Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coagulation disorders and Perthes disease causes
Uploaded by
Nkk Aqnd MgdnglOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Coagulation disorders and Perthes disease causes
Uploaded by
Nkk Aqnd MgdnglCopyright:
Available Formats
Coagulation disorders Protein C or S deficiency Thrombophilia Hypofibrinolysis Altered arterial status Angiographic studies have shown obstruction of superior
rior capsular arteries and decreased flow in medial circumflex femoral arteries . The intracapsular ring has been found to be incomplete. Abnormal venous drainage Increased venous pressure in the femoral neck Congestion in the metaphysis Venous outflow exits more distally in the diaphysis. Abnormal growth and development A delay in Bone age of 1.5 to 2 years Low birth weight Low levels of somatomedin C Trauma. In the developing femur (4 7 yrs),the major lateral epiphyseal vessels must course through a narrow passage ,which could make it susceptible to trauma. Hyperactivity or attention deficit disorder Genetic component Familial association. X-Linked recessive inheritance. Environmental influences Low socioeconomic status. Sequel to synovitis Synovitis of the hip occurs early in Perthes disease. Increased pressure in synovitis may cause a tamponade effect on the vasculature Bone resorption is the process by which osteoclasts break down bone and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone fluid to the blood. Ossification (or osteogenesis) is the process of laying down new bone material by cells called osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. procallus = fibrocartilaginous callus = soft callus - the first stage (approximately one week) in the healing of a bone fracture; connective tissue stem cells and capillary blood vessels penetrate the inflamed fracture hematoma and as phagocytes clear the debris from the injury, new fibrous connective tissue matrix, then new cartilage matrix, and finally new bone matrix begin to form; the procallus material usually extends beyond the volume previously occupied by the uninjured bone; it represents the second stage in repair of a bone fracture.
Hyperaemia or hyperemia is the increase of blood flow to different tissues in the body.
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Wedding Planning ChecklistDocument11 pagesWedding Planning ChecklistNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Ra 121 - Installation of Cladding For Duct & Refrigerant PipesDocument8 pagesRa 121 - Installation of Cladding For Duct & Refrigerant PipeszahidNo ratings yet
- Strength Training For KidsDocument8 pagesStrength Training For KidsMike HaughtNo ratings yet
- Intra Aortic Balloon PumpDocument3 pagesIntra Aortic Balloon PumpNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Chapter Test ReviewDocument6 pagesMuscular System Chapter Test ReviewLynda Obi100% (2)
- OsteomyelitisDocument147 pagesOsteomyelitisAnkit Agur100% (1)
- Installing the 3-3-5 DefenseDocument216 pagesInstalling the 3-3-5 Defensejimy45100% (12)
- NCP ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP ConstipationNkk Aqnd Mgdngl100% (4)
- NCP ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP ConstipationNkk Aqnd Mgdngl100% (4)
- Soccer Drills & Practice PlansDocument60 pagesSoccer Drills & Practice PlansPaulo RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Immediate Post-Operative CareDocument4 pagesImmediate Post-Operative CareHeidi Avediz Del Fuerte100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Hip BoneDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Hip BoneNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology FracturesDocument2 pagesPathophysiology FracturesSewyel Garburi71% (7)
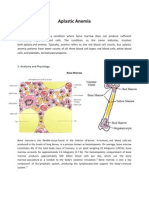
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument5 pagesAplastic AnemiaVenice Marie GargantaNo ratings yet
- Venous DiseaseDocument45 pagesVenous DiseaseNinch Nagac100% (1)
- 2002 UW-Platteville Spread Offense Implementation Week 1Document105 pages2002 UW-Platteville Spread Offense Implementation Week 1dacoachmoNo ratings yet
- Head Injury: Causes, Types, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument53 pagesHead Injury: Causes, Types, Diagnosis and ManagementkarthicpraveenNo ratings yet
- PanosteitisDocument5 pagesPanosteitisElEffe100% (1)
- Nclex DiseasesDocument6 pagesNclex Diseasesshangguanlongkui95% (21)
- Pagets DiseaseDocument62 pagesPagets DiseaseKush PathakNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve PerthesDocument7 pagesLegg Calve PerthesAdrian Mallar100% (1)
- Nurse Jane's AccidentDocument2 pagesNurse Jane's AccidentUmiyanti AzizahNo ratings yet
- Decubitus UlcersDocument4 pagesDecubitus UlcersNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- QualifiedPhysio MSK Interview Preparation Pack PDFDocument48 pagesQualifiedPhysio MSK Interview Preparation Pack PDFUkpabi GinikachiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Pathology ANSWERSDocument4 pagesSkeletal System Pathology ANSWERSNathanNo ratings yet
- Basic Surgical Skills 2014Document108 pagesBasic Surgical Skills 2014Mi Zulfahmi Sha'ari100% (1)
- Blood Supply of Long BonesDocument4 pagesBlood Supply of Long BonesmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- Pyogenic Osteomyelitis NotesDocument10 pagesPyogenic Osteomyelitis Noteskep1313No ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document27 pagesChapter 13Zaky DavidiaNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve Perthes Disease - RP's Ortho NotesDocument2 pagesLegg Calve Perthes Disease - RP's Ortho NotesSabari NathNo ratings yet
- Avascular Necrosis: Necrosis Blood Supply JointDocument9 pagesAvascular Necrosis: Necrosis Blood Supply JointAyaba RoselynNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis LaikaDocument4 pagesOsteomyelitis LaikaAl Lai KaNo ratings yet
- Osteonecrosis Humeral Head: A Case SeriesDocument8 pagesOsteonecrosis Humeral Head: A Case SeriesrapannikaNo ratings yet
- BSE Viva v1.0 PDFDocument173 pagesBSE Viva v1.0 PDFKavivarma Raj RajendranNo ratings yet
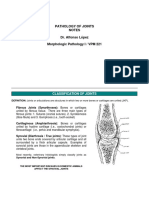
- Pathology of JointsDocument13 pagesPathology of JointswobblegobbleNo ratings yet
- The Pathology of Perthes DiseaseDocument1 pageThe Pathology of Perthes DiseaseMalai MohanNo ratings yet
- Due To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryDocument6 pagesDue To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryBashar EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Jaw DiseasesDocument55 pagesMetabolic Jaw DiseasesoladunniNo ratings yet
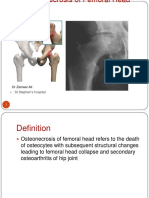
- DR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's HospitalDocument152 pagesDR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's Hospitalagnes trianaNo ratings yet
- Venous Disease: Understanding the Anatomy and PathophysiologyDocument50 pagesVenous Disease: Understanding the Anatomy and PathophysiologychristianNo ratings yet
- Bone & Joint Pathology GuideDocument8 pagesBone & Joint Pathology Guidelovelyc95No ratings yet
- Venous Disease: Chronic Venous Insufficiency Anatomical BackgroundDocument16 pagesVenous Disease: Chronic Venous Insufficiency Anatomical BackgroundSteve ColbertNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Lesions of The JAW: Bhavika Pol Vhatkar 1 Yr PGDocument132 pagesInflammatory Lesions of The JAW: Bhavika Pol Vhatkar 1 Yr PGArpita SankhwarNo ratings yet
- Christopher W DiGiovanni Article PDFDocument10 pagesChristopher W DiGiovanni Article PDFStefano Pareschi PasténNo ratings yet
- Septic ArthritisDocument12 pagesSeptic ArthritisRashi JainNo ratings yet
- CH 06 Lecture OutlineDocument6 pagesCH 06 Lecture OutlineTameka HedgepethNo ratings yet
- Bones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasDocument34 pagesBones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Coxa PlanaDocument13 pagesCoxa PlanaJustin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Kidney Stones and Blood Vessel Diseases ExplainedDocument19 pagesKidney Stones and Blood Vessel Diseases ExplainedmadhuNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITISDocument7 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE HEMATOGENOUS OSTEOMYELITISSyahrir RusdyNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Spine StenosisDocument12 pagesLumbar Spine StenosisParag DashatwarNo ratings yet
- Acute Haematogenous Osteomyelitis (Aho)Document33 pagesAcute Haematogenous Osteomyelitis (Aho)anggi dwi puteraNo ratings yet
- Paget's DiseaseDocument13 pagesPaget's DiseasePooja PatilNo ratings yet
- Apley OA 2Document11 pagesApley OA 2Koko AgungNo ratings yet
- Pagetsdiseaseofthebone 180107110929Document28 pagesPagetsdiseaseofthebone 180107110929Lolo TotoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1&2Document10 pagesLecture 1&2Irfan NashadNo ratings yet
- General Osteology: DefinitionsDocument45 pagesGeneral Osteology: DefinitionsAndreeaNo ratings yet
- DR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's HospitalDocument152 pagesDR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's Hospitalagnes trianaNo ratings yet
- Osteochondritis Dissecans in The Dog: Issue 1 Article 12Document7 pagesOsteochondritis Dissecans in The Dog: Issue 1 Article 12rizky holijaNo ratings yet
- Bone Growth Factors and ProcessesDocument7 pagesBone Growth Factors and ProcessesAmanuel TarekegnNo ratings yet
- Venous InsufficiencyDocument32 pagesVenous InsufficiencyRalucaNo ratings yet
- Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Perthes DiseaseDocument44 pagesAvascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Perthes DiseaseRohit NathNo ratings yet
- Paget's Disease: Support. Bones Provide A Framework For The Attachment of Muscles andDocument11 pagesPaget's Disease: Support. Bones Provide A Framework For The Attachment of Muscles andAndrew MckinleyNo ratings yet
- Bone Infection Guide: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of OsteomyelitisDocument5 pagesBone Infection Guide: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of OsteomyelitisAyanne ArcenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture: Histology of Cartilage and BoneDocument49 pagesLecture: Histology of Cartilage and BonevictorNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Bone II-2Document59 pagesDisorders of Bone II-2Guhan DergNo ratings yet
- Formation: Blood Calcium Level - Calcium HydroxyapatiteDocument13 pagesFormation: Blood Calcium Level - Calcium HydroxyapatiteClarissa IsuriñaNo ratings yet
- 2 Ra OaDocument17 pages2 Ra OaLilianna Ireen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Fabroa, Maria Jessica Erlinda P. BSN Iii Thrombotic Disorders Narrative PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesFabroa, Maria Jessica Erlinda P. BSN Iii Thrombotic Disorders Narrative PathophysiologyJulianne Jeamer FabroaNo ratings yet
- Avn and Perthes DiseaseDocument29 pagesAvn and Perthes DiseaseRoopa Lexmy MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Pathologic Bone FractureDocument5 pagesPathologic Bone FractureJaysellePuguonTabijeNo ratings yet
- Peng 等 - 2020 - Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeliDocument11 pagesPeng 等 - 2020 - Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeliDr.QiuNo ratings yet
- 34 W11 OsteomylitisDocument32 pages34 W11 OsteomylitisAbdulelah MurshidNo ratings yet
- MBS 200 DEFERRED TEST QUESTIONSDocument23 pagesMBS 200 DEFERRED TEST QUESTIONSlucky mbaselaNo ratings yet
- Osteonecrosis: Jamal Abu Helal Orthopedic Consultant EGHDocument50 pagesOsteonecrosis: Jamal Abu Helal Orthopedic Consultant EGHlina jamalNo ratings yet
- Bones and Skeletal Tissues Skeletal CartilagesDocument7 pagesBones and Skeletal Tissues Skeletal CartilagesChelsey ReaumeNo ratings yet
- Journal of NursingDocument5 pagesJournal of NursingNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Sample QatarDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae Sample QatarNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1Document3 pagesAssessment 1Nkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument1 pageCognitive DisordersNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Coagulation disorders and Perthes disease causesDocument1 pageCoagulation disorders and Perthes disease causesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
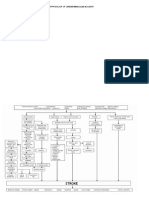
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Breast and LymphDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Breast and LymphNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Unintentional InjuriesDocument16 pagesPediatric Unintentional InjuriesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- President Benigno Simeon Cojuangco Aquino IIIDocument8 pagesPresident Benigno Simeon Cojuangco Aquino IIINkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Cues&CluesDocument2 pagesCues&CluesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Family Health CareDocument131 pagesLec 4 Family Health CareNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Gordon'sDocument4 pagesGordon'sJetch DyNo ratings yet
- Amba's Tragic Fate Revealed as Bhishma, Shalva Refuse Her HandDocument4 pagesAmba's Tragic Fate Revealed as Bhishma, Shalva Refuse Her HandanjalibhatsNo ratings yet
- Tort Law Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTort Law Tutorial 2Molly0% (4)
- Rule: Motor Vehicle Safety Standards: Head Restraints For Passenger Cars and Light Multipurpose Vehicles, Trucks, and BusesDocument42 pagesRule: Motor Vehicle Safety Standards: Head Restraints For Passenger Cars and Light Multipurpose Vehicles, Trucks, and BusesJustia.comNo ratings yet
- LCBM GuideDocument26 pagesLCBM GuidenecrotisisNo ratings yet
- Sec2 8 PDFDocument3 pagesSec2 8 PDFpolistaNo ratings yet
- Wound Management Formulary NHS PeterboroughDocument77 pagesWound Management Formulary NHS PeterboroughBrian HarrisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Musculoskeletal, Circulatory and Respiratory System TermsDocument6 pagesLesson 3: Musculoskeletal, Circulatory and Respiratory System TermsClaudine NaturalNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Netters Illustrations Moores Tables and SnellDocument50 pagesCompilation of Netters Illustrations Moores Tables and SnellAyres EvangNo ratings yet
- Peepers by C.L. KattanDocument132 pagesPeepers by C.L. KattanDurrod University PressNo ratings yet
- Seat Design - Sarang BireDocument20 pagesSeat Design - Sarang BireSarang r BireNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma in Athletic Medicine - Article.Document7 pagesChest Trauma in Athletic Medicine - Article.salmankhan09215No ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJhay NovioNo ratings yet
- Setup: Encounter D6: The Wrath of Orcus Encounter D6: The Wrath of OrcusDocument2 pagesSetup: Encounter D6: The Wrath of Orcus Encounter D6: The Wrath of OrcusBloodencrow Van DrakeNo ratings yet
- MiChal JacksonDocument135 pagesMiChal Jacksonrabbijosiah0% (1)
- Acromioclavicular Joint Injuries and Physical Therapy ManagementDocument12 pagesAcromioclavicular Joint Injuries and Physical Therapy ManagementSereinNo ratings yet
- Pearl Harbor Is A Classic Tale of Romance Set During A War That Complicates EverythingDocument4 pagesPearl Harbor Is A Classic Tale of Romance Set During A War That Complicates EverythingStephanie Sundiang100% (1)
- ZXSDR BTS& Node B Maintenance Guide v1.0Document93 pagesZXSDR BTS& Node B Maintenance Guide v1.0danesh_ieee100% (1)
- A Study On Management of Bothbones Forearm Fractures With Dynamic Compression PlateDocument5 pagesA Study On Management of Bothbones Forearm Fractures With Dynamic Compression PlateIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- 3rd Q Health9-1Document16 pages3rd Q Health9-1Bernard LuisagaNo ratings yet
- Canon FAX L200 ManualDocument108 pagesCanon FAX L200 Manualmmchokies100% (1)