Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Telecoms
Basic Telecoms
Uploaded by
Abu-Abdullah SameerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Telecoms
Basic Telecoms
Uploaded by
Abu-Abdullah SameerCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Telecom Course
CONTEN
Transmission Lines Basic
Analogue and Digital Signal
ISDN Basic
Circuit switch system Vs Packet switched
system
GSM Network Overview
ADSL Network
1
2
Transmission Lines Basic
Telecommunications means:
The electronic transmission of all
types of information audio, video,
voice, graphics, pictures, animation
from a location to another over a
communications link.
3
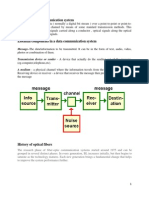
Basic Elements of a Telecommunication System
Transmitter
Receiver
Transmitter
Source
Destination
Channel
4
Telecommunications Channels
Transmission lines - carrier is electrical energy - channel is
normally copper cable
Optical fibers - carrier is electromagnetic energy at light
frequencies - channel is the optical fiber cable
Radio waves - carrier is electromagnetic energy at radio
frequencies - channel is free space between transmitting Antenna
and receiving Antenna.
5
Transmission Media
Transmission Medium
Physical path between transmitter and receiver
Guided Media
Waves are guided along a solid medium
E.g., copper twisted pair, copper coaxial cable, optical fiber
Unguided Media
Provides means of transmission but does not guide
electromagnetic signals
Usually referred to as wireless transmission
E.g., atmosphere, outer space
6
Copper transmission line
Coaxial cable - this is called an unbalanced line ( has one
conductor grounded or exposed to the outside elements
in greater magnitude than the other conductor.)
Twisted Pair Cable- this is called a balanced line (each
line has equal impedance relative to ground or its
surroundings)
Guided Media
Fiber optic Transmission Line
Unguided Media
Electromagnetic waves, called wireless transmission
7
PSTN Architecture, Lines and Trunks
PBX
PBX
Telephone
Telephone
Individual
user
stations,
Linens or
Ext
Residential
Services
CPE
Local Loop Backbone,
or Core
Network
Local
Exchange
Trunks
Subs Line
Subs Line
Interexchange
Trunks
Local
Exchanges
Tandem
Trunks
International Gateway
For routing calls between
countries
Toll/Transit Switch
for routing calls to or
from other cities
Tandem/Junction Exc
for routing calls between local
Exc within the city
8
Local Exchange
Main Exchange
Main Exchange
Main Exchange
Subs
Subs
Subs
Subs
Cell Tower
Mobile Exchange
International
Exchange
Cell
Phone Box
Telephone
Poles
River
Payphone Box
Payphone
Fiber Optic
Cables
Local Ex. Is connected to
all the phones in a small
geographical area
Signal leaves your house
to a telephone box outside
From the Local & Mobile
Exs. Calls are routed to
the main Ex.
Cell phone calls travel to
the cell tower & from
there, on to a mobile ex.
9
Local Exchane
Main Exchange
Subs
Subs
Subs
Subs
Phone Box
Telephone
Poles
River
International
Exchange
International
Exchange
Undersea
Cable
Satellite
To Other
Countries
The Calls are sent to the other
countries via undersea cables or
satellite systems
10
Analog Signals and Digital Signal
A continuously varying electromagnetic wave that may be
propagated over a variety of media, depending on frequency
Examples of media:
Copper wire media (twisted pair and coaxial cable)
Fiber optic cable
Atmosphere or space propagation
Analog signals can propagate analog and digital data
11
Analog and Digital Transmission
Analog Transmission
12
Digital Signals
A sequence of voltage pulses that may be transmitted over a copper wire medium
Generally cheaper than analog signaling
Less susceptible to noise interference
Suffer more from attenuation
Digital signals can propagate analog and digital data
13
ISDN Basic
What is ISDN?
Integrated Service Digital Network,
A system of digital phone connections, which allow
voice and data to be transmitted simultaneously
using end-to-end digital connectivity.
14
Integrated Service Digital Networks
ISDN - is a digital telephone service which
provides fast, accurate voice & data transmission
over existing copper telephone wiring.
ISDN
based on a number of fundamental building blocks.
First, there are two types of ISDN
"channels" or communication paths:
15
Integrated Service Digital Networks
B-channel
The Bearer ("B") channel is a 64 kbps channel
This channel can be used for video, data, voice, or
multimedia calls.
D-channel
The Delta ("D") channel can be either a 16 kbps or 64
kbps channel
Mainly this channel is used for communications (or
"signaling") between switching equipment in the ISDN
network & the ISDN equipment at your location.
16
Integrated Service Digital Networks
These channels are delivered to the user in one of two pre-defined
configurations:
Basic Rate Interface (BRI)
BRI is the ISDN service used to connect to the Internet. BRI connection
supports two channels B and D over a standard phone line. often called
"2B+D".
Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
ISDN PRI service is used primarily by large organizations with intensive
communications needs. This PRI connection supports 30 64kbps
European- (23 64 kbps) American B-channels and one 64 kbps D-channel
(30B+D , 23B+D) over a high speed (T1 or E1) circuit.
17
Circuit Switching
Circuit switching
Dedicated communications path between two stations
E.g., public telephone network ( Plain Old Telephone System- POTS)
Phases of Circuit Switching
Circuit establishment
An end to end circuit is established through switching nodes
Information Transfer ( call progress and transfer)
Information transmitted through the network
Data may be analog voice, digitized voice, or binary data
Circuit disconnect
Circuit is terminated
Each node de-allocates dedicated resources
18
Circuit Switched
Telephone
Telephone
Switch 1 Switch 2
Switch 3 Switch 4
Three phases of circuit switched:
- Establish,
- Transfer,
- Disconnect
To establish a
connection:
Must have
switching Capacity
& Channel Capacity
Must have
intelligence
to workout
routing
Subs
Loop
Trunk
19
Packet Switching
computer2
computer2
D C B A
Packet switching
Message is broken into a series of packets
Each node determines next leg of transmission for each
packet
20
Packet Switching Advantages
Line efficiency is greater
Many packets over time can dynamically share the
same node to node link
Packet-switching networks can carry out data-rate
conversion
Two stations with different data rates can
exchange information
Unlike circuit-switching networks that block calls
when traffic is heavy, packet-switching still accepts
packets, but with increased delivery delay
Priorities can be used
21
Disadvantages of Packet Switching
Each packet switching node introduces a delay
Overall packet delay can vary substantially
This is referred to as jitter
Caused by differing packet sizes, routes taken
and varying delay in the switches
Each packet requires overhead information
Includes destination and sequencing
information
Reduces communication capacity
More processing required at each node
22
Comparison between packet switching networks and circuit switching networks
Circuit Switching
Dedicated transmission path
Continuous transmission
No storage of data/messages
Same path for duration of
connection
Call setup required
Overload may block call
Busy signal if called busy
Fixed bandwidth transmission
Charging by minute
Packet Switching
No dedicated path
Transmission of packets
Packets may be stored
Each packet may take
different route
No call setup needed
Overload increases packet
delay
No busy signal
dynamic use of bandwidth
Charging by packet
23
Leased Line
Leased Line (Private Line or Dedicated Line)
Point-to-point connection
Always on
Lower cost per minute than dial-up service
Must be provisioned (set up)
24
GSM
GSM stands for
Global System for Mobile
telecommunications.
Cell Structure
the coverage area of an operator is divided
into cells
A cell is the area that one or more transmitters
can cover
25
Introduction
Types of Cells
Different types of cells are used depending of
the population density in a country
Macrocells
Microcells
Selective or sectorized cells
Umbrella cells
Nano-cells
Pico-cells
26
Cell Types
Macrocells
Large cells for remote and separate populated areas
Can be larger than 3 to 35 km
Microcells
Used for densely populated areas by splitting the
existing cell into smaller cells
May be as small as .1 to 1 km
Pico-cells
smaller version of microcells
Covers approximately .01 to 1 km
27
Cell Types cont.
Nano-cells
Smaller and smaller segments
Covers .01 to .001 km
Umbrella Cells
Covers several micro-cells to solve the problem of
overabundance of handovers among the different small
neighboring cells
When the speed of is too high, the is handed off to
umbrella cell
28
GSM Architecture
A GSM networks consists of
several functional entities
SIM
Mobile TE
Um
Abis
A BSS
NSS
MSC
BSC
BTS
ME
HLR VLR AuC EIR
PSTN
29
Cellular System Architecture
MSC MSC
HLR
VLR
HLR
VLR
To other
MSCs
PSTN PSTN
30
Cellular System Architecture
Each cell is served by a base station (BS)
Each BS is connected to a mobile switching
center (MSC) through fixed links
Each MSC is connected to other MSCs and
PSTN
31
Each MSC is a local switching exchange that
handles switching of mobile user from one base
station to another
Locating the current cell of a mobile user
Home Location Register (HLR): database recording
the current location of each mobile that belongs to
the MSC
Visitor Location Register (VLR): database recording
the cell of visiting mobiles
Interfacing with other MSCs and PSTN
Cellular System Architecture
32
One channel in each cell is set aside for signaling
information between BS and mobiles
Mobile-to-BS: location, call setup for outgoing,
response to incoming
BS-to-Mobile: cell identity, call setup for
incoming, location updating
Cellular System Architecture
33
The Network & Switching Subsystem
The switching system (SS) is responsible for performing call processing
and subscriber-related functions. The switching system includes the following
functional units:
home location register (HLR) The HLR is a database used for storage and
management of subscriptions. it stores permanent data about subscribers, including a
subscriber's service profile, location information, and activity status.
buys a subscription from one of the PCS operators, he or she is registered in the
HLR of that operator
Mobile Services Switching Center (MSC) - MSC performs the telephony
switching functions of the system
controls calls to and from other telephone and data systems
also performs such functions as toll ticketing, network interfacing, common
channel signaling, and others.
Visitor location register (VLR) - VLR is a database that contains temporary
information about subscribers that is needed by the MSC in order to service visiting
subscribers.
The VLR is always integrated with the MSC. When a mobile station roams into a new MSC
area, the VLR connected to that MSC will request data about the mobile station from the HLR.
Later, if the mobile station makes a call, the VLR will have the information needed for call
setup without having to interrogate the HLR each time.
34
Authentication center (AUC) - A unit called the AUC provides
authentication and encryption parameters that verify the user's identity and
ensure the confidentiality of each call.
The AUC protects network operators from different types of fraud
found in today's cellular world.
Equipment identity register (EIR) - The EIR is a database that contains
information about the identity of mobile equipment that prevents calls from
stolen, unauthorized, or defective mobile stations
The AUC and EIR are implemented as stand-alone nodes or as a
combined AUC/EIR node.
The Network & Switching Subsystem Cont.
35
Base Station System (BSS)
All radio-related functions are performed in the BSS, which consists of base station
controllers (BSCs) and the base transceiver stations (BTSs)
BSC - The BSC provides all the control functions and physical links between the MSC
and BTS.
It is a high-capacity switch that provides functions such as handover, cell configuration data,
and control of radio frequency (RF) power levels in base transceiver stations. A number of
BSCs are served by an MSC.
BTS - The BTS handles the radio interface to the mobile station. The BTS is the radio
equipment (transceivers and antennas) needed to service each cell in the network. A
group of BTSs are controlled by a BSC.
36
ADSL
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
37
Heres What You Will Learn About ADSL!
What is it?
What are the benefits?
How fast is it?
How does it work?
What can I use it for?
38
What is ADSL?
ADSL is a latest broadband
communication technology
that creates high-speed
access to the Internet and
remote networks using the
phone lines that are already
present in your home.
ADSL is an asymmetric communication technology designed
for residential users; it is not suitable for businesses.
Note
39
What are the benefits of ADSL?
You can talk on the phone and use the Internet at
the same time on a single phone line
You can connect to the Internet at up to 140 times
faster than analog modems
Your connection to the Internet is always on
Your home has its own dedicated connection
Your connection is highly reliability
Your connection is highly secure
40
Simultaneous Connections
Talk on the phone and surf the Internet at the same time on the
same phone line!
You do not have to disable call waiting to connect to the Internet.
Even if the power goes out, you will still be able to make phone
calls.
Unlike cable modems, your connection speed will not be affected by
how much bandwidth your neighbors use.
ADSL Reliability
41
Always On
Because the information is transmitted separately from
the voice/fax calls, your Internet connection can stay on
all the time.
No more logging on and off
No more busy signals
No more waiting
just open your browser and go!
42
ADSL Security
The dedicated connection that ADSL uses
provides more security than cable.
Cable modem users share bandwidth with their
neighbors. Information traveling across the
network is easier to snoop.
43
ADSL modem
44
DSLAM
To interconnect multiple ADSL users a Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer
(DSLAM) is used
DSLAM is used at the telephone central office that separates the data signals
from the telephone line
45
What can I use ADSL for?
Faster downloads of anything digital
CD-quality audio
Graphics-rich websites
Faster and better multimedia
High-speed multiplayer games
46
Types of DSL
ADSL Asymmetric DSL
R-ADSL Rate Adaptive DSL
HDSL High Bit Rate DSL
SDSL Single Line DSL
VDSL Very High Bit Rate DSL
47
ADSL Summary
ADSL provides a new way to use existing phone
lines.
Its faster!
Its always on!
Voice and data on one line at the same time!
ADSL is the best way to get online!
You might also like
- 8661 - Solutions For AS A Level Year 1 Edexcel Stats Mechanics Challenge Set A v1.2Document18 pages8661 - Solutions For AS A Level Year 1 Edexcel Stats Mechanics Challenge Set A v1.2Cherie ChowNo ratings yet
- Telecom-Chapter OneDocument7 pagesTelecom-Chapter Onetsegab bekele100% (2)
- Ewsd Training ModuleDocument149 pagesEwsd Training ModuleAnkush Yadav100% (1)
- Conversations With God, Book 3Document7 pagesConversations With God, Book 3Brisaiguy100% (3)
- Chapter 3 - Transmission MediaDocument36 pagesChapter 3 - Transmission MediaDiorella PaguioNo ratings yet
- Ab BaffaDocument7 pagesAb BaffaIbrahim Said AhmadNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument33 pagesTransmission MediaWayan MardikaNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument36 pagesTransmission MediaAnmolDhillonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Prepared by Amanuel Admassu! Prepared by Amanuel Admassu!Document46 pagesChapter Two: Prepared by Amanuel Admassu! Prepared by Amanuel Admassu!Desalegn sirnaNo ratings yet
- DCCN Chap2Document46 pagesDCCN Chap2bayisabayecha51No ratings yet
- 08 Computer Networks - PPSXDocument72 pages08 Computer Networks - PPSXBinu RaveendranNo ratings yet
- Network Media-70413Document37 pagesNetwork Media-70413hanaNo ratings yet
- Bbit 213 Lecture 2Document25 pagesBbit 213 Lecture 2SamgishikaNo ratings yet
- Network & InternetDocument24 pagesNetwork & InternetPallab KumarNo ratings yet
- Tandingan Gabriel Data Communication B.S Cp.E 4-5:30 PM / TTHDocument4 pagesTandingan Gabriel Data Communication B.S Cp.E 4-5:30 PM / TTHRoel BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03Document8 pagesAssignment 03Ying-Chieh ChenNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 1Document75 pagesChapter6 1prajwalsitoula7No ratings yet
- WAN Terms::-Wan Is Known As Wide Area Network and It Connects Two or More LAN Together Over LargeDocument10 pagesWAN Terms::-Wan Is Known As Wide Area Network and It Connects Two or More LAN Together Over LargePankaj GargNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Exam CN NotesDocument44 pagesUnit 1 Exam CN NotesChandrabhushan kumarNo ratings yet
- DATA CommunicationsUNIT 3Document69 pagesDATA CommunicationsUNIT 3Anonymous l0bNv6G0% (1)
- Network Components EnamDocument5 pagesNetwork Components EnamturiagabaNo ratings yet
- Γηαλδξζ 6 Δπηγδηα Μηκροκτμασηκζ Εδτξζ (Mw Link) - ΒαΗκδ ΔννοηδDocument53 pagesΓηαλδξζ 6 Δπηγδηα Μηκροκτμασηκζ Εδτξζ (Mw Link) - ΒαΗκδ ΔννοηδEnder SaliNo ratings yet
- Communication and Networking: CSC 134 Lecture OutlineDocument8 pagesCommunication and Networking: CSC 134 Lecture Outlineshahera rosdiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document29 pagesLecture 1Esraa SamirNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Networking: ContentDocument42 pagesData Communication and Computer Networking: ContentMubaarak NuurNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media & Networking Components: Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument11 pagesTransmission Media & Networking Components: Electrical Engineering DepartmentHazel Ann ManlapazNo ratings yet
- Basics of Networking and RoutingDocument39 pagesBasics of Networking and RoutingSaurabh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication: 1) Transmission ModesDocument8 pagesWireless Communication: 1) Transmission ModesWasim WaseemNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication and NetworksDocument58 pagesTelecommunication and NetworksWaqas AfzalNo ratings yet
- Practical No.1 AIM: Brief Study of A Communication System LifeDocument32 pagesPractical No.1 AIM: Brief Study of A Communication System LifeReenav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemkirankumarikanchanNo ratings yet
- Physical Connections Wired Vs WirelessDocument26 pagesPhysical Connections Wired Vs WirelessMustafa ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Network TrainingDocument368 pagesNetwork TrainingCool hunk100% (3)
- CH Four Introduction To ComputerDocument32 pagesCH Four Introduction To Computersamita2721No ratings yet
- Computer Network - CS610 Power Point Slides Lecture 03Document37 pagesComputer Network - CS610 Power Point Slides Lecture 03Ibrahim ChoudaryNo ratings yet
- Data Communication CircuitsDocument19 pagesData Communication Circuitsshikha singhNo ratings yet
- 7 Telephone NetworksDocument7 pages7 Telephone NetworksKuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- 7 Telephone NetworksDocument7 pages7 Telephone NetworksKuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- 7 Telephone NetworksDocument7 pages7 Telephone NetworksKuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - A Top Down Approach: Notes (Chapters 1, 2, 3, 9)Document69 pagesComputer Networks - A Top Down Approach: Notes (Chapters 1, 2, 3, 9)Joe MamaNo ratings yet
- WMCDocument53 pagesWMCkirtidahiya123No ratings yet
- Information Technology: Networks and TelecommunicationsDocument46 pagesInformation Technology: Networks and TelecommunicationsshradhajoshiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Networking and RoutingDocument89 pagesBasics of Networking and RoutingVinay Aggarwal100% (1)
- Chapter 03Document8 pagesChapter 03Muqadas HakimNo ratings yet
- Project Report On: Submitted By:-GAURAV CHANDRA Abes Engineering CollegeDocument69 pagesProject Report On: Submitted By:-GAURAV CHANDRA Abes Engineering CollegeGaurav ChandraNo ratings yet
- 0567 - Data Communication and NetworkingDocument9 pages0567 - Data Communication and NetworkingAdil HassanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Networking and RoutingDocument89 pagesBasics of Networking and RoutingShafraz Jagger RahimNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication - MIDTERMDocument18 pagesWireless Communication - MIDTERMhoneysharmathehackerNo ratings yet
- Rajeshbasicsofnetworkingandrouting 110529033226 Phpapp02Document73 pagesRajeshbasicsofnetworkingandrouting 110529033226 Phpapp02prashant_padteNo ratings yet
- Ws 7Document33 pagesWs 7123vidyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Transmission Media and Network Devices: Type DescriptionDocument17 pagesChapter Four Transmission Media and Network Devices: Type DescriptionAbdul Basith ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Notes3 WANDocument40 pagesNotes3 WANsamitha deshanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Switching and Telephone NetworkDocument59 pagesCircuit Switching and Telephone NetworkmakubexiiiNo ratings yet
- Connecting With Computer Science Chapter 4 Review: Chapter SummaryDocument7 pagesConnecting With Computer Science Chapter 4 Review: Chapter SummaryWalid_Sassi_TunNo ratings yet
- Superior University Lahore, Pakistan: The Data Communication & Networking - Spring 2019Document12 pagesSuperior University Lahore, Pakistan: The Data Communication & Networking - Spring 2019Aqib HameedNo ratings yet
- Voice and Data Communications: Lecturer: Ngwa Collins A. Tel:676425241Document57 pagesVoice and Data Communications: Lecturer: Ngwa Collins A. Tel:676425241VershiyiLambertNo ratings yet
- Telephone Network and DSL Technology: U.K.P. Mihiranga (MBA in MOT, B.Sc. Eng. (Hons), PMP-PMI (USA), AMIESL)Document37 pagesTelephone Network and DSL Technology: U.K.P. Mihiranga (MBA in MOT, B.Sc. Eng. (Hons), PMP-PMI (USA), AMIESL)Pathum MihirangaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Telecommunication OverviewDocument34 pagesLecture 1 - Telecommunication OverviewsadeeqhardoNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication SystemsDocument33 pagesTelecommunication SystemsAlexander PhiriNo ratings yet
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- Telecommunications, The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets: Fundamentals of Information Systems, Second Edition 1Document42 pagesTelecommunications, The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets: Fundamentals of Information Systems, Second Edition 1sameer_omNo ratings yet
- Basic Telecom For Non-Technical Staff: Target AudienceDocument2 pagesBasic Telecom For Non-Technical Staff: Target Audiencesameer_omNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity: Eng. Sameer Technical Courses ContentDocument2 pagesBasic Electricity: Eng. Sameer Technical Courses Contentsameer_omNo ratings yet
- CISCOM Training Center: Microwave Planning and DesignDocument236 pagesCISCOM Training Center: Microwave Planning and Designsameer_omNo ratings yet
- Test SampleDocument3 pagesTest Samplesameer_omNo ratings yet
- GPON FundamentalsDocument266 pagesGPON Fundamentalspunokhail khan67% (3)
- 12B 0#jdzdefrpDocument166 pages12B 0#jdzdefrpsameer_omNo ratings yet
- 103 Projects Using LED's - T.R. MishraDocument168 pages103 Projects Using LED's - T.R. MishrasiromexNo ratings yet
- Permanent Magnet Rotor AssemblyDocument3 pagesPermanent Magnet Rotor Assemblysameer_omNo ratings yet
- HUA-GPON Fundamentals PDFDocument56 pagesHUA-GPON Fundamentals PDFalirazat2No ratings yet
- 02 Code of Ethics For Professional Accountants in The PhilippinesDocument22 pages02 Code of Ethics For Professional Accountants in The PhilippinesJoevitt Louis DelfinadoNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Wikipedia,: From Today's Featured Article in The NewsDocument6 pagesWelcome To Wikipedia,: From Today's Featured Article in The NewsRobert BonisoloNo ratings yet
- Travel Guide - Chiang Rai and Chiang MaiDocument69 pagesTravel Guide - Chiang Rai and Chiang MaiKalyan ChatterjeaNo ratings yet
- Newton Raphson Method Exp No 4Document7 pagesNewton Raphson Method Exp No 4Sri DeviNo ratings yet
- Term Assessments ResultsDocument2 pagesTerm Assessments Resultsj3n9j3n9No ratings yet
- Finals Ece Laws ReviewerDocument2 pagesFinals Ece Laws ReviewerAbigail Joy HernandezNo ratings yet
- Publisher BermasalahDocument29 pagesPublisher BermasalahMekaTronNo ratings yet
- Bushing and CT MonitoringDocument11 pagesBushing and CT MonitoringTravis WoodNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Semi-Detailed Lesson Planramon picayoNo ratings yet
- Joydeep Saha: Summary of QualitiesDocument3 pagesJoydeep Saha: Summary of QualitiesjoydeepsahaNo ratings yet
- Aerogenerador Southwest Windpower Air 30 Land ManualDocument32 pagesAerogenerador Southwest Windpower Air 30 Land ManualFlashgirl AmadorNo ratings yet
- Phast and Safeti OverviewDocument24 pagesPhast and Safeti OverviewlopezmoramiguelNo ratings yet
- s10639 019 09886 3 PDFDocument24 pagess10639 019 09886 3 PDFKokak DelightsNo ratings yet
- Business Models in Emerging Technologies: Data Science, AI, and BlockchainDocument30 pagesBusiness Models in Emerging Technologies: Data Science, AI, and BlockchainCharlene KronstedtNo ratings yet
- Mad About Modern Physics - F. Potter, C. Jargodzki PDFDocument311 pagesMad About Modern Physics - F. Potter, C. Jargodzki PDFIonut Dragan100% (2)
- Test ReachDocument5 pagesTest ReachizazNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W5Document4 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W5KRISTINE JOAN BARREDONo ratings yet
- Generic Environmental SOP Apr 2010Document42 pagesGeneric Environmental SOP Apr 2010Steven SloanNo ratings yet
- Classification GTR-1Document49 pagesClassification GTR-1Krouma RedhouaneNo ratings yet
- Autocalculator v. 16.00 i113001ENDocument53 pagesAutocalculator v. 16.00 i113001ENstikss100% (1)
- Información: Estado Tipo de Participantes Rangos de EdadDocument11 pagesInformación: Estado Tipo de Participantes Rangos de EdadAlondraNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument27 pagesDX DiagAlkithyar AdithyargioNo ratings yet
- A330 MelDocument1,065 pagesA330 MelAbu Tariq ZiadNo ratings yet
- 06 WFSDocument11 pages06 WFSCosmin Ion BlajaNo ratings yet
- HydrodynamicsDocument7 pagesHydrodynamicsSajit Chandra Shakya100% (1)
- Preboard Hge 1Document4 pagesPreboard Hge 1Winter DeeneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Divisibility Rules For 4, 8, 12 and 11Document12 pagesLesson 3 - Divisibility Rules For 4, 8, 12 and 11ranulfo mayolNo ratings yet
- Gregorio Zara (Scientist)Document2 pagesGregorio Zara (Scientist)Charina BantilanNo ratings yet