Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review Chapter Chap 0
Uploaded by
karatmanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review Chapter Chap 0
Uploaded by
karatmanCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING CALCULUS 1 (MTH 1112) CHAPTER 0. REVIEW 1.
Definitions Function, Domain and Range A function f is a rule that assigns exactly one element in a set B to each element in a set A, written as = ( ). Set A is called the domain of f while the set of all values ( ) in B is called the range of f i.e. { ( )| }. Thus set A of is referred to as independent variable and set B of as dependent variable. 2. Vertical Line Test Any correspondence meeting the requirement of a function i.e. matching exactly one to each , could be graphically verified using a vertical line test, any vertical line should intersect the graph in at most one point. 3. Definition Inverse Function Let and have domains and , respectively , and that . If ( ) = ( ) = ( ) = ( ) is defined for all and
( ) is defined for all then
is the inverse of , written
( )
, ,
and
. Equivalently,
is the inverse of ,
Note that
4. Definition (1) One-to-One Function A function A function is a one-to-one function when for every { } for which = ( ). { }, there is exactly one
= [ ( )]
5. Definition (2) One-to-One Function
6. Horizontal Line Test
is one-to-one if and only if the equality ( ) = ( ) implies
In graphical terms, a function is a one-to-one iff every horizontal line intersects the graph in at most one point usually referred to as the horizontal line test. 7. Theorem A function has an inverse if and only if it is one-to-one.
8. The symmetry of a function and its inverse - The graph of an inverse function ( ) is essentially the reflection of the function ( ) through the = line, making it possible to map an unknown inverse function. 1|Page
ENGINEERING CALCULUS 1 (MTH 1112)
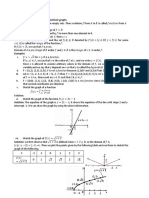
Example: Let f ( x )
x 3 1 , then f 1 ( x ) 3 x 2 1 . The plot below shows the relation between f ( x) and
25 20 15 10 5 0 -10 -5 -5 -10 0 5 10 15 20 25 y=sqrt(x^3+1) y=x y=(x^2-1)^1/3
f 1 ( x ) i.e. reflection upon the line y x .
2|Page
You might also like
- Brief Review Chap 0 S1 1213Document2 pagesBrief Review Chap 0 S1 1213Furkan KirmaciNo ratings yet
- bpc5 ch02-06Document18 pagesbpc5 ch02-06Jiung WeiNo ratings yet
- Functions HandoutDocument7 pagesFunctions HandoutTruKNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics 11 Notes 1ST SemDocument25 pagesGeneral Mathematics 11 Notes 1ST SemPhilippine Expeditionary Force to RonogradNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Vocabulary ListDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Vocabulary ListLeetz123456No ratings yet
- Gen Math Q1 Mod 3Document16 pagesGen Math Q1 Mod 3Joselito Ubaldo100% (2)
- Inbound 6153025579738585635Document65 pagesInbound 6153025579738585635Justin Ralph GanzonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Relations and FunctionsDocument31 pagesLecture 1 - Relations and FunctionsAnthony BalatarNo ratings yet
- Applied I Full-1Document125 pagesApplied I Full-1nebyuNo ratings yet
- Functions: Week 1 ContentDocument33 pagesFunctions: Week 1 ContentPHENYO SEICHOKONo ratings yet
- Relation Is A Set of Ordered PairsDocument17 pagesRelation Is A Set of Ordered PairsJeoffrey MagtotoNo ratings yet
- Exploring FunctionsDocument5 pagesExploring FunctionsPetra LaribaNo ratings yet
- Maths - Summary of ChaptersDocument11 pagesMaths - Summary of ChapterssidNo ratings yet
- 4 Vertical Line and Horizontal Line TestDocument11 pages4 Vertical Line and Horizontal Line TestMellat AdnyNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter General MathematicsDocument6 pages1st Quarter General MathematicsAlfred Lawrence HonralesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Functional Analysis - Lec08Document12 pagesIntroduction To Functional Analysis - Lec08Kofi Appiah-DanquahNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 - Functions and Equivalence RelationDocument87 pagesTOPIC 2 - Functions and Equivalence RelationDomz Sensei100% (1)
- Discrete PPT 11 11 22Document143 pagesDiscrete PPT 11 11 22DenjiNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument26 pagesMaths Projectchaudhary.vansh2307No ratings yet
- College and Advanced Algebra Handout # 1 - Chapter 1. FunctionsDocument8 pagesCollege and Advanced Algebra Handout # 1 - Chapter 1. FunctionsMary Jane BugarinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 FunctionsDocument40 pagesLesson 2 Functionsagarao.kieshelynNo ratings yet
- F (X) 3x + 2 and G (X) 2x - 1: Warm-UpDocument33 pagesF (X) 3x + 2 and G (X) 2x - 1: Warm-UpRolyn Grace Domagoso VergaraNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic Functions and Their GraphsDocument22 pagesLogarithmic Functions and Their Graphscass dumpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Function and LimitDocument98 pagesChapter 1 - Function and LimitAndDanNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer 2Document3 pagesMath Reviewer 2danniellekaye14No ratings yet
- Introduction To Fourrier AnalysisDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Fourrier AnalysisWashington BrownNo ratings yet
- Functions and RelationsDocument15 pagesFunctions and RelationsAiza OchentaNo ratings yet
- Maths (T) Coursework STPM 2017 Term 1Document5 pagesMaths (T) Coursework STPM 2017 Term 1KennethLoJinChanNo ratings yet
- Svprecis 12 Maths Module 1 NewDocument20 pagesSvprecis 12 Maths Module 1 Newapi-252136290No ratings yet
- Assignment of CalculusDocument12 pagesAssignment of CalculusAyesha SaddiqueNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math Module 12 FunctionsDocument20 pagesDiscrete Math Module 12 FunctionsJayNo ratings yet
- Inverse of One-To-One FunctionDocument4 pagesInverse of One-To-One FunctionKathFaye EdaNo ratings yet
- Class 12th FormulaeDocument39 pagesClass 12th Formulaesushil tripathiNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics PowerPointDocument20 pagesGeneral Mathematics PowerPointMarie DirmaNo ratings yet
- Function and LimitDocument87 pagesFunction and LimitVũ Thái Anh100% (1)
- General Mathematics 11 Module 1 2021Document15 pagesGeneral Mathematics 11 Module 1 2021Mica Ella OlivarNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionDocument6 pagesRelation and FunctionJitesh RatawaNo ratings yet
- Jacobian Matrix and Determinant - Line IntegralDocument11 pagesJacobian Matrix and Determinant - Line IntegralAbdisaa GirmaNo ratings yet
- So How Do We Find The Inverse of A Function?Document6 pagesSo How Do We Find The Inverse of A Function?sherryl v floresNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument12 pagesFunctionsMuhammad Aamir FeroziNo ratings yet
- Bab 1Document8 pagesBab 1jak92No ratings yet
- Types of FunctionDocument20 pagesTypes of FunctionJonald Lopez100% (2)
- Week 4 - Graph of Inverse FunctionsDocument9 pagesWeek 4 - Graph of Inverse Functionscristinemacababbad1No ratings yet
- Week1 FunctionDocument16 pagesWeek1 FunctionNode FavNo ratings yet
- ch4 NotesDocument7 pagesch4 Notesapi-318471085No ratings yet
- Lesson10: Inverse of One - To-One FunctionsDocument36 pagesLesson10: Inverse of One - To-One FunctionsRex FajardoNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structure 3Document17 pagesDiscrete Structure 3malikabdullah0120No ratings yet
- Math A 10FDocument9 pagesMath A 10FBrian MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Slideshow PresentationDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Slideshow PresentationJohn Ralph GenabeNo ratings yet
- Physics 731 Lecture Notes 1Document57 pagesPhysics 731 Lecture Notes 1Yung-Ta SungNo ratings yet
- Introductory CalculusDocument46 pagesIntroductory CalculusNana Kofi JuniorNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument10 pagesFunctionsAna Marie ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Functions 2: 577/6553 Mathematical Methods / General Mathematics G 2014/s1Document25 pagesFunctions 2: 577/6553 Mathematical Methods / General Mathematics G 2014/s1Sabrina JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math Module 4Document4 pagesGen. Math Module 4Robert ClavoNo ratings yet
- + BX + C, Is An Example of A Polynomial FunctionDocument1 page+ BX + C, Is An Example of A Polynomial FunctionAlyssa Rae Garcia SorianoNo ratings yet
- Tuesday September 13: (Refers To Section 1.2 To 1.5 in Your Text)Document4 pagesTuesday September 13: (Refers To Section 1.2 To 1.5 in Your Text)S>No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Uniform Convergence and IntegrationDocument27 pagesChapter 9 Uniform Convergence and Integrationnormal@backup100% (1)
- Composite Function Classification of FunctionDocument12 pagesComposite Function Classification of FunctionanandNo ratings yet