Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3-Phase Induction Machines: Performance Calculation
Uploaded by
Asepta Surya WardhanaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3-Phase Induction Machines: Performance Calculation
Uploaded by
Asepta Surya WardhanaCopyright:
Available Formats
3-Phase Induction Machines
Performance calculation
2
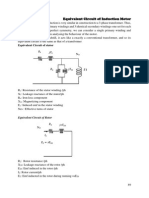
Equivalent circuit
3
Power calculations
1
2
1
3
1
R I P
loss R stator
=
P
c
: core losses
{ }
*
1 1
Re 3 I V P
i
=
( )
s
R
I P R I P P
c i AG
'
2
2
2 1
2
1
3 3 3 = + =
Power crossing the air gap
'
2
2
2
3 R I P P P P
AG em d conv
= = =
Electromagnetic power
Developed power
Rotor losses
4
Power calculations
|
|
.
|
\
|
= =
'
2
'
2
'
2
'
2
'
2
'
2
2 '
2
3 3 3 R
s
R
I R I
s
R
I P
em
( ) ( ) s P s
s
R
I
s
s
R I P P
AG em conv
= =
|
.
|
\
|
= = 1 1 3
1
3
'
2
2 '
2
'
2
2 '
2
r em
P P P =
0
Rotational losses
To load
1
R i g
P P P = ( )
g em
P s P = 1
1
2
1
1
R I P
R
=
'
2
2
2
2
R I P
R
=
P
i
P
0
Rotational
losses
5
Power calculations
6
Power calculations
m
T P e =
| |
em em
P P 3
3
=
m em em
T P e
|
=
3
( )
|
.
|
\
|
= =
s
s
R I
P
T
m m
em
em
1 3
'
2
2
1
3
e e
|
sync
m sync
s
e
e e
=
( )
sync m
s e e = 1
s
R
I T
sync
em
'
2
2
1
3
e
= 0 //
m c
X R
Recall
assume
s
R
I P
AG
'
2
2
1
=
| |
e
AG
sync
em
P T
3
=
7
Power calculations
Also note
rpm n
n
sync
sync
sync
:
60
2t e =
2
1
'
2
2
20
I
s
R
n
T
sync
em
t
=
friction load
m
em
T T
dt
d
J T + + =
e
8
Induction generator
For induction generators
e
m
>e
sync
that is mechanical power supplied by the prime mover
e
m
and e
sync
are rotating in the same direction
generator action: Electrical power is supplied to the network via
stator terminals
Also note for this case (e
m
>e
sync
)
0 <
=
sync
m sync
s
e
e e
that is the slip s is negative.
Therefore negative slip
means generator action.
e
sync
N
S
S
N
e
sync
e
m
T
m
T
ext
9
Special cases
Stand still condition (e
m
=0)
that is s=1 implies stand still
s=0 implies e
m
=e
sync
that is the induction machine is
running at synch speed. Induction machine can not run at
e
sync
= e
m
since f
r
=sf
s
=> f
r
=0 (No power transmission)
1
0
=
=
sync
sync
s
e
e
You might also like
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Induction Machines: Steady State Torque Speed CharacteristicDocument9 pagesInduction Machines: Steady State Torque Speed CharacteristicRyan Benjamin100% (1)
- Induction Machines: Torque Speed CharacteristicsDocument22 pagesInduction Machines: Torque Speed CharacteristicsGogioman Myhay100% (1)
- ELEC 2032 (3) Electromechanical System: Induction Motor IIIDocument19 pagesELEC 2032 (3) Electromechanical System: Induction Motor IIIAshvin AshNo ratings yet
- Kramer DriveDocument42 pagesKramer DriveSenthil Kumar100% (1)
- Ac DrivesDocument36 pagesAc DrivesSeshagirirao GalamNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument65 pagesInduction MotorAhmad Nawawi Ngah100% (1)
- Diode RectifiersDocument64 pagesDiode RectifiersAmineNo ratings yet
- Machine Reviewer 2Document4 pagesMachine Reviewer 2Jimmy OrajayNo ratings yet
- Eq SheetDocument1 pageEq Sheetuama87No ratings yet
- Motor 3 Fase-TorqueDocument13 pagesMotor 3 Fase-TorqueAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- InductionMotors Gate Material PartBDocument38 pagesInductionMotors Gate Material PartBpraveen6494No ratings yet
- Three Phase TransformersDocument26 pagesThree Phase TransformersElardZP100% (1)
- Final Exam SEE3433 Mei (Solution)Document9 pagesFinal Exam SEE3433 Mei (Solution)Fizah Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Power CircuitDocument15 pagesElectronics Power CircuitImrul AshrafNo ratings yet
- Fault Level - ProcedureDocument8 pagesFault Level - ProcedureAmrut ShishirNo ratings yet
- 7 - Axial Flow TurbineDocument43 pages7 - Axial Flow TurbineAmechNo ratings yet
- 7 Asynchronous StudentDocument33 pages7 Asynchronous Studentwanted_JMTINo ratings yet
- Zadatak 1. Trofazna Četvoropolna Kliznokolutna Asinhrona MašinaDocument19 pagesZadatak 1. Trofazna Četvoropolna Kliznokolutna Asinhrona MašinaAA RRNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Modeling - Steady StateDocument43 pagesInduction Motor Modeling - Steady Statedivinelight100% (3)
- Development of The Phasor Diagram and Equivalent Circuit For The Salient Pole Synchronous MachineDocument4 pagesDevelopment of The Phasor Diagram and Equivalent Circuit For The Salient Pole Synchronous MachineNabeel MosawedNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled RectifiersDocument43 pagesUncontrolled RectifiersAbhijeet Singh KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Servo MotorDocument15 pagesServo MotorMinh HảiNo ratings yet
- Basic 3 PhaseDocument17 pagesBasic 3 PhaseUnknownNo ratings yet
- Design of Compensators Using Root Locus DiagramDocument20 pagesDesign of Compensators Using Root Locus DiagramAhmed ElbadrawiNo ratings yet
- MECHDocument36 pagesMECHPalak AriwalaNo ratings yet
- L N I NBS I NS I NI R NS R L M M MH e L Di DT A S V MVDocument18 pagesL N I NBS I NS I NI R NS R L M M MH e L Di DT A S V MVAnxo Do ForteNo ratings yet
- The Peripheral Speeds Are,: 1800 1 2 60 3 FT 62.8 S 3 3 62.8 FT 188.4 SDocument10 pagesThe Peripheral Speeds Are,: 1800 1 2 60 3 FT 62.8 S 3 3 62.8 FT 188.4 SseethiniratnakarNo ratings yet
- Polyphase Induction MachinesDocument7 pagesPolyphase Induction Machinespurushg62No ratings yet
- Solid State Drives Short BookDocument25 pagesSolid State Drives Short BookGomathi Raja MNo ratings yet
- EEE C364/INSTR C 364 Analog ElectronicsDocument21 pagesEEE C364/INSTR C 364 Analog ElectronicsAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- EE 521 Analysis of Power Systems: Problem Set 1Document7 pagesEE 521 Analysis of Power Systems: Problem Set 1sayedmhNo ratings yet
- Chapter No: 04: Measurement of Power & Power Factor CorrectionDocument26 pagesChapter No: 04: Measurement of Power & Power Factor CorrectionChandrakant BhattarNo ratings yet
- PSOC Lab Manual 2017-18 (Final) - 1Document72 pagesPSOC Lab Manual 2017-18 (Final) - 1Nitin AdamNo ratings yet
- 1 - Testing of DC Machines (Part 1)Document6 pages1 - Testing of DC Machines (Part 1)Oliver KemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document27 pagesChapter 13vishiwizardNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickDocument35 pagesPower System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickNnaabyendu SahaNo ratings yet
- Trofazna StrujaDocument35 pagesTrofazna StrujaAlmir MahmutovicNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickDocument35 pagesPower System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickAtabat AduduNo ratings yet
- D C Motors Starter DesignDocument14 pagesD C Motors Starter DesignDnyanesh Gole0% (1)
- Symmetrical Components PDFDocument24 pagesSymmetrical Components PDFtanayspatel100% (1)
- Quisp e 2015Document6 pagesQuisp e 2015Muhamad Awal UdinNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument39 pagesInduction MotorAhmed MagdyNo ratings yet
- Pratica 2Document14 pagesPratica 2Eberton SantosNo ratings yet
- Space (Park) Vectors Definition of Space Vectors:: T X A T X A T X T XDocument19 pagesSpace (Park) Vectors Definition of Space Vectors:: T X A T X A T X T XGovor CristianNo ratings yet
- Solid State Drives: Notes of Lesson PlanDocument24 pagesSolid State Drives: Notes of Lesson PlanetasureshNo ratings yet
- Axial, Radial TurbinesDocument91 pagesAxial, Radial TurbinesAkshay Deshpande100% (2)
- Chapter Two: Line or Naturally Commutated ConvertersDocument32 pagesChapter Two: Line or Naturally Commutated ConvertersMichael Adu-boahenNo ratings yet
- Manual Performance Analysis of A 2.2kw Refurbished Three-Phase Induction MotorDocument7 pagesManual Performance Analysis of A 2.2kw Refurbished Three-Phase Induction MotorInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Power System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickDocument35 pagesPower System Analysis: Fault Analysis Tom Overbye and Ross Baldicka_r_vijayanand6550No ratings yet
- JNTUK EDC-Unit-IV Notes PDFDocument32 pagesJNTUK EDC-Unit-IV Notes PDFkarthiha12No ratings yet
- Fault Level Calculation - MethodsDocument46 pagesFault Level Calculation - MethodsPichumani100% (4)
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Electrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsFrom EverandElectrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- A Practical Neuro-Fuzzy Mapping and Control For A 2 DOF Robotic Arm SystemDocument13 pagesA Practical Neuro-Fuzzy Mapping and Control For A 2 DOF Robotic Arm SystemAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Monte Carlo Simulation in Thermal Radiative Transfer: Method Review, Validation and Parameter SensitivityDocument8 pagesMonte Carlo Simulation in Thermal Radiative Transfer: Method Review, Validation and Parameter SensitivityAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Design of ANFIS Based Estimation and Control For MIMO SystemsDocument7 pagesDesign of ANFIS Based Estimation and Control For MIMO SystemsEmre SezişliNo ratings yet
- Ijarcce 206Document5 pagesIjarcce 206Asepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- 17 3jesa BrooksDocument10 pages17 3jesa BrooksAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- 07095286Document5 pages07095286Asepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing and Testing of A V-Type Stirling Engine: B. Demir, A. GüngörDocument6 pagesManufacturing and Testing of A V-Type Stirling Engine: B. Demir, A. GüngörAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Energy Equations For Computation of Parabolic-Trough Collector Efficiency Using Solar Position CoordinatesDocument9 pagesEnergy Equations For Computation of Parabolic-Trough Collector Efficiency Using Solar Position CoordinatesAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Compute A&b From Yp, x1, Y1 Rev02Document2 pagesCompute A&b From Yp, x1, Y1 Rev02Asepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Cassegrain PDFDocument11 pagesCassegrain PDFAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Design and Testing of Solar Powered Stirling Engine: AbstractDocument6 pagesDesign and Testing of Solar Powered Stirling Engine: AbstractTisyam Noor FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Two New Designs of Parabolic Solar CollectorsDocument12 pagesTwo New Designs of Parabolic Solar CollectorsAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- 2804Document4 pages2804Asepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Nerd Girls: Maximum Power Point TrackerDocument66 pagesNerd Girls: Maximum Power Point TrackerRohit AthavaleNo ratings yet
- Motor ListrikDocument76 pagesMotor ListrikAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Graphite As A Compliant Thermoelectric Material PDFDocument3 pagesFlexible Graphite As A Compliant Thermoelectric Material PDFAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Parabolic Dish Engine Based On Rankine CycleDocument5 pagesAn Efficient Parabolic Dish Engine Based On Rankine CycleAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Design and Testing of A Solar Parabolic Concentrating CollectorDocument5 pagesDesign and Testing of A Solar Parabolic Concentrating CollectorAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Wind Turbine Power, Energy and TorqueDocument54 pages04 - Wind Turbine Power, Energy and Torquebiosbg100% (1)
- Wiring NSXDocument9 pagesWiring NSXAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Horizontal A.C. Motors: Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled, Hazardous Location MotorsDocument2 pagesHorizontal A.C. Motors: Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled, Hazardous Location MotorsAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Solar GardenDocument9 pagesSolar GardenAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Specifications - Electric MotorsDocument8 pagesSpecifications - Electric MotorsAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Modify Sine-1500 WattDocument1 pageModify Sine-1500 WattAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- List of Candidates For JSPS Invitation Fellowship Program (Short-Term)Document2 pagesList of Candidates For JSPS Invitation Fellowship Program (Short-Term)Asepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Ii. Passive Filters: V o I VDocument21 pagesIi. Passive Filters: V o I VĐỗ Quang ViệtNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Direct On Line, Star DeltaDocument6 pagesComparison Between Direct On Line, Star DeltaReza Kandhy WindakaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Passive Analog Filters: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperiment 7 Passive Analog Filters: ObjectivesAsepta Surya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- DigiWare PriceListDocument36 pagesDigiWare PriceListIik Mubarak100% (1)
- Calculations of Protective Relay SettingsDocument65 pagesCalculations of Protective Relay SettingsAngga Wira Pramana100% (12)
- Modeling and Simulation of Wind Turbine Generator Using Matlab-SimulinkDocument20 pagesModeling and Simulation of Wind Turbine Generator Using Matlab-SimulinkAbhishek BhagatNo ratings yet
- TR007-PAT Report - 132kV SWGR CB TestDocument9 pagesTR007-PAT Report - 132kV SWGR CB TestPrabaNo ratings yet
- Insight - How Current Transformer WorksDocument8 pagesInsight - How Current Transformer Workslam266No ratings yet
- General Notes Legend:: Main BreakerDocument1 pageGeneral Notes Legend:: Main BreakerMark Christian EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Q&A Part-1 - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument46 pagesElectrical Q&A Part-1 - Electrical Notes & ArticlesAbdelrahman shokryNo ratings yet
- Brochure Industrial SolutionsDocument12 pagesBrochure Industrial SolutionsGab_SandovalR7175No ratings yet
- The Application of Fiber Optic Distributed Temperature Sensor To Fault Detection of XLPE Insulated Underground Cable - Google SearchDocument2 pagesThe Application of Fiber Optic Distributed Temperature Sensor To Fault Detection of XLPE Insulated Underground Cable - Google SearchUG CABLENo ratings yet
- Centrale Incendie Horib LihDocument4 pagesCentrale Incendie Horib Lihcold storageNo ratings yet
- Switchgear Standard Operating ProceduresDocument22 pagesSwitchgear Standard Operating ProceduresM DuraiNo ratings yet
- AlternatorDocument20 pagesAlternatortusarNo ratings yet
- Ups / Inverter Batterys Product Details and Application EngineeringDocument49 pagesUps / Inverter Batterys Product Details and Application EngineeringAditya BhushanNo ratings yet
- Hubbell ManuaPartsDocument13 pagesHubbell ManuaPartspeda0007No ratings yet
- Russian Federation: (21) (22) Application: 2015125603, 29.06.2015Document7 pagesRussian Federation: (21) (22) Application: 2015125603, 29.06.2015Mihai DanielNo ratings yet
- 46TMSS07R0 DC-DC ConvertorsDocument18 pages46TMSS07R0 DC-DC ConvertorsMohamed NasrNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Questions PDFDocument1 pagePower Supply Questions PDFNarayanan MayandiNo ratings yet
- FAW 15kva 3 Phase SpecsDocument2 pagesFAW 15kva 3 Phase SpecsfosterNo ratings yet
- PMV-SERIES - Cabinet Filter FansDocument3 pagesPMV-SERIES - Cabinet Filter Fansluat1983No ratings yet
- ABB DPU 2000R Distribution Protection Unit PDFDocument28 pagesABB DPU 2000R Distribution Protection Unit PDFBenjaminNo ratings yet
- Manual Canadian CSI-1.5K-TL and CSI-3K-TLDocument2 pagesManual Canadian CSI-1.5K-TL and CSI-3K-TLGuilherme RebecaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Induction Motors - NoteDocument41 pagesElectrical Machines: Induction Motors - NotealeeshaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier Testing PDFDocument1 pageBridge Rectifier Testing PDFScott MorrisonNo ratings yet
- 4CP7Document79 pages4CP7Rajesh MauryaNo ratings yet
- 12.an Enhanced MPPT Technique For Small-Scale Wind Energy Conversion SystemsDocument7 pages12.an Enhanced MPPT Technique For Small-Scale Wind Energy Conversion SystemsRamesh KomarasamiNo ratings yet
- Earth Fault RelayDocument2 pagesEarth Fault RelayTaslim50% (2)
- araña3CR285DME Eng MANUAL-DE-OPERACIONDocument20 pagesaraña3CR285DME Eng MANUAL-DE-OPERACIONtincho_0026No ratings yet
- UPI Semiconductor UP7534 Current-Limited, Power Distribution Switches DatasheetDocument16 pagesUPI Semiconductor UP7534 Current-Limited, Power Distribution Switches DatasheetSultan SinghNo ratings yet
- JD CT DatasheetDocument4 pagesJD CT DatasheetMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- PINOYBIX1Document5 pagesPINOYBIX1andreareyesmalinao7No ratings yet
- PFC Device Corporation: 40A 60V MOS Schottky RectifierDocument7 pagesPFC Device Corporation: 40A 60V MOS Schottky RectifierАндрей АкимовNo ratings yet