Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Weld Intro
Uploaded by
bhatti19Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Weld Intro
Uploaded by
bhatti19Copyright:
Available Formats
1.
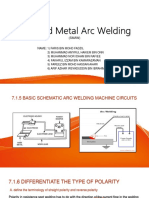
1 WELDING Welding may be described as a metal working process in which metals are joined by heating to the melting point and allowing the molten portions to fuse or flow together. Welding is basically a metallurgical process. The weld metal is a cast material; the solidification occurs in a metallic mould, the adjoining plates serving as the mould material and help to extract the heat. The rate of solidification is, however, extremely rapid compared to steel castings, for the amount of weld metal is very small compared to the amount of parent metal. 1.2 WELDABILITY The capacity of a metal to be welded under the fabrication conditions imposed into a specific, suitably designed structure and to perform satisfactorily in the intended service. 1.3 ARC A comparatively low voltage electrical discharge through a gas, between spaced electrodes. Basically there are three kinds of arc 1) Arc due to direct current 2) Arc due to alternating current 3) Arc due to pulse current Direct current is further divided into DCSP and DCRP. 1.4 DCSP In this case electrode is negative and base metal is positive.2/3 heat is produced at the base metal and 1/3 at the electrode. 1.5 DCRP In this case electrode is positive and work piece is negative. With two-thirds of the heat released at the electrode in DCRP, the electrode metal and the shielding gas are superheated. This superheating causes the molten metal in the electrode to travel across the arc at a very high rate of speed. Deep penetration results from the force of the high velocity arc. 1.6 ARC WELDING A group of welding processes which produce coalescence of metals by heating with Arc or Arcs, with or without the application of pressure and with or without the use of filler. 1.7 GOUGING & AIR CARBON ARC CUTTING An arc cutting process that melts base metal by the heat of a carbon arc and removes the molten metal by a blast of air. 1.8 ARC BLOW An electric current flowing through the electrode sets up magnetic field in a continuous series of circles in a plane perpendicular to the axis of the rod. Similarly magnetic lines are also formed around the work piece and ground cables. When the fields around the work piece or around the electrode are unbalanced, the arc bends away from
You might also like
- Amta5 6 Applying Shielded Metal Arc Welding Smaw TechniquesDocument132 pagesAmta5 6 Applying Shielded Metal Arc Welding Smaw TechniquesSaurav Kumaar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Smaw and Tig WeldingDocument46 pagesSmaw and Tig WeldingRajesh Kumar Ravi100% (1)
- Welding LectureDocument101 pagesWelding Lecturesumit sengarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Vehicle Dynamics by Thomas D GillespieDocument99 pagesFundamentals of Vehicle Dynamics by Thomas D GillespieYogesh Chandrawanshi0% (1)
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding in DetailDocument34 pagesArc Welding in DetailSohen PatelNo ratings yet
- Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument29 pagesShielded Metal Arc WeldingobijistephenNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer and Heat Flow in Arc WeldingDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer and Heat Flow in Arc WeldingPrathamesh Kesarkar100% (1)
- Plasma CuttingDocument229 pagesPlasma CuttingTilak MoundekarNo ratings yet
- ElectroplatingDocument5 pagesElectroplatingPraneet PokhriyalNo ratings yet
- Physics of WeldingDocument3 pagesPhysics of WeldingKhurram RehmanNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding FundamentalsDocument2 pagesArc Welding FundamentalsDananjaya Yogie HartantoNo ratings yet
- Types of Welding ArcsDocument14 pagesTypes of Welding ArcsArnab GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Welding Process 4Document38 pagesWelding Process 4Janmayjoy Halder SwagataNo ratings yet
- Arc WeldingDocument2 pagesArc Weldingapi-368991103No ratings yet
- SMAW Basci Concept DoxDocument30 pagesSMAW Basci Concept DoxAmrut KajveNo ratings yet
- Welding, Soldering and BrazingDocument11 pagesWelding, Soldering and BrazingAyush 100niNo ratings yet
- 1.6 - Introduction To Gas-Shielded Arc WeldingDocument36 pages1.6 - Introduction To Gas-Shielded Arc WeldingReza DhonyNo ratings yet
- Metal JoiningDocument62 pagesMetal Joiningbhavna agarwalNo ratings yet
- Specific Welding DetalsDocument17 pagesSpecific Welding DetalsradiantsteelNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding FundamentalsDocument2 pagesArc Welding FundamentalsSankar NNo ratings yet
- F Arcwelding 131118222251 Phpapp02Document42 pagesF Arcwelding 131118222251 Phpapp02hassan aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Metal Joinig ProcessesDocument88 pagesChapter 5 Metal Joinig Processesdagimawgchew777No ratings yet
- Keje Welding DaamDocument12 pagesKeje Welding Daamdzuko shamNo ratings yet
- Polarity in Arc WeldingDocument3 pagesPolarity in Arc WeldingBabuli KumarNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding SessionalDocument13 pagesArc Welding Sessionalnehar shubheschaNo ratings yet
- WELD-Arc Welding - Maine Welding CompanyDocument7 pagesWELD-Arc Welding - Maine Welding CompanypeterNo ratings yet
- 5.arc WeldDocument40 pages5.arc Weldalinader20022No ratings yet
- Arc Welding: Prof. H. K. Khaira MSME Deptt., MANIT, BhopalDocument49 pagesArc Welding: Prof. H. K. Khaira MSME Deptt., MANIT, BhopalNordiana IdrisNo ratings yet
- MFG II 3182 Chapter 3Document38 pagesMFG II 3182 Chapter 3Naol EmanaNo ratings yet
- Arc and Special Welding TechniquesDocument10 pagesArc and Special Welding TechniquesAvinash ChandraNo ratings yet
- 1 Arc Welding 1Document40 pages1 Arc Welding 1ali100% (1)
- UeetDocument21 pagesUeetIts FickNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Principles of OperationDocument2 pagesLesson 1. Principles of OperationElla MaeNo ratings yet
- Esw and Plasma Arc WeldingDocument36 pagesEsw and Plasma Arc WeldingaravindanilNo ratings yet
- Electroplating: Electroplating Is A General Name For Processes That Create A MetalDocument9 pagesElectroplating: Electroplating Is A General Name For Processes That Create A MetalLollllNo ratings yet
- Electric Arc Welding or Smaw: Fernando O. Paras JRDocument17 pagesElectric Arc Welding or Smaw: Fernando O. Paras JRMirasol Nilo GumbaNo ratings yet
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding or Often Called TIGDocument1 pageGas Tungsten Arc Welding or Often Called TIGadiko1986No ratings yet
- CH06 SmawDocument33 pagesCH06 Smawakmalisyraf9No ratings yet
- 4-GAS TUNGSTEN ARC WELDING (GTAW) and PLASMA Arc WeldingDocument19 pages4-GAS TUNGSTEN ARC WELDING (GTAW) and PLASMA Arc WeldingabastosuaptNo ratings yet
- Q1Document5 pagesQ1اوس محمد رؤوف لؤيNo ratings yet
- PART 166 What Is Spot WeldingDocument4 pagesPART 166 What Is Spot Weldingravindra_jivaniNo ratings yet
- BMP (Class 11-Class 12) WeldingDocument26 pagesBMP (Class 11-Class 12) WeldingAsesh PramanikNo ratings yet
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (Smaw) : Kristiana Pasau, ST., MTDocument43 pagesShielded Metal Arc Welding (Smaw) : Kristiana Pasau, ST., MTRobinson PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Arc WeldingDocument16 pagesArc WeldingManohara BabuNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (Welding (BENG) HandoutDocument67 pagesManufacturing Processes (Welding (BENG) HandoutbananaNo ratings yet
- Welding: Welding Is A Process of Metal Joining by Applying Heat and Sometime PressureDocument41 pagesWelding: Welding Is A Process of Metal Joining by Applying Heat and Sometime PressureJith Viswa100% (1)
- 3-Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)Document13 pages3-Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)abastosuaptNo ratings yet
- Primary Manufacturing Process (ME403) : Prepared byDocument5 pagesPrimary Manufacturing Process (ME403) : Prepared byArterixpestcontrolNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture2 PDFKaushal GandhiNo ratings yet
- Welding Processes PDFDocument27 pagesWelding Processes PDFSarjitoNo ratings yet
- Welding Techniques NEWDocument95 pagesWelding Techniques NEWबंदनेश पाण्डेयNo ratings yet
- CH 48Document32 pagesCH 48islammonirNo ratings yet
- Lec 11Document28 pagesLec 11Navneet KumarNo ratings yet
- I. Welding: (What About Flux Cored Arc Welding??)Document4 pagesI. Welding: (What About Flux Cored Arc Welding??)Ravi PoudelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document65 pagesLecture 4Ishtiaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Welding Machine ProcessDocument3 pagesWelding Machine ProcessM.suresh SureshNo ratings yet
- 3 SmawDocument55 pages3 SmawPutra Daha PratamaNo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsNo ratings yet
- Mono108 01 PDFDocument36 pagesMono108 01 PDFGuillermo Galvis PrinsNo ratings yet
- Iso 7919Document1 pageIso 7919bhatti19No ratings yet
- KarachiDocument1 pageKarachibhatti19No ratings yet
- 27 Health and Nutrition Tips That Are Actually Evidence-BasedDocument10 pages27 Health and Nutrition Tips That Are Actually Evidence-Basedbhatti19No ratings yet
- Ear InfectionDocument7 pagesEar Infectionbhatti19No ratings yet
- SenseDocument1 pageSensebhatti19No ratings yet
- ClientsDocument1 pageClientsbhatti19No ratings yet
- Doors With LockDocument1 pageDoors With Lockbhatti19No ratings yet
- CurtainsDocument1 pageCurtainsbhatti19No ratings yet
- SheetsDocument1 pageSheetsbhatti19No ratings yet
- LocksDocument1 pageLocksbhatti19No ratings yet
- Windows With No DoorsDocument1 pageWindows With No Doorsbhatti19No ratings yet
- ClocksDocument1 pageClocksbhatti19No ratings yet
- EntertainmentDocument1 pageEntertainmentbhatti19No ratings yet
- Best ServicesDocument1 pageBest Servicesbhatti19No ratings yet
- FitnessDocument2 pagesFitnessbhatti19No ratings yet
- LensDocument1 pageLensbhatti19No ratings yet
- MindDocument1 pageMindbhatti19No ratings yet
- GlassesDocument1 pageGlassesbhatti19No ratings yet
- Hope FullDocument1 pageHope Fullbhatti19No ratings yet
- OpticsDocument1 pageOpticsbhatti19No ratings yet
- MindDocument1 pageMindbhatti19No ratings yet
- HardnessDocument2 pagesHardnessbhatti19No ratings yet
- FutureDocument2 pagesFuturebhatti19No ratings yet
- PracticesDocument2 pagesPracticesbhatti19No ratings yet
- SoftnessDocument2 pagesSoftnessbhatti19No ratings yet
- CraftDocument2 pagesCraftbhatti19No ratings yet
- IndustryDocument1 pageIndustrybhatti19No ratings yet
- WeldingDocument1 pageWeldingbhatti19No ratings yet
- MediumDocument2 pagesMediumbhatti19No ratings yet