocument21 pagesQues1 218abc1mcKerimberdiNo ratings yet
- AlkaloidDocument10 pagesAlkaloidAde Rizki AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Alkaloid Grupo-1Document6 pagesAlkaloid Grupo-1BRENDA MARYSABEL ESTEBAN HUARINo ratings yet
- 동양시약 제품리스트Document42 pages동양시약 제품리스트purin phokhunNo ratings yet
- International Gcse: Combined ScienceDocument32 pagesInternational Gcse: Combined ScienceBrandon LeeNo ratings yet
- Life in The World's Oceans: SmithsonianDocument372 pagesLife in The World's Oceans: SmithsonianNasirun KhanNo ratings yet
- Alkymiens MysterierDocument78 pagesAlkymiens MysterierLorcan HeerNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Chromatography: Parsa Karthik M.PHARM-1 100603013 PharmaceuticsDocument29 pagesIon Exchange Chromatography: Parsa Karthik M.PHARM-1 100603013 PharmaceuticsShafique AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hubbard-Hall Metal Processing Guide Oct. 2013Document18 pagesHubbard-Hall Metal Processing Guide Oct. 2013andrew_yeap_2No ratings yet
- Acids Bases Salts NotesDocument5 pagesAcids Bases Salts NotesAbhi ShahNo ratings yet
- Incompatibilidades Entre QuimicosDocument3 pagesIncompatibilidades Entre QuimicosPedro GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: Equilibrium Top ConceptsDocument10 pagesSubject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: Equilibrium Top ConceptsSridhar MarellaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Dyes.Document10 pagesDifferent Types of Dyes.Imran Anwar100% (3)
- Thermodynamic Properties of Strong Electrolytes in Aqueous SolutionsDocument8 pagesThermodynamic Properties of Strong Electrolytes in Aqueous SolutionsAlberto Vázquez ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids PDFDocument62 pagesAlkaloids PDFritwik maitiNo ratings yet
- Conductivity of Ionic SolutionsDocument3 pagesConductivity of Ionic SolutionsCristina AreolaNo ratings yet
- 2012 PSPM Kedah Kimia 3 W Ans PDFDocument20 pages2012 PSPM Kedah Kimia 3 W Ans PDFKavinesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- Corrosion AstroCosmosDocument11 pagesCorrosion AstroCosmosNattapong PongbootNo ratings yet
- Notes-Acids and BasesDocument9 pagesNotes-Acids and Baseshyun0124No ratings yet
- Polymers: Application of Polymers For Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery: A ReviewDocument39 pagesPolymers: Application of Polymers For Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery: A Reviewshawbo.haydar.mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes For The Deposition of Metal CoatingsDocument31 pagesElectrolytes For The Deposition of Metal CoatingsEudes SantosNo ratings yet
- Experiment Salt Analysis Lead Nitrate 2223Document2 pagesExperiment Salt Analysis Lead Nitrate 2223ARYAN GOELNo ratings yet