Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EM Induction Summary
EM Induction Summary
Uploaded by
Voyce Xavier PehCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EM Induction Summary
EM Induction Summary
Uploaded by
Voyce Xavier PehCopyright:
Available Formats
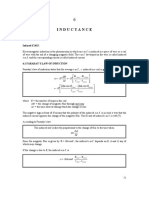
The laws of electromagnetic induction
Faradays law
The magnitude of the induced electromotive force is directly proportional to
the rate of change of flux linkage or the rate of flux cutting
Induced e.m.f, | E |
dt
d
where is the flux linkage
E = -
dt
d
The minus in the equation indicates the direction of the induced e.m.f. opposes
the change of flux linkage. (Lenzs Law)
For certain Calculations, Faradays law is expressed as
E =
t
, where change :
For cutting of flux by a metal rod,
E = BLv
Lenzs law
Lenz's law states that the direction of the induced current is such as to
produce an effect that opposes the change of the magnetic flux that
gives rise to it.
The minus sign in the equation E = -
dt
d
(N) expresses the Lenzs law.
Lenzs law is an example of the principle of the conservation of energy.
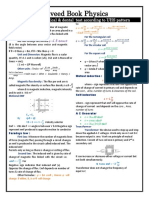
Magnetic flux and the weber Wb
The magnetic flux through a small plane surface is defined as the product
of the magnetic flux density normal to the area and the area of the surface.
) A )( cos B ( =
or ) A )( sin B ( =
Magnetic flux linkage ()
If a coil of N turns and area A is placed in a magnetic field of flux density B with
its axis along the field, the total flux, known as flux linkage, is given by
= N
= N B A cos , where N: Number of turns of the coil
B
B cos
B sin
Normal
Faradays Law of EMI: E =
t
E =
t
cos NBA
: N : B : A : ) (cos
E =
t
N ) cos BA (
E=
t
B ) cos NA (
E=
t
A ) cos NB (
E=
t
) (cos ) NBA (
S N
t/s
/Wb
E/V
t/s
B (into page)
v
/Wb
t/s
E/V
t/s
To induce emf, the numerator
cannot be zero, hence at least one
of the four quantities (N, B, A, )
must be a variable.
Removing the
coil out of the
B-Field, i.e.
B
f
= 0
Force Force
Exerting a force
on two ends of
the coil, thus
reducing the
number of turns
of the coil, N.
Electromagnetic Induction
Eddy Current Small, circulating, unwanted currents generated by a magnetically induced electromotive
force in a closed conductive path, such as a large metal plate, resulting in a waste of energy.
If a large metal plate is moved through a magnetic field which intersects perpendicularly to the sheet, the
magnetic field will induce small circulating current which will actually create internal magnetic fields
opposing the change, thus slowing the object down. (Lenzs Law)
In effect, the kinetic energy will go into driving small currents inside the metal which will give off that energy
as heat as they push through the metal.
N S
Bar
magnet
B (into page)
www.TopPhysicsTuition.com
Hp: 9620 7426 / Mr Tan Kheng Siang
You might also like
- Electromagnetic Induction 2nd Year PhysicsDocument82 pagesElectromagnetic Induction 2nd Year PhysicsWafa Zainab67% (3)
- Manual Book Microscope CX22 LEDDocument28 pagesManual Book Microscope CX22 LEDtomatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Lecture Notes: FormulasDocument13 pagesChapter 21 Lecture Notes: Formulasapi-3710134No ratings yet
- Chapter17 Electromagnetic Induction STPM PhsyicsDocument15 pagesChapter17 Electromagnetic Induction STPM PhsyicsSurianathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Electromagnetic Induction For SharingDocument42 pagesChapter 4 - Electromagnetic Induction For SharingTrisha Mae PerezNo ratings yet
- 4 1 Formulae Electromagnetic InductionDocument6 pages4 1 Formulae Electromagnetic InductionNathanianNo ratings yet
- (Y&F Chapters 30, 31 Ohanian Chapter 32) : Electromagnetic InductionDocument10 pages(Y&F Chapters 30, 31 Ohanian Chapter 32) : Electromagnetic InductionShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical MachinesDocument63 pagesIntroduction To Electrical MachinessureshNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 13 and 14 Notes (1) - 1Document8 pagesLecture - 13 and 14 Notes (1) - 1Irene NziluNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction and WavestheoryDocument26 pagesElectromagnetic Induction and WavestheoryShivani GautamNo ratings yet
- Key Concept in Magnetic FluxDocument25 pagesKey Concept in Magnetic FluxmvmbappleNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic InductionMAHESH DNo ratings yet
- Electromanetic Induction Points To Remember: ElectromagneticsDocument8 pagesElectromanetic Induction Points To Remember: ElectromagneticsMAHESH DNo ratings yet
- 6 - InductanceDocument10 pages6 - InductanceRichie BobbyNo ratings yet
- E 59 Kbro 1 JHWPPD 4 XdvraDocument16 pagesE 59 Kbro 1 JHWPPD 4 XdvraNitinNo ratings yet
- Faraday'S LAW: Emf Ve - D /DT ... (Xii)Document4 pagesFaraday'S LAW: Emf Ve - D /DT ... (Xii)ekta39No ratings yet
- Emi NotesDocument30 pagesEmi NotesAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- Faradays Law of InductionDocument9 pagesFaradays Law of InductionaaaaNo ratings yet
- Induction PowerpointDocument48 pagesInduction PowerpointIsaac DunkleyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic InductionPranshu PatelNo ratings yet
- HET316 L11 Time Vaying B FieldsDocument41 pagesHET316 L11 Time Vaying B FieldsMohammed ZainNo ratings yet
- Chapter30 Induction and InductanceDocument46 pagesChapter30 Induction and InductanceAshish ParasharNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday's Law of InductionDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Faraday's Law of InductionDisha KatariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Maxwell's Equations Electromagnetic WavesDocument15 pagesChapter 34 Maxwell's Equations Electromagnetic WavesAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Unit 4 - Electromagnetic Induction NotesDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Unit 4 - Electromagnetic Induction NotesAaron KebedeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Document27 pagesLecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Mircea PanteaNo ratings yet
- Handout 10Document6 pagesHandout 10Prabhakar KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Document27 pagesLecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Mircea PanteaNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - PHY121 - Magnetic Field - InductionDocument8 pagesCh4 - PHY121 - Magnetic Field - Inductionrhrazz6No ratings yet
- Module 21: Faraday's Law of InductionDocument32 pagesModule 21: Faraday's Law of InductionMuhammad FayazNo ratings yet
- 23 - EmiDocument16 pages23 - EmiPratima MondalNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction CH6Document18 pagesElectromagnetic Induction CH6Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- 51 Ch29 InductionDocument37 pages51 Ch29 InductionKesalan TerasaNo ratings yet
- FARADAYDocument6 pagesFARADAYoseisilasyawNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 28Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 28harshanauocNo ratings yet
- HW10Document18 pagesHW10Vinay Aanand AanandNo ratings yet
- FaradayDocument3 pagesFaradaymadhavNo ratings yet
- Notes For Chapter 20Document28 pagesNotes For Chapter 20edsoneiccNo ratings yet
- p112 Lecture13 PDFDocument20 pagesp112 Lecture13 PDFGauravNo ratings yet
- 1 Electromagnetic InductionDocument20 pages1 Electromagnetic InductionRizan SaopNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11: Faraday's Law of InductionDocument3 pagesExperiment 11: Faraday's Law of InductionGabriel DavidNo ratings yet
- Magnetic CircuitDocument29 pagesMagnetic Circuitsujalshirke1904No ratings yet
- L2 2 Maxwell EquationsDocument37 pagesL2 2 Maxwell Equationskwaleed717No ratings yet
- 20-21 Electromagnetism and Induced EMFDocument19 pages20-21 Electromagnetism and Induced EMFkw2533No ratings yet
- Mid Term Exam: Fall Term 2002 Introduction To Plasma Physics I 22.611J, 6.651J, 8.613JDocument3 pagesMid Term Exam: Fall Term 2002 Introduction To Plasma Physics I 22.611J, 6.651J, 8.613JmkpsrtmNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 1 Induced Electromotive ForceDocument32 pagesTopic 12 1 Induced Electromotive ForceAli Qasim0% (1)
- Lne13 PDFDocument18 pagesLne13 PDFSahasrajit SarmasarkarNo ratings yet
- Induction Motors Part ADocument88 pagesInduction Motors Part AArpit PatelNo ratings yet
- 6 Electromagnetic InductionDocument4 pages6 Electromagnetic InductionRajender ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument106 pagesElectromagnetic InductiondynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Notes For Lecture #16: Electromagnetic Waves and ConductorsDocument8 pagesNotes For Lecture #16: Electromagnetic Waves and ConductorsJoanna Modupeh HodasiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Document36 pagesLecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Mircea PanteaNo ratings yet
- Lecture19 Faraday's Law Induction Lenz's Law Generators Motional EmfDocument76 pagesLecture19 Faraday's Law Induction Lenz's Law Generators Motional EmfTaqi ShahNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptDocument56 pagesBasic ConceptHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- Time Vaying FieldsDocument16 pagesTime Vaying FieldsPuneeth SiddappaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction by Naveed BalouchDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Induction by Naveed BalouchHafiz AbdulRehman100% (1)
- AnswerDocument1 pageAnswerPM GBERNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction and Motional EMFDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic Induction and Motional EMF140557No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Basic 2 - 2012/13 Writing Task 1 Personal InfoDocument2 pagesBasic 2 - 2012/13 Writing Task 1 Personal InfoJulio Alvarez SNo ratings yet
- LISTENING: Second Family Jessica Talks About Her Host Family in SpainDocument1 pageLISTENING: Second Family Jessica Talks About Her Host Family in SpainJulio Alvarez SNo ratings yet
- Speaing Interaction Going RestaurantDocument1 pageSpeaing Interaction Going RestaurantJulio Alvarez SNo ratings yet
- PostcardsDocument4 pagesPostcardsJulio Alvarez SNo ratings yet
- Talking About Your School DaysDocument2 pagesTalking About Your School DaysJulio Alvarez SNo ratings yet
- Task 1 (Monologue) : Daily Routine: Read The Following Information and Talk About The Subject For Two MinutesDocument1 pageTask 1 (Monologue) : Daily Routine: Read The Following Information and Talk About The Subject For Two MinutesJulio Alvarez SNo ratings yet
- Job and Work DialogueDocument2 pagesJob and Work DialogueJulio Alvarez S100% (1)
- In On atDocument1 pageIn On atJulio Alvarez SNo ratings yet
- Beer's Law - Why Absorbance Depends (Almost) Linearly On ConcentrationDocument5 pagesBeer's Law - Why Absorbance Depends (Almost) Linearly On ConcentrationViệt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Compilation Physics TestbanksDocument21 pagesCompilation Physics Testbankschristine geronimoNo ratings yet
- Holophane Module 600 Series Brochure 12-74Document12 pagesHolophane Module 600 Series Brochure 12-74Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1 MICROSDocument9 pagesLab Exercise 1 MICROSCrizzajen IsipNo ratings yet
- III. Choose The Letter(s) of The BEST ANSWER. Write Your Answers On A Separate Sheet of PaperDocument2 pagesIII. Choose The Letter(s) of The BEST ANSWER. Write Your Answers On A Separate Sheet of PaperJoewen Vicente AnarconNo ratings yet
- BITS Edu Campus - Varnama Engineering Electromagnetics (2151002) Tutorial No. 4Document2 pagesBITS Edu Campus - Varnama Engineering Electromagnetics (2151002) Tutorial No. 4everlovingmansiNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 11: Moment of Inertia (Steiner's Theorem) : ApparatusDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT 11: Moment of Inertia (Steiner's Theorem) : ApparatusSuraj ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PDFDocument11 pagesModule 3 PDFVincee SamsonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7: Uniform Circular Motion: PurposeDocument4 pagesExperiment 7: Uniform Circular Motion: PurposeDeadly ChillerNo ratings yet
- Agfa Beginners Book IIDocument35 pagesAgfa Beginners Book IIGabriel Ma del CaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers (EMATs) UTDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Acoustic Transducers (EMATs) UTMomo ItachiNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticDocument2 pagesElectrostaticAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Lab EquipmentDocument23 pagesLesson 2 Lab EquipmentMarvin De JonggoyNo ratings yet
- 6mm KBT 140Document2 pages6mm KBT 140TBaenasNo ratings yet
- NEET - 2018: Physics - Set - QQ Date of Exam - 6 May, 2018Document17 pagesNEET - 2018: Physics - Set - QQ Date of Exam - 6 May, 2018vivek kumarNo ratings yet
- Olympus BHM BH 2 BrochureDocument32 pagesOlympus BHM BH 2 Brochurevyhtran4731No ratings yet
- Vibration-Rotation Spectrum of Co: Rice University Physics 332Document10 pagesVibration-Rotation Spectrum of Co: Rice University Physics 332Bishnu RakshitNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - 2.1 Waves and Particle Nature of Light - Edexcel IAL Physics A-LevelDocument77 pagesFlashcards - 2.1 Waves and Particle Nature of Light - Edexcel IAL Physics A-LevelMelody NationNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Testing Program EOC Physics Sample Items Goal 3Document8 pagesNorth Carolina Testing Program EOC Physics Sample Items Goal 3faithinhim7515No ratings yet
- Ring Laser Gyroscopes: Sagnac EffectDocument11 pagesRing Laser Gyroscopes: Sagnac EffectSELVAKUMAR RNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: 18.1 Electric ChargeDocument19 pagesElectrostatics: 18.1 Electric ChargeManishKumarNo ratings yet
- Keratometer PDFDocument3 pagesKeratometer PDFDanielle SangalangNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion 1Document1 pageCircular Motion 1Sunaree M. Chinnarat0% (1)
- Tutorial Raya Haji PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial Raya Haji PDFLuqman BenNo ratings yet
- Sriharsha KarumuriDocument12 pagesSriharsha KarumuriAn DangNo ratings yet
- Review Notes For SLRC-GenSan For RevieweesDocument54 pagesReview Notes For SLRC-GenSan For RevieweesMelcon S. Lapina100% (5)
- Microwave - Pathloss IV TrainingDocument3 pagesMicrowave - Pathloss IV TrainingbantunnaNo ratings yet
- New Syllabus - B.sc. PhysicsDocument39 pagesNew Syllabus - B.sc. PhysicsenochrajeshNo ratings yet