Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculation of Combustions
Uploaded by
Vinay MathadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculation of Combustions
Uploaded by
Vinay MathadCopyright:
Available Formats
Q
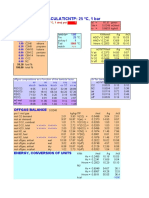
Calculate minimum volume of air required(both on KG basis and mole basis) to burn 1 KG of coal hav C-82 % H- 4% N-1% O- 5% S-1% M-2% A-5%
Solution: Combustion equationsC+O2=CO2 12 KG of C combines with 32 Kg of O2 to give 44 KG of CO2 1 mole of C combines with 1 mole of O2 to give 1 mole of CO2 2H2+O2=2H2O 4 KG of H2 combines with 32 Kg of O2 to give 36 KG of H2O 2 mole of H2 combines with 1 mole of O2 to give 2 mole of H2O S+O2=SO2 32 KG of S combines with 32 Kg of O2 to give 64 KG of SO2 1 mole of S combines with 1 mole of O2 to give 1 mole of SO2 Note: other molecules apart from these three does not take part in combustion.
Theoritical O2 required for combustion of thefuel-
Kmole basis
%Composition (by Molecular weight in weight weight) KG C-82 % 0.82 12 H- 4% 0.04 2 N-1% 0.01 28 O- 5% 0.05 32 S-1% 0.01 32 M-2% 0.02 18 A-5% 0.05 Tola O2 required for the combustion of th given fuel O2 already present in the fuel is Net O2 required for combustion is
Kmole 0.068333 0.020000 0.000357 0.001563 0.000313 0.001111
0.21 Kmloe of O2 is present in 1 Kmole of air Thus to supply 0.077083 kmole of O2 requirement of air will be= 1 Kmole = 22.4 m3 thus, 0.367063 Kmole=
8.2 m3
Kg basis %Composition (by O2 required to burn 1 KG(from weight) weight in Kg combustion equations) C-82 % 0.82 32/12 H- 4% 0.04 32/4 N-1% 0.01 0 O- 5% 0.05 NA S-1% 0.01 32/32 M-2% 0.02 0 A-5% 0.05 0 Tola O2 required for the combustion of th given fuel O2 already present in the fuel is Net O2 required for combustion is 0.232 KG of O2 is present in 1 Kg of air Thus to supply 2.467 KG of O2 requirement of air will be=
ole basis) to burn 1 KG of coal having the following composition by weight
combustion.
O2 required for combustion in Kmole 0.068333 0.01 0 0 0.000313 0 0 0.078646 Kmole 0.001563 Kmole 0.077083 Kmole
0.367063 Kmole
O2 required for combustion in Kg 2.186667 0.32 0 0 0.01 0 0 2.52 Kg 0.05 Kg 2.467 Kg
10.63218 KG
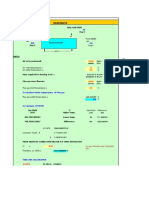
Calculate % volumetric composition of flue gas we and dry basis C-82 % H- 4% N-1% O- 5% S-1% M-2% A-5%
Solution Method I- By determining weight Step I
Composition C-82 % H- 4% N-1% O- 5% S-1% M-2% A-5%
Weight/Kg 0.82 0.04 0.01 0.05 0.01 0.02 0.05
Flue gas CO2 H2O N2 SO2 H2O
Wt of flue gas in KG with the help of combustion equations Volume of flue gas in M 3.006667 0.38 8.175517 0.02
Total volume of flue gas wet Volume of flue gas on dry basis Method II- By determing Kmole Wt of flue gas in Weight of Kmole with the help composition in of combustion Kmole equations 0.068333333 0.068333 0.02 0.021111 0.000357143 0.290337 0.0015625 0 0.015625 0.03125 0.001111111 0
Composition C-82 % H- 4% N-1% O- 5% S-1% M-2% A-5%
Weight of composition in Kg 0.82 0.04 0.01 0.05 0.01 0.02 0.05
Volume in m3
Total volume of flue gas wet
Volume of flue gas on dry basis
Step II
Volume of flue gas in M3 1.53066667 0.47288889 6.54041379 0.007
% Volume Wet basis 17.9005 5.530237 76.4874 0 0.081862
% Volume Dry 18.9484 80.96495 0 0.086654
8.551 m3 8.078 m3
Volume in m3 0.06833 0.02111 0.29034 0.00000 0.03125 0
% Volume % Volume Wet basis Dry 16.62 17.52 5.14 70.64 74.46 0.00 0.00 7.60 8.01
0.411 m3
0.390 m3
Q.
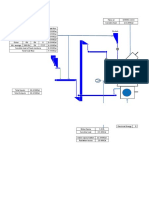
Calculate fuel composition by weight and % excess air from dry flue gas analysis as shown below(by volume Kmole) CO2-10.7% O2-5.1% N2-84.2% Assume that fuel contains only C,H and does not have N,O,S
Solution:
Part I
Calculation of Fuel composition What to find out Air supplied Oxygen present in total air supplied Excess oxygen present Thus Oxygen used for combustion is Oxygen required for combustion of C Oxygen required for combustion of H2 Amount of H2 present in fuel
Approach 1/(amount of N2 present in a mole of air)* N2 present in total kmole of air supplied-amount of N2 present (from flue gas composition) total Kmole of O2 present in supplied air- O2 present flue (1 mole of O2 is required for combustion of 1 mole of C) Total oxygen used for combustion-oxygen used foe comb 1 Mole of O2 is required fro combustion of 2 mole of H2 The above analysis gives-
Part II
Calculation of excess air What to find out % of excess air
Approach O2 in flue gas/(theritical O2 required for combustion)*10
Problems -26/09/2012
excess air from dry flue gas analysis as shown below-
not have N,O,S
Approach 1/(amount of N2 present in a mole of air)* N2 present in the fuel total kmole of air supplied-amount of N2 present (from flue gas composition) total Kmole of O2 present in supplied air- O2 present flue gas (1 mole of O2 is required for combustion of 1 mole of C) Total oxygen used for combustion-oxygen used foe combustion of C 1 Mole of O2 is required fro combustion of 2 mole of H2 The above analysis givesComposition H2 C
value 106.5822785 22.38227848 5.1 17.28227848 10.7 6.582278481 13.16455696
Unit Kmole Kmole Kmole Kmole Kmole Kmole Kmole
in Kmloe in KG %Wt 13.16455696 26.329114 17.01626 10.7 128.4 82.98374
Approach O2 in flue gas/(theritical O2 required for combustion)*100
value
Unit 29.510 %
You might also like
- Elements of Short Story WORKBOOKDocument26 pagesElements of Short Story WORKBOOKDavid Velez Gonzalez100% (2)
- Combination CircuitsDocument6 pagesCombination CircuitsGordanPešićNo ratings yet
- TractatusDocument185 pagesTractatusSattyaki BasuNo ratings yet
- LNAT EssayDocument2 pagesLNAT EssayFaisal . BathawabNo ratings yet
- My Dream Job Essay WritingDocument3 pagesMy Dream Job Essay WritingAnne NgNo ratings yet
- 10 Laws of Love: Principles That Will Transform Your Life!Document72 pages10 Laws of Love: Principles That Will Transform Your Life!rammohan2bNo ratings yet
- Waste .Is Not To WasteDocument60 pagesWaste .Is Not To WasteVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- TACH DWELL Tester Instructions PDFDocument7 pagesTACH DWELL Tester Instructions PDFVinay Mathad100% (1)
- Iep CritiqueDocument11 pagesIep Critiqueapi-357058154No ratings yet
- Stoichiometric Calc VisaDocument4 pagesStoichiometric Calc Visamkchy12No ratings yet
- Memory Management and LatchingDocument34 pagesMemory Management and Latchingrockerabc123No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document29 pagesChapter 7Vinay Mathad100% (1)
- Heat Balance-1Document85 pagesHeat Balance-1Ravi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Fuels & CombustionDocument154 pagesFuels & CombustionArul Sankaran100% (1)
- H&M CalculationsDocument14 pagesH&M CalculationsNITINNo ratings yet
- Coal Drying (Dry Basis)Document9 pagesCoal Drying (Dry Basis)billyNo ratings yet
- Fuel Analysis CalculationDocument2 pagesFuel Analysis CalculationRamachandran Venkatesh100% (1)
- Conversion Factor For NOx and SOx CalculationsDocument2 pagesConversion Factor For NOx and SOx CalculationsvvijaybhanNo ratings yet
- Pheater Heat BalanceDocument2 pagesPheater Heat BalanceRaji SuriNo ratings yet
- Priya Cement Raw MixDocument6 pagesPriya Cement Raw MixJCS100% (1)
- Total Cement Cost (Fuel+Material+Power) : Kiln Feed Option-1 Option-2Document6 pagesTotal Cement Cost (Fuel+Material+Power) : Kiln Feed Option-1 Option-2Amir HabibNo ratings yet
- Combustion CalculationDocument16 pagesCombustion Calculationmohamed Elsayed0% (1)
- Case Study ResearchDocument20 pagesCase Study ResearchManish PuttyahNo ratings yet
- HT-2.2 RMR Heat Belance 5 Stage T17 M7,9Document1 pageHT-2.2 RMR Heat Belance 5 Stage T17 M7,9GiequatNo ratings yet
- Calculated Primary AirDocument1 pageCalculated Primary AirIrfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Coal Analysis ParameterDocument21 pagesCoal Analysis ParameterYuliyanti YuliyantiNo ratings yet
- Fan Flow Calculation For FBC BoilerDocument3 pagesFan Flow Calculation For FBC BoilerOmprakaash MokideNo ratings yet
- Line III Heat BalanceDocument65 pagesLine III Heat Balancehmaza shakeelNo ratings yet
- Cement Kiln Pyro BalanceDocument44 pagesCement Kiln Pyro BalanceirfanNo ratings yet
- Calciner Op Ex CalculationDocument9 pagesCalciner Op Ex CalculationNair YadukrishnanNo ratings yet
- 2 Static Separators:: 2.1 CyclonesDocument17 pages2 Static Separators:: 2.1 CyclonesFDLTLSNo ratings yet
- Calciner Resitence TimeDocument2 pagesCalciner Resitence TimeIrfan Ahmed100% (1)
- Heat Balance GrindingDocument13 pagesHeat Balance GrindingAbhijeet JhankalNo ratings yet
- German Short Stories For BeginnersDocument82 pagesGerman Short Stories For BeginnersHùynh Ngọc DiễmNo ratings yet
- 1.5 NPS RecuperatorDocument7 pages1.5 NPS RecuperatorAnonymous pVoSWn8yh0No ratings yet
- Draught CalculationDocument4 pagesDraught CalculationBrijesh SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Biomass Combustion ManojDocument16 pagesBiomass Combustion Manojsugandaraj522No ratings yet
- Utilization of Coking Coal in Metallurgical ProcessDocument14 pagesUtilization of Coking Coal in Metallurgical ProcessVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- Najran Cement Company:: Najran: NCC Line-2 Kiln By-Pass ReportDocument2 pagesNajran Cement Company:: Najran: NCC Line-2 Kiln By-Pass ReportIrfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fuels 1 SlidesDocument19 pagesFuels 1 Slidesengr_saifNo ratings yet
- Specific Gas Ratio - SwapnilDocument33 pagesSpecific Gas Ratio - SwapnilYhane100% (1)
- Plant InvesticationDocument3 pagesPlant InvesticationirfanNo ratings yet
- Design Coal Worst Coal Coal Consumption Capacity CalculationDocument6 pagesDesign Coal Worst Coal Coal Consumption Capacity CalculationPrasanna kumar subudhiNo ratings yet
- Effect of False Air On Heat Consumption: Note Change Values Only in Shaded CellsDocument7 pagesEffect of False Air On Heat Consumption: Note Change Values Only in Shaded Cellshmaza shakeelNo ratings yet
- Coal CombustionDocument3 pagesCoal CombustionRahul ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Overall Heat Balance - 11.08.2008Document8 pagesOverall Heat Balance - 11.08.2008Tamer FathyNo ratings yet
- 02-Stoichiometric CalculationsDocument47 pages02-Stoichiometric CalculationsHandayani KesumadewiNo ratings yet
- Cyclone Performance and Design PDFDocument23 pagesCyclone Performance and Design PDFIstván SzékelyNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cost ComaparaisionDocument8 pagesFuel Cost ComaparaisionIrfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3.basics of CombustionDocument5 pages3.basics of CombustionVan Nguyen Huu VanNo ratings yet
- Alkali - Chlorine - Sulfur - Balance: Grate PreheaterDocument4 pagesAlkali - Chlorine - Sulfur - Balance: Grate PreheaterElwathig BakhietNo ratings yet
- Effects of Ash in ClinkerDocument16 pagesEffects of Ash in ClinkerirfanNo ratings yet
- Hot AirDocument6 pagesHot AirElancheran RengaNo ratings yet
- Combustion CalculationDocument2 pagesCombustion CalculationRamachandran VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Go Betweens For HitlerDocument402 pagesGo Betweens For HitlerSagyan Regmi Regmi100% (1)
- Heat Calculation by SGDocument42 pagesHeat Calculation by SGaaa100% (1)
- Lower and Higher Heating ValuesDocument1 pageLower and Higher Heating ValuesPierangelo CarozzaNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument111 pagesCombustionTesfahun TegegneNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance For Kiln: Jasveer SinghDocument4 pagesHeat Balance For Kiln: Jasveer SinghAlok RanjanNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance GCLDocument6 pagesHeat Balance GCLIrshad HussainNo ratings yet
- Circulating Fluidized Bed Technology: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Circulating Fluidized Beds, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, November 18-20, 1985From EverandCirculating Fluidized Bed Technology: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Circulating Fluidized Beds, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, November 18-20, 1985P. BasuRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Home Exercises - AllDocument6 pagesHome Exercises - AllRajithaSomathilakeNo ratings yet
- Ultimate AnalysisDocument3 pagesUltimate AnalysisComputer Maintainance Hardware and softwareNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Mass Transfer: A Textbook with Multiple-Choice Exercises for Engineering StudentsFrom EverandCombustion and Mass Transfer: A Textbook with Multiple-Choice Exercises for Engineering StudentsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- CalculationsDocument14 pagesCalculationsPratyush BadrinarayanNo ratings yet
- Teacher Induction Program Module 2Document54 pagesTeacher Induction Program Module 2Acee Lagarto75% (8)
- 1 Heat BalanceDocument4 pages1 Heat BalanceKiran Veerubhotla100% (1)
- Calculations in Furnace Technology: Division of Materials Science and TechnologyFrom EverandCalculations in Furnace Technology: Division of Materials Science and TechnologyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Combustion of Pulverised Coal in a Mixture of Oxygen and Recycled Flue GasFrom EverandCombustion of Pulverised Coal in a Mixture of Oxygen and Recycled Flue GasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document48 pagesChapter 3Jeevanandam ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- Cement PlantDocument1 pageCement PlantElwathig BakhietNo ratings yet
- 2012 - Design, Fabrication and Commissioning of RDF PDFDocument72 pages2012 - Design, Fabrication and Commissioning of RDF PDFHilmi Gazali TvkNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance ComparisionDocument5 pagesHeat Balance Comparisiongvrr1954No ratings yet
- QIP Short Term Course On Emerging Trends in Development of Alternative Fuelled Dual Fuel Compression Ignition EngineDocument1 pageQIP Short Term Course On Emerging Trends in Development of Alternative Fuelled Dual Fuel Compression Ignition EngineVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- How To Specify The Limits of Quality Requirements To Develop A Low Cost and Yet A Highly Efficient Software System ?Document1 pageHow To Specify The Limits of Quality Requirements To Develop A Low Cost and Yet A Highly Efficient Software System ?Vinay MathadNo ratings yet
- 4 TH SEM. AUTO. E.D.M.VDocument2 pages4 TH SEM. AUTO. E.D.M.VVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- PassportApplicationForm Main English V1.0Document1 pagePassportApplicationForm Main English V1.0Vinay MathadNo ratings yet
- What Is An Impact?: The Impact of An Activity Is A Deviation (A Change) From The That Is Caused by The ActivityDocument21 pagesWhat Is An Impact?: The Impact of An Activity Is A Deviation (A Change) From The That Is Caused by The ActivityVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- LCD Display Technology: ProgramDocument18 pagesLCD Display Technology: ProgramVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- Recommendations From ExpertsDocument3 pagesRecommendations From ExpertsVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- VTH VsemDocument30 pagesVTH VsemVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- Vinaya C MathadDocument1 pageVinaya C MathadVinay MathadNo ratings yet
- Marine Fuels & EnginesDocument4 pagesMarine Fuels & EnginesDidit RizkyNo ratings yet
- Laguda, Clemente (Judicial Counter-Affidavit)Document19 pagesLaguda, Clemente (Judicial Counter-Affidavit)SelurongNo ratings yet
- Central Limit TheoremDocument46 pagesCentral Limit TheoremAneesh Gopinath 2027914No ratings yet
- Photo-Realistic 3D Model Extraction From Camera Array CaptureDocument11 pagesPhoto-Realistic 3D Model Extraction From Camera Array CaptureJohn NaylorNo ratings yet
- It (Cesec - Form 4 - 5) OutlineDocument7 pagesIt (Cesec - Form 4 - 5) Outlineapi-287025606No ratings yet
- Evermotion Archmodels Vol 40 PDFDocument2 pagesEvermotion Archmodels Vol 40 PDFJustinNo ratings yet
- Eindhoven University of Technology: Award Date: 2008Document65 pagesEindhoven University of Technology: Award Date: 2008Jay Mark VillarealNo ratings yet
- Expository Essay Rough DraftDocument4 pagesExpository Essay Rough Draftapi-292792461No ratings yet
- Psychosocial Problem and Its Associated Factors Among Adolescents in The Secondary Schools in Pasir Gudang, JohorDocument11 pagesPsychosocial Problem and Its Associated Factors Among Adolescents in The Secondary Schools in Pasir Gudang, JohorMaysoun AtoumNo ratings yet
- Teoria Do MSR ADocument4 pagesTeoria Do MSR AAlexandre Valeriano da SilvaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Relationship Management Practices of Commercial Banks in Thanjavur DistrictDocument6 pagesA Study On Customer Relationship Management Practices of Commercial Banks in Thanjavur DistrictarcherselevatorsNo ratings yet
- Shell Paper Machine Oil S3 M 220Document3 pagesShell Paper Machine Oil S3 M 220DENNY BAYUAJINo ratings yet
- Challenges To FreedomDocument11 pagesChallenges To Freedomgerlie orqueNo ratings yet
- Primate City & Rank Size Rule: O P A DDocument7 pagesPrimate City & Rank Size Rule: O P A DOmkar G. ParishwadNo ratings yet
- Qlikview 10 Accesspoint SSODocument21 pagesQlikview 10 Accesspoint SSOAlberto AlavezNo ratings yet
- Interpersonel Need of Management Student-Acilitor in The Choice of ElectivesDocument180 pagesInterpersonel Need of Management Student-Acilitor in The Choice of ElectivesnerdjumboNo ratings yet
- The Future of Humanity ProjectDocument9 pagesThe Future of Humanity Projectapi-479088697No ratings yet
- ზოგადი და არაორგანულიქ იმია ქრისტინე გიორგაძე 1Document301 pagesზოგადი და არაორგანულიქ იმია ქრისტინე გიორგაძე 1Giorgi KartsidzeNo ratings yet
- Conditional Power of One Proportion Tests PDFDocument7 pagesConditional Power of One Proportion Tests PDFscjofyWFawlroa2r06YFVabfbajNo ratings yet