Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1-1basic Principle of PV (Day1)
Uploaded by
mohmmad1972Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1-1basic Principle of PV (Day1)
Uploaded by
mohmmad1972Copyright:
Available Formats
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
1
1. Solar Photovoltaic Theory
1-1. Basic principles of PV
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
2
1-1.Basic principle of PV
1-1. Basic principles of PV
1-1-1. Mechanism of generation
1-1-2. Various type of PV cell
1-1-3. Installation example
1-1-4. Basic characteristic
1-1-5. Case sturdy
Contents
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
3
Photo Voltaic cell
Electrode
P-Type Semiconductor
N-Type Semiconductor
Reflect-Proof Film
Electrode
Solar Energy
Load
E
l
e
c
t
r
i
c
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
1-1-1. Mechanism of generation
Mechanism of generation
The solar cell is composed of a P-type semiconductor and an N-type
semiconductor. Solar light hitting the cell produces two types of electrons,
negatively and positively charged electrons in the semiconductors.
Negatively charged (-) electrons gather around the N-type semiconductor
while positively charged (+) electrons gather around the P-type
semiconductor. When you connect loads such as a light bulb, electric
current flows between the two electrodes.
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
4
1-1-1. Mechanism of generation
Direction of current inside PV cell
P
N
Current appears
to be in the
reverse direction ?
Inside current of PV cell looks like
Reverse direction. Why?
?
By Solar Energy, current is pumped
up from N-pole to P-pole.
In generation, current appears reverse.
It is the same as for battery.
P
N
Looks like
reverse
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
5
1-1-1. Mechanism of generation
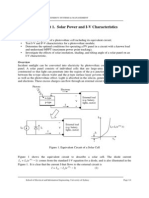
Voltage and Current of PV cell ( I-V Curve )
(V)
(A)
Voltage(V)
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
I
)
P
N
A
Short Circuit
Open Circuit
P
N
V
about 0.5V
(Silicon)
High insolation
Voltage on normal operation point
0.5V (in case of Silicon PV)
Current depend on
- Intensity of insolation
- Size of cell
Low insolation
Normal operation point
(Maximum Power point)
I x V = W
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
6
1-1-1. Mechanism of generation
Typical I-V Curve
(V)
(A)
Voltage(V)
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
I
)
0.49 V 0.62 V
4.95A
5.55A
Depend on
type of cell or
cell-material
( Si = 0.5V )
Depend on cell-size
Depend on
Solar insolation
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
7
Crystalline
Non-crystalline
Single crystal
Poly crystalline
Amorphous
Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)
Conversion Efficiency
of Module
10 - 17%
10 - 13%
7 - 10%
18 - 30%
Conversion Efficiency =
Electric Energy Output
Energy of Insolation on cell
x
100%
Dye-sensitized Type
Organic Thin Layer Type
7 - 8%
2 - 3%
1-1-2. Various type of PV cell
Types and Conversion Efficiency of Solar Cell
Silicon
Semiconductor
Compound
Semiconductor
Solar
Cell
Organic
Semiconductor
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
8
Crystal cell (Single crystal and Poly crystalline Silicon)
Single crystal Poly crystalline
1-1-2. Various type of PV cell
Formed by melting high purity
silicon like as Integrated Circuit
For mass production, cell is sliced
from roughly crystallized ingot.
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
9
Surface of PV cell
1-1-2. Various type of PV cell
Front Surface
(N-Type side)
Aluminum Electrode
(Silver colored wire)
To avoid shading,
electrode is very fine.
Anti reflection film
(Blue colored film)
Back surface is P-
type.
All back surface is
aluminum electrode
with full reflection.
Example of Poly Crystalline PV
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
10
Single crystal Poly crystalline
120W
(25.7V ,
4.7A)
1200mm
800mm
800mm
1200mm
1-1-2. Various type of PV cell
PV Module (Single crystal, Poly crystalline Silicon)
(3.93ft)
2.62ft
3.93ft
(2.62ft)
128W
(26.5V ,
4.8A)
Efficiency is higher Efficiency is lower
Same size
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
11
1-1-2. Various type of PV cell
Hierarchy of PV
2 3 W
100 - 200 W
10 - 50 kW
Cell
Array
Module,Panel
Volt Ampere Watt Size
Cell 0.5V 5-6A 2-3W about 10cm
Module 20-30V 5-6A 100-200W about 1m
Array 200-300V 50A-200A 10-50kW about 30m
6x9=54 (cells) 100-300 (modules)
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
12
1-1-2. Various type of PV cell
Roughly size of PV Power Station.
How much PV can we install in this conference room?
1 kw PV need 10 m
2
Please
remember
10m(33feet)
2
0
m
(
6
6
f
e
e
t
)
Conference
Room
(We are now)
Our room has about 200 m
2
We can install about
20 kW PV in this room
(108 feet
2
)
(2,178 feet
2
)
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
13
1-1-3. Installation example
Roof top of residence ( Grid connected )
Most popular installation
style in Japan.
(Almost 85% PV in Japan )
Owner can sell excess
power to power utility.
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
14
1-1-3. Installation example
Roof top of school ,community-center building.
(For education and emergency power)
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
15
1-1-3. Installation example
Distant and independent power supply ( Off grid )
Relay station on top of mountain
Advertising sign beside highway
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
16
1-1-3. Installation example
Mountain lodge ( Off grid )
1.2kW system
Inverter and controller
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
17
1-1-3. Installation example
Stationary power station (Grid connected )
Site: Funafuti Tuvalu
Installation: Feb. in 2008
Capacity: 40kW
Purpose: Grid connected power supply for fuel conservation
and CO2 reduction.
e8 & PPA project in Tuvalu
30kW array 10kW array
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
18
1-1-3. Installation example
Stationary power station (Off grid or mini grid )
Solar cell capacity: 3.4kW
Wind Power capacity: 1.8kW
Inverter capacity: 5kVA
Site: Mongolia
Installation: May & June in 1999
Purpose: For lighting, refrigerator
and outlet in a hospital.
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
19
1-1-3. Installation example
Solar Home System (SHS)
Solar array
Solar array
Solar array
Solar array
Controller
Light
Storage battery
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
20
1-1-4. Basic Characteristic
I / V curve and P-Max control
P
N
A
V
To obtain maximum power, current
control (or voltage control) is very
important.
(V)
(A)
Voltage(V)
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
I
)
I x V = W
P2
PMAX
P1
V
pmax
I
pmax
I/V curve
P- Max control
Power conditioner (mentioned
later) will adjusts to be most suitable
voltage and current automatically.
Power curve
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
21
1-1-4. Basic Characteristic
Estimate obtained power by I / V curve
(V)
(A)
Voltage(V)
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
I
)
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
P
N
A
) ( 05 . 0 R
PV character
( I/V curve )
If the load has 0.05 ohm resistance,
cross point of resistance character and
PV-Character will be following point.
Then power is 10x0.5=5 W
) ( 05 . 0 R
05 . 0 / V I
R
V
I
Ohms theory
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
22
1-1-4. Basic Characteristic
I / V curve vs. Insolation intensity
P
N
P
N
Mismatch
5A
1A
P
N
P
N
Bypass
Diode
5A
1A 4A
(V)
(A)
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
I
)
High intensity insolation
Low intensity insolation
I x V = W
5A
1A
Current is affected largely by change
of insolation intensity.
Partially shaded serial cell will
produce current mismatch.
Bypass Diode
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
23
1-1-4. Basic Characteristic
Temperature and efficiency
4
6
8
10
12
14
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Module Temperature (deg.C)
E
f
f
i
c
i
e
n
c
y
(
%
)
Crystalline cell
Amorphous cell
Typical
(25C)
Summer time
on roof top
(65C)
2%
down
When module temperature rises up, efficiency decreases.
The module must be cooled by natural ventilation, etc.
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
24
1-1-5. Case sturdy
1.Maximum power control
P
N
P
N
P
N
) ( 05 . 0 R
) ( 10 . 0 R
) ( 02 . 0 R
Q : Calculate how much power you can get by following three
resistance. ( I / V curve is next page)
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
25
1-1-5. Case sturdy
1.Maximum power control
(V)
(A)
Voltage(V)
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
I
)
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
R
V
I
I/V curve of current insolation.
e
8
/
P
P
A
S
o
l
a
r
P
V
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
O
&
M
M
a
r
s
h
a
l
l
I
s
l
a
n
d
s
M
a
r
c
h
3
1
-
A
p
r
i
l
1
1
,
2
0
0
8
26
1-1-5. Case sturdy
2.Temperature vs. Efficiency
Q: There is 50 kW Crystalline PV system.
If surface temperature rises from 25C to 65C, How much
the capacity will be?
You might also like
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Eead422 TransformerDocument183 pagesEead422 TransformerRenzJohnAmpostaNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- High Frequency Power Transformers - Design A High-Frequency Power Transformer Based On Flyback TopologyDocument6 pagesHigh Frequency Power Transformers - Design A High-Frequency Power Transformer Based On Flyback TopologyShyam Bin JamilNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Solar Cells PresentationDocument23 pagesPhotovoltaic Solar Cells Presentationmohmmad1972No ratings yet
- Basic of 400KV Substation DesignDocument62 pagesBasic of 400KV Substation Designtkdrt2166100% (1)
- Introduction To Power Electronics SystemDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics Systemrakesh_pal_3No ratings yet
- Automatic Solar Tracking SystemDocument82 pagesAutomatic Solar Tracking SystemDebashishParidaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Management For Industrial PlantsDocument35 pagesPower Management For Industrial PlantsSeindahNya100% (1)
- Energy Systems PhotoVoltaic SystemDocument59 pagesEnergy Systems PhotoVoltaic SystemMustafa Yılmaz100% (2)
- Electric Snap Circuits 102-305Document76 pagesElectric Snap Circuits 102-305Science HouseNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine Lab ManualDocument61 pagesElectrical Machine Lab ManualPrem SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Solar Module Manufacturing Unit (10 Mw/year)Document6 pagesProject Report On Solar Module Manufacturing Unit (10 Mw/year)EIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers100% (1)
- LAB-VOLT 3-Phase Induction (Squirrel-Cage) MachinesDocument11 pagesLAB-VOLT 3-Phase Induction (Squirrel-Cage) Machinesanyr2No ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Switches and ConvertersFrom EverandPower Electronics: Switches and ConvertersRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- 1-1basic Principle of PV (Day1)Document26 pages1-1basic Principle of PV (Day1)Tejinder SinghNo ratings yet
- S S D - C W MPPT F S H L S: OFT Witching C DC Onverters ITH OR Olar OME Ighting YstemDocument63 pagesS S D - C W MPPT F S H L S: OFT Witching C DC Onverters ITH OR Olar OME Ighting YstemShankar NaikNo ratings yet
- I-V Characteristics of Solar PanelDocument17 pagesI-V Characteristics of Solar PanelZarif KhanNo ratings yet
- BQ 25570Document40 pagesBQ 25570Magyar András TamásNo ratings yet
- Physics Inves Project 12thDocument10 pagesPhysics Inves Project 12thBharathi PonnuduraiNo ratings yet
- Prof Jyothi C PattenshettiDocument20 pagesProf Jyothi C PattenshettianushkaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of P&O and IP&O MPPT Techniques For Photovoltaic SystemDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of P&O and IP&O MPPT Techniques For Photovoltaic SystemIJMERNo ratings yet
- State Estimator Design For Solar Battery ChargerDocument6 pagesState Estimator Design For Solar Battery ChargerEdison PicoNo ratings yet
- Exp 04 M2kDocument20 pagesExp 04 M2kHuyThaiNo ratings yet
- CS-531, CP-533, CS-533, CS-573 Electrical System & CS-583 Vibratory CompactorsDocument2 pagesCS-531, CP-533, CS-533, CS-573 Electrical System & CS-583 Vibratory CompactorsomarNo ratings yet
- ICA Lab Manual PDFDocument193 pagesICA Lab Manual PDFVijay MNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical EngineeringDocument37 pagesBasics of Electrical Engineeringlp mishraNo ratings yet
- Self Powered Emitter Turnoff ThyristorDocument9 pagesSelf Powered Emitter Turnoff ThyristorSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab PDFDocument92 pagesPe Lab PDFVenkateshSrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Äñ Æ÷Éè Æ Ó ©Document6 pagesÄñ Æ÷Éè Æ Ó ©Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Pub 12 SMC Smesc Energies-04-02180Document16 pagesPub 12 SMC Smesc Energies-04-02180atam azerNo ratings yet
- PHOTOGATEDocument3 pagesPHOTOGATEIsmi HafsariNo ratings yet
- Experiment Manual 14thnov2011Document40 pagesExperiment Manual 14thnov2011Arpit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel PDFDocument4 pagesSolar Panel PDFRavinder SinghNo ratings yet
- BK Precision 1660Document48 pagesBK Precision 1660JabrokaNo ratings yet
- Charge Controller TopologyDocument23 pagesCharge Controller TopologyAbhilash MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- CISE 412 Mechatronics Lab ManualDocument46 pagesCISE 412 Mechatronics Lab ManualkarthisanNo ratings yet
- Nippon Pulse 2011 CatalogDocument98 pagesNippon Pulse 2011 CatalogElectromateNo ratings yet
- Ae Lab Ivsem EceDocument60 pagesAe Lab Ivsem EceNavneet KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Characterization and Measurement of Solar CellsDocument37 pagesElectrical Characterization and Measurement of Solar CellsTego Hadi PujiantoNo ratings yet
- Methods of Energy GenerationDocument20 pagesMethods of Energy GenerationSridhar PatilNo ratings yet
- Regular Paper Stand-Alone PV System Simulation For DG Applications, Part I: PV Module Modeling and Inverters Adel El ShahatDocument19 pagesRegular Paper Stand-Alone PV System Simulation For DG Applications, Part I: PV Module Modeling and Inverters Adel El Shahatyong_fanNo ratings yet
- NPTEL Solar Cells SlidesDocument147 pagesNPTEL Solar Cells SlidesMadhur MayankNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Electronics Devices & Circuits-II Lab ManualDocument35 pagesDepartment of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Electronics Devices & Circuits-II Lab ManualBhartendu goyalNo ratings yet
- Solar Battery Charging and Single Phase Supply System: 1) What Is A Solar Cell?Document14 pagesSolar Battery Charging and Single Phase Supply System: 1) What Is A Solar Cell?ayushhjaveriNo ratings yet
- How Can Electromagnets Be Used To Carry Out Switching Functions? EEP 6.4Document6 pagesHow Can Electromagnets Be Used To Carry Out Switching Functions? EEP 6.4ANGEL FIGUEROA DELGADONo ratings yet
- Power Management For Industrial PlantsDocument35 pagesPower Management For Industrial PlantsRavi GargNo ratings yet
- ULN2803A Darlington Transistor Arrays: Features DescriptionDocument14 pagesULN2803A Darlington Transistor Arrays: Features DescriptionJohn Joshua MontañezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Clearance in Substation Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument16 pagesElectrical Clearance in Substation Electrical Notes & Articles4usangeetNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabDocument15 pagesGovernment Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabTapobroto Chatterjee100% (1)
- Overview of Nuclear Power Reactor and Research ReactorDocument40 pagesOverview of Nuclear Power Reactor and Research ReactorRyan DagsilNo ratings yet
- ULN2803APG, ULN2803AFWG, ULN2804APG, ULN2804AFWG: 8ch Darlington Sink DriverDocument14 pagesULN2803APG, ULN2803AFWG, ULN2804APG, ULN2804AFWG: 8ch Darlington Sink DriverFelipe Ponce EspinosaNo ratings yet
- 1 Performance DataDocument9 pages1 Performance DataYusep KurniaNo ratings yet
- 1.fabrication of Steam Power PlantDocument25 pages1.fabrication of Steam Power PlantClement StephensonNo ratings yet
- Eead422 Transformer PPT UpdatedDocument190 pagesEead422 Transformer PPT UpdatedFrinz Mardie GañoNo ratings yet
- TP Sur Les Défauts Des Systèmes PVDocument9 pagesTP Sur Les Défauts Des Systèmes PVSamah Ali BenamaraNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument20 pagesBatterymohmmad1972100% (1)
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Fariba Besharat, Ali A. Dehghan, Ahmad R. FaghihDocument24 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Fariba Besharat, Ali A. Dehghan, Ahmad R. Faghihmohmmad1972No ratings yet
- Entropy: Statistical Vibroacoustics and Entropy ConceptDocument18 pagesEntropy: Statistical Vibroacoustics and Entropy Conceptmohmmad1972No ratings yet
- Chapter1 2Document16 pagesChapter1 2mohmmad1972No ratings yet
- KA Eco Project ListDocument2 pagesKA Eco Project Listprajwal tapaseNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Roads: Made By:-Muthuvel ROLL NO.:-18BCE8008 Civil EngineeringDocument12 pagesKinetic Roads: Made By:-Muthuvel ROLL NO.:-18BCE8008 Civil EngineeringMuthuvel44% (9)
- Summer Intern - ReportDocument23 pagesSummer Intern - Report08mpe026No ratings yet
- Vestas Wind, Solar, StorageDocument8 pagesVestas Wind, Solar, StorageTumzangwanaNo ratings yet
- 275W Poly CrystallineDocument2 pages275W Poly CrystallineGael Noé TjombNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas DA - ScholarsDocument36 pagesNatural Gas DA - ScholarsAffNeg.ComNo ratings yet
- EdL Statistic Yearbook 2018Document21 pagesEdL Statistic Yearbook 2018Huy Lê QuangNo ratings yet
- Icct2020 Assessment of Hydrogen Production Costs v1Document72 pagesIcct2020 Assessment of Hydrogen Production Costs v1Zakiah Darajat NurfajrinNo ratings yet
- Automatic Solar Tracker-2Document17 pagesAutomatic Solar Tracker-2ShahnawazNo ratings yet
- 1.11 Tidal Power Plants: - Extracting The Potential Energy of Tides Moving in Vertical Direction, KnownDocument3 pages1.11 Tidal Power Plants: - Extracting The Potential Energy of Tides Moving in Vertical Direction, KnownbehroozNo ratings yet
- Renewable - Energy - SourcesDocument12 pagesRenewable - Energy - SourcesErRajeshNo ratings yet
- Prithvi P (1oq17at037) Green Building DesignDocument3 pagesPrithvi P (1oq17at037) Green Building Designprithvi5p5gowdaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Application in TextilesDocument4 pagesSolar Energy Application in TextilesShruti KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Solar Project REPORTDocument15 pagesSolar Project REPORTismailNo ratings yet
- Thesis Sander MeppelinkDocument99 pagesThesis Sander Meppelinkamith100% (1)
- ICASolar PV On Grid BookDocument7 pagesICASolar PV On Grid BooktemonsoejadiNo ratings yet
- ALMMDocument16 pagesALMMJigar PatelNo ratings yet
- Energie Wende Future Cost of Onshore WindDocument38 pagesEnergie Wende Future Cost of Onshore WindJeferson Tondo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Wind Farms Tulcea South PresentationDocument11 pagesWind Farms Tulcea South PresentationAndrei PavelNo ratings yet
- WIP TechnicalDocument3 pagesWIP TechnicalSuehNo ratings yet
- HSPE-144M M6 HC Bifacial 450W Rev.00Document2 pagesHSPE-144M M6 HC Bifacial 450W Rev.00Alejandro Holguin QuinteroNo ratings yet
- 2 TTTGDocument2 pages2 TTTGAbebawBelayNo ratings yet
- Updates On The Geothermal Energy Development in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesUpdates On The Geothermal Energy Development in The PhilippinesHarold SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Application For Qualified End-User (Qe) - Coc: Energy Regulatory CommissionDocument2 pagesApplication For Qualified End-User (Qe) - Coc: Energy Regulatory Commissionmaykee01No ratings yet
- State - Wise Solar Installed Capacity Break-UpDocument60 pagesState - Wise Solar Installed Capacity Break-UpPratik PrakashNo ratings yet
- 23.solar EnergyDocument7 pages23.solar EnergymariyaNo ratings yet
- BritCham Vietnam Renewable Energy Sector Briefing 2021Document14 pagesBritCham Vietnam Renewable Energy Sector Briefing 2021Tran VINo ratings yet
- Resume - Sanket D MankarDocument2 pagesResume - Sanket D MankariyergvNo ratings yet
- Mokenergy Brochure 2Document4 pagesMokenergy Brochure 2William MookNo ratings yet