Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Formulary - 2013
Drug Formulary - 2013
Uploaded by
Sunil Basnet0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views16 pagesdrug
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdrug
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views16 pagesDrug Formulary - 2013
Drug Formulary - 2013
Uploaded by
Sunil Basnetdrug
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
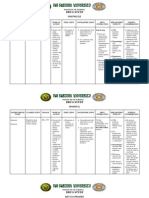
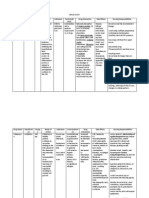
ANTIBIOTICS FOR UTI
Drug Name Brand Name Mechanism of action Adverse Effects
Ceftriaxone
(Cephalosporin)
Acrexon Bactericidal activity result from
inhibiting cell wall synthesis by
binding to one or more penicillin
binding proteins
Shock. Hypersensitivity.
Blood abnormality. Liver &
Kidney failure. GI &
Respiratory disturbances.
Superinfection. Vitamin
deficiency.
Cefotaxime
(Third-
generation
cephalosporins)
2 World
Cefotaxime
Cephalosporins bind to PBPs on
bacterial cell membranes to
inhibit bacterial cell wall
synthesis by mechanisms similar
to those of the penicillins.
Cephalosporins are bactericidal
against susceptible organisms.
Pain at IM injection sites
and phlebitis after IV
administration.
Gentamicin
(Aminoglycoside)
Genom Interferes with bacterial protein
synthesis by binding to 30s and
50s ribosomal subunits
Increased BUN, NPN,
serum creatinine, or
oliguria. Neurotoxicity.
Ampicillin
(Penicillin)
Ampinex Interferes with bacterial cell wall
synthesis during active
replication, causing a
bactericidal activity against
susceptible organisms
Skin rashes (urticarial or
maculopapular). Diarrhea.
n/v. pseudomembranous
colitis.
Amoxicillin and Addex Amoxicillin inhibits bacterial Diarrhea. n/v. Skin rash.
Clavunate
(Penicillin)
cell wall synthesis by binding to
penicillin-binding proteins
Clavunate inhibits beta
lactamase producing bacteria
Urticarial. Vaginitis. Rarely,
pseudomembranous
enterocolitis, stomatitis &
candidiasis, erythema
multiforme, & other skin
effects. Hepatic, renal,
hematologic, or CNS
effects.
Sulfamethoxazole
and
Trimethoprim
(Antibacterial
combination)
Bactrinol TMP: inhibits dihydrofolate
reductase
SMX: competes with para-
aminobenzoic acid
GI disturbances. Skin
reactions.
Cefalexin
(Cephalosporin)
Airex By binding to 1 or more
penicillin-binding proteins, it
arrest bacterial cell wall
synthesis and inhibits bacterial
growth
GI discomfort. Diarrhea.
Skin rashes. Urticarial.
Eosinophilia. Angioedema.
Anaphylaxis.
Cefixime
(Cephalosporin)
Actimax By binding to 1 or more
penicillin-binding proteins, it
arrest bacterial cell wall
synthesis and inhibits bacterial
growth
Diarrhea. Stool changes.
N/V. Abdominal pain.
Dyspepsia. Vomiting.
Flatulence.
Pseudomembranous
colitis. Headache.
Dizziness. Rash. Pruritus.
Urticaria. Drug fever.
Arthralgia.
Thrombocytopenia.
Leukopenia. Eosinophilia.
Cefpodoxime Cefadox Inhibits cell wall synthesis Chest pain. Hypotension.
Fungal skin infection. Skin
scaling/peeling. Menstrual
irregularity. Pruritus.
Diarrhea. Flatulence.
Decreased salivation.
Candidiasis.
Pseudomembranous
colitis. Anaphylactic shock.
Decreased appetite.
Dizziness. Fatigue.
Anxiety. Insomnia.
Flushing. Nightmares.
Weakness. Cough.
Epistaxis. Taste alteration.
Eye itching. Tinnitus.
Malaise. Fever.
Nitrofurantoin
(urinary
antiseptic)
Macrodantin Synthetic nitrofurantoin that
interferes with bacterial
carbohydrate metabolism by
inhibiting acetylcoenzyme A.
Nausea. Emesis. Anorexia.
Abdominal pain. Diarrhea.
Pulmonary hypersensitivity
reaction. Peripheral
Bacteriostatic at low
concentration (5-10 mcg/ml)
and is bactericidal at higher
concentration.
neuropathy. Exfoliative
dermatitis. Erythema
multiforme. Lupus-like
syndrome. Urticaria. Rash.
Agranulocytosis.
Leukopenia.
Granulocytopenia.
Ciprofloxacin
(Quinolone)
Baxolyn. Fluoroquinolone that inhibit
bacterial DNA synthesis and
consequently, growth by
inhibiting DNA gyrase and
topoisomerases, which are
required for replication,
transcription, and translation of
genetic materials. Promotes
breakage of double stranded
DNA
Nausea. Diarrhea.
Vomiting. Abdominal pain.
Flatulence. Anorexia.
Dizziness. Headache.
Tiredness. Agitation.
Trembling. Skin rashes.
Pruritus. Drug fever. Joint
pains. Photosensitivity.
Transient renal
impairment. SJS. Lyell
syndrome.
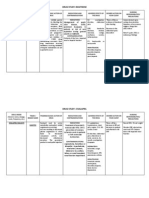
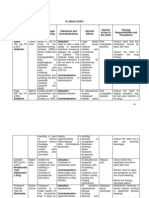
ANTI-TB DRUGS
Drug Name Brand Name Mechanism of action Adverse Effects
Isoniazid Rifater,
Rifamate
Blocks mycolic acid synthesis Immunologic: fever, rash,
SLE
Peripheral neuropathy,
hepatitis, CNS toxicity,
jaundice, psychosis
Rifampicin Rifater,
Rifamate
Inhibit RNA synthesis by binding
to the B subunit of DNA
dependent RNA polymerase of M.
TB
Causes light chain
proteinuria, impair
antibody response, skin
rash, thrombocytopenia,
nephritis, liver
dynsfunction, jaundice,
flu-like syndrome, anemia,
orange discoloration of
body fluids, oliguria,
albuminuria, convulsion
Pyrazinamide Rifater UNKNOWN Non-gouty polyathralgia,
hyperuricemia, drug fever,
jaundice
Ethambutol Myambutol Inhibit mycobacterial arabinosyl
transferase
Optic neuritis, retinal
damage, peripheral
neuropathy, confusion,
headache
Streptomycin Irreversible inhibitors of protein
synthesis; binds to 30S subunit
Fever, rash, vertigo, loss of
balance, nephrotoxic,
ototoxic, oliguria,
albuminuria
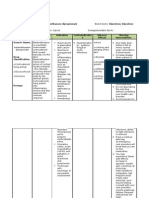
DRUGS USED IN ANGINA
Drug Name Brand Name Mechanism of Action Adverse Effect
Nitroglycerine
(Nitrate)
Nitrostat Vasodilation
of the venous
capacitance vessels by stimulating
the endothelium-derived relaxing
factor (EDRF)
orthostatic hypotension
headache (30-60%)
tachycardia
glaucoma
Metoprolol
(Beta Blocker)
Lopressor Competes with the adrenergic
neurotransmitter for binding of
beta adrenergic receptor in the
heart
contraindicated in asthma,
diabetes, COPD, severe AV
block, bradycardia-
tachycardia syndrome,
severe heart failure
abrupt discontinuation
lead to rebound
Verapamil Isoptin SR prevent entry of calcium into Flushing
(Calcium
Channel
Blocker)
cardiac and smooth muscle; dilate
the coronary and peripheral
arteries and have negative
inotropic and chronotropic effects
Hypotension
Headache
peripheral edema
constipation
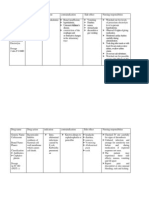
ANTI-HISTAMINES
Drug Name Brand Name Mechanism of action Adverse Effects
(Old 1
st
Gen.
Histamine H1
Antagonist)
Diphenhydramine
Benadril
H1 blockers are competitive
pharmacologic antagonists at the
H1 receptor; these drugs have no
effect on histamine release from
storage sites.
CV & CNS effects. Blood
disorders. GI
disturbances.
Antimuscarinic effects.
Allergic reactions.
(New 1
st
Gen. Sedation. Lassitude.
Histamine H1
Antagonist)
Chlorpheniramine
Antamin
Elation or Depression.
Irritability. Paranoid
psychosis. Delusion.
Hallucination. Muscular
weakness.
Incoordination. GIT
disturbances. Headache.
Tinnitus. Difficulty in
micturition. CV effects.
Allergic reactions.
(2
nd
Gen.
Histamine H1
Antagonists)
Cetirizine
Fexofenadine
Loratadine
Ceritec
Fexodine
Claritin
Agitation. Dry mouth.
Headache.
Hypersensitivity
reactions.
Occasionally GI effects
including n/v, diarrhea or
epigastric pain.
Palpitation, ventricular
arrhythmia.
Fatigue. Headache.
Somnolence. Dry mouth.
Rash. GI disorders like
nausea, gastritis.
(Histamine H2
Antagonists)
Cimetidine
Ranitidine
Famotidine
Tagamet
Ranifin
H2 Bloc
H2 antagonists produce a
surmountable pharmacologic
blockade of histamine H2
receptors. They are relatively
selective and have no significant
blocking actions at H1 or
autonomic receptors.
Mild & transient diarrhea.
Tiredness. Dizziness.
Severe & reversible
alopecia. Skin rash.
Reversible gynecomastia.
Decreased white cell
count. Agranulocytosis.
Thrombocytopenia.
Leukopenia. Increases in
plasma creatinine &
serum transaminase
levels. Reversible
confusion in elderly.
Headache. Dizziness.
Myalgia.
Diarrhea & other GI
disturbances. Dizziness.
Tiredness. Headache.
Rashes.
Headache. Anorexia. Dry
mouth. N/V.
Constipation. Diarrhea.
ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE AGENTS
Drug Name Brand Name Mechanism of action Adverse Effects
Propranolol
(Beta Blocker)
Inderal Competes with the adrenergic
neurotransmitter for binding of
beta adrenergic receptor in the
heart
Bradycardia, cardiac
failure, hypotension
Verapamil
(Calcium
Channel
blocker)
Isoptin SR Inhibits slow inward calcium
current responsible for sinus and
AV nodal depolarization
Headache, confusion
Losartan
(Angiotensin
Receptor
Blocker)
Cozaar Blocks binding of angiotensin II to
type I receptors. Blocks the
vasoconstrictor and aldosterone
secreting effects of angiotensin II
Fatigue, hypoglycemia,
chest pain
Captopril
( ACE
Inhibitors)
Capoten Prevents convertion of angiotensin I
to angiotensin II through inhibition
of ACE by competing with
physiologic subsrate for active site
of ACE,
hyperkalemia
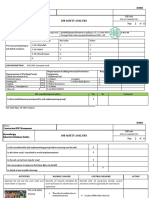
DRUGS USED IN ACID PEPTIC DISEASE
Drug Name Brand Name Mechanism of Action Adverse Effects
Sodium
bicarbonate
(Antacids)
Neut Neutralization of hydrochloric acid
by forming sodium chloride and
carbon dioxide
Rebound hyperacidity
Milk-alkali syndrome
Magnesium-
aluminum
hydroxide
(Antacids)
Gaviscon Neutralization of hydrochloric acid
by forming magnesium or
aluminum chloride and water
Nausea
Constipation
Diarrhea
Ranitidine
(H2 blocker)
Zantac Competitively inhibits gastric acid
secretion by blocking the effect of
histamine on H2 receptors
Headache
Abdominal pain
Constipation
Omeprazole
(Proton pump
inhibitor)
Losec Blocks the final step of acid
production by inhibiting the
H+/K+ ATPase system at the
secretory surface of the gastric
parietal cell
Headache
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Clarithromycin
(Antibiotics)
Biaxin Acts by binding to the 50S
ribosomal subunit of susceptible
organisms
Diarrhea
Abdominal pain
Nausea
Amoxicillin
(Antibiotics)
Amoxil Binds to penicillin-binding proteins
and inhibit cell wall synthesis
Nausea
Vomiting
Gastritis
Stomatitis
Metronidazole
(Antibiotics)
Flagyl Binds to DNA, resulting in loss of
helical structure, strand breakage,
inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
and cell death
Headache
Vaginitis
Nausea
DRUGS USED IN DIABETES
Drug Name Brand Name Mechanism of Action Adverse Effects
Metformin
(Biguanide)
Glucophage Decreased hepatic glucose
production
Hypoglycemia
Lactic acidosis
Diarrhea
Glipizide
(Sulfonylurea)
Glucotrol Lowers blood glucose by
stimulating the release of insulin
Hypoglycemia
Headache
Dizziness
Repaglinide
(Meglitinides)
Prandin Lowers blood glucose by
stimulating release of insulin from
the pancreas
Hypoglycemia
Headache
Nausea
Rositiglitazon
e
(Thiazolidine
diones)
Avandia Improves blood glucose levels by
improving insulin sensitivity in DM2
Headache
Edema
Back pain
Pioglitazone Actos Decreases insulin resistance in the
periphery and liver resulting in
increased insulin-dependent
glucose disposal and decreased
hepatic glucose output
Hypoglycemia
URTI
Headache
Acarbose
(Alpha-
glucosidase
inhibitor)
Precise Causes a competitive, reversible
inhibition of pancreatic alpha
amylase and membrane-bound
intestinal alpha-glucosidase
hydrolase enzymes
Flatulence
Diarrhea
Abdominal pain
Rapid-acting: Lispro
(Humalog), aspart
(Novolog), glulisine
Short-acting: Regular
(Semilente)
Intermediate-acting: NPH
(Lente)
Long-acting: Detemir,
glargine (Lantus)
(Insulin)
Activates insulin receptors thereby
reducing circulating glucose
Hypoglycemia
Hypokalemia
Injection site reaction
Lipodystrophy
Pruritus
Rash
Exenatid
e
(Incretin
-based
drugs)
Byetta Enhances glucose-dependent
insulin secretion by pancreatic
beta-cells, suppresses
inappropriately elevated glucagon
secretion, and slows gastric
Nausea
Vomiting
Headache
emptying
Pramlinti
de
(Amylin
analog)
Symlin Modulation of gastric emptying,
prevention of the postprandial rise
in plasma glucagon, satiety leading
to decrease caloric intake and
potential weight loss
Hypoglycemia
Headache
Nausea
You might also like
- TL Design Manual - Rev0.5Document64 pagesTL Design Manual - Rev0.5Syed Ahsan Ali Sherazi100% (2)
- Love Sewing - Issue 125 2023 Sanet - STDocument84 pagesLove Sewing - Issue 125 2023 Sanet - STNyi Nyi AungNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Ceftriaxone)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Ceftriaxone)Keij Araneta93% (15)
- Dumper Cycle Time Transport Digging Capacity CalculationDocument10 pagesDumper Cycle Time Transport Digging Capacity Calculationuttamksr100% (3)
- Drug Study - HRZEDocument4 pagesDrug Study - HRZEEunice Ordonez67% (3)
- Drug Study: OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Omeprazoleclau_latojaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyBheiatriz de VeraNo ratings yet
- Design of Biaxial ColumnDocument1 pageDesign of Biaxial Columnnishusaini0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJann Zaniel Allayne RiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cap RHPDocument7 pagesDrug Study Cap RHPJan DeeNo ratings yet
- Pharma Sheet1Document7 pagesPharma Sheet1Lyssa ShannenNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole Cefalexin: Therapeutic IndexDocument6 pagesMetronidazole Cefalexin: Therapeutic IndexBo ChoiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study... MyomaDocument12 pagesDrug Study... MyomaChristine Joy Bautista- CastroNo ratings yet
- WarfarinDocument10 pagesWarfarinMar Ordanza100% (1)
- Drug Study DengueDocument3 pagesDrug Study DengueiamELHIZANo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Indications For Ferrous Sulfate: Mechanism of ActionDocument4 pagesIndications For Ferrous Sulfate: Mechanism of ActionErelle John Vasquez EscaraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBij Hilario100% (1)
- Drug Study 2Document9 pagesDrug Study 2Justin PasaronNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Drug STUDY CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug STUDY CefotaximeJeffrey Calicdan Bucala75% (8)
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument30 pagesDrug Study Template2230299No ratings yet
- Jam (Drug Study)Document11 pagesJam (Drug Study)Vincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2roxybabesNo ratings yet
- Drug and NCPDocument15 pagesDrug and NCPgeelawlietNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Drug-Study PharmacologyDocument11 pagesDrug-Study PharmacologyEmmanuel CaracalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyjeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- Drug 1Document5 pagesDrug 1Jesamine MayNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsVal Ian Palmes SumampongNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Ma. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesMa. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesTricia_De_Leon_6494No ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Drug To Drug Interaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Drug To Drug Interaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesSkyerexNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 pagesDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5No ratings yet
- Drugstudy Omeprazole and Pen GDocument3 pagesDrugstudy Omeprazole and Pen GGil Joseph GodoyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudytrinaLCNo ratings yet
- Cagalingan DrugsDocument2 pagesCagalingan Drugscherocus8No ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ceftriaxone Brand Name: (Kept Rix) IV, 1g, q12Document5 pagesGeneric Name: Ceftriaxone Brand Name: (Kept Rix) IV, 1g, q12De Sesto Rhys CarloNo ratings yet
- Nicu Drug StudyDocument8 pagesNicu Drug StudyMike SoySauce LibrojoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Hepatitis: Dr.M.Sharmila Assistant Professor M7 (Prof CR Unit) Institute of Internal MedicineDocument21 pagesDrug Induced Hepatitis: Dr.M.Sharmila Assistant Professor M7 (Prof CR Unit) Institute of Internal MedicineAtakan Yeşil100% (1)
- Unit 06: Drugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument9 pagesUnit 06: Drugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal SystemDental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy For ElderlyDocument14 pagesDrugstudy For ElderlyJenniferP.BarrosoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRye IbarraNo ratings yet
- Sample - Drug Index DatabaseDocument12 pagesSample - Drug Index DatabaseEubert John VenturinaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyEdward Baes33% (3)
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMike Faustino SolangonNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal PharmacologyDocument18 pagesMusculoskeletal PharmacologyBLEEMAGE100% (2)
- MedicationsDocument11 pagesMedicationsHussein MohsenNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument4 pagesGeneric Namejustin biscochoNo ratings yet
- Side Effects of AmoxicillinDocument4 pagesSide Effects of AmoxicillinAphro DhiteNo ratings yet
- A.1. Community-Acquired: Use Antibiotics JudiciouslyDocument33 pagesA.1. Community-Acquired: Use Antibiotics JudiciouslymaxgroovesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- 5 - Drugs Used For Treatment of Gout EditedDocument35 pages5 - Drugs Used For Treatment of Gout EditedSakariye hasanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyMäc LäntinNo ratings yet
- Assignment Society (T)Document5 pagesAssignment Society (T)Noor FatihahNo ratings yet
- Countrys ClimateDocument20 pagesCountrys ClimateErika Jayne100% (1)
- Simulator TutorialsDocument29 pagesSimulator TutorialstmadamolekunNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledBrenda M. Martínez GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Cern Zechariah 11 and The Mysterious Stranger No 44 I1 PDFDocument38 pagesCern Zechariah 11 and The Mysterious Stranger No 44 I1 PDFVincit Omnia Veritas100% (1)
- Worksheet CH 7 Metamorphic Rocks MarshakDocument2 pagesWorksheet CH 7 Metamorphic Rocks MarshakTaylorNo ratings yet
- Train Resistance CalculationsDocument6 pagesTrain Resistance Calculationssalkan_rahmanovic810No ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document22 pagesChapter 19Tawhid Ahmed sifatNo ratings yet
- Thyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions (India) Job Safety Analysis 1 6Document6 pagesThyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions (India) Job Safety Analysis 1 6Nitesh kumar yadavNo ratings yet
- Vol6 No.2-11Document10 pagesVol6 No.2-11SahrulRashidNo ratings yet
- 2 Quarter: Understanding OverexertionDocument15 pages2 Quarter: Understanding OverexertionJhon Keneth NamiasNo ratings yet
- Gear Hobbers, Kashifuji, CNC Gear Hobbing Machines, CNC Gear Griinding Machines, Gear FinishersDocument7 pagesGear Hobbers, Kashifuji, CNC Gear Hobbing Machines, CNC Gear Griinding Machines, Gear FinishersinvolutegearNo ratings yet
- Funambulist - Rouzbeh Akhbari & Felix KalmensonDocument3 pagesFunambulist - Rouzbeh Akhbari & Felix Kalmensonfelixkalm01No ratings yet
- Specification For The Book ScannerDocument2 pagesSpecification For The Book ScannerH L S ChandrajithNo ratings yet
- Earth Systems: Cryosphere: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIADocument12 pagesEarth Systems: Cryosphere: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIAMangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Interim Budget 2014-15 - Key Highlights From P Chidambaram's Speech - Business TodayDocument2 pagesInterim Budget 2014-15 - Key Highlights From P Chidambaram's Speech - Business TodayAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Robert Rosen How Are Organisms DifferentDocument17 pagesRobert Rosen How Are Organisms Differentcrdewitt100% (1)
- 40 Cau Part 5 Kem Loi Giai Chi TietDocument14 pages40 Cau Part 5 Kem Loi Giai Chi TietTrần DũngNo ratings yet
- Strategic Methods For Talaash Who Only A Few Know About.20121210.184809Document2 pagesStrategic Methods For Talaash Who Only A Few Know About.20121210.184809anon_378198209No ratings yet
- Frank S. Wolski: Schuck & Sons Construction Company - Glensdale, AzDocument3 pagesFrank S. Wolski: Schuck & Sons Construction Company - Glensdale, AzAbrar_AshrafNo ratings yet
- L30-L132 RSDocument8 pagesL30-L132 RSMaulana FathanyNo ratings yet
- Vie Lat Training CentreDocument19 pagesVie Lat Training CentreManny ManNo ratings yet
- Small Miracles: Today YOU WILL..Document2 pagesSmall Miracles: Today YOU WILL..Гоар МкртичянNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document19 pagesGroup 3Fredimar CondeNo ratings yet
- POLS235 Exam 1Document6 pagesPOLS235 Exam 1defran 262No ratings yet
- Inoculum Development For Industrial Fermentation PDFDocument15 pagesInoculum Development For Industrial Fermentation PDFSabarishNo ratings yet