Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sizing Generator
Sizing Generator
Uploaded by
Jonas Ricafrente Mojica0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pages
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documents
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageSizing Generator
Sizing Generator
Uploaded by
Jonas Ricafrente Mojicas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
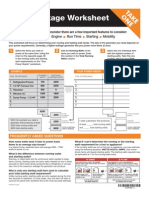
Determining the right size generator
To select an engine-driven generator, youll
need to determine the power (kilowatt)
requirements which must be met under
operating conditions.
Undersizing the generator can be avoided
by considering all of the loads that will be
connected to the generator, and by deter-
mining the starting requirements (motor
start) of electric motor-operated devices.
Be sure the generator you select is large
enough to handle your present requirements
and anticipated needs.
To determine the right size generator, add
up the total watts of all lights, appliances,
tools, or other equipment to be connected to
the generator.
Check the nameplates to determine wattage.
If wattage is not shown, but amps and volts
are given, the following simplified formula
may be used:
Amps x Volts = Watts
(Ex. 12.5 amps x 120 volts = 1,500 watts)
To determine kilowatts (kW), use the
following formula:
1,000 Watts = 1 Kilowatt
(Ex. 1,500 Watts/1,000 = 1.5 kW)
Charts 1, 2, and 3 shown will help you
in selecting the proper size generator. With
Equipment Wattage
Air conditioner, 10,000-Btu 2,0003,000
Blanket, electric 150
Broiler 1,400
Clothes dryer, electric 5,00010,000
Coffee maker 850
Dishwasher 1,5002,500
Fan, attic 375
Fan, furnace 8001,200
Fan, window 200
Freezer, food 300500
Heater, radiant 1,300
Hot plate 1,250
Refrigerator/freezer 6002,000
Sump pump 4003,000
Toaster 1,1001,700
TV, color 100350
Water heater 3,0004,500
Water pump 1,0003,000
Equipment Wattage
Blower, electric
1
23 hp
Compressors
1
43 hp
Concrete vibrators,
3
4-hp 840
Concrete vibrators, 1-hp 1,080
Concrete vibrators, 2-hp 1,560
Concrete vibrators, 3-hp 2,400
Drain cleaners 250
Drills,
1
4-in. 250600
Drills,
3
8-in. 300600
Drills,
1
2-in. 3501,200
Drills, 1-in. 1,000
Grinders, bench
1
41 hp
Grinders, portable 1,0002,500
Hammers, demolition 1,260
Hammers, rotary 1,200
Heaters, space
1
42 hp
Lights check wattage on bulb
Equipment Wattage
Pump, electric
1
2 hp and up
Routers 9001,100
Sanders, belt 6001,500
Sanders, disc 1,200
Sanders, orbital 250
Saws, chain 8001,500
Saws, circular, 6-in. 1,0002,500
Saws, cutoff 2,500
Saws, jig 200800
Saws, masonry 25 hp
Saws, radial arm 15 hp
Saws, table 13 hp
Screwdrivers 550
Shears, metal-cutting 750
Wrenches, impact,
1
2-in. 600
Wrenches, impact,
3
4-in. 720
Wrenches, impact, 1-in. 1,200
Chart 3: Motor starting requirements
Watts required to start motor
Running Repulsion Split
Motor (hp) watts induction Capacitor phase
1
8 275 600 850 1,200
1
6 275 600 850 2,050
1
4 400 850 1,050 2,400
1
3 450 975 1,350 2,700
1
2 600 1,300 1,800 3,600
3
4 850 1,900 2,600
1 1,100 2,500 3,300
Chart 4: Insulated copper wire size
Load in watts Maximum allowable cable length
Current at at
in 120 240 #4 #6 #8 #10 #12 #14 #16 #18
amperage volts volts wire wire wire wire wire wire wire wire
2.5 300 600 1,000 600 375 250 150
5.0 600 1,200 500 300 200 125 75
7.5 900 1,800 330 200 125 80 50
10.0 1,200 2,400 625 400 250 150 100 50 35
15.0 1,800 3,600 650 400 265 165 100 50
20.0 2,400 4,800 500 300 200 125 80
25.0 3,000 6,000 400 250 150 100
30.0 3,600 7,200 325 200 125
35.0 4,200 8,400 275 175 100
40.0 4,800 9,600 250 150
45.0 5,400 10,800 225
50.0 6,000 12,000 200
lights, heaters, and small appliances, simply
add the nameplate ratings or see Chart 1 for
average wattage requirements. For portable
electric tools and equipment, check the
nameplate rating or use Chart 2 for average
requirements. If watts and/or amps are not
given and only the horsepower is shown,
use Chart 3 to determine the starting and
running watts.
Chart 4 is furnished as a guide for select-
ing the proper size of insulated copper wire
when extension cables are used. We recom-
mend the use of outdoor-rated (U.L.) cable,
recognized type SJTW-A.
Chart 1: Home applications
approximate wattage requirements
Chart 2: Portable electric tools approximate wattage requirements
These are suggested guidelines only, please contact a qualified
electrician or licensed contractor for assistance.
Note:
You might also like
- Caravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideFrom EverandCaravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Standby Power Generator - Sizing Guide PDFDocument32 pagesStandby Power Generator - Sizing Guide PDFMadhavasrinivasan SathiamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Voltage Drop Calculations - U.S FormulaDocument3 pagesVoltage Drop Calculations - U.S FormulaOsama_Othman01No ratings yet
- Cable Size Calculator InstructionsDocument3 pagesCable Size Calculator InstructionsShahid SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Generator Sizing: This Section Will Help Walk You Through That ProcessDocument4 pagesGenerator Sizing: This Section Will Help Walk You Through That ProcessArnelCorpuzNo ratings yet
- Generator Power Application Guide: Blue Star 145/185 Bobcat 225Document16 pagesGenerator Power Application Guide: Blue Star 145/185 Bobcat 225Younus BakshiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Unit ConversionDocument12 pagesElectrical Unit ConversionIka SolikahNo ratings yet
- Gen Sizing Guide-SiemensDocument16 pagesGen Sizing Guide-Siemensdinesh_kp7647No ratings yet
- Wattage Worksheet: Engine Run Time Starting Wattage MobilityDocument4 pagesWattage Worksheet: Engine Run Time Starting Wattage Mobilityg665013No ratings yet
- DAFL6775321853807447Document14 pagesDAFL6775321853807447HeinrichErnst1No ratings yet
- Wire Gauge Tables: Ample Power CompanyDocument1 pageWire Gauge Tables: Ample Power CompanyDharang ShahNo ratings yet
- Generator HandbookDocument8 pagesGenerator HandbookchaitutatineniNo ratings yet
- Project Cell 1Document12 pagesProject Cell 1muzzershawNo ratings yet
- 20 - How To Calculate Wire & Fuse Sizes For Electric MotorsDocument2 pages20 - How To Calculate Wire & Fuse Sizes For Electric MotorsLNo ratings yet
- Load CalculationDocument6 pagesLoad CalculationBharathi100% (1)
- Home Generator Systems: Wattage WorksheetDocument6 pagesHome Generator Systems: Wattage WorksheetDeborah Rivera NaugleNo ratings yet
- Sola Transformer SelectionDocument6 pagesSola Transformer SelectionchandruhbkkNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design (Proposed Residential House Electrical Plan) Parts of An Electrical PlanDocument18 pagesElectrical Design (Proposed Residential House Electrical Plan) Parts of An Electrical PlanJereemy PaloyoNo ratings yet
- Generator Sizing GuidelinesDocument1 pageGenerator Sizing Guidelinescoolside111No ratings yet
- Workshop Manual Alternator enDocument25 pagesWorkshop Manual Alternator enakaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design 101 40Document1 pageElectrical Design 101 40jungatbuntonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Plan DesignDocument4 pagesElectrical Plan Designmark lumbres100% (1)
- BET Assignment 1Document3 pagesBET Assignment 1Prashant KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESDocument17 pages4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESJoebert SabidoNo ratings yet
- Electrical UnitsDocument4 pagesElectrical UnitsMuthu KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Optimal Selection of GeneratorsDocument6 pagesOptimal Selection of GeneratorsAzhar HussainNo ratings yet
- Pyrotenax Comprehensive Voltage Drop CalcsDocument2 pagesPyrotenax Comprehensive Voltage Drop Calcsmdc2013No ratings yet
- DC Experiment 4Document3 pagesDC Experiment 4nepNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Managment RPM BookletDocument72 pagesReactive Power Managment RPM BookletPramod B.WankhadeNo ratings yet
- 1year Lab Manual - EeeDocument26 pages1year Lab Manual - Eeesivasuper1873No ratings yet
- Voltage Drop:: How To Calculate Voltage Drop For Long Paired Wire RunsDocument4 pagesVoltage Drop:: How To Calculate Voltage Drop For Long Paired Wire RunsRoberto ValenciNo ratings yet
- Appliance/Equipment Rules of ThumbDocument4 pagesAppliance/Equipment Rules of ThumbPongsathorn SumuntakulNo ratings yet
- Generator Power Calculator: Home About Us Specials Power Calculator Contact UsDocument5 pagesGenerator Power Calculator: Home About Us Specials Power Calculator Contact UsSri Sakthi SumananNo ratings yet
- Solar PV SizingDocument18 pagesSolar PV SizingMuhammad Jawad AfzalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation - CircuitsDocument8 pagesElectrical Installation - CircuitsAmos KormeNo ratings yet
- Metrosils For High Impedance RelaysDocument4 pagesMetrosils For High Impedance RelaysPramod B.WankhadeNo ratings yet
- Rewinding GeneratorsDocument4 pagesRewinding GeneratorsSherehan ShawkatNo ratings yet
- Basic Measurements: Experiment 1Document8 pagesBasic Measurements: Experiment 1arunkumar_gtsNo ratings yet
- Second Year Laboratory Report ES2B1-Electric Motors Lab L2: University of WarwickDocument11 pagesSecond Year Laboratory Report ES2B1-Electric Motors Lab L2: University of Warwicksunilas218408No ratings yet
- Electric CalculationDocument4 pagesElectric CalculationSatish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Awg Copper Wire Table Current LimitsDocument37 pagesAwg Copper Wire Table Current LimitsCristopher Entena100% (2)
- 10 Questions To Test Your Electrician SkillsDocument5 pages10 Questions To Test Your Electrician SkillsSugeng SumarnoNo ratings yet
- EV Car Load ClaculationDocument3 pagesEV Car Load ClaculationBurhaan TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Contactor For Capacitor SwitchingDocument21 pagesContactor For Capacitor SwitchingUrsula JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Generator TroubleshootingDocument22 pagesGenerator TroubleshootingMichael Cabrera Rabino100% (1)
- Power Capacitors and Reactive Power Management Products CatalogueDocument28 pagesPower Capacitors and Reactive Power Management Products CatalogueBoreda RahulNo ratings yet
- Resistance: Voltage Drop in CablesDocument7 pagesResistance: Voltage Drop in CableskumarNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Breaker Size, Wire Size and Wattages: AnotherDocument9 pagesHow To Calculate Breaker Size, Wire Size and Wattages: AnotherLlenzycris SalazarNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Load Capacity of A HomeDocument16 pagesHow To Calculate Load Capacity of A HomeMarine OpsNo ratings yet
- Cables CSA Norma CanadienseDocument98 pagesCables CSA Norma CanadienseJesús EstévezNo ratings yet
- How To Find The Suitable Size of Cable & WireDocument10 pagesHow To Find The Suitable Size of Cable & WireM iqbalNo ratings yet
- VA To Watts and KVA To KilowattsDocument12 pagesVA To Watts and KVA To KilowattsS.senthil KuamrNo ratings yet
- Susol MCCB ManualDocument18 pagesSusol MCCB ManualMan MadhanNo ratings yet
- 10 Questions To Test Your Electrician Skills - EEPDocument6 pages10 Questions To Test Your Electrician Skills - EEPSokibWarsoNo ratings yet
- Demand FactorDocument37 pagesDemand FactoruddinnadeemNo ratings yet
- NEXANS Electricians HandbookDocument98 pagesNEXANS Electricians HandbookMyong FernandezNo ratings yet
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL LIGHTING - Email Version PDFDocument84 pagesGENERAL LIGHTING - Email Version PDFelectricalconsultantNo ratings yet
- Diary 2013Document68 pagesDiary 2013Raheem CpNo ratings yet
- EEE Questions Anna University ChennaiDocument42 pagesEEE Questions Anna University ChennaielectricalconsultantNo ratings yet
- Cable Drop CalculationsDocument1 pageCable Drop CalculationselectricalconsultantNo ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument1 pagePower SystemelectricalconsultantNo ratings yet
- Electrical Transients in Power SystemsDocument1 pageElectrical Transients in Power Systemselectricalconsultant100% (1)
- R2RLRjPn PYCDocument509 pagesR2RLRjPn PYCelectricalconsultantNo ratings yet
- Ps 9276 Wind Energy Conversion SystemsDocument1 pagePs 9276 Wind Energy Conversion Systemselectricalconsultant100% (1)
- Electrical Transients in Power SystemsDocument1 pageElectrical Transients in Power Systemselectricalconsultant100% (1)
- Time Table For M.E./M.Tech. Degree Examinations - Nov. /dec.-2013Document74 pagesTime Table For M.E./M.Tech. Degree Examinations - Nov. /dec.-2013electricalconsultantNo ratings yet