Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EC1401 VLSI Question Bank N Shanmuga Sundaram
EC1401 VLSI Question Bank N Shanmuga Sundaram
Uploaded by
saintkhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views35 pagesDIGITAL VLSI QUESTIONS
Original Title
17027322 EC1401 VLSI Question Bank N Shanmuga Sundaram
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDIGITAL VLSI QUESTIONS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views35 pagesEC1401 VLSI Question Bank N Shanmuga Sundaram
EC1401 VLSI Question Bank N Shanmuga Sundaram
Uploaded by
saintkhanDIGITAL VLSI QUESTIONS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 35
EC1401 VLSI Design
Question and Answers
Prepared by
N.SHANMUGA SUNDARAM
Assistant Professor
Department of ECE
Mahendra Engg College
Namakkal Dt. - 637503.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 1
EC1401 VLSI Design
2 Marks - Question and Answers
Unit I
1. What is Intrinsic and Extrinsic Semiconductor?
The pure Silicon is known as Intrinsic Semiconductor.
When impurity is added with pure Silicon, its electrical properties are varied.
This is known as Extrinsic Semiconductor.
2. What is CMOS Technology?
The fabrication of an IC using CMOS transistors is known as CMOS Technology.
CMOS transistor is nothing but an inverter, made up of an n-MOS and p-MOS
transistor connected in series.
3. Give the advantages of CMOS IC?
Size is less
High Speed
Less Power Dissipation
4. What are four generations of Integration Circuits?
SSI (Small Scale Integration)
MSI (Medium Scale Integration)
LSI (Large Scale Integration)
VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration)
5. Give the variety of Integrated Circuits?
More Specialized Circuits
Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs)
Systems-On-Chips
6. Why NMOS technology is preferred more than PMOS technology?
N-channel transistors have greater switching speed when compared to PMOS
transistors. Hence, NMOS is preferred than PMOS.
7. What are the different MOS layers?
n-diffusion
p-diffusion
Polysilicon
Metal
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 2
8. What are the different layers in MOS transistor?
The layers are Substrate, diffused Drain & Source, Insulator (SiO
2
) & Gate.
9. What are the different operating regions for an MOS transistor?
Cutoff Region
Non- Saturated (Linear) Region
Saturated Region
10. What is Enhancement mode transistor?
The device that is normally cut-off with zero gate bias is called Enhancement
mode transistor.
11. What is Depletion mode device?
The Device that conducts with zero gate bias is called Depletion mode device.
12. When the channel is said to be pinched off?
If a large V
ds
is applied, this voltage will deplete the inversion layer. This Voltage
effectively pinches off the channel near the drain.
13. What are the steps involved in manufacturing of IC?
Silicon wafer Preparation
Epitaxial Growth
Oxidation
Photo-lithography
Diffusion
Ion Implantation
Isolation technique
Metallization
Assembly processing & Packaging
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 3
14. What is meant by Epitaxy?
Epitaxy means arranging atoms in single crystal fashion upon a single crystal
substrate.
15. What are the processes involved in photo lithography?
(1) Masking process
(2) Photo etching process.
These are important processes involved in photolithography.
16. What is the purpose of masking in fabrication of IC?
Masking is used to identify the location in which Ion-Implantation should not take
place.
17. What lire the materials used for masking?
Photo resist, Si02, SiN, Poly Silicon.
18. What are the types of Photo etching?
Wet etching and dry etching are the types of photo etching.
19. What is diffusion process? What are doping impurities?
Diffusion is a process in which impurities are diffused into the Silicon chip at
1000C temperature. B
2
0
3
and P
2
0
5
are used as impurities used.
20. What is Ion-Implantation process?
It is process in which the Si material is doped with an impurity by making the
accelerated impurity atoms to strike the Si layer at high temperature.
21. What are the various Silicon wafer Preparation?
Crystal growth & doping
Ingot trimming & grinding
Ingot slicing
Wafer polishing & etching
Wafer cleaning.
22. What are the different types of oxidation?
The two types of oxidation are Dry & Wet Oxidation.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 4
23. What is Isolation?
It is a process used to provide electrical isolation between different components
and interconnections.
24. Give the different types of CMOS process?
p-well process
n-well process
twin-tub process
SOI process
25. What is Channel-stop Implantation?
In n-well fabrication, n-well is protected with the resist material. (Because, it
should not be affected during Boron implantation). Then Boron is implanted
except n-well. The above said process is done using photo resist mask. This type
of implantation is known as Channel-stop implantation.
26. What is LOCOS?
LOCOS mean Local Oxidation of Silicon. This is one type of oxide construction.
27. What is SWAMI?
SWAMI means Side Wall Masked Isolation. It is used to reduce bird's beak effect.
28. What is LDD?
LDD means Lightly Doped Drain Structures.
It is used for implantation of n
-
region in n-well process.
29. What is Twin-tub process? Why it is called so?
Twin-tub process is one of the CMOS technologies. Two wells (the other name
for well is Tub) are created in this process. So, because of these two tubs, this
process is known as Twin-tub process.
30. What are the steps involved in twin-tub process?
Tub Formation
Thin-oxide Construction
Source & Drain Implantation
Contact cut definition
Metallization.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 5
31. What are the special features of Twin-tub process?
In Twin-tub process, Threshold voltage, body effects of n and p devices are
independently optimized.
32. What are the advantages of Twin-tub process?
Advantages of Twin-tub process are
(1) Separate optimized wells are available.
(2) Balanced performance is obtained for n and p transistors.
33. What is SOI? What is the material used as Insulator?
SOI means Silicon-on-Insulator.
In this process, a Silicon based transistor is built on an insulating material like
Sapphire or SiO
2
.
34. What are the advantages and disadvantages of SOI process?
Advantages of SOI process:
1. There is no well formation in this process.
2. There is no field-Inversion problem.
3. There is no body effect problem.
Disadvantages of SOI process:
1. It is very difficult to protect inputs in this process.
2. Device gain is low.
3. The coupling capacitance between wires always exists.
35. What are the advantages of CMOS process?
Low Input Impedance
Low delay Sensitivity to load.
36. What are the various etching processes used in SOI process?
Various etching processes used in SOI are,
(A. FULLY ANISTROPHIC ETCHING)
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 6
(B. PREFERENTIAL ETCHING)
(C. ISOTROPHIC ETCHING)
37. What is BiCMOS Technology?
It is the combination of Bipolar technology & CMOS technology.
38. What are the basic processing steps involved in BiCMOS process?
Additional masks defining P base region
N Collector area
Buried Sub collector (SCCD)
Processing steps in CMOS process
39. What is meant by interconnect? What are the types are of interconnect?
Interconnect means connection between various components in an IC.
Types of Inter connect:
1. Metal Inter connect
2. PolySilicon Inter connect
3. Local Inter connect.
40. What is Silicide?
The combination of Silicon and tantaleum is known as Silicide.
It is used as gate material in Polysilicon Interconnect.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 7
41. What is Polycide?
The combination of Silicide and Polysilicon is known as Polycide.
It is used as gate material.
42. What is Stick diagram?
The diagram which conveys the layer information through the use of various
colours is known as Stick diagram. It is also the cartoon of a chip layout.
43. What are the uses of Stick diagram?
It can be drawn much easier and faster than a complex layout.
These are especially important tools for layout built from large cells.
44. Give the various color coding used in stick diagram?
Green - n-diffusion
Red - polysilicon
Blue - metal
Yellow - implant
Black - contact areas.
45. Compare between CMOS and bipolar technologies.
CMOS Technology Bi-polar Technology
Low static power dissipation
High input impedance
(low drive current)
Scalable threshold voltage
High noise margin
High packing density
High delay sensitivity to load
(fanout limitations)
Low output drive current
Low gm (gm Vin)
Bidirectional capability
A near ideal switching device
High power dissipation
Low input impedance
(high drive current)
Low voltage swing logic
Low packing density
Low delay sensitivity to load
High output drive current
High gm (gm a eVin)
High ft at low current
Essentially unidirectional
46. Define Threshold voltage in CMOS?
The Threshold voltage, VT for a MOS transistor can be defined as the voltage
applied between the gate and the source of the MOS transistor below which the
drain to source current, IDS effectively drops to zero.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 8
47. What is Body effect?
The threshold voltage V
Th
is not a constant with respect to the voltage difference
between the substrate and the source of MOS transistor. This effect is called
substrate-bias effect or body effect.
48. What is Channel-length modulation?
The current between drain and source terminals is constant and independent of the
applied voltage over the terminals. This is not entirely correct. The effective
length of the conductive channel is actually modulated by the applied V
DS
,
increasing V
DS
causes the depletion region at the drain junction to grow, reducing
the length of the effective channel.
49. What is Latch up?
Latch-up is a condition in which the parasitic components give rise to the
establishment of low resistance conducting paths between V
DD
and V
SS
with
disastrous results. Careful control during fabrication is necessary to avoid this
problem.
50. What is demarcation line?
Demarcation line is an imaginary line used in stick diagram, to separate p-MOS
and n-MOS transistors.
All p-MOS transistors are placed above demarcation line and n-MOS below the
demarcation line
51. What are the two types of Layout design rules?
Lambda design rules and micron rules are major types of layout design rules.
52. What is Lay-out design rule?
The rules followed to prepare the photo mask are known as Layout design rules.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 9
53. What are LVS and DRL tools?
LVS means Layout Versus Schematic.
It checks layout against schematic diagram. It is very important to verify layout.
DRC means Design Rule Checker.
This tool checks every occurrence of design rule list on layout.
Width, spacing of every metal line in layout are checked with this tool.
54. What is instance? What is instancing?
To construct big complex circuit, the basic cells (small cells) can be copied. This
process is known as Instancing. The cell which is copied is known as Instance.
55. What is flat cell?
The cell which is independent and not related to other objects is known as flat cell.
56. What are the cells available in primitive library?
NOT, NAND, NOR, are the basic cells in primitive library.
57. What is Design Hierarchy?
When we want to design AND-4 input gate, we use NAND-2 and NOR-2 basic
blocks. By combining NAND-2 and NOR-2, we create AND-4 input gate. This is
known as Design Hierarchy.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 10
Unit II
1. Draw the symbol of n-MOS and p-MOS.
Three terminals are shown here.
2. Draw the characteristics graph of enhancement mode of n-MOS.
When V
gs
= 0;
the device will be cut-off.
3. Draw the graph of n-MOS depletion mode.
The device will conduct;
Even if V
gs
= 0.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 11
4. Draw the graph of p-MOS enhancement mode.
Vos = gate-to-source voltage
Ids = drain-to-source current
Vtp = Threshold voltage
of a p-MOS transistor
If V
gs
crosses V
tp
;
then device will conduct.
5. Draw the graph of p-MOS depletion mode characteristics.
Vos = gate-to-source voltage
Ids = drain-to-source current
Vtp = Threshold voltage
of a p-MOS transistor
Even if V
gs
= 0;
the device will be conducting.
6. What are the three modes in an enhancement MOS transistor?
The different modes are a) Accumulation mode
b) Inversion Mode
c) Depletion Mode
7. Draw the diagram for Accumulation mode.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 12
8. Draw the diagram of depletion mode in MOS Transistor.
9. How an Inversion layer is formed in MOS Transistor?
In Inversion mode, the gate is applied with voltage larger than its threshold
voltage (Vgs>Vth).
As the gate voltage is increased, the electrons in the substrate are attracted towards
the region below the gate, pushing the holes to other side of the substrate. Thus, a
layer of electrons is formed below the gate, which is called as Inversion layer.
These electrons constitute the channel for conduction between source and drain.
10. What are the different regions that can be defined in n-MOS depending upon
the voltages applied?
Case (1) Cut-off Region : Vds = 0.
Case (2) Non-Saturated (or) Linear region : Vds < (Vgs Vth)
Case (3) Saturated Region : Vgs > Vth
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 13
11. What is the relationship between mobility and electric field?
12. What is Impact Ionization?
When gate length of MOS transistor is reduced, electric field at the drain of the
transistor (in saturation) is increased.
In submicron technology, the field is high, so, electrons are imparted with enough
energy to become 'hot'. These hot electrons impact the drain, and remove the holes
from that place and then swept towards the negatively charged substrate and
appear as a substrate current. This is known as 'Impact Ionization'.
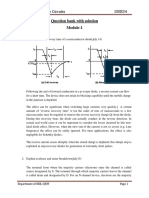
13. Draw the DC transfer characteristics curve to show its various regions.
14. Draw the graph of V
out
Vs V
in
for various n / p ratio.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 14
15. Define Noise Margin.
The parameter which gives the quantitative measure of how stable the inputs are
with respect to coupled electromagnetic signal interference.
NML = | V
IL
V
OL
|
NMH = | V
IH
V
OH
|
16. What is full-rail output?
Logic swing V
L
is defined as V
L
= V
OH
- V
OL
= V
DD
, V
L
= V
DD
VL = VDD = full value of power supply. This is known as full rail output.
17. Define Fall time.
The time needed for V
out
to fall from 0.9 V
DD
to 0.1 V
DD
is known as Fall time.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 15
18. Define Rise Time.
The time needed for V
out
to rise from 0.1 V
DD
to 0.9 V
DD
is known as Rise time.
19. What is Maximum signal frequency?
It is defined as the largest frequency (f) applied to gate and allow the output to
settle to a definable state.
1
f = -----------
tr + tf
where, tr - Rise time
tf - fall time
f - maximum signal frequency
20. Define Delay time
Delay time, t
d
is the time difference between input transition (50%) and the 50%
output level. This is the time taken for a logic transition to pass from input to
output.
21. Define propagation Delay.
It is defined as average of two time intervals.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 16
22. What are two components of Power dissipation?
There are two components that establish the amount of power dissipated in a
CMOS circuit.
These are: i) Static dissipation due to leakage current or other current drawn
continuously from the power supply.
ii) Dynamic dissipation due to
Switching transient current
Charging and discharging of load capacitances.
23. What is the formula for power dissipation for CMOS Inverter?
24. Draw the symbol and switching model of Transmission gate.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 17
25. Draw the Symbol of Tri-state Inverter.
26. What is the fundamental goal in Device modeling?
To obtain the functional relationship among the terminal electrical variables of the
device that is to be modeled.
27. Define Short Channel devices?
Transistors with Channel length less than 3- 5 microns are termed as Short
channel devices. With short channel devices the ratio between the lateral &
vertical dimensions are reduced.
28. What is pull-down device?
A device connected so as to pull the output voltage to the lower supply voltage
usually 0V is called pull down device.
29. What is pull-up device?
A device connected so as to pull the output voltage to the upper supply voltage
usually V
DD
is called pull up device.
33. Give the basic inverter circuit.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 18
Unit III:
1. Give some of the important CAD tools.
Some of the important CAD tools are:
i) Layout editors
ii) Design Rule checkers (DRC)
iii) Circuit extraction
2. What is meant by HDL?
It means Hardware Description Language.
It is used to model digital circuit design.
3. What is Verilog?
Verilog is a general purpose hardware descriptor language. It is similar in syntax
to the C programming language. It can be used to model a digital system at many
levels of abstraction ranging from the algorithmic level to the switch level.
4. What are the data types in Verilog?
Net type: It represents physical connection between structural elements.
Register type: It represents data storage elements.
5. What is wire in Verilog?
It is one of the net type. If S is the output of one gate, and input of the next block;
S should be mentioned as wire.
6. What is the use of parameter?
It is a constant used to specify delays and widths of variable.
Eg. Parameter BIT = 1, BYTE = 8;
7. What is Time Register?
It is used to store and manipulate time values.
Eg. Time current time; // current time holds one time value.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 19
8. How to specify nMOS in Verilog?
Syntax: nMOS n, (o/p, i/p, control).
9. What is Gate Delay?
The signal propagation delay from the gate i/p to the gate o/p is specified by using
gate delay.
Eg: nand #2 (c, a, b):
Here; Rise delay = 2 and fall delay = 2.
10. What is RTL?
RTL means Register-Transfer Modeling.
11. Give the examples for procedural statement.
Loop statement
Wait statement
Conditional statement
Case statement
are some of the examples for procedural statement.
12. What are the types of conditional statements?
1. If statement (with no else)
Syntax : if ( [expression] ) true statement;
2. If Statement (with One else statement)
Syntax : if ( [expression] ) true statement;
else false-statement;
3. Nested if-else-if
Syntax : if ( [expression1] ) true statement 1;
else if ( [expression2] ) true-statement 2;
else if ( [expression3] ) true-statement 3;
else default-statement;
The [expression] is evaluated. If it is true (1 or a non-zero value) true-statement is
executed. If it is false (zero) or ambiguous (x), the false-statement is executed.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 20
13. What are the various modeling used in Verilog?
1. Gate-level modeling
2. Data-flow modeling
3. Switch-level modeling
4. Behavioral modeling
14. What is the structural gate-level modeling?
Structural modeling describes a digital logic networks in terms of the components
that make up the system. Gate-level modeling is based on using primitive logic
gates and specifying how they are wired together.
15. What is Switch-level modeling?
Verilog allows switch-level modeling that is based on the behavior of MOSFETs.
Digital circuits at the MOS-transistor level are described using the MOSFET
switches.
16. What are identifiers?
Identifiers are names of modules, variables and other objects that we can reference
in the design.
Identifiers consists of upper and lower case letters, digits 0 through 9, the
underscore character(_) and the dollar sign($). It must be a single group of
characters.
Examples: A014, a, b, in_o, s_out, etc.
17. What are the value sets in Verilog?
Verilog supports four levels for the values needed to describe hardware referred to
as value sets.
Value levels Condition in hardware circuits
0 Logic zero, false condition
1 Logic one, true condition
X Unknown logic value
Z High impedance, floating state
18. What are the types of gate arrays in ASIC?
1) Channeled gate arrays
2) Channel less gate arrays
3) Structured gate arrays
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 21
19. Give the classifications of timing control.
Methods of timing control:
1. Delay-based timing control
2. Event-based timing control
3. Level-sensitive timing control
Types of delay-based timing control:
1. Regular delay control
2. Intra-assignment delay control
3. Zero delay control
Types of event-based timing control:
1. Regular event control
2. Named event control
3. Event OR control
4. Level-sensitive timing control
20. Give the different arithmetic operators.
Operator symbol Operation performed Number of operands
* Multiply Two
/ Divide Two
+ Add Two
- Subtract Two
% Modulus Two
** Power (exponent) Two
21. Give the different bitwise operators.
Operator symbol Operation performed Number of operands
~ Bitwise negation One
& Bitwise AND Two
| Bitwise OR Two
^ Bitwise XOR Two
^~ or ~^ Bitwise XNOR Two
~& Bitwise NAND Two
~| Bitwise NOR Two
22. Write the program for OR gate using Dataflow modeling.
module or gate (c, a, b)
input a;
input b;
output c;
assign c = a/b;
end module.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 22
23. What are gate primitives?
Verilog supports basic logic gates as predefined primitives. Primitive logic
function keyword provide the basics for structural modeling at gate level. These
primitives are instantiated like modules except that they are predefined in Verilog
and do not need a module definition. The important operations are AND, NAND,
OR, XOR, XNOR, and BUF (non-inverting drive buffer).
24. What are resistive primitives?
rnMOS, rpMOS, rcMOS are some of the resistive primitives.
25. Give the two blocks in behavioral modeling.
1. An initial block executes once in the simulation and is used to set up initial
conditions and step-by-step data flow.
2. An always block executes in a loop and repeats during the simulation.
26. Name the types of ports in Verilog
Types of port Keyword
Input port Input
Output port Output
Bidirectional port Input
27. Initialize port A as input, port b as output, and port c as inout port.
module name (a, b, c)
input a ;
output b;
inout c;
28. What are the types of procedural assignments?
1. Blocking assignment
2. Non-blocking assignment
29. Give the different symbols for transmission gate.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 23
Unit IV:
1. Give the different types of ASIC.
1. Full custom ASICs
2. Semi-custom ASICs
* Standard cell based ASICs
* Gate-array based ASICs
3. Programmable ASICs
* Programmable Logic Device (PLD)
* Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA).
2. What is the full custom ASIC design?
In a full custom ASIC, an engineer designs some or all of the logic cells, circuits
or layout specifically for one ASIC. It makes sense to take this approach only if
there are no suitable existing cell libraries available that can be used for the entire
design.
3. What is the standard cell-based ASIC design?
A cell-based ASIC (CBIC) uses pre-designed logic cells known as standard cells.
The standard cell areas also called fle4xible blocks in a CBIC are built of rows of
standard cells. The ASIC designer defines only the placement of standard cells
and the interconnect in a CBIC. All the mask layers of a CBIC are customized and
are unique to a particular customer.
4. Differentiate between channeled & channel less gate array.
Channeled Gate Array Channel less Gate Array
1. Only interconnect is customized.
Only the top few mask layers are
customized.
2. The interconnect uses predefined
spaces between rows of base cells.
No predefined areas are set aside for
routing between cells.
3. Routing is done using the spaces. Routing is done using the area of
transistors unused.
4. Logic density is less. Logic density is higher.
5. What is a FPGA?
A field programmable gate array (FPGA) is a programmable logic device that
supports implementation of relatively large logic circuits. FPGAs can be used to
implement a logic circuit with more than 20,000 gates whereas a CPLD can
implement circuits of upto about 20,000 equivalent gates.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 24
6. Give the constituent of I/O cell in 22V10.
2V10 I/O cell consists of
1. a register
2. an output 4:1 mux
3. a tristate buffer
4. a 2:1 input mux
It has the following characteristics:
* 12 inputs
* 10 I/Os
* product time 9 10 12 14 16 14 12 10 8
* 24 pins
7. What are the different methods of programming of PALs?
The programming of PALs is done in three main ways:
Fusible links
UV erasable EPROM
EEPROM (E2PROM) Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM
8. What is an antifuse?
An antifuse is normally high resistance (>100MW). On application of appropriate
programming voltages, the antifuse is changed permanently to a low-resistance
structure (200-500W).
9. What are the different levels of design abstraction at physical design?
Architectural or functional level
Register Transfer-level (RTL)
Logic level
Circuit level
10. What are macros?
The logic cells in a gate-array library are often called macros.
11. What are Programmable Interconnects?
In a PAL, the device is programmed by changing the characteristics if the
switching element. An alternative would be to program the routing.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 25
12. Give the steps in ASIC design flow.
a. Design entry
b. Logic synthesis and System partitioning
c. Pre-layout simulation.
d. Floor planning
e. Placement
f. Routing
g. Extraction
1. Post layout simulation
13. Give the XILINX Configurable Logic Block (CLB).
14. Give the XILINX FPGA architecture.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 26
Unit V:
1. Mention the levels at which testing of a chip can be done?
a) At the wafer level
b) At the packaged-chip level
c) At the board level
d) At the system level
e) In the field
2. What are the categories of testing?
a) Functionality tests
b) Manufacturing tests
3. Write notes on functionality tests?
Functionality tests verify that the chip performs its intended function.
These tests assert that all the gates in the chip, acting in concert, achieve a desired
function. These tests are usually used early in the design cycle to verify the
functionality of the circuit.
4. Write notes on manufacturing tests?
Manufacturing tests verify that every gate and register in the chip functions
correctly. These tests are used after the chip is manufactured to verify that the
silicon is intact.
5. Mention the defects that occur in a chip?
a) layer-to-layer shorts
b) discontinous wires
c) thin-oxide shorts to substrate or well
6. Give some circuit maladies to overcome the defects?
i. nodes shorted to power or ground
ii. nodes shorted to each other
iii. inputs floating/outputs disconnected
7. What are the tests for I/O integrity?
i. I/O level test
ii. Speed test
iii. IDD test
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 27
8. What is meant by fault models?
Fault model is a model for how faults occur and their impact on circuits.
9. Give some examples of fault models?
i. Stuck-At Faults
ii. Short-Circuit and Open-Circuit Faults
10. What is stuckat fault?
With this model, a faulty gate input is modeled as a stuck at zero or stuck at
one. These faults most frequently occur due to thin-oxide shorts or metal-to-
metal shorts.
11. What is meant by observability?
The observability of a particular internal circuit node is the degree to which one
can observe that node at the outputs of an integrated circuit.
12. What is meant by controllability?
The controllability of an internal circuit node within a chip is a measure of the
ease of setting the node to a 1 or 0 state.
13. What is known as percentage-fault coverage?
The total number of nodes that, when set to 1 or 0, do result in the detection of the
fault, divided by the total number of nodes in the circuit, is called the percentage-
fault coverage.
14. What is fault grading?
Fault grading consists of two steps. First, the node to be faulted is selected.
A simulation is run with no faults inserted, and the results of this simulation are
saved. Each node or line to be faulted is set to 0 and then 1 and the test vector set
is applied. If and when a discrepancy is detected between the faulted circuit
response and the good circuit response, the fault is said to be detected and the
simulation is stopped.
15. Mention the ideas to increase the speed of fault simulation?
a. parallel simulation
b. concurrent simulation
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 28
16. What is fault sampling?
An approach to fault analysis is known as fault sampling. This is used in circuits
where it is impossible to fault every node in the circuit. Nodes are randomly
selected and faulted. The resulting fault detection rate may be statistically inferred
from the number of faults that are detected in the fault set and the size of the set.
The randomly selected faults are unbiased. It will determine whether the fault
coverage exceeds a desired level.
17. What are the approaches in design for testability?
a. ad hoc testing
b. scan-based approaches
c. self-test and built-in testing
18. Mention the common techniques involved in ad hoc testing?
a. partitioning large sequential circuits
b. adding test points
c. adding multiplexers
d. providing for easy state reset
19. What are the scan-based test techniques?
a) Level sensitive scan design
b) Serial scan
c) Partial serial scan
d) Parallel scan
20. What are the two tenets in LSSD?
a. The circuit is level-sensitive.
b. Each register may be converted to a serial shift register.
21. What are the self-test techniques?
a. Signature analysis and BILBO
b. Memory self-test
c. Iterative logic array testing
22. What is known as BILBO?
Signature analysis can be merged with the scan technique to create a structure
known as BILBO (Built In Logic Block Observation).
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 29
23. What is known as IDDQ testing?
A popular method of testing for bridging faults is called IDDQ or current supply
monitoring. This relies on the fact that when a complementary CMOS logic gate is
not switching, it draws no DC current. When a bridging fault occurs, for some
combination of input conditions a measurable DC IDD will flow.
24. What are the applications of chip level test techniques?
a. Regular logic arrays
b. Memories
c. Random logic
25. What is Boundary scan?
The increasing complexity of boards and the movement to technologies like multi-
chip modules and surface-mount technologies resulted in system designers
agreeing on a unified scan-based methodology for testing chips at the board. This
is called Boundary scan.
26. What is the Test Access Port?
The Test Access Port (TAP) is a definition of the interface that needs to be
included in an IC to make it capable of being included in a boundary-scan
architecture.
The port has four or five single bit connections, as follows:
TCK(The Test Clock Input)
TMS(The Test Mode Select)
TDI(The Test Data Input)
TDO(The Test Data Output)
It also has an optional signal
TRST*(The Test Reset Signal)
27. What are the contents of the test architecture?
The test architecture consists of:
The TAP interface pins
A set of test-data registers
An instruction register
A TAP controller
28. What is the TAP controller?
The TAP controller is a 16-state FSM that proceeds from state to state based on
the TCK and TMS signals. It provides signals that control the test data registers,
and the instruction register. These include serial-shift clocks and update clocks.
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 30
29. What is known as test data register?
The test-data registers are used to set the inputs of modules to be tested, and to
collect the results of running tests.
30. What is known as boundary scan register?
The boundary scan register is a special case of a data register. It allows circuit-
board interconnections to be tested, external components tested, and the state of
chip digital I/Os to be sampled.
*************** X ***************
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 31
BIG QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
1. Derive the CMOS inverter DC characteristics and obtain the relationship for
output voltage at different region in the transfer characteristics.
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
CMOS inverter (2)
DC characteristics (5)
Transfer characteristics (5)
2. Explain with neat diagrams the various CMOS fabrication technology
P-well process (4)
N-well process (4)
Silicon-On-Insulator Process (4)
Twin- tub Process (4)
3. Explain the latch up prevention techniques.
Definition (2)
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
4. Explain the operation of PMOS Enhancement transistor
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Operation (4)
5. Explain the threshold voltage equation
Definition (2)
Explanation (2)
Derivation (4)
6. Explain the silicon semiconductor fabrication process.
Silicon wafer Preparation (2)
Epitaxial Growth (2)
Oxidation (2)
Photolithography (2)
Diffusion(2)
Ion Implantation (2)
Isolation technique (2)
Metallization (1)
Assembly processing & Packaging (1)
7. Explain various CAD tool sets.
Layout editors (4)
Design Rule checkers (DRC) (4)
Circuit extraction (4)
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 32
8. Explain the operation of NMOS Enhancement transistor.
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Operation (4)
9. Explain the Transmission gate and the tristate inverter briefly.
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Operation (4)
10. Explain about the various non ideal conditions in MOS device model.
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Operation (4)
11. Explain the design hierarchies.
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Concept (2)
12. Explain the concept involved in Timing control in VERILOG.
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Delay-based timing control (4)
Event-based timing control (4)
Level-sensitive timing control (4)
13. Explain with neat diagrams the Multiplexer and latches using transmission Gate.
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Multiplexer (4)
latches(4)
14. Explain the concept of gate delay in VERILOG with example
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Concept (2)
15. Explain the concept of MOSFET as switches and also bring the various logic
gates using the switching concept.
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Gate Concepts (4)
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 33
16. Explain the concept involved in structural gate level modeling and also give the
description for Half adder and Full adder.
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Gate Concepts (6)
Half adder (3)
Full adder (3)
17. What is ASIC? Explain the types of ASIC.
Definition (2)
Types (2)
Full custom ASICs (4)
Semi-custom ASICs(4)
Programmable ASICs(4)
18. Explain the VLSI design flow with a neat diagram
Explanation (2)
Flow Diagram (2)
Concepts (4)
19. Explain the concept of MOSFET as switches
Explanation (2)
Diagram (2)
Concepts (4)
20. Explain the ASIC design flow with a neat diagram
Design entry (2)
Logic synthesis and System partitioning (2)
Pre-layout simulation. (2)
Floor planning (2)
Placement (2)
Routing (2)
Extraction (2)
Post layout simulation (2)
21. a) Explain fault models.
Stuck-At Faults
Definition (2)
Diagram (2)
Short-circuit and Open-circuit faults
Definition (2)
Diagram (2)
b) Explain ATPG.
Definition (2)
Truth tables (2)
Five valued logic (2)
Testability measures (2)
Mahendra Engineering College EC1401 VLSI Design
NSS / ECE 34
22. Briefly explain
a) Fault grading & fault simulation
Fault grading (2)
Fault simulation (2)
b) Delay fault testing
Diagram (2)
Description (2)
c) Statistical fault analysis
Definition (1)
Statistics (3)
d) Fault sampling (4)
23. Explain scan-based test techniques.
Level sensitive scan design (4)
Serial scan (4)
Partial serial scan (4)
Parallel scan (4)
24. Explain Ad-Hoc testing and chip level test techniques.
Ad-Hoc testing
Parallel-load feature (2)
Test signal block (2)
Use of the bus (2)
Use of multiplexer (2)
Chip level test techniques
Definition (2)
Regular logic arrays (2)
Memories (2)
Random logic (2)
25. Explain self-test techniques and IDDQ testing.
Signature analysis and BILBO (6)
Memory-self test (4)
Iterative logic array testing (3)
IDDQ testing (3)
26. Explain system-level test techniques.
Boundary scan definition (2)
The Test Access Port (2)
The Test Architecture (2)
The TAP Controller (3)
The Instruction Register (2)
Test-Data Registers (2)
Boundary Scan Registers (3)
You might also like
- EI2403 - VLSI Design 2 Marks With AnswersDocument23 pagesEI2403 - VLSI Design 2 Marks With AnswersAnand GvphNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8085 - NotesDocument36 pagesMicroprocessor 8085 - NotesDr. N.Shanmugasundaram92% (72)
- Vlsi Design Question Bank EEC 703Document10 pagesVlsi Design Question Bank EEC 703selvi0412No ratings yet
- Anallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsshankarNo ratings yet
- Dr. N.G.P. Institute of Technology - Coimbatore-48: Analog and Digital Integrated CircuitsDocument48 pagesDr. N.G.P. Institute of Technology - Coimbatore-48: Analog and Digital Integrated CircuitsMrs.S.Divya BMENo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With AnswersDocument41 pagesAnalog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With Answerspriya adhavanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Questions ECE VLSI NITTDocument6 pagesAssignment Questions ECE VLSI NITTAkhilGovindNo ratings yet
- Memories and PLDsDocument47 pagesMemories and PLDsHimanshu Khanduri100% (1)
- A1429 VlsiDocument8 pagesA1429 VlsiratnamsNo ratings yet
- CMOS Question Bank 1Document3 pagesCMOS Question Bank 1Sameer R. KhanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Device and Circuits - Lab Viva QuestionsDocument2 pagesElectronic Device and Circuits - Lab Viva QuestionsAnirudhan Ravi100% (1)
- 355 - EC8451 Electromagnetic Fields - 2 Marks With Answers 1 PDFDocument32 pages355 - EC8451 Electromagnetic Fields - 2 Marks With Answers 1 PDFBala913100% (1)
- UNIT 1 Question BankDocument6 pagesUNIT 1 Question BankUjjwalNo ratings yet
- VLSIDocument107 pagesVLSItamil selvam100% (1)
- Electronic Devices Model Question PapersDocument2 pagesElectronic Devices Model Question Papersk_kunarajNo ratings yet
- Multiplier in Vlsi PDFDocument23 pagesMultiplier in Vlsi PDFvmspraneeth100% (1)
- Vlsi Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesVlsi Important QuestionsSowmya Chowdary50% (2)
- Cmos Analog Ic Design Course Plan NewDocument9 pagesCmos Analog Ic Design Course Plan Newjim2001No ratings yet
- Ec 3 Lab Viva QuestionsDocument4 pagesEc 3 Lab Viva QuestionsDeepti Chandrasekharan0% (1)
- EI2353-Digital System DesignDocument13 pagesEI2353-Digital System DesignSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 MarksDocument30 pages2 MarksAnitha Kumari SivathanuNo ratings yet
- VLSI Objective Questions and Answers 1Document7 pagesVLSI Objective Questions and Answers 1avinashrai92% (12)
- II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-VDocument5 pagesII yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-VanunilaNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - SolutionDocument48 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - SolutionchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Subsystem Design: Architectural IssuesDocument26 pagesSubsystem Design: Architectural IssuesSanjana M PNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller & RISC Architecture (2 Marks - Question Bank)Document61 pagesMicrocontroller & RISC Architecture (2 Marks - Question Bank)Dr. N.Shanmugasundaram100% (3)
- Electric Circuits &electronics Device Question PaperDocument5 pagesElectric Circuits &electronics Device Question PaperSalai Kishwar JahanNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Interview and Viva QuestionsDocument44 pagesAnalog Electronics Interview and Viva QuestionsPranay DumbhareNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED ANALOG IC DESIGN Lab ManualDocument27 pagesADVANCED ANALOG IC DESIGN Lab ManualJahnavi Ratnam0% (1)
- VLSI Design MethodologyDocument72 pagesVLSI Design MethodologyMandovi BorthakurNo ratings yet
- Microelectronics MCQs-QuestionsDocument16 pagesMicroelectronics MCQs-QuestionsKimberly TaboraNo ratings yet
- Stick Diagram and LayoutDocument61 pagesStick Diagram and LayoutSwetha AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Unit IV & V Question BankDocument5 pagesUnit IV & V Question BanknithyasaviNo ratings yet
- VL5101 Periodical 1Document4 pagesVL5101 Periodical 1DarwinNo ratings yet
- VLSI Questions Answers r3Document79 pagesVLSI Questions Answers r3Gowtham HariNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument28 pagesMCQkrishgkkd3339No ratings yet
- Interview Questions With Answers: Ch.V.V.RamanaDocument16 pagesInterview Questions With Answers: Ch.V.V.Ramanaram12_leoNo ratings yet
- LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT - Question Bank (ECE, EIE & BME)Document7 pagesLINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT - Question Bank (ECE, EIE & BME)MATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-1913104-Design of Embedded SystemsDocument12 pagesQuestion Bank-1913104-Design of Embedded SystemsHasib Al-ariki100% (1)
- Digital Lab VIVA QuestionsDocument4 pagesDigital Lab VIVA QuestionsAnirudhan RaviNo ratings yet
- MOSFET OperationDocument26 pagesMOSFET OperationAbhishek Singh100% (1)
- CMOS BasicsDocument41 pagesCMOS BasicsYeshoda MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- Tunnel DiodeDocument17 pagesTunnel DiodeShubham GoyalNo ratings yet
- Tcs Digital Sample Questions: Advanced Aptitude Set 2Document2 pagesTcs Digital Sample Questions: Advanced Aptitude Set 2Yaqub AnsariNo ratings yet
- Rfic Question BankDocument25 pagesRfic Question BankJenny ThanushawNo ratings yet
- Mes Question-BankDocument4 pagesMes Question-BankGanaraj KaruvajeNo ratings yet
- Modulation & Need For ModulationDocument7 pagesModulation & Need For ModulationragulNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument6 pagesQuestion PaperLavanya Vaishnavi D.A.No ratings yet
- Unit III - MCQsDocument15 pagesUnit III - MCQsMission Gate2021No ratings yet
- 2 Marks Ldica NotesDocument8 pages2 Marks Ldica NotesRAJOLI GIRISAI MADHAV100% (2)
- Wave Propagation (Unit VI)Document65 pagesWave Propagation (Unit VI)Nuzhath FathimaNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Lab ManualDocument27 pagesVlsi Lab ManualSandeep V GowdaNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Interview Questions: 1) What Is The Difference Between Latch and Flip-Flop?Document11 pagesDigital Electronics Interview Questions: 1) What Is The Difference Between Latch and Flip-Flop?yashuNo ratings yet
- Unit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveDocument12 pagesUnit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveHemant TulsaniNo ratings yet
- Asic - Design Question BankDocument4 pagesAsic - Design Question BankHarshit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - ADC TestingDocument87 pagesChapter 12 - ADC TestingMonal Bhoyar100% (1)
- Fabrication of PMOS TransistorsDocument11 pagesFabrication of PMOS TransistorsNash Anderson50% (4)
- Vlsi Basic Viva Questions and Answers PDFDocument12 pagesVlsi Basic Viva Questions and Answers PDFAnonymous BVp7iZNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Lab Viva Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesVlsi Lab Viva Questions and AnswersNiranjan Mamadapur Assistant Professor - ECENo ratings yet
- VLSI Lab Viva Questions and Answers 1Document21 pagesVLSI Lab Viva Questions and Answers 1anand_duraiswamyNo ratings yet
- VLSI Lab Viva Questio Ns and Answers PDF - Sushanth KJ - Academia - Edu PDFDocument7 pagesVLSI Lab Viva Questio Ns and Answers PDF - Sushanth KJ - Academia - Edu PDFVishnuNo ratings yet
- Embedded System - Question Bank (BE-ECE, VII Semester, R2008)Document52 pagesEmbedded System - Question Bank (BE-ECE, VII Semester, R2008)Dr. N.Shanmugasundaram100% (2)
- Embedded System Unit V (Prepared by N.Shanmugasundaram)Document18 pagesEmbedded System Unit V (Prepared by N.Shanmugasundaram)Dr. N.Shanmugasundaram71% (7)
- Microcontroller & RISC Architecture (2 Marks - Question Bank)Document61 pagesMicrocontroller & RISC Architecture (2 Marks - Question Bank)Dr. N.Shanmugasundaram100% (3)
- Microprocessor Lab Manual - FinalDocument157 pagesMicroprocessor Lab Manual - FinalDr. N.Shanmugasundaram100% (6)
- 8051 Microcontroller (2 Marks - Question Bank)Document13 pages8051 Microcontroller (2 Marks - Question Bank)Dr. N.Shanmugasundaram97% (34)
- Circuits and Devices Lab Manual (II Sem BE-ECE, AU-CBE)Document105 pagesCircuits and Devices Lab Manual (II Sem BE-ECE, AU-CBE)Dr. N.Shanmugasundaram83% (6)
- Microprocessor and Applications (EC1303) - Question BankDocument39 pagesMicroprocessor and Applications (EC1303) - Question BankDr. N.Shanmugasundaram86% (21)
- 8086 - Microprocessor and Applications (AU-CBE, R2008)Document25 pages8086 - Microprocessor and Applications (AU-CBE, R2008)Dr. N.Shanmugasundaram67% (3)
- Embedded Systems - Question Bank (AU-CBE, ECE-R2007)Document36 pagesEmbedded Systems - Question Bank (AU-CBE, ECE-R2007)Dr. N.ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- IT1353 Embedded System (All 5 Units)Document71 pagesIT1353 Embedded System (All 5 Units)Dr. N.ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- Mg1401 TQM (Unit V Iso)Document20 pagesMg1401 TQM (Unit V Iso)Dr. N.ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- Stm32f4 Discovery DatasheetDocument154 pagesStm32f4 Discovery DatasheetArtur JunqueiraNo ratings yet
- 18 FSMDocument16 pages18 FSMAchuNo ratings yet
- PLC Basic Exercises For OmronDocument3 pagesPLC Basic Exercises For Omronraj3885No ratings yet
- A.L.S.E Application Note Using The LT24 / ILI9341Document11 pagesA.L.S.E Application Note Using The LT24 / ILI9341Jules BernardNo ratings yet
- Vs1001 Mpeg Audio CodecDocument58 pagesVs1001 Mpeg Audio CodecChuchi Chichu100% (1)
- Low Power High Performance PMOS Biased Sense AmplifierDocument4 pagesLow Power High Performance PMOS Biased Sense AmplifierDebashish KalitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document45 pagesChapter 16sitiNo ratings yet
- Unit-6: Stack and Subroutine: (MPI) GTU # 3160712Document53 pagesUnit-6: Stack and Subroutine: (MPI) GTU # 3160712GajjuNo ratings yet
- Memory and Its TypesDocument4 pagesMemory and Its TypesNikku100% (2)
- TOC IndexDocument28 pagesTOC IndexDaniel VerdezotoNo ratings yet
- List of Intel Pentium 4 Microproce PDFDocument10 pagesList of Intel Pentium 4 Microproce PDFJoao47xNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Digital Computer:: MicroprocessorDocument25 pagesBlock Diagram of Digital Computer:: MicroprocessorRobotrixNo ratings yet
- GSM Based System Design For Industrial AutomationDocument8 pagesGSM Based System Design For Industrial AutomationAnurag DalviNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 14: Computer Logic Design Functions of Combinational LogicDocument25 pagesLecture No. 14: Computer Logic Design Functions of Combinational LogicMuhammad AnasNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 1Document29 pagesCh-1 1A_b_qNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Gajski Kuhn Y ChartDocument18 pagesLecture 6 Gajski Kuhn Y ChartShiraz HusainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3a-MP DSBDocument28 pagesChapter 3a-MP DSBsheham ihjamNo ratings yet
- Identifying MotherboardDocument9 pagesIdentifying MotherboardRoroRichardsNo ratings yet
- Hpux ScsiDocument8 pagesHpux ScsiPredrag TerzicNo ratings yet
- Cache Mapping FunctionsDocument39 pagesCache Mapping FunctionssalithakkNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Methodology For Achieving Optimal Power and Speed in AsicDocument22 pagesAn Efficient Methodology For Achieving Optimal Power and Speed in Asickumarbsnsp50% (2)
- SyllDocument2 pagesSyllSabbirNo ratings yet
- Atmel AT91SAM9263 Reference ManualDocument1,110 pagesAtmel AT91SAM9263 Reference ManualleadfiguresNo ratings yet
- ICO100-839 User's Manual VA1 - 07-14-2017Document54 pagesICO100-839 User's Manual VA1 - 07-14-2017WildanNo ratings yet
- Realization of Gates Using Discrete ComponentsDocument6 pagesRealization of Gates Using Discrete ComponentskishorebabNo ratings yet
- Exper5 Digital Adders-SubtractorsDocument5 pagesExper5 Digital Adders-SubtractorsPECMURUGANNo ratings yet
- NY8A053D v1.6Document75 pagesNY8A053D v1.6Desenvolvimento QualitronixNo ratings yet
- Labview Fpga ModuleDocument5 pagesLabview Fpga Modulevanhai_hvktqs41No ratings yet
- PIN Diagram of Intel 8085 Microprocessor - Lecture 3Document14 pagesPIN Diagram of Intel 8085 Microprocessor - Lecture 3ojasbhosale07No ratings yet
- CodeDocument11 pagesCodevlsNo ratings yet