Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compliled Drugstudy
Compliled Drugstudy
Uploaded by
April Jan D. AlagonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compliled Drugstudy
Compliled Drugstudy
Uploaded by
April Jan D. AlagonCopyright:
Available Formats
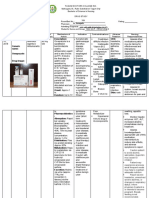
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Telmisartan BRAND: Micardis
DOSAGE 80 mg once a day
CLASSIFICATION Angiotensin receptor blockers
MECHANISM OF ACTION This drug works by blocking the hormone angiotensin thereby relaxing blood vessels, causing them to widen.
INDICATIONS mild-to-moderate high blood pressure
CONTAINDICATIONS anyone who is allergic to any of the ingredients of the product pregnant women
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES INSTRUCT THE CLIENT: * not to take a double dose to make up for a missed one. * not to stop taking this medication without consulting your doctor. * to store telmisartan at normal room temperature in a dry place (not in the bathroom) and keep it out of the reach of children. Do not remove tablets from their blister-pack until you are ready to take them. * not to dispose of medications in wastewater (e.g. down the sink or in the toilet) or in household garbage. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medications that are no longer needed or have expired. NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES *Take cefixime with food or milk. *Take the missed dose as soon as you remember it. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one. *Shake the liquid well before each use to mix the medication evenly. The tablets should be swallowed whole and taken with a full glass of water. Continue to take cefixime even if you feel well. Do not stop taking cefixime without talking to your doctor.
back pain constipation diarrhea difficulty sleeping dizziness eczema or skin rash headache heartburn joint pain rash upper respiratory tract infection (such as colds or sinus infections) SIDE EFFECTS
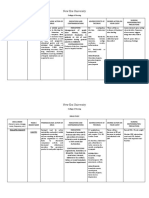
DRUG NAME GENERIC: cefixime BRAND: Tergecef
DOSAGE Adult: PO Susceptible infections 200400 mg/day
CLASSIFICATION Cephalosporins
MECHANISM OF ACTION Tergecef acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Its mode of action is bactericidal. It has high affinity for penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) 1 (1a, 1b, 1c) and 3, with the site of activity varying according to organisms.
INDICATIONS Uncomplicated gonorrhoea
CONTAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to cephalosporin History of allergy to penicillins pregnancy lactation renal failure GI disease.
upset stomach diarrhea vomiting mild skin rash headache severe skin rash itching hives difficulty breathing or swallowing wheezing vaginal infection
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Salbutamol BRAND: Duavent
DOSAGE *Adult, adolescent >12 yr & elderly Treatment of acute attacks 1-2 pulmoneb. Maintenance: 1 pulmoneb every 6-8 hours. *Children 2-12 yr 3 drops/kg/dose. Max: 2.5 mg of salbutamol every 6-8 hours. MDI Adult & children >12 yr 2 actuations every 6 hours. Max: 12 actuations in 24h
CLASSIFICATION Respiratory/ Drugs for Asthma/COPD/ Anticholinergics
MECHANISM OF ACTION Salbutamol stimulates adenyl cyclase, the enzyme which catalyzes the formation of cyclic3', 5'-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) from adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The cAMP thus formed mediates the cellular response eg, bronchial smooth muscle relaxation. In vitro and in vivo pharmacologic studies have demonstrated that salbutamol has a preferential effect on adrenergic receptors that are especially found in respiratory tract compared with isoproterenol.
INDICATIONS Management of reversible bronchospasm associated w/ obstructive airway diseases eg. bronchial asthma, COPD.
CONTAINDICATIONS Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy or tachyarrythmia. Hypersensitivity to soya lecithin or related food products (for MDI).
SIDE EFFECTS Headache pain influenza chest pain nausea Bronchitis Dyspnea coughing pneumonia bronchospasm pharyngitis sinusitis rhinitis
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES *Patients should avoid spraying the aerosol into the eyes since this may result in precipitation or worsening of narrow-angle glaucoma, eye pain or discomfort, temporary blurring of vision, visual halos or colored images in association of red eyes from conjunctival and corneal congestion.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Albuterol BRAND: Ventolin
DOSAGE *1-2 inhalations every 4-6 hours by aerosol. * The usual nebulizer dose is 0.63 mg, 1.25 mg or 2.5 mg 3-4 times a day. *tablets or syrup is 2 or 4 mg given 3 or 4 times daily *extended release tablets is 4 or 8 mg every 12 hours.
CLASSIFICATION Bronchodilator beta II adrenergic agonist
MECHANISM OF ACTION Salbutamol is a beta (2)adrenergic agonist and thus it stimulates beta(2)-adrenergic receptors. Binding of albuterol to beta(2)-receptors in the lungs results in relaxation of bronchial smooth muscles. Increased intracellular cyclic AMP increases the activity of cAMPdependent protein kinase A, which inhibits the phosphorylation of myosin and lowers intracellular calcium concentrations and also cause an inhibition of the release of mediators from mast cells in the airways. A lowered intracellular calcium concentration leads to a smooth muscle relaxation.. MECHANISM OF ACTION Erdosteine is an original derivative of natural mercaptoamino acid in thiolactonic form. Following oral administration erdosteine is rapidly metabolized in the liver. The product acts as a prodrug and its metabolites are mainly responsible for mucolytic activity, due to the presence of free thiol groups which cause the splitting up of the intra- and intermolecular disulfide bridges of several proteins and mucoproteins present in the expectoration, resulting in a reduction of the mucus elasticity and viscosity MECHANISM OF ACTION Ebastine has been shown to produce a rapid and long-lasting inhibition of histamine-induced effect and to have a strong affinity towards H1-receptors. Following oral administration neither ebastine nor its metabolites cross the blood-brain barrier. This characteristic is consistent with the low sedative profile seen in the results of experiments studying the effects of ebastine on the CNS.
INDICATIONS Ventolin is used to treat or prevent bronchospasm in people with reversible obstructive airway disease. It is also used to prevent exerciseinduced bronchospasm.
CONTAINDICATIONS hypersensitive to drug W/ CAUTION: ischemic heart HTN arrhythmias hypokalemia diabetes mellitus seizure disorder hyperthyroidism pheochromocytoma pregnancy elderly pts
SIDE EFFECTS Side effects include nervousness, tremor, headache, palpitations, fast heart rate, elevated blood pressure, nausea, dizziness, and heartburn. Throat irritation and nosebleeds can also occur. Allergic reactions may rarely occur and may manifest as rash, hives, swelling, bronchospasm, or anaphylaxis (shock). Worsening of diabetes and lowering of potassium have also been reported. In rare patients, inhaled albuterol can paradoxically precipitate lifethreatening bronchospasm.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES *Shake the Ventolin canister well just before each spray. *Uncap the mouthpiece of the inhaler. Breathe out fully. Put the mouthpiece into your mouth and close your lips. Breathe in slowly while pushing down on the canister. Hold your breath for 10 seconds, then breathe out slowly. *If you use more than one inhalation at a time, wait at least 1 minute before using the second inhalation and shake the inhaler again. *Keep your Ventolin inhaler clean and dry, and store it with the cap on the mouthpiece. Clean your inhaler once a week by removing the canister and placing the mouthpiece under warm running water for at least 30 seconds. Shake out the excess water and allow the parts to air dry completely before putting the inhaler back together.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Erdosteine BRAND: Zertin, Biopulmin, Dostol, Ectrin, Edotin, Ilvico, Mucofor, Mucotec, Recustein, Tantong, Vectrine
DOSAGE Capsule: 300 mg twice daily Suspension: 35mL 60mL 100mL
CLASSIFICATION Mucolytics
INDICATION Treatment of acute & chronic bronchopulmonar y diseases, rhinosinusitis, laryngopharyngiti s or exacerbations of these chronic diseases in association w/ mucus production & transport.
CONTRAINDICATION Hepatic disorders & abnormalities, renal insufficiency, homocystinuria, phenylketonuria.
SIDE EFFECTS G.I: Gastric burning, nausea, and rarely diarrhea. Hypersensitivity reactions: Skin rash, urticaria, unexpected hyperpyrexia
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY In case of appearance of classical hypersensitivity signs and symptoms, the treatment with erdosteine must be immediately suspended. May be taken with or without food
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Ebastine 10mg BRAND: Co-Aleva Betamethasone 500 mcg
DOSAGE Antihistamine Antiallergics
CLASSIFICATION Adult : 1tab twice daily
INDICATION Treatment of seasonal/perenni al allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to Ebastine and Betamethasone or any of tablet ingredients. Patients with severe liver insufficiency.
SIDE EFFECTS Headache, dry mouth and drowsiness. Pharyngitis, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, asthenia, epistaxis, rhinitis, sinusitis, nausea and insomnia. .
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Should be taken with foods Betamethasone should only be used systematically with great caution in the presence of heart failure, recent myocardial infarction or hypertension, in patients with diabetes mellitus, epilepsy, glaucoma, hypothyroidism, hepatic failure, osteoporosis, peptic ulceration, psychoses or severe affective disorders and renal impairment.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Ranitidine Hydrochloride BRAND: Apo-Ranitidine, Zantac, ZantacC, Zantac 75, Zantac 150, Zantac EFFERdose Tablets, Zantac 150 GELdose, Zantac 300, Zantac 300 GELdose
DOSAGE Children 1 month to 16 years of age: 24 mg/kg twice daily. Maximum 300 mg daily. Adults: 150 mg twice daily.
CLASSIFICATION H2 receptor antagonist
MECHANISM OF ACTION Competitively inhibits action of Histamine on the H2 at receptor sites of parietal cells, decreasing gastric acid secretion
INDICATION Active duodenal and gastric ulcer Maintenance therapy for duodenal or gastric ulcer. Pathologic hypersecretory conditions such as ZollingerEllison syndrome (ZES) Gastroesophagea l reflux disease Erosive esophagitis Heartburn INDICATION Tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis,sinusitis , otitis media, tracheobronchitis, pneumonia, bronchopneumon ia Intra-abdominal infections Gynecological infections Urinary tract infections Skin and skin structure infection INDICATION As for the other cephalosporins, although as a secondgeneration it is less susceptible to Beta-lactamase and so may have greater activity against Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Lyme disease.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and those with acute porphyria
SIDE EFFECTS CNS: headache, malaise, vertigo EENT: blurred vision Hepatic: Jaundice Other: anaphylaxis, angioedema, burning and itching at injection site.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Assess patient for abdominal pain. Note presence of blood in emesis, stool, or gastric aspirate. Drug may be added to total parenteral nutrition solutions. Dont confuse ranitidine with rimantadine; dont confuse Zantac with Xanax or Zyrtec.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Amoxicillin BRAND:: Ultramox
DOSAGE Tablet: 500mg/500mg x 8s Suspension: 60 mL
CLASSIFICATION Penicillin
MECHANISM OF ACTION Amoxicillin is a semi-synthetic penicillin which kills bacteria by interfering with the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall. It binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) on the bacterial cell wall and blocks peptidoglycan synthesis. Peptidoglycan is a heteropolymeric structure that gives the cell wall its mechanical stability. The final stage of the peptidoglycan synthesis involves the completion of the crosslinking with the terminal glycine residue of the pentaglycine bridge linking to the 4th residue of the pentapeptide. MECHANISM OF ACTION Cefuroxime, like the penicillins, is a beta-lactam antibiotic. By binding to specific penicillinbinding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, it inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that cefuroxime interferes with an autolysin inhibitor.
CONTRAINDICATION History of hypersensitivity to penicillins and/or cephalosporins. The risk-benefit ratio should be carefully evaluated in patients with a history of GI disease, particularly ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis or antibiotic-associated colitis and infectious mononucleosis.
SIDE EFFECTS G.I: Nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, stomatitis, sour mouth and tongue and diarrhea Hypersensitivity reactions: Oral candidiasis, urticaria Renal: Interstitial nephritis and hematuria
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Patient w/ history GI disease eg ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis/antibiotic-associated colitis & infectious mononucleosis. Consider pseudomembranous colitis in patients who present w/ diarrhea following administration of antibiotics. Monitor hepatic, renal & hematopoietic functions. Renal impairment. :Young infant <6 mth. Elderly. Pregnancy & lactation.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: CEFUROXIME BRAND: Ecocef (750mg IV) (Xeno Pharmaceutic als), Philippines
DOSAGE *Adults and teenagers750 mg every 68hours usually for 5-14 days,IM/IV. *Infants and children 1 month of age and older12.5 to 150 mg/ kg of bodyweight every 6-8 hours IM/IV *Newborns30100 mg/ kg (of body weight very 8-12 hours,IV
CLASSIFICATION Antibiotic
CONTRAINDICATION Cefuroxime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics. Solutions containing dextrose may be contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to corn products.
SIDE EFEECTS Allergic reaction: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Serious Side effects: diarrhea that is watery or bloody; fever, sore throat, and headache with a severe blistering, peeling, and red skin rash; seizure (black-out or convulsions); or jaundice(yellowing of the eyes or skin). Less Serious Side Effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain; headache, dizziness; fussiness
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES *Determine history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins,and history of allergies, particularly to drugs, before therapy is initiated. Inspect IM and IV Injection sites frequently for signs of phlebitis. Report onset of loose stools or diarrhea. Although pseudomembranous colitis rarely occurs, this potentially life-threatening complication should be ruled out as the cause of diarrhea during and after antibiotic therapy. Monitor for manifestati ons of hypersensitivity .Discontinue drug and report their appearance promptly. Monitor I&O rates and patte
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Metoprolol BRAND: Apo-Metoprolol (CAN), Betaloc (CAN), Lopresor (CAN), Lopressor, Novometoprol (CAN), NuMetop (CAN), Toprol XL Brand Name: Norvasc
DOSAGE ADULTS Hypertension: 50100 mg/day PO as 1 dose. Angina: 100 mg/day PO as 1 dose. CHF: 12.525 mg/day Toprol XL for 2 wk; may then be increased by 25 mg every 2 wk to a maximum of 200 mg. PEDIATRIC PATIENTS Safety and efficacy not established
CLASSIFICATION -Beta1-selective adrenergic blocker Antihypertensive
MECHANISM OF ACTION Competitively blocks betaadrenergic receptors in the heart and juxtaglomerular apparatus, decreasing the influence of the sympathetic nervous system on these tissues and the excitability of the heart, decreasing cardiac output and the release of renin, and lowering BP; acts in the CNS to reduce sympathetic outflow and vasoconstrictor tone.
INDICATION -Hypertension, alone or with other drugs, especially diuretics Immediate-release tablets and injection: Prevention of reinfarction in MI patients who are hemodynamically stable or within 310 days of the acute MI Treatment of angina pectoris Toprol XL only: Treatment of stable, symptomatic CHF of ischemic, hypertensive, or cardiomyopathic origin
CONTRAINDICATION -Contraindicated with sinus bradycardia (HR < 45 beats/min), second- or thirddegree heart block (PR interval > 0.24 sec), cardiogenic shock, CHF, systolic BP < 100 mm Hg; lactation. Use cautiously with diabetes or thyrotoxicosis; asthma or COPD; pregnancy
SIDE EFFECT Allergic: Pharyngitis, erythematous rash, fever, sore throat, laryngospasm CNS: Dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, fatigue, emotional depression, paresthesias, sleep disturbances, hallucinations, disorientation, memory loss, slurred speech CV:CHF, cardiac arrhythmias, peripheral vascular insufficiency, claudication, CVA, pulmonary edema, hypotension Dermatologic: Rash, pruritus, sweating, dry skin EENT: Eye irritation, dry eyes conjunctivitis, blurred vision GI: Gastric pain, flatulence, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting,anorexia,ischemic colitis, renal and mesenteric arterial thrombosis, retroperitoneal fibrosis, hepatomegaly, acute pancreatitis GU: Impotence, decreased libido, Peyronie's disease, dysuria, nocturia, frequent urination Musculoskeletal: Joint pain, arthralgia, muscle cramp Respiratory: Bronchospasm, dyspnea,cough, bronchial obstruction, nasal stuffiness, rhinitis, pharyngitis Other: Decreased exercise tolerance, development of antinuclear antibodies (ANA), hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, elevated serum transaminase, alkaline phosphatas
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY -Do not discontinue drug abruptly after long-term therapy (hypersensitivity to catecholamines may have developed, causing exacerbation of angina, MI, and ventricular arrhythmias). Taper drug gradually over 2 wk with monitoring. Ensure that patient swallows the ER tablets whole; do not cut, crush, or chew them. Consult physician about withdrawing drug if patient is to undergo surgery (controversial). Give oral drug with food to facilitate absorption. Provide continual cardiac monitoring for patients receiving IV metoprolol.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: :Amlodipine BRAND: Norvasc
DOSAGE PO (Adults): 510mg (OD) PO (Geriatric Patients): 2.5mg/day,
CLASSIFICATION Therapeutic: Antihypertensives Pharmacologic: Calcium Channel Blockers
MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibits the transport of calcium into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells, resulting in inhibition of excitation contraction coupling and subsequent contraction.Therapeutic Effects: Systematic Vasodilation resulting in decreased blood pressure. Coronary Vasodilation resulting in decreased frequency and severity of attacks of Angina
INDICATION Alone or with other agents in the management of Hypertension, Angina Pectoris, and Vasospastic (Prinzmetals) Angina.
CONTRAINDICATION Hypersensitivity; Blood Pressure <90 mmHg
SIDE EFFECT CNS: headache, dizziness, fatigue CV: Peripheral Edema, Angina, Bradycardia, Hypotension, and Palpitations GI: Gingival Hyperplasia, Nausea Derm:Flushing
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY General Info: Monitor blood pressure and pulse before therapy, during dose titration, and periodically during therapy, Monitor ECG periodically during prolonged therapy. Monitor intake and output ratios and daily weight. Assess for signs of CHF. Angina: Assess location, duration, intensity, and precipitating factors of patients anginal pain. Lab Test Considerations: Total serum calcium concentrations are not affected by calcium channel blockers
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Citicoline BRAND: Zynapse
DOSAGE CVD, in acute recovery phase, in signs & symptoms of cerebral vascular insufficiency & in cranial traumatism & their sequelae.
CLASSIFICATION
MECHANISM OF ACTION Citicoline activates the biosynthesis of structural phospholipids in the neuronal membrane, increases cerebral metabolism and the level of various neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine and dopamine Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that citicoline restores the activity of mitochondrial ATPase and of membranal Na+/K+ ATPase, inhibits the activation of phospholipase A2 and accelerates the reabsorption of cerebral edema in various experimental models.
INDICATION CVD, in acute recovery phase, in signs & symptoms of cerebral vascular insufficiency & in cranial traumatism & their sequelae.
CONTRAINDICATION Patients with hypertonia of the parasympathetic.
SIDE EFEECTS Occasionally, citicoline may exert a stimulating action of the parasympathetic, as well as a fleeting and discrete hypotensive effect.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Glibenclamide BRAND: Daonil/Euglucon , Diabeta, Glynase,Micron ase
DOSAGE 5 mg once daily upto a maximum of 15 mg daily
CLASSIFICATION Antidiabetic
MECHANISM OF ACTION The drug works by inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels in pancreatic beta cells. This inhibition causes cell membrane depolarization, which causes voltage-dependent calcium channels to open, which causes an increase in intracellular calcium in the beta cell, which stimulates insulin release.
INDICATION .In type 2 diabetes (non insulin requiring).
CONTRAINDICATION Patients with severe kidney and liver damage should not be using Glibenclamide. Patients with porphyra should not be prescribed Glibenclamide.
SIDE EFEECTS The common side effects include, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and constipation. They may cause disturbance in liver function and skin rashes are also known to occur
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES *For best result, administer 30 minutes prior to meals. *Review dose and frequency of administration. *Record finger sticks at various times. *Continue regular daily exercise, life style changes, BP control, and dietary restrictions to control cholesterol in addition to drug therapy. *Avoid alcohol and OTC agents without provider approval. *Repost as scheduled for teaching,reinforcement, F/U labs, foot/ eye exams and medication evaluation. NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES *Document age at diabetes onset, previous therapies, utilized, and the outcome *Monitor BP, CBC, BS, Electrolytes, HbA1c, urinalysis, micro albumin, liver and renal function studies. Assess for liver or renal failure. *Monitor known or suspected alcoholics carefully for decreased liver function. *Monitor cardiopulmonary status throughout course of therapy; cardiopulmonary insufficiency may predispose to lactic acidosis.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Metformin BRAND: I-Max
DOSAGE Usual Adult Metformin Dose for Diabetes Mellitus Type II: 500 mg orally twice a day (with the morning and evening meal)
CLASSIFICATION Antidiabetic
MECHANISM OF ACTION Metformin is an antihyperglycemic agent which improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. With metformin therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may actually decrease.
INDICATION *Alone as an adjunct to diet to lower blood glucose in clients having NIDDM * *Extended release form used to treat type 2 diabetes as initial therapy or in combination with a sulfonylurea or insulin in clients aged 17 years and older.
CONTRAINDICATION * Renal disease or renal dysfunction (e.g., as suggested by serum creatinine levels 1.5 mg/dL [males], 1.4 mg/dL [females] or abnormal creatinine clearance) which may also result from conditions such as cardiovascular collapse (shock), acute myocardial infarction, and septicemia . *Known hypersensitivity to metformin hydrochloride. *Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis, with or without coma. Diabetic ketoacidosis should be treated with insulin.
SIDE EFEECTS Metabolic: Lactic Acidosis GI: Diarrhea, N&V, abdominal bloating, flatulence, anorexi, unpleasant or metallic taste, abnormal stools, taste disorder. CNS: Lightheadedness, headache Hematologic: Asymptomatic subnormal serum Vitamin B12 levels. Body as a whole: Asthenia, rash, chills, flu syndrome, flushing, increases sweating. Miscellaneous: Hypoglycemia, myalgia, dyspnea, nail disorder, chest discomfort, palpitation.
DRUG NAME GENERIC NAME: levocetirizine dihydrochloride BRAND NAME: Xyzal
DOSAGE Oral administration: 5 mg tablet
CLASSIFICATION Antihistamine
MECHANISM OF ACTION The active component of Xyzal, Levocetirizine dihydrochloride, is the R enantiomer of cetirizine hydrochloride, a racemic compound with antihistaminic properties. It is an orally active and selective H1-receptor antagonist. Histamines act on H1 receptors, causing the symptoms commonly seen in allergic reactions. Xyzal inhibits these H1 receptors.
INDICATION Relief of symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis (seasonal and perennial) in adults and children 6 years of age and older Treatment of the uncomplicated skin manifestations of chronic idiopathic urticaria in adults and children 6 years of age and older INDICATION Treatment of susceptible infections eg chancroid, endocarditis, gastroenteritis, gonorrhea, Lyme disease, meningitis, septicemia, surgical infection, syphilis, typhoid fever & Whipple's disease. INDICATION *Tx of upper and lower respiratory infections such as acute tonsillopharyngitis , otitis media, acute sinusitis, acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis and community acquired pneumonia. *Skin and soft tissue infections
CONTRAINDICATION Children 6 months to 11 years of age with impaired kidney function should not take XYZAL
SIDE EFFECTS Adverse events associated with the use of Xyzal in adult and pediatric subjects aged 12 years and older may include, but are not limited to, the following: Somnolence Nasopharyngitis Fatigue Dry Mouth Pharyngitis Adverse events associated with the use of Xyzal in pediatric subjects aged 6 to 12 years may include, but are not limited to, the following: Pyrexia Cough Somnolence Epistaxis
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Do not take XYZAL if you are allergic to XYZAL, cetirizine or ZYRTEC Taking XYZAL with alcohol or sedatives should be avoided Patients taking XYZAL should avoid operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle Do not increase the dose due to increased risk of sleepiness.
DRUG NAME GENERIC NAME: Ceftriaxone BRAND NAME: Pneumoslov
DOSAGE Adult 1-2 g daily as a single dose or in 2 divided doses. Childn & infant 20-50 mg/kg body wt once daily.. Neonate Max dose: 50 mg/kg IV over 60 min.
CLASSIFICATION Anti-infectives/ Antibiotics/ Cephalosporins/ 3rd Generation Cephalosporin
MECHANISM OF ACTION Ceftriaxone usually is bactericidal in action. Like other cephalosporins, the antibacterial activity of the drug results from inhibition of mucopeptide synthesis in the bacterial cell wall
CONTRAINDICATION History of previous allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) to penicillins or cephalosporins. History of GI disease esp ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis or antibiotic-associated colitis. Renal function impairment.
SIDE EFFECTS Superinfections, anaphylaxis, diarrhea, local reactions, blood dyscrasias, rash, fever, pruritus, elevated transaminases & alkaline phosphatase, leucopenia, neutropenia. Potentially fatal: Pseudomembranous colitis,nephrotoxicity.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Assess for allergy to cephalosporins
DRUG NAME GENERIC NAME: Clarithromycin BRAND NAME: klaricid
DOSAGE 1 tab once or bid. More severe infections: 2 tab once or bid
CLASSIFICATION Anti-Infective
MECHANISM OF ACTION Klaricid, a macrolide antibiotic similar to erythromycin and azithromycin, is effective against Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) and is used for the treatment of Helicobacter pyloriassociated peptic ulcer disease, community-acquired pneumonia, sinusitis, and chronic bronchitis. Klaricid is also used to treat respiratory tract, sexually transmitted, otitis media, and AIDS-related infections
CONTRAINDICATION Decreased kidney function Decreased liver function Abnormal heart rhythm seen on the heart monitoring trace (ECG) as a 'prolonged QT interval', or people at risk of this (your doctor will know).
SIDE EFFECTS Nausea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain & diarrhea, headache & skin rash.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Consider cross-sensitivity with other macrolides Monitor serum levels of theophyline and carbamazepine Instruct client not to take antijistamines.
DRUG NAME GENERIC Lactic acid, sodium pyrrolidone carboxylate BRAND lacticare
DOSAGE Apply to the affected area bid-qid.
CLASSIFICATION Hydrocortisone
MECHANISM OF ACTION Hydrocortisone is a corticosteroid used for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. Its anti-inflammatory action is due to the suppression of migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and reversal of increased capillary permeability. It may also be used as replacement therapy in adrenocortical insufficiency.
INDICATION LactiCare is indicated for the symptomatic relief of hyperkeratotic and other chronic dry skin conditions, and for dry skin conditions caused by low humidity or the use of detergents. INDICATION for the relief of moderate to severe pain
CONTRAINDICATION Skin lesions caused by viral, fungal or bacterial infections.
SIDE EFFECTS Occasionally a transient mild stinging sensation may occur. Should prolonged irritation develop when used on abraded or inflamed skin, discontinue use.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Keep away from the eyes and mucous membranes. Should contact with the eyes occur, remove with water. Keep out of the reach of children.
DRUG NAME GENERIC Nubain BRAND Nalbuphine
DOSAGE nalbuphine hydrochloride 10 milligram in 1 milliliter
CLASSIFICATION Analgesic
MECHANISM OF ACTION NUBAIN is a potent analgesic. Its analgesic potency is essentially equivalent to that of morphine on a milligram basis. Receptor studies show that NUBAIN binds to mu, kappa, and delta receptors, but not to sigma receptors. NUBAIN is primarily a kappa agonist/partial mu antagonist analgesic. MECHANISM OF ACTION Disrupts DNA and protein synthesis in susceptible organisms Bactericidal, or amebicidal action
CONTRAINDICATION if you have asthma or other breathing disorder, liver or kidney disease, gallbladder disease, mental illness, or a history of drug or alcohol addiction
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY *discuss to patient that this may cause drowsiness or dizziness,advice the patient to have assistance and to avoid driving *assess blood pressure pulse and respirations before and periodically during administration cause it may affect the respiratory rate of the patient.
weak or shallow breathing; fast or slow heart rate; cold, clammy skin; confusion, hallucinations, unusual thoughts or behavior; severe weakness or dizziness; or feeling like you might pass out.
DRUG NAME GENERIC Metronidazole BRAND Flagyl
DOSAGE PO 7.5 mg/kg q6hr (not to exceed 4g/day)
CLASSIFICATION Anti-infectives, Anti-protozoals
INDICATION Indicated for intestinal and extraintestinal amebiasis as well as infections with Trichomonas vaginalis and Giardia lamblia
CONTRAINDICATION hypersensitivity
SIDE EFFECTS CNS: seizures, dizziness, headache GI: abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, diarrhea, dry mouth, furry tongue, glossitis, unpleasant taste, vomiting Hematologic: leukopenia Skin: rashes, urticaria
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Administer with food or milk to minimize GI irritation. Tablets may be crushed for patients with difficulty swallowing. Instruct patient to take medication exactly as directed evenly spaced times between dose, even if feeling better. Do not skip doses or double up on missed doses. If a dose is missed, take as soon as remembered if not almost time for next dose. May cause dizziness or light-headedness. Caution patient or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Inform patient that medication may cause an unpleasant metallic taste. Inform patient that medication may cause urine to turn dark. Advise patient to consult health care professional if no improvement in a few days or if signs and symptoms of superinfection (black furry overgrowth on tongue; loose or foul-smelling stools develop).
DRUG NAME GENERIC Diclofenac sodium BRAND : Voltaren
DOSAGE Tablets (delayed release): 25, 50, and 75 mg. Tablets (immediate release): 50 mg. Tablets (extended release): 100mg
CLASSIFICATION Anti-inflammatory -Analgesic
MECHANISM OF ACTION The exact mechanism of action is not entirely known, but it is thought that the primary mechanism responsible for its antiinflammatory/antipyretic/analgesic action is inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX). Diclofenac, it seems, may also be a unique member of the NSAIDs. There is some evidence that diclofenac inhibits the lipooxygenase pathways, thus reducing formation of the leukotrienes (also proinflammatory autacoids).
INDICATION Diclofenac is used for musculoskeletal complaints, especially arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, osteoarthritis, dental pain, TMJ, spondylarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout attacks,[8] and pain management in cases of kidney stones and gallstones - An additional indication is the treatment of acute migraines INDICATION Relief of pain Including muscular, rheumatic, traumatic,dental, post-op and postpartum pain,headache, migraine,fever, dysmenorrhea INDICATION For the treatment of respiratory tract infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniaeand Streptococcus pyogenes
CONTRAINDICATION Hypersensitivity against diclofenac History of allergic reactions (bronchospasm, shock, rhinitis, urticaria) following the use of Aspirin or another NSAID Third-trimester pregnancy Active stomach and/or duodenal ulceration or gastrointestinal bleeding Inflammative intestinal disorders such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis
SIDE EFFECTS gastrointestinal adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Monitor BP for hypertension and blood sugar for hyperglycemia. Monitor diabetics closely for loss of diabetic control. Monitor for increased serum sodium and potassium in patients receiving potassiumsparing diuretics. Monitor weight and report gains greater than 1 kg (2 lb)/24 h. Monitor for signs and symptoms of GI irritation and ulceration.
DRUG NAME GENERIC Mefenamic acid BRAND: Dolfenal
DOSAGE Adult: start with 75150mcg BID Severe HPN 300mg BID
CLASSIFICATION . Analgesics Non-Narcotic Analgesics NSAIDs
MECHANISM OF ACTION Aspirin-like drug that has analgesic,antipyretic, & antiinflammatory activities
CONTRAINDICATION Pregnancy & lactation, hypersensitivity, active ulceration or chronic inflammation of either upper or lower GIT, blood disorders, poor platelet function, kidney or liver impairment, children < 14 yr CONTRAINDICATION For the treatment of respiratory tract infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniaeand Streptococcus pyogenes
SIDE EFFECTS GI discomfor,diarrhea or constipation, gas pain, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY > assess pt.s pain before therapy >monitor for possible drug Induced adverse reactions >advice pt. not to take drug for more than 7 days >advice pt. to report Immediately persistence or failure to relieve pain
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Cephalexin BRAND: Keflex
DOSAGE Adult: PO Susceptible infections 1-2 g/day in div. doses. Up to 6 g/day in moreserious infections. Prophylaxis against recurrent UTI 125 mg/day at night
CLASSIFICATION Anti-bacterial Agents Cephalosporins
MECHANISM OF ACTION Cephalexin, like the penicillins, is a beta-lactam antibiotic. By binding to specific penicillinbinding proteins PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, it inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wallautolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that cephalexin interferes with an autolysin inhibitor.
SIDE EFFECTS Pain at injection site; hypersensitivity; GI disturbances; eosinophilia, neutropenia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia Potentially Fatal: Anaphylactic reactions; nephrotoxicity
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY >The drug should be taken with or without food. (May be taken with meals to reduce GI discomfort) >Before administration, ask patient if he is allergic to penicillins or cephalosporins. >Tell patient to take entire amount of drug exactly as prescribed, even after he feels better. >Advise patient to notify prescriber if rash develops or signs and symptoms of superinfection appear. >Inform patient not to crush, cut or chew extended-release tablets.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Augmentin BRAND: Co-Amoxiclav
DOSAGE Infants <3 m: 30 mg/kg/day div q 12h using the 125 mg/5 mL suspension Children >=3 m and <40 kg: 20-90 mg/kg/day div q 8-12 h Children >40 kg and Adults: 250-500 mg q 8h or 875 mg q 12h Skin abscess: 875 mg q12h
CLASSIFICATION Broad-spectrum penicillin
MECHANISM OF ACTION An antibiotic that combines amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. It destroys bacteria by disrupting their ability to form cell walls. Clavulanic acid blocks the chemical defence, known as beta-lactamase, that some bacteria have against penicillins. l Co-amoxiclav is active against bacterial infections that have become resistant to amoxicillin.
INDICATION Known or suspected amoxicillin resistant infections including respiratory tract, skin and soft tissue, genitourinary, and ear, nose and throat infections. Effective against strains of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pneumoniae and some beta lactamase-producing organisms. INDICATION >Treatment of patients at risk for ischemic events history of MI, ischemic stroke, peripheral artery disease >Treatment of patients with acute coronary syndrome
CONTRAINDICATION Penicillin hypersensitivity. History of co-amoxiclavassociated or penicillinassociated jaundice or hepatic dysfunction.
SIDE EFFECTS > Hepatitis. >Cholestatic jaundice. > Erythema multiforme (including StevensJohnson syndrome). > Toxic epidermal necrolysis. > Exfoliative dermatitis. > Vasculitis. > Dizziness. > Headache. > Convulsions (especially in high doses or in renal impairment). > Superficial teeth staining when using the suspension. > Phlebitis at injection site.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY - Assess bowel pattern before and during treatment as pseudomembranous colitis may occur. - Report haematuria or oliguria as high doses can be nephrotoxic. - Assess respiratory status. - Observe for anaphylaxis. - Ensure that the patient has adequate fluid intake during any diarrhoea attack.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Clopidogrel BRAND: Platexan, Plavix
DOSAGE Adult: PO Prophylaxis of thromboembolic events 75 mg once daily.
CLASSIFICATION .Antiplatelet agents
MECHANISM OF ACTION Clopidogrel is a potent, noncompetitive inhibitor of adenosine diphosphate- (ADP) induced platelet aggregation, irreversibly inhibiting the binding of ADP to its platelet membrane receptors. Consequently, platelets exposed to clopidogrel are affected for the remainder of their lifespan (approximately 7 10 days). The inhibition is specific and does not significantly affect cyclooxygenase (COX) or arachidonic acid metabolism. It can also indirectly inhibit platelet aggregation induced by agonists other than ADP by blocking the amplification of platelet activation by released ADP: ADP binding is necessary for activation of the GPIIb/IIIa receptor, which is the binding site for fibrinogen. Fibrinogen links different platelets together to form the platelet aggregate. it thus ultimately inhibits the activation of the GPIIb/IIIa receptor, its binding to fibrinogen and further platelet aggregation.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with allergy to clopidogrel, active pathological bleeding such as peptic ulcer or intracranial hemorrhage, lactation.
SIDE EFFECTS CNS: Headache,dizziness, weakness, syncope, flushing CV: Hypertension, edema Dermatologic:Rash,pruritus GI: Nausea, GI distress, constipation, diarrhea, GI bleed Other:Increased bleeding risk
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY >Assess for symptoms of stroke, MI during treatment >Monitor liver function studies: AST, ALT, bilirubin, creatinine if patient is on ong-term therapy >Monitor blood studies: CBC,Hgb, Hct, protime, cholesterol if the patient is on long-term therapy; thrombocytopenia and neutropenia may occur.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Lagundi leaf (Vitex negundo L.) BRAND: Ascof Forte
DOSAGE Tablet: Adult: 300-600 mg tidqid. Children: 7-12 yr 300 mg tid-qid. Syrup: Adult: 300-600 mg (510 mL) 1-2 tsp tid-qid. Children: 15 mg/kg/dose tid, >40 kg 2 tsp tid, 6-12 yr (2040 kg) 1 tsp tid, 4-6 yr (15.5-20 kg) 1 tsp tid, 2-4 yr (10-15.5 kg) tsp tid. DOSAGE Tablet/syrup: Adults: daily dose of 30 mg)to 120) taken in 2 to 3 divided doses Children up to 2 years: half a tsp twice daily Children 2 - 5 years: half a tsp 3 x daily Children over 5 years: One tsp 23 x daily. DOSAGE Inhalation Asthma Adult 100/250/500 mcg/dose of inhalation powder: 1 inhalation bid. 50/125/250 mcg/dose of pressurised inhalation: 2 inhalation bid. Child: 4-12 yr: 100 mcg/ dose of inhalation powder: 1 inhalation bid
CLASSIFICATION . Cough & Cold Preparations. Natural antiviral
MECHANISM OF ACTION Antiviral activity; inhibits the secretion of mucous secretions to expectorate easily.
INDICATION Relief of cough due to common colds & flu. Treatment of bronchospasm in acute bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis & other bronchopulmonary disorders. Relief of reversible, mild to moderate bronchospasm (prophylactic/maintenance medication) in adults & childn w/ obstructive airway disease.
CONTRAINDICATION No known contraindication
SIDE EFFECTS Itchiness, nausea and vomiting, tachycardia, diarrhea, drowsiness and body malaise
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Give drug with food or after meals. Encourage client to cough to expectorate the secretions. Take note color and consistency of secretion. Encourage to drink liquids especially water. If cough is longer than two weeks, ask client to visit a physician.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Ambrolex BRAND: Ambroxol HCl
CLASSIFICATION Antiasthmatic, Mucolytic agent
MECHANISM OF ACTION Mucolytic which changes the structure of Bronchial secretions by reduction and fragmentation of the Mucopolysaccharide fibers, leading to reduce viscosity of Mucous, thus expectoration is facilitated.
INDICATION Acute and Chronic disorders of the respiratory tract associated with Pathologically thickened mucus and impaired mucus transport.
CONTRAINDICATION This medicine should not be used if you are allergic to one or any of its ingredients
SIDE EFFECTS Mild GI side effects, Rash
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY *The patient should be instructed to swallow the tablet whole and not chew to prevent choking or reduced effectiveness. *Encourage the patient to spit into a tissue rather than swallow the sputum. *Take note of the color and consistency and report any changes to the physician. *Suctioning equipment to clear the airways of excess mucus should be kept nearby. *Prior to administering and immediately after, listen to the patient's lung sounds and note any abnormalities. *Regularly assess these sounds to ensure the medication is working properly. NURSING RESPONSIBILITY *Pulmonary tuberculosis, severe cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, hypokalaemia, thyrotoxicosis. Paradoxical bronchospasm; discontinue immediately. *Prolonged treatment with high doses increases risk of adrenal suppression and systemic effects; monitor adrenal function. *Monitor height of children on prolonged therapy. *Should not be initiated during an exacerbation or if patients have significantly worsening or acutely deteriorating asthma. *Consider additional steroid therapy during stress or surgery. *Pregnancy, lactation. Withdraw gradually.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Fluticasone propionate and Salmeterol xinafoate BRAND: Seretide Accuhaler, Seretide Evohaler
CLASSIFICATION . Antiasthmatic & COPD Preparations
MECHANISM OF ACTION Seretide contains salmeterol and fluticasone propionate which have different modes of action. Salmeterol protects against symptoms, fluticasone propionate improves lung function and prevents exacerbations of the condition.
INDICATION Regular treatment of reversible obstructive airways disease (ROAD), including asthma where use of combination therapy (bronchodilator & inhaled corticosteroid) is appropriate. Maintenance treatment of COPD including chronic bronchitis & emphysema.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to any of the active substances or to the excipient. Also, other acute attacks of asthma.
SIDE EFFECTS Mouth and throat candidiasis, throat irritation, hoarseness/dysphonia, nasopharyngitis, lower respiratory tract infections (e.g. pneumonia and bronchitis), hypokalaemia, headache, tremors, palpitation, muscle cramps. Prolonged high dose use may cause Cushing's syndrome, Cushingoid features, adrenal suppression, retardation of growth in children and adolescents, bone mineral density decrease, cataract and glaucoma. Potentially Fatal: Paradoxical bronchospasm.
DRUG NAME GENERIC: Aspirin BRAND: Aspergum, Bayer, Easpirin
DOSAGE oral and suppository forms.,chewable tablet, gums, enteric coated, SR and buffered preparations. Adults:SR: 1300mg, then 650-1300mg q 8h Gum: chew 454mg q 4 h. Children:1015mg/kg/dose q 4h. Classification Antibiotic Penicillin antibiotic
CLASSIFICATION Analgesic (nonopioid) Anti-inflammatory Antiplatelet Antipyretic NSAID
MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins, which are important mediators of inflammation.
INDICATION Mild to moderate pain, fever, inflammatory condition (rheumatic fever, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis), reduction of risk of recurrent TIAs or CVA in patient with history of TIA.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with allergy to salicylates or NSAIDs, allergy to tartrazine; hemophilia, bleeding ulcers, hemorrhagic states, blood coagulation defects, hypoprothrombinemia, Vitamin K deficiency.
SIDE EFFECTS Acute aspirin toxicity: Respiratory alkalosis, tachypnea, hemorrhage, confusion, excitement, pulmonary edema, seizures, tetany, metabolic acidosis, fever Aspirin intolerance: exacerbation of bronchospasm, rhinitis GI: nausea, dyspepsia, heartburn, epigastric discomfort, anorexia Hematologic: occult blood loss, hemostatic defects Salicylism: dizziness, tinnitus, difficulty hearing, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, mental confusion. Side Effects *CNS: lethargy, hallucinations, seizures *GI: glossitis, stomatitis, gastritis, sore mouth, furry tongue, blackhairy tongue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, enterocolitis, pseudomem-branous colitis, non-specific hepatitis *GU: Nephritis *Hematologic: anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, prolonged bleeding time (more common than with other penicillinase-resistant penicillins) *Hypersensitivity: rash, fever, wheezing, anaphylaxis *Local: pain, phlebitis, thrombosis at injection site, Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction when used to treat syphilis *Other: superinfections, sodium overload, leading to heart failure Side Effects *CNS: headache, dizziness asthenia, vertigo, insomnia, apathy, anxiety, paresthesias, dream abnormalities *Dermatologic: rash, inflammation, urticaria, pruritus, alopecia, dry skin *GI: diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, dry mouth, tongue atrophy. *Respiratory: URI symptoms, cough, epistaxis *Other: cancer in preclinical studies, back pain, fever
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Give drug with food or after meals if GI upset occurs. Give drug with full glass of water to reduce risk of tablet or capsule lodging in the esophagus. Do not crush, and ensure that patient does not chew SR preparations. Do not use aspirin that has strong vinegar like odor.
Drug Name Brand : Bicillin L-A, Permapen Generic Name: Penicillin G
Dosage Injection: 600,000, 1.2 million, 2.4 million unit/dose
Mode of Action Bactericidal: Inhibits synthesis of cell wall of sensitive organisms, causing cell death
Indication Severe infections caused by sensitive organisms (streptococci) URI caused by sensitive streptococci Treatment of syphilis, bejel, congenital syphilis, pinta yaws Prophylaxis of rheumatic fever and chorea
Contraindication Contraindicated with allergies to penicillins, cephalosporins, or other allergens. Use cautiously with renal disorders, pregnancy lactation (may cause diarrhea or candidiasis in the infant).
Nursing Responsibility Culture infection before giving treatment; reculture if response is not as expected. Give by IM route only. Continue therapy for atleast 2 days after an infection has disappeared, usually 7-10 days. Give IM injection upper outer quadrant of the buttocks. In infants and small children, the midlateral aspect of the thigh may be preferred.
Drug Name Brand: Losec(CAN) Generic: Omepron
Classification Antisecretory Drug Proton pump inhibitor
Dosage DR capsules; 10, 20, 40 mg DR tablets: 20mg(OTC)
Action Gastric acid-pump inhibitor: suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the hydrogen-potassium ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cells blocks the final step of acid production.
Indication Short term treatment of active duodenal cancer Treatment of heartburn or symptoms of GERD Short term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer GERD, severe erosive esophagitis, poorly responsive symptomatic GERD Long term treatment of pathologic hypersecretory conditions. Eradication of helicobacter pylori with amoxicillin or metronidazole and clarithromycin
Contraindication Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to omepron or its components. Use cautiously with pregnancy and lactation.
Nursing Responsibility Administer before meals. Caution patient to swallow capsule whole---not to open, chew or crush them. Administer abtacids with, if needed. If patient cant swallow combine it with 1 tablespoon applesauce.
Drug Name Brand: Catapres Generic: Clonidine
Classification Antihypertensive Central Analgesic Symphatolytic (centally acting)
Dosage Initial dose is 0.1mg BID
Action Stimulates CNS alpha2adrenergic receptors, inhibits sympathetic cardio accelerator and vasoconstrictor centers, and decreases sympathetic outflow of the CNS.
Indication Hypertension, use alone or as part of combination therapy. Treatment of severe pain in cancer patients in combination with opiates; epidural more effective with neuropathic pain
Contraindication Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to clonidine or any adhesive layer components of the transdermal system. Use cautiously with severe coronary insufficiency, recent MI, cerebrovascular disease, chronic renal failure, pregnancy, lactation.
Side Effects *CNS: drowsiness, sedation, dizziness, headache, fatigue that ends to diminish within 4-6wks, dreams, nightmares, insomnia, hallucinations, delirium, nervousness, restlessness, anxiety, depression, retinal degeneration *CV: heart failure, orthostatic hypotension, palpitations, tachycardia, bradycardia, Raynauds phenomenon, ECG abnormalities *Dermatologic: resh, angioneurotic edema, hives, urticaria, hair thinning and alopesia, pruritus, dryness, itching or burning of the eyes, pallor *GI: dry mouth, constipation, anorexia, malaise, nausea, vomiting, parotid pain, parotitis *GU: impotence, sexual dysfunction, nocturia, difficulty micturition, urinary retention *Other: weight gain, transient hyperglycemia, gynecomastia, weakness, muscle or joint pain, cramps of the lower limbs, dryness of nasal mucosa, fever Side Effects Occasionaly patients have experienced gastric upset, nausea and headache.
Nursing Responsibility Do not discontinue, use abruptly. Continue oral clonidine therapy 4hrs after surgery then resume as soon as possible there after. Store epidural injection at room temperature; discard any unused portions. Reevaluate therapy if clonidine tolerance occurs. Use caution with alcohol. Your sensitivity may increase while using this drug.
Drug Name Brand: Serc Generic: Betahistine dihydrochloride
Classification Anti emetics Anti vertigo
Dosage Adults: 24-48 mg divided over the day 8 mg tablets- 1-2 tablets, 3 times/day 16 mg tablets: 1 tablet, 3 times/day
Action Betahistine was found to have a histamine-like action in animals. Since parenteral histamine has been used in the treatment of Meniere's disease, studies were conducted to test the action of betahistine in this condition. Unlike some other anti-vertigo drugs, testing with nystagmus induced by caloric and rotational stimulation has demonstrated that betahistine does not decrease the vestibular response, as recorded by electronystagmography. In addition, the absorption, metabolism and action of betahistine when administered by the oral route are not known. may be useful in reducing the vertigo of Meniere's disease.
Indication Menieres disease, Meniere-like syndrome (with symptoms of vertigo, tinnitus and sensorineural deafness) and vertigo of peripheral origin.
Contraindication Hypersensitivity to any component of the product
Nursing Responsibility Avoid contact of oral solution or injection with skin Raise bed rails, institute safety measures, supervise ambulation
DRUG NAME BRAND: Ansimar GENERIC: Doxofylline
CLASSIFICATION Antiasthmatic & COPD Preparations
DOSAGE Tab Adult 1 tab bid-tid. Syr Childn >12 yr 10 mL once-tid, <12 yr 6-9 mg/kg
MECHANISM OF ACTION Adrenergic bronchodilators and phosphodiesterase inhibitors both work by increasing intracellular level of cyclic3,5- adenosine monophosphate(cAMP); adrenergics by increasing production and phosphodiesterase inhibitorsby decreasing breakdown. Increased levels of cAMP produce bronchodilation.Corticoster oids act by decreasing airway inflammation. Anticholinergics(ipratropiu m) produce brondhodilation by decreasing intracellular levels ofcyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Leukotriene receptor antagonists andmast cell stabilizers decrease the release of substances that can contribute tobronchospasm MECHANISM OF ACTION View CoAleva mechanism of action for pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics details.
INDICATION Bronchial asthma & pulmonary disease w/ spastic bronchial component.
CONTRAINDICATION Acute MI, hypotension, lactation.
SIDE EFFECTS Nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, cephalalgia, irritability, insomnia, tachycardia, extrasystole, tachypnea, hyperglycemia, albuminuria.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY > Use with caution in patients with hypoxemia, hyperthyroidism, liver disease, renal disease, in those with history of peptic ulcer and in elderly. Frequently, patients with CHF have markedly prolonged drug serum levels following discontinuation of Ansimar. > assess for allergic reaction > assess for breath sounds >should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
DRUG NAME Brand: Co-aleva Generic: Betamethasone, ebastine
DOSAGE
CLASSIFICATION . Antihistamines & Antiallergics
INDICATION Treatment of seasonal/perennial allergic rhinitis & chronic urticaria.
CONTRAINDICATION Severe liver insufficiency. Lactation.
SIDE EFFECTS Headache, dry mouth, drowsiness. Less common are pharyngitis, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, asthenia, epistaxis, rhinitis, sinusitis, nausea & insomnia.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Systemic use Give daily dose before 9 AM to miminormal peak corticosteroid blood levels. Increase dosage when patient is subject to stress. Taper doses when discontinuing highdose or long-term therapy. Do not give live virus vaccines with immunosuppressive doses of corticosteroids. Topical dermatologic preparations Examine area for infections, skin integrity before application. Administer cautiously to pregnant patients; topical corticosteroids have caused teratogenic effects and can be absorbed from systemic site. WARNING: Use caution when occlusive dressings or tight diapers cover affected area; these can increase systemic absorption of the drug. Avoid prolonged use near eyes, in genital and rectal areas, and in skin creases.
DRUG NAME Brand: Myonal Generic: Eperisone
DOSAGE 1 tab tid
CLASSIFICATION . Muscle relaxants
MECHANISM OF ACTION Eperisone is centrallyacting skeletal muscle relaxant used to improve myotonic symptoms.\
INDICATION Spastic paralysis in cerebrovascular diseases, spastic spinal paralysis, cervical spondylosis, postop sequelae (including cerebrospinal tumor), sequelae to trauma (spinal trauma, head injury), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, cerebral palsy, spinocerebellar degeneration, spinal vascular diseases, other encephalomyelopathies. Improvement of myotonic symptoms in cervical syndrome,periarthritis of the shoulders & lumbago, tension-type headache.
CONTRAINDICATION Eperisone is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug.[8] Side Effects: very rare excessive relaxation, stomachache, nausea, vertigo, anorexia, drowsiness, skin rashes, diarrhoea, vomiting, indigestion, GI disturbances, insomnia, headache, constipation etc.[9]
SIDE EFFECTS Weakness, dizziness, insomnia, drowsiness, numbness in the extremities, hepatic & renal dysfunction, hematological changes, rashes, GI disturbances, urinary disorders
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY 1. Careful Administration (MYONAL should be administered with care in the following patients.) (1)Patients with a history of drug hypersensitivity (2) Patients with hepatic function disorder 2. Important Precautions Weakness, light-headedness, sleepiness or other symptoms may occur. In the event of such symptoms, the dosage should be reduced or treatment discontinued. Patients should be cautioned against engaging in potentially hazardous activities requiring alertness, such as operating machinery or driving a car. [USE IN THE ELDERLY] Since the elderly often have a physiological hypofunction, it is advisable to take measures, such as reduction in dosage under careful supervision. [PREGNANCY AND LACTATION] 1. Use During Pregnancy MYONAL should only be used in pregnant women or women suspected of being pregnant, if the expected therapeutic benefits are evaluated to outweigh the possible risk of treatment. 2. Use During Lactation It is advisable to avoid the administration of MYONAL to nursing mothers. When MYONAL must be used, breast feeding should be discontinued during treatment 3. [PEDIATRIC USE] Safety in children has not been established. NURSING RESPONSIBILITY Watch for behavioral disturbances esp. in children. -Dont stop drug abruptly because this may worsen seizures. Call prescriber at once if adverse reactions develop. -Assess elderly patients response closely. -Monitor patient for oversedation. -Monitor CBC and liver function tests. -Withdrawal symptoms are similar to those of barbiturates
DRUG NAME Brand: Klonopin Generic: rivotril or clonazepam
DOSAGE Adult: 1.5 mg P.O daily in three divided doses. Children: 0.01 to 0.03 mg P.O daily in two or three divided doses
CLASSIFICATION Benzodiazepine Antiepileptic .
MECHANISM OF ACTION Probablyfacilitatesthe effects of thenhibitory neurotransmitterGABA.
INDICATION -Lennox-Gaustat syndrome, atypical absence seizures, akinetic and mycolonic seizures. -Panic disorder -Acute manic episodes of bipolar disorder -Adjunct treatment for schizophrenia -Periodic leg movements during sleep -Parkinsonian dysarthria.
CONTRAINDICATION -Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to benzodiazepinees and in those with significant hepatic Use cautiously in patients with mixed type seizures because drug may cause generalized tonic-clonic seizures. -Use cautiously in children and in patients with chronic respiratory disease or open-angle glaucoma.
SIDE EFFECTS
anxiety increased heart rate tremor general unwell feeling Behavior problems drowsiness lack of muscular coordination an allergic reaction (difficulty breathing; closing of the throat; swelling of hallucinations or severe confusion yellowing of the skin or eyes
DRUG NAME GENERIC: BRAND:
DOSAGE .
CLASSIFICATION
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
You might also like
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudySarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Tip: Urinary Proteins Less Than 300 MG Is Not Detectable by Urine DipstickDocument11 pagesTip: Urinary Proteins Less Than 300 MG Is Not Detectable by Urine DipstickAsif Newaz100% (2)
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenDocument20 pagesChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenMark oliver Gonzales100% (1)
- MCQ TherapeuticDocument170 pagesMCQ Therapeutickarlosmena50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLee JennyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyKristine Joy A. AniNo ratings yet
- AtorvastatinDocument2 pagesAtorvastatinJasmin T LarizaNo ratings yet
- ClonidineDocument1 pageClonidineKhryss Paula BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Losartan Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Drug StudyXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 pagesDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNo ratings yet
- DS (Fenofibrate)Document5 pagesDS (Fenofibrate)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin and Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCiprofloxacin and Paracetamol Drug StudyRichard MendejaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Risk Category B DIN RD TrimesterDocument7 pagesPregnancy Risk Category B DIN RD TrimesterLheajane SocratesNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- Timolol MaleateDocument3 pagesTimolol MaleateAP TOROBXNo ratings yet
- Doxorubicin: Mechanism of ActionDocument3 pagesDoxorubicin: Mechanism of ActionGeorge FogNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocument4 pagesMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Drug Study TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Study TramadolLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Solu CortefDocument1 pageSolu CortefKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLarah Mae AndogNo ratings yet
- ISONIAZIDDocument2 pagesISONIAZIDXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1 (Done)Document3 pagesDrug Study 1 (Done)Otaku MiyoNo ratings yet
- BiperidenDocument1 pageBiperidenMFQ.RN100% (2)
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocument4 pagesAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyTin BernardezNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Drug StudyaagNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRej Gallien PontalbaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyMarychen Cabunas100% (1)
- Drug Study #2Document3 pagesDrug Study #2mharjoe pulmanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyHennah ReblandoNo ratings yet
- Mycophenolate MofetilDocument1 pageMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- ItoprideDocument2 pagesItoprideLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On AlendronateDocument12 pagesA Drug Study On AlendronateTrio San LuisNo ratings yet
- Check The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutDocument2 pagesCheck The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutJust nowNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PonstanDocument1 pageDrug Study PonstanRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSalbutamol Drug StudyVinz Khyl G. CastillonNo ratings yet
- Dextrose 50 InjectionDocument6 pagesDextrose 50 InjectionLip StickNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- ChlorpromazineDocument2 pagesChlorpromazineFay Dominguez100% (1)
- Drug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- TrimetazidineDocument2 pagesTrimetazidinemasheennavirgoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OmeprazoleDocument3 pagesDrug Study OmeprazoleSandeepNo ratings yet
- Pravastatin SodiumDocument3 pagesPravastatin Sodiumapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug Study AzithromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study AzithromycinYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- Levetiracetam PDFDocument3 pagesLevetiracetam PDFShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDsquared100% (1)
- Nitroglycerin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNitroglycerin Drug StudyBeatrizz P GellaNo ratings yet
- DRUG SpirivaDocument1 pageDRUG SpirivarholiboiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate)Document13 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate)Flauros Ryu Jabien50% (2)
- Drug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)Document3 pagesDrug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)amitNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LeukemiaDocument7 pagesDrug Study LeukemiaLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Ranitidine, Citicoline, Enalapril, Aspilet, Cefuroxime Etc)Document9 pagesDrug Study (Ranitidine, Citicoline, Enalapril, Aspilet, Cefuroxime Etc)gino_23_28No ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Drug Study (Pedia)Document7 pagesDrug Study (Pedia)Caurrine Monsalud100% (1)
- Drug Study AGEDocument9 pagesDrug Study AGECherry Jani OlmedoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykamirure02No ratings yet
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Drug Study - CaseDocument9 pagesDrug Study - CaseMay EvelynNo ratings yet
- Case Report MicrocephalyDocument22 pagesCase Report MicrocephalyApril Jan D. AlagonNo ratings yet
- Compliled DrugstudyDocument15 pagesCompliled DrugstudyApril Jan D. Alagon0% (1)
- CiticholineDocument2 pagesCiticholineApril Jan D. AlagonNo ratings yet
- CiticholineDocument2 pagesCiticholineApril Jan D. AlagonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineDocument10 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- CVD Case StudyDocument23 pagesCVD Case StudyMsRhyxelle80% (5)
- Evolving Consumer HouseholdDocument3 pagesEvolving Consumer HouseholdApril Jan D. AlagonNo ratings yet
- BeteN105 TreatmentDocument2 pagesBeteN105 TreatmentApril Jan D. AlagonNo ratings yet
- Iv. Psychodynamics Schematic Diagram: Psychosocial Factor Wjsgjshjknjffffafa Ctorcal Factor EnvironmentalDocument2 pagesIv. Psychodynamics Schematic Diagram: Psychosocial Factor Wjsgjshjknjffffafa Ctorcal Factor EnvironmentalApril Jan D. AlagonNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Date of Rotation: - Score: - Pediatrics Shifting ExamDocument5 pagesName: - Date: - Date of Rotation: - Score: - Pediatrics Shifting ExamKristine Seredrica100% (1)
- -renalเ -adrenalเ -aortaเ: FeverDocument4 pages-renalเ -adrenalเ -aortaเ: FeverWipaporn ChaengsriNo ratings yet
- Recapitulare TestDocument38 pagesRecapitulare TestDana ChitoiNo ratings yet
- Galvus (Vildagliptin) : How Does It Work?Document5 pagesGalvus (Vildagliptin) : How Does It Work?Radhakrishna KurupNo ratings yet
- Anti Amoebic DrugsDocument17 pagesAnti Amoebic DrugsSaurabh Gautam100% (2)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Case PresentationDocument4 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome: Case PresentationJunathan L. DelgadoNo ratings yet
- 2018 01 15 Lijst Antibiotica Met DDDA Informatie (Update 15-01-2018) - 167 PDFDocument11 pages2018 01 15 Lijst Antibiotica Met DDDA Informatie (Update 15-01-2018) - 167 PDFMatthew HsuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJenny YenNo ratings yet
- Diabetes WorksheetDocument1 pageDiabetes WorksheetUSMP FN ARCHIVOSNo ratings yet
- Guia-Taller Ingles - Grado Tercero PDFDocument2 pagesGuia-Taller Ingles - Grado Tercero PDFAngel Mateo100% (1)
- SIGNIFICANT SAQsDocument407 pagesSIGNIFICANT SAQsFarid Iqbal100% (2)
- Practical Notes On Antibiotics - Emtyazology Book 2nd EditionDocument18 pagesPractical Notes On Antibiotics - Emtyazology Book 2nd EditionmajdNo ratings yet
- CreatePDF (3) - DikonversiDocument504 pagesCreatePDF (3) - Dikonversidewi ratnasariNo ratings yet
- List HargaDocument40 pagesList HargaReza PahleviNo ratings yet
- Botulism DiseaseDocument2 pagesBotulism DiseasenadiaNo ratings yet
- Feeling IllDocument2 pagesFeeling IllIoanaAruncuteanNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Disorders Research AssignmentDocument2 pagesDigestive System Disorders Research Assignmentapi-305436791No ratings yet
- HPL All Product ListDocument10 pagesHPL All Product Listelectryfing asifNo ratings yet
- United Kingdom National Guideline On The Management of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (2007)Document5 pagesUnited Kingdom National Guideline On The Management of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (2007)Anonymous Tzn8RGBZ4No ratings yet
- Chapter 132: Lower Urinary Tract Infection: Where Is The Bathroom? Level I Problem IdentificationDocument4 pagesChapter 132: Lower Urinary Tract Infection: Where Is The Bathroom? Level I Problem IdentificationReen ChavezNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin and Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCiprofloxacin and Paracetamol Drug StudyRichard MendejaNo ratings yet
- Copy of Integumentary Student Resources 1Document12 pagesCopy of Integumentary Student Resources 1Alondra Hernandez ReyesNo ratings yet
- NO Produk: List Harga Dexa Per Oktober 2020Document6 pagesNO Produk: List Harga Dexa Per Oktober 2020Rina RaehanaNo ratings yet
- MARET 2021 RevDocument20 pagesMARET 2021 Revklinik stiesiaNo ratings yet
- Iap Guide Book On Immunization Immunization in Special Situations PDFDocument8 pagesIap Guide Book On Immunization Immunization in Special Situations PDFGirdhari Lal Saini100% (1)
- Penatalaksanaan Terapi ArvDocument23 pagesPenatalaksanaan Terapi ArvSri AlfatihaNo ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B Recommendations: Topic Description GradeDocument3 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations: Topic Description GradeSantiago AldayNo ratings yet