Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ce Lec04
Ce Lec04
Uploaded by
Junaid Y0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views11 pagescontrol system
Original Title
ce-lec04
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcontrol system
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views11 pagesCe Lec04
Ce Lec04
Uploaded by
Junaid Ycontrol system
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Control Engineering
Lecture #4 22nd March,2008
Models of Physical Systems (Contd)
Models of Mechanical Systems
Mechanical translational systems.
Newtons second law: Device with friction (shock absorber):
B is damping coefficient. Translational system to be defined is a spring (Hookes law): K is spring coefficient
Mechanical linear translational elements
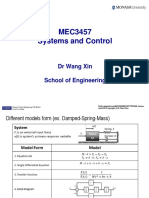
Model of a mass-spring-damper system:
Note that linear physical systems are modeled by linear differential equations for which linear components can be added together. See example of a mass-spring-damper system.
Simplified automobile suspension system:
Mechanical rotational systems.
Moment of inertia:
Viscous friction:
Torsion:
Model of electromechanical systems.
Model of a servomotor:
Model of a Servo-Motor
You might also like
- UNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFDocument40 pagesUNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFAravind MuddebihalNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Mathematical Modeling of Physical SystemsDocument29 pagesChapter Two: Mathematical Modeling of Physical SystemsWabe KemalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial LimbergDocument110 pagesTutorial LimbergMluzama GumedeNo ratings yet
- FEEDCON - Lesson 08 - Closed-Loop Control Systems Part 2Document36 pagesFEEDCON - Lesson 08 - Closed-Loop Control Systems Part 2Junaid YNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 Modeling of Mechanical SystemsDocument53 pagesLecture-2 Modeling of Mechanical SystemsOwais JafriNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines PDFDocument7 pagesMechanics of Machines PDFChamala Daksheeswara Reddy100% (1)
- CH 2 MechatronicsDocument28 pagesCH 2 MechatronicsMihret kochitoNo ratings yet
- 3 Lecture Notes-3 BEM2053 EM218 - Additional NotesXDocument32 pages3 Lecture Notes-3 BEM2053 EM218 - Additional NotesXMuhammad Abdullah ImranNo ratings yet
- Translational Mechanical SystemsDocument12 pagesTranslational Mechanical SystemsDurveshNo ratings yet
- Hanani Abdul Wahab BDA3073Document33 pagesHanani Abdul Wahab BDA3073Shahidin ShahNo ratings yet
- Actuation Systems For MechatronicsDocument26 pagesActuation Systems For Mechatronicsabdulkerim seidNo ratings yet
- Syllabus (New2013 Pattern) - TOM-IDocument14 pagesSyllabus (New2013 Pattern) - TOM-IAkshayNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Mechanical Systems 5Document71 pagesModelling of Mechanical Systems 5MoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Electrical Systems and (Lec-15Document41 pagesChapter 6 Electrical Systems and (Lec-15Mohammed AlqbahNo ratings yet
- ME2104 - Slide 1 Intro+Kinematic DiagramDocument36 pagesME2104 - Slide 1 Intro+Kinematic DiagramiqbalNo ratings yet
- 4 - Mathematical Modeling of Physical Systems A - Mech - SysDocument23 pages4 - Mathematical Modeling of Physical Systems A - Mech - SysAhmed Al AbasereyNo ratings yet
- Basic System ModelDocument26 pagesBasic System ModelVijay ShakarNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFkhanNo ratings yet
- EEE436 BasicMechanicalSystemModelDocument26 pagesEEE436 BasicMechanicalSystemModelAmr IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Student Handout 01 2014Document17 pagesStudent Handout 01 2014kietniNo ratings yet
- Course Objectives:: Me3262:Dynamics of MachinesDocument4 pagesCourse Objectives:: Me3262:Dynamics of Machinesgiriaj kokareNo ratings yet
- Mechanotrix 1Document37 pagesMechanotrix 1Mansif HossainNo ratings yet
- A Design Approach For Gravity Compensators Using Planar Four-Bar Mechanism and Linear SpringsDocument30 pagesA Design Approach For Gravity Compensators Using Planar Four-Bar Mechanism and Linear Springsadissu K/MNo ratings yet
- Final TOM Lab Manual New PDFDocument10 pagesFinal TOM Lab Manual New PDFdab111No ratings yet
- Acceleration in MechanismsDocument22 pagesAcceleration in Mechanismsadilshahzad2001100% (2)
- Mech Sylabus 21Document1 pageMech Sylabus 21Honey SinghNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines Part 1Document27 pagesMechanics of Machines Part 1kimosave99No ratings yet
- ENTC 395: Lecture 3b Rotational Mechanical SystemsDocument9 pagesENTC 395: Lecture 3b Rotational Mechanical SystemssyakirruddinNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 02 (Vibration Modeling)Document23 pagesLecture # 02 (Vibration Modeling)Alina ShahidNo ratings yet
- Co-Simulation of A Crank - Slider Servo Mechanism: October 2015Document8 pagesCo-Simulation of A Crank - Slider Servo Mechanism: October 2015Douai LinNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Rotational SystemsDocument12 pagesMechanical Rotational SystemsRenuka PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Modelling of Dynamic SystemsDocument19 pagesLecture 3 Modelling of Dynamic Systemskobamelo LetowaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MechanismsDocument75 pagesChapter 1 Mechanismsrobel metikuNo ratings yet
- Control of A Double Inverted Pendulum On ADocument12 pagesControl of A Double Inverted Pendulum On AJoseph CassarNo ratings yet
- KMDocument120 pagesKMsady1967No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Modelling - Mechanical Electical SystemsDocument27 pagesLecture 3 Modelling - Mechanical Electical SystemsSean ChanNo ratings yet
- Implementation of An Elevator's Position-Controlled Electric DriveDocument5 pagesImplementation of An Elevator's Position-Controlled Electric DriveKonstantinos ToutounasNo ratings yet
- KOM Lect5Document36 pagesKOM Lect5Pranav C PNo ratings yet
- Mechanism KinematicsDocument4 pagesMechanism KinematicsLuis OscarNo ratings yet
- Me6401 KomDocument128 pagesMe6401 KomThomas LafontaineNo ratings yet
- Rtmnu Mechanical Engineering SyllabusDocument85 pagesRtmnu Mechanical Engineering SyllabusShobit JainNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines-Lecture 1Document31 pagesTheory of Machines-Lecture 1Mohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- 00 Introduction of MachineDocument9 pages00 Introduction of Machineहुमागाँई शिशिरNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Kinematics of Mechanisms - 1Document52 pagesChapter 4 - Kinematics of Mechanisms - 1ﺃﻧﺲﺻﺪﻳﻖNo ratings yet
- OIE 751 ROBOTICS Unit 2 Class 1 (26-8-2020)Document10 pagesOIE 751 ROBOTICS Unit 2 Class 1 (26-8-2020)MICHEL RAJ0% (1)
- SnS-SD-02!3!10 Modeling of Dynamics SystemsDocument25 pagesSnS-SD-02!3!10 Modeling of Dynamics Systemspd_orleansNo ratings yet
- Introduction MVDocument41 pagesIntroduction MVAnonymous ABPUPbKNo ratings yet
- Mom Final ReportDocument23 pagesMom Final ReportAsim ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Governing Equations of FluidDocument31 pagesGoverning Equations of FluidhaftommmmNo ratings yet
- MECH3030 01 Intro Spr2015Document59 pagesMECH3030 01 Intro Spr2015BillyNo ratings yet
- CH 1 FundamentalsDocument56 pagesCH 1 FundamentalsHussain MuslimNo ratings yet
- ME-309: Mechanics of Machines Spring 2011/2012: Instructor: Office: E-Mail: Catalogue Description: (3-0-3)Document14 pagesME-309: Mechanics of Machines Spring 2011/2012: Instructor: Office: E-Mail: Catalogue Description: (3-0-3)Diala DurubiNo ratings yet
- Machine Tool - Part3Document19 pagesMachine Tool - Part3Sam RagNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements Quiz 1Document17 pagesMachine Elements Quiz 1Quen CuestaNo ratings yet
- Fine and Simplified Dynamic Modelling of Complex Hydraulic SystemsDocument6 pagesFine and Simplified Dynamic Modelling of Complex Hydraulic SystemsJesús CastellanosNo ratings yet
- ME3001 Week4 5Document36 pagesME3001 Week4 5Khang NhậtNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document8 pagesExperiment 2Usama NadeemNo ratings yet
- Actuators WDocument15 pagesActuators Wsandeep5No ratings yet
- RTS DC Servo DriveDocument4 pagesRTS DC Servo DriveJunaid YNo ratings yet
- Asme JMDDocument6 pagesAsme JMDJunaid YNo ratings yet
- Field Representation:: Kinematics of The MotionDocument7 pagesField Representation:: Kinematics of The MotionJunaid YNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks MotionDocument1 pageSolidWorks MotionJunaid YNo ratings yet
- FluidsDesignProjectReport DesDocument9 pagesFluidsDesignProjectReport DesJunaid YNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument11 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentJunaid YNo ratings yet
- 9 ICMS Instructions For AuthorsDocument3 pages9 ICMS Instructions For AuthorsJunaid YNo ratings yet
- Die Casting 1Document11 pagesDie Casting 1Junaid YNo ratings yet
- Project Report 31Document21 pagesProject Report 31Junaid YNo ratings yet
- Ce Lec05 (Ocms)Document7 pagesCe Lec05 (Ocms)Junaid YNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering: Assistant Professor, UET TaxilaDocument18 pagesControl Engineering: Assistant Professor, UET TaxilaJunaid YNo ratings yet
- Ce Lec06Document28 pagesCe Lec06Junaid YNo ratings yet