Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Otto Cycle
Uploaded by
Nazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Otto Cycle
Uploaded by
Nazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryCopyright:
Available Formats
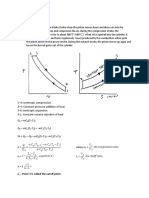
OTTO CYCLE
Basis of Spark Ignition Engines.
0 -1 : Suction
1 -2 : Isentropic
Compression
2 -3 : Constant Vol.
Heat Addition
3 -4 : Isentropic
Expansion
1 -0 : Exhaust
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
Qs
1
2
T
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
,
T
Entropy, s
3
Isochoric
4
Q
R
4 -1 : Constant Vol.
Heat Rejection
OTTO CYCLE
) (
) (
1
) (
) ( ) (
) (
) ( ) (
2 3
1 4
2 3
1 4 2 3
2 3
1 4 2 3
T T
T T
T T
T T T T
T T C m
T T C m T T C m
Q
Q Q
otto
otto
V
V V
otto
S
R S
otto
=
q
q
q
q
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
( ) ( ) 1
3
4
4
3
1
2
1
1
2
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
k k
V
V
T
T
AND
V
V
T
T
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
= =
3
4
2
1
V
V
AND
V
V
Ratio n Compressio r
OTTO CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
4
3
1
2
3
4
2
1
T
T
T
T
V
V
V
V
r
2 3
1 4
2
1
3
4
T T
T T
T
T
T
T
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
( ) 1
2
1
2
1
1
1
1
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
k
otto
V
V
T
T
q
( ) 1
1
1
=
k
otto
r
q
OTTO CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
( ) 1
1
1
=
q
r
otto
Thermal Efficiency is a function of :
1. Compression Ratio (r) and
2. Ratio of Specific Heat (k)
) , ( k r f
th
= q
Thermal Efficiency is a Independent of :
1. Pressure Ratio r
p
= (P
2
/ P
1
) and
2. Heat Supplied (Qs)
OTTO CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
1 1
1 1 2 2 4 4 3 3
=
k
V P V P
k
V P V P
W
) ....(
1
4
2
3
4
3
1
2
say r
P
P
P
P
AND r
P
P
P
P
P
k
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
3 4 2 1
V r V AND V r V = =
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
1
1
1
1
1 1
1 1
1 1
2 2
1 1
4 4
1 1
3 3 1 1
1 1 2 2 4 4 3 3
r
r
r
r
r r
k
V P
W
V P
V P
V P
V P
V P
V P
k
V P
W
k
V P V P
k
V P V P
W
k
P
k
P
( ) ( ) | | 1 1
1
1
1 1
=
k
P
r r
k
V P
W
OTTO CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
( ) ( ) | |
) 1 (
1 1
1
1
2
1
1 1
=
r V
r r V P
k
P
k
P
m
Volume Swept
Output Work
P
m
=
) 1 (
2 2 1
= = r V V V Volume Swept
( ) ( )
( ) ) 1 ( 1
1 1
1
1
=
r k
r r r P
P
k
P
m
Work Output Pr. Ratio, (r
p
)
&, MEP Internal Work Output
Pr. Ratio MEP
OTTO CYCLE MEAN EFFECTIVE PRESSURE
DIESEL CYCLE
In S. I. Engines, max. compression ratio (r) is limited by self ignition of the fuel.
This can be released if air and fuel are compressed separately and brought
together
at the time of combustion.
i.e. Fuel can be injected into the cylinder with compressed air at high temperature.
i.e. Fuel ignites on its own and no special device for ignition is required.
This is known as Compression Ignition (C. I.) Engine.
Ideal Cycle corresponding to this process is known as Diesel Cycle.
Main Difference :
Otto Cycle Heat Addition at Constant
Volume.
Diesel Cycle Heat Addition at Constant Pressure.
DIESEL CYCLE
Basis of Compression Ignition Engines.
0 -1 : Suction
1 -2 : Isentropic
Compression
2 -3 : Constant Pr.
Heat Addition
3 -4 : Isentropic
Expansion
1 -0 : Exhaust
Qs
1
2
T
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
,
T
Entropy, s
3
Isobaric
4
Q
R
4 -1 : Constant Vol.
Heat Rejection
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
Isochoric
DIESEL CYCLE
) (
) ( 1
1
) (
) ( ) (
) (
) ( ) (
2 3
1 4
2 3
1 4 2 3
2 3
1 4 2 3
T T
T T
k
T T C
T T C T T C
T T C m
T T C m T T C m
Q
Q Q
Diesel
P
V P
Diesel
P
V P
Diesel
S
R S
Diesel
=
q
q
q
q
C
r
V
V
T
T
Isobaric
T
V
T
V
= = =
2
3
2
3
3
3
2
2
......
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
2
1
V
V
r Ratio n Compressio = =
2
3
V
V
r Ratio off Cut
C
= =
DIESEL CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
1
1
2
1
1
2
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
k
k
r
V
V
T
T
1
1
1
3
1
4
2
2
3
3 4
1
4
3
3
4
- =
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
- =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
k
C
k
C
k k
r T
r
r
T
V
V
V
V
T T
V
V
T
T
( )
( )
( )
( )
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
1 1
1 1
1
1
.
1 1
1
.
1 1
1
k
C
k
k
C
k
C
k
k
C
otto
r r r
r
k
r r r T
r T
k
q
( )
( )
( )
(
=
1
1 1
1
1
C
k
C
k
otto
r k
r
r
q
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
( )
1
1
2 3
T r r T r T
k
C C
- = - =
AND
DIESEL CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
Efficiency of Diesel Cycle is different than that
of the Otto Cycle by the bracketed factor.
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
( )
( )
( )
(
=
1
1 1
1
1
C
k
C
k
otto
r k
r
r
q
This factor is always more than unity. (> 1)
Otto Cycle is more efficient than Diesel Cycle,
for given Compression Ratio
In practice, however, operating Compression
Ratio for Diesel Engines (16 24) are much
higher than that for Otto Engines (6 10).
Efficiency of Diesel Engine is higher than that
of Otto Engine
DIESEL CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
( )
( )( ) ( )
( )( ) ( ) ( )
(
+
=
(
+
=
+ =
+ =
1
1 . 1 1
1
. 1 1
1 1
1
1 1
) (
1 1
2 2
1 2 4 3 2
2
2 1 2 2 4 4 2 3
2 2
1 1 2 2 4 4 3 3
2 3 2
k
r r r r k r
V P W
k
r P P r P r P k r P
V W
k
V r P V P
k
V r P V r P
r V P W
k
V P V P
k
V P V P
V V P W
k k
k
C C C
C C
C
C
( ) ( )
(
1
1 . 1
.
1
1
1 1
k
r r r k
r V P W
k
C
k
C
k
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
DIESEL CYCLE WORK OUTPUT
( ) ( )
( )
(
(
(
(
|
.
|
\
|
=
k
k
V k
r r r
V P P
k
C C
k
m
1
1
1 1 . .
1
1
1 1
Volume Swept
Output Work
P
m
=
( ) ( )
( )( )
(
=
1 1
1 . 1 . .
1
r k
r r r r
P P
k
C C
k
m
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
DIESEL CYCLE MEAN EFFECTIVE PRESSURE
DUAL CYCLE
Combustion process is neither Constant Volume nor Constant Pressure
Process.
Real engine requires :
1. Finite time for chemical reaction during combustion process.
Combustion can not take place at Constant Volume.
2. Rapid uncontrolled combustion at the end.
Combustion can not take place at Constant Pressure.
Hence, a blend / mixture of both the processes are proposed as a
compromise.
DUAL CYCLE
0 -1 : Suction
1 -2 : Isentropic
Compression
2 -3 : Constant Vol.
Heat Addition
3 -4 : Isentropic
Expansion
1 -0 : Exhaust
4 -1 : Constant Vol.
Heat Rejection
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
5
Qs
Qs
1
2
T
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
,
T
Entropy, s
3
Isobaric
4
Q
R
Isochoric
Isochoric
5
Qs
2 -3 : Constant Pr.
Heat Addition
DUAL CYCLE
) ( ) (
) (
) ( ) (
) ( ) ( ) (
3 4 2 3
1 5
3 4 2 3
1 5 3 4 2 3
T T k T T
T T
T T C m T T C m
T T C m T T C m T T C m
Q
Q Q
Dual
P V
V P V
Dual
S
R S
Dual
+
=
+
+
=
=
q
q
q
1
1 2
1
2
1
1
2
.
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
k
k
r T T
V
V
T
T
2
1
V
V
r Ratio n Compressio = =
2
3
V
V
r Ratio off Cut
C
= =
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
5
Qs
2
3
Pr
P
P
r Ratio
P
= =
1
1
2
3
2 3
2
3
2
3
. .
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
= =
k
P
r r T
P
P
T T
P
P
T
T
DUAL CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
1
1 3 4
3
4
3
4
. . . .
= = =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
k
P C C C
r r r T r T T r
V
V
T
T
( )
( )
( ) ( )
(
+
=
1 . 1
1 . 1
1
1
C P P
k
C P
k
Dual
r k r r
r r
r
q
. . .
. . .
. . .
.
1 5
1
1
1 5
1
5
4
1
1 5
1
5
4
4 5
P
k
C
k
C
k
P C
k
k
P C
k
r r T T
r
r
r r r T T
V
V
r r r T T
V
V
T T
=
|
.
|
\
|
- =
|
|
.
|
\
|
- =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
5
Qs
DUAL CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
5
Qs
( )
( )
( ) ( )
(
+
=
1 . 1
1 . 1
1
1
C P P
k
C P
k
Dual
r k r r
r r
r
q
For ( r
p
) > 1;
Dual
for given ( r
c
) and ( k )
Efficiency of Dual Cycle lies in
between that of Otto Cycle and
Diesel Cycle.
With ( r
c
) = 1 Otto Cycle
With ( r
p
) = 1 Diesel Cycle
DUAL CYCLE THERMAL EFFICIENCY
( )
(
+ +
=
(
+ +
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
1
1 . . . . . . .
1 1
1
1 1
) (
1 1 1 1
1 1
1 1
2 2
1 1
5 5
1 1
4 4
1 1
3 3
1 1
4 4 1 1
1 1 2 2 5 5 4 4
3 4 3
k
r r r r r r r k r r r k
V P
V P
V P
V P
V P
V P
V P
V P
V P
V P
V P
k
k
V P
k
V P V P
k
V P V P
V V P W
k
k
C P
k
P
k
P
k
P C
( ) ( ) ( )
(
+
=
1
1 . 1 1 . .
1 1
1 1
k
r r r r r r r k
V P W
k
C P P
k
C
k
P
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
Isentropic
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
5
Qs
DUAL CYCLE WORK OUTPUT
( )
( ) ( ) ( )
( )
(
=
1
1 . 1 . 1 . . .
.
1
1 1
1 1
2 1
k
r r r r r r r k
V P
V V
P
k
C P P
k
C
k
P
m
Volume Swept
Output Work
P
m
=
( ) ( ) ( )
( )( )
(
+
=
1 1
1 . . 1 . 1 . . .
1
r k
r r r r r r r r k
P P
k
C P P
k
C
k
P
m
0 1
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
Volume, V
2
Qs
3
4
Q
R
5
Qs
DUAL CYCLE MEAN EFFECTIVE PRESSURE
Four Stroke / Compression Ignition (C.I.)
Engine
Four Stroke / Compression Ignition (C.I.)
Engine
Two Stroke / Spark Ignition (S.I.) Engine
Two Stroke / Spark Ignition (S.I.) Engine
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING
THERMODYNAMICS (MORAN J.)
Sheet 6: on chapter 9 (Gas cycle, I.C. Engine)
Questions: (9.7), (9.17) & (9.26)
You might also like
- Thermodynamic CyclesDocument32 pagesThermodynamic CyclessunitbhaumikNo ratings yet
- IC Engines 2012 Edition Theory & QuestionsDocument178 pagesIC Engines 2012 Edition Theory & Questionskumarrohit91No ratings yet
- Thermodynamic CyclesDocument30 pagesThermodynamic CyclesRudra PratapNo ratings yet
- FORMULARIO PARÁMETROS OPERATIVOSDocument2 pagesFORMULARIO PARÁMETROS OPERATIVOSWildor Cordova SanchezNo ratings yet
- L27 - The Brayton CycleDocument12 pagesL27 - The Brayton CycleHaliunaa BatboldNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDocument68 pagesGas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyManjunatha TnNo ratings yet
- Prelim Ito Na PreDocument8 pagesPrelim Ito Na PreJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointDocument7 pagesDiesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointDocument8 pagesDiesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
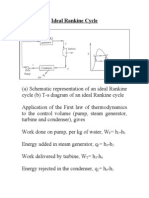
- Ideal Rankine CycleDocument27 pagesIdeal Rankine Cycleslv_prasaadNo ratings yet
- Ideal Rankine Cycle: P P P P S S S SDocument4 pagesIdeal Rankine Cycle: P P P P S S S SYosef Goldberg100% (1)
- TERMODINAMIKA PROSES DAN HUKUMDocument27 pagesTERMODINAMIKA PROSES DAN HUKUMAnonymous GTCOMvNo ratings yet
- Well Testing Data Analysis and Productivity Index CalculationsDocument48 pagesWell Testing Data Analysis and Productivity Index CalculationsAhmed RaafatNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument5 pagesInternal Combustion EnginenidhidarklordNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine CyclesDocument21 pagesHeat Engine CyclesMagdy RiadNo ratings yet
- Deal With Systems That Produce Power in Which The Working Fluid Remains A Gas Throughout The Cycle, I.e., No Change in PhaseDocument22 pagesDeal With Systems That Produce Power in Which The Working Fluid Remains A Gas Throughout The Cycle, I.e., No Change in PhasePushpa Mohan RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document13 pagesLecture 7Nely JayNo ratings yet
- Optimal Location of Multiple Bleed Points in Rankine Cycle: Sincere Efforts For Best Returns .Document28 pagesOptimal Location of Multiple Bleed Points in Rankine Cycle: Sincere Efforts For Best Returns .pvenky_kkdNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine Cycles 1Document85 pagesIc Engine Cycles 1jhpandiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Elevator Energy BalanceDocument13 pagesThermal Elevator Energy BalanceAlbert_LZK100% (4)
- CH 02Document20 pagesCH 02Pauline Nguyen100% (1)
- Nozzles and Steam Turbines ExplainedDocument17 pagesNozzles and Steam Turbines Explainedm_mukbel8752No ratings yet
- Turbomachinery Equations SummaryDocument6 pagesTurbomachinery Equations SummaryMasood Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Rheology Lab ExperimentDocument25 pagesRheology Lab ExperimentRobert FetchNo ratings yet
- Final Exam StuffDocument12 pagesFinal Exam StuffjunusubsubNo ratings yet
- ⎟⎟ ⎠ ⎞ ⎜⎜ ⎝ ⎛ − − = T T 1 T T 1 1 η: www.freestudy.co.ukDocument1 page⎟⎟ ⎠ ⎞ ⎜⎜ ⎝ ⎛ − − = T T 1 T T 1 1 η: www.freestudy.co.ukcataiceNo ratings yet
- Vapour Power CycleDocument12 pagesVapour Power Cyclelakshmikanth97No ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointDocument5 pagesDiesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer - Unit IDocument37 pagesApplied Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer - Unit IArun ShankarNo ratings yet
- Principle of TurbomachineryDocument159 pagesPrinciple of TurbomachinerySharath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Formula Overview (Aeronautics)Document8 pagesFormula Overview (Aeronautics)Aishwarya RaviNo ratings yet
- Termodinamika LanjutDocument44 pagesTermodinamika LanjutRyan Tw ChoumingNo ratings yet
- Outline: Unit Eleven - Cycle AnalysisDocument5 pagesOutline: Unit Eleven - Cycle AnalysisbarelihbNo ratings yet
- Analisa Siklus OttoDocument9 pagesAnalisa Siklus OttochandraNo ratings yet
- Kmme Te101-3Document6 pagesKmme Te101-3ayla sözenNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Design of Engine PerformanceDocument66 pagesThermodynamic Design of Engine PerformancealagurmNo ratings yet
- Theoretical CyclesDocument49 pagesTheoretical CyclesMariaEzzaSyUyNo ratings yet
- Otto Diesel Dual Ideal Cycle - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Document16 pagesOtto Diesel Dual Ideal Cycle - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Danang Wahdiat Aulia Ishaq0% (1)
- Internal Combustion Engines: LecturDocument32 pagesInternal Combustion Engines: LecturPuneet GargNo ratings yet
- Stirling Heat Engine - Internal Combustion Engine (Otto Cycle) - Diesel Engine - Steam Engine (Rankine Cycle) - Kitchen RefrigeratorDocument11 pagesStirling Heat Engine - Internal Combustion Engine (Otto Cycle) - Diesel Engine - Steam Engine (Rankine Cycle) - Kitchen RefrigeratormarzinusNo ratings yet
- Dual CycleDocument3 pagesDual CycleMohammad Faraz AkhterNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines - MidtermsDocument29 pagesInternal Combustion Engines - Midtermsfoj90532No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes OnDocument200 pagesLecture Notes Onananth k r100% (3)
- Stagnation PropertiesDocument25 pagesStagnation PropertiesMSK6567% (3)
- Nptel - Ac.in Courses IIT-MADRAS Applied Thermodynamics Module 4 6 AsdcDocument4 pagesNptel - Ac.in Courses IIT-MADRAS Applied Thermodynamics Module 4 6 AsdcSanjeev PrakashNo ratings yet
- Exercises of Ch5 (w9) - AnswerDocument8 pagesExercises of Ch5 (w9) - AnswerNguyễn Nam AnhNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (Prausnitz) Manual SolutionDocument195 pagesThermodynamics (Prausnitz) Manual SolutionColin Zhang78% (9)
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- Sweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesFrom EverandSweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeFrom EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNo ratings yet
- Shaped Afghans: 6 Beautiful DesignsFrom EverandShaped Afghans: 6 Beautiful DesignsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- ScrapDocument22 pagesScrapranda perdanaNo ratings yet
- 43sany Group Products ManualDocument2 pages43sany Group Products ManualNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Isri Scrap Specifications Circular 2006 PDFDocument57 pagesIsri Scrap Specifications Circular 2006 PDFNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Annex 3 RFQ Lot 3 Schedule 3 Bill of Quantities SR-RW-AAS-00Document10 pagesAnnex 3 RFQ Lot 3 Schedule 3 Bill of Quantities SR-RW-AAS-00Nazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Principles of Seed TechnologyDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Seed TechnologyTanvi Patel0% (2)
- Global Scrap Market Recovery - An Isri Town Hall SeriesDocument2 pagesGlobal Scrap Market Recovery - An Isri Town Hall SeriesNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- List of Secret Codes PDFDocument1 pageList of Secret Codes PDFmudassir264083% (6)
- ABB March 2011Document5 pagesABB March 2011Nazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Rotary Twin Screw Compressor Packages: Specifications & DimensionsDocument4 pagesRotary Twin Screw Compressor Packages: Specifications & DimensionsNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Starting a Business Guide - How to Legally Register Your CompanyDocument8 pagesStarting a Business Guide - How to Legally Register Your CompanyNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Jiu Rep 2010 4 ADocument89 pagesJiu Rep 2010 4 ANazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Rotary Shaft Oil Seals For Cement and Coal Mill Pulverizers: Technical HandbookDocument6 pagesRotary Shaft Oil Seals For Cement and Coal Mill Pulverizers: Technical HandbookNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- A Study of the Scrap Metal Trade in KumasiDocument82 pagesA Study of the Scrap Metal Trade in KumasiNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Waste HeatDocument10 pagesWaste HeatRizwanKhanNo ratings yet
- Trends in Food Science & Technology: C. LongaDocument1 pageTrends in Food Science & Technology: C. LongaNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Ice Plant CatDocument4 pagesIce Plant CatNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Starting a Business Guide - How to Legally Register Your CompanyDocument8 pagesStarting a Business Guide - How to Legally Register Your CompanyNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- 2016 Toyota Hilux DPL en PDFDocument48 pages2016 Toyota Hilux DPL en PDFNguyễn Kim TùngNo ratings yet
- Sheet No. 2Document3 pagesSheet No. 2Nazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- 2016 Toyota Hilux DPL en PDFDocument48 pages2016 Toyota Hilux DPL en PDFNguyễn Kim TùngNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter IxDocument7 pages09 - Chapter IxNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- LME Zinc FactsheetDocument6 pagesLME Zinc FactsheetOscar Zuñiga SolariNo ratings yet
- Methods For Design of Hoppers, Silo's, Bins & BunkersDocument10 pagesMethods For Design of Hoppers, Silo's, Bins & BunkersJaco KotzeNo ratings yet
- List of Secret Codes PDFDocument1 pageList of Secret Codes PDFmudassir264083% (6)
- Techspec QJ240 PDFDocument2 pagesTechspec QJ240 PDFNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- 1140523021191Document110 pages1140523021191Irimia Matei Alex100% (3)
- Dimensions and Units: SheetDocument2 pagesDimensions and Units: SheetNazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- SI F09 Ch29 PDFDocument10 pagesSI F09 Ch29 PDFrenoyaboNo ratings yet
- Si F09 AddDocument3 pagesSi F09 AddJitendra Laxmikant WaniNo ratings yet
- Appendix A - Table of Time Zone CodesDocument4 pagesAppendix A - Table of Time Zone CodesSergio SemmNo ratings yet






















































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)