Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 2
Uploaded by
Dinesh KurubaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 2
Uploaded by
Dinesh KurubaCopyright:
Available Formats
EE334, EE Dept, IIT Bombay TUTORIAL - 2 1. Three single-phase transformers, each rated 25 MVA, 38.1/3.
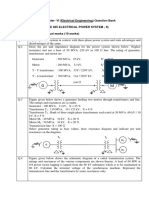
81 kV are connected Y- with a balanced load of 0.8 , Y-connected resistors. Choose a base of 75 MVA, 66 kV for the high voltage side of the transformer. Select the corresponding base for the low voltage side. Determine the pu resistance of the load referred to the low voltage side. Then, determine the load resistance in ohms referred to the high voltage side and the pu value of this resistance with the chosen base. 2. A three-phase, wye-connected, 10 MVA, 11 kV synchronous generator has a reactance of 10 per phase. Using the rated MVA and voltage as base values, determine the per-unit reactance. Also, find per-unit value with 12.5 kV and 15 MVA as the base values. 3. Consider the ac load shown in figure 2. It is fed from 500-volt source. Compute the various powers absorbed in the two load branches after expressing all quantities in pu, choosing a common base of 100 KVA and 500 V.
.
V
I to t
I1 8
I2
6 2
.
F ig u re 2
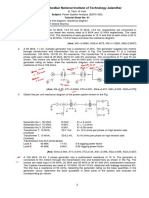
4. Draw the impedance diagram for the power system shown in figure 3 by using the values of the impedances in pu choosing a common base of 30 MVA, 33 kV on the transmission line.
L1 G 1 T1 L2 T3 L oad A F ig u re 3 T4 L oad B T2
G 2 G 3
The ratings of various components in the power systems are: Generator 1: 25 MVA, 10.5 kV, X = 1.5 Generator 2: 15 MVA, 6.6 kV, X = 1.1 Generator 3: 25 MVA, 6.6 kV, X = 0.53 Transformers T1 and T3 are each rated for 15 MVA, 33/11 kV, X = 15.3 per phase referred to HV side. Transformers T2 and T4 are each rated for 15 MVA, 33/6.6 kV, X = 15.0 per phase referred to HV side. Transmission lines L1 and L2: 20.0 per phase. Load A: 30 MW at a nominal voltage of 11 kV, 0.9 power factor lagging. Load B: 30 MW at a nominal voltage of 6.6 kV, 0.85 power factor lagging. 1
You might also like
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1sadNo ratings yet
- Pse Problems Group AssignmentDocument14 pagesPse Problems Group AssignmentSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Perunit Calculations and Impedance DiagramsDocument3 pagesExperiment 6 Perunit Calculations and Impedance DiagramsJaved Ahmed LaghariNo ratings yet
- Powersystem ExerciseDocument3 pagesPowersystem ExerciseHabib FirdausNo ratings yet
- EE 109 System ProtectionDocument4 pagesEE 109 System ProtectionIan Acuzar PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2ksajjNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument23 pagesPower System AnalysisSaeed Al BlooshiNo ratings yet
- ECE4762011 - Lect9 Transformer PuDocument43 pagesECE4762011 - Lect9 Transformer PuSudhir SainiNo ratings yet
- PSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSDocument33 pagesPSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSMahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Pse - 2012-2013Document23 pagesTutorial Pse - 2012-2013Mahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Homework 02 Electric Power NetworksDocument2 pagesHomework 02 Electric Power NetworkswaleedNo ratings yet
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 1Document2 pagesTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 1eh2asham1No ratings yet
- Problem Set 3Document2 pagesProblem Set 3Waljer 1No ratings yet
- PSADocument25 pagesPSAramyadspNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I: Per Unit (PU) Representation of Power System Elements (Contd)Document9 pagesChapter - I: Per Unit (PU) Representation of Power System Elements (Contd)Asrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis and Stability Subject Question BankDocument7 pagesPower System Analysis and Stability Subject Question BankNaveen RajNo ratings yet
- EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT-I INTRODUCTIONDocument11 pagesEE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT-I INTRODUCTIONdrmsrmurty9473No ratings yet
- Ee2351 Psa Im 2013Document11 pagesEe2351 Psa Im 2013ZARGHAM KHAN100% (1)
- Power System Analysis: Transformers, Per UnitDocument43 pagesPower System Analysis: Transformers, Per UnitMamta MrjnNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PSE 2011-2012Document23 pagesTutorial PSE 2011-2012Mahesh Singh100% (1)
- 1: Choose The Best Answer of The Following (20 Marks) : P P S SDocument4 pages1: Choose The Best Answer of The Following (20 Marks) : P P S Sshubha christopher100% (1)
- Pu Assignment 1Document2 pagesPu Assignment 1jasonNo ratings yet
- Per Unit ExamplesDocument7 pagesPer Unit ExamplesteddydemerewNo ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument4 pagesPower Systemj settyNo ratings yet
- Protective Relaying and Switchgear ProblemsDocument5 pagesProtective Relaying and Switchgear ProblemsRishabh KaliaNo ratings yet
- BE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Document5 pagesBE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Adesh Bhortakke100% (1)
- Power System Analysis Tutorial Sheet 01Document4 pagesPower System Analysis Tutorial Sheet 01Goyal100% (1)
- Transformers PDFDocument2 pagesTransformers PDFusama_gculNo ratings yet
- Lab QPDocument8 pagesLab QPpmahesh268No ratings yet
- Power System Analysis NotesDocument40 pagesPower System Analysis NotesAkhtarNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis (Jan-2014)Document10 pagesPower System Analysis (Jan-2014)Likhitha YerraNo ratings yet
- Tut 2Document3 pagesTut 2MOHIT SINGHALNo ratings yet
- PS-III Assignment QuestionsDocument2 pagesPS-III Assignment QuestionsSanoxNo ratings yet
- EE2029 - Introduction To Electrical Energy Systems Tutorial # 1 TransformersDocument2 pagesEE2029 - Introduction To Electrical Energy Systems Tutorial # 1 TransformersToh Wei WenNo ratings yet
- PSA SolutionDocument5 pagesPSA SolutionviswaNo ratings yet
- Fault analysis and sequence networks of power systemsDocument7 pagesFault analysis and sequence networks of power systemsDenish Gupta0% (1)
- ELEG 330 Power System Analysis Homework 1Document2 pagesELEG 330 Power System Analysis Homework 1gigiNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-IDocument8 pagesPower Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-ISoniya GJNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument5 pagesAssignment IPrasenjit DeyNo ratings yet
- Tuto 4 PuDocument3 pagesTuto 4 PuVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Preetham ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document2 pagesTutorial 8AyrtonNo ratings yet
- VOLTAGE TRANSFORMERS LAB EXPERIMENTDocument10 pagesVOLTAGE TRANSFORMERS LAB EXPERIMENTMohammed Abu Al HaijaNo ratings yet
- 018631123Document3 pages018631123muhammad javedNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument8 pagesQuestionewan koNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Singlephase TransformerDocument2 pagesTutorial Singlephase TransformerRishi Kant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Syed Faras HaiderNo ratings yet
- EE-311 Tutorial Sheet Fault CurrentsDocument5 pagesEE-311 Tutorial Sheet Fault CurrentsRishabh Kalia100% (1)
- Per Unit CalculationsDocument7 pagesPer Unit Calculationsanbuelectrical100% (1)
- Unit - 1 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Document6 pagesUnit - 1 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Sujit KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PsDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 PsAmin RafidNo ratings yet
- Ece5377 6377 HW02 (20150211)Document1 pageEce5377 6377 HW02 (20150211)bilalhanjra246No ratings yet
- Tutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFDocument6 pagesTutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFnanangNo ratings yet
- W6 - Lecture 6 (1) - 220418 - 123913Document28 pagesW6 - Lecture 6 (1) - 220418 - 123913saiedali2005No ratings yet
- Power System Componets and Per Unit ReprsentationDocument26 pagesPower System Componets and Per Unit ReprsentationVinit SinghNo ratings yet
- UEE602 Tut Sheets 1Document12 pagesUEE602 Tut Sheets 1Kulvinder Singh0% (1)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document2 pagesTutorial 8Dinesh KurubaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document26 pagesChap 4Dinesh KurubaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document26 pagesChap 4Dinesh KurubaNo ratings yet
- 9 EE 334 Powfbdzer Flow SolutionsDocument41 pages9 EE 334 Powfbdzer Flow SolutionsDinesh KurubaNo ratings yet