Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab5 Assignment
Uploaded by
Selva KumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab5 Assignment
Uploaded by
Selva KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
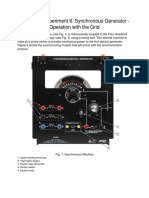
Sequence Networks of a Synchronous Machine
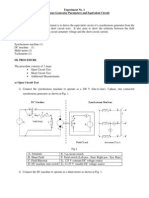
1. OBJECTIVES
Determine the sequence parameters of the equivalent circuit for a synchronous machine
and build the positive, negative and zero sequence equivalent circuits.
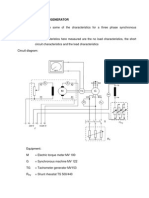
2. EQUIPMENT
Synchronous machine:
Hampden SM-100-3 Motor
Prime mover:
Hampden DM-100A DC Machine
Multimeter
Oscilloscope: Hewlet Packard, 100 MHZ, 2 channel
3. PROCEDURE
a) Positive-Sequence Impedance
1) Connect the synchronous machine to operate as a 173 V (line
Y-connected (armature winding) synchronous motor, grounded through a neutral,
with the field winding open, and positive sequence voltages (sequence A
applied to the stator windings as shown in Fig. 1.
Lab-work # 5
equence Networks of a Synchronous Machine
arameters of the equivalent circuit for a synchronous machine
ative and zero sequence equivalent circuits.
tor & Alternator
C Machine
ard, 100 MHZ, 2 channel, Voltage probe, current probe
dance
nous machine to operate as a 173 V (line
e winding) synchronous motor, grounded through a neutral,
g open, and positive sequence voltages (sequence A
ndings as shown in Fig. 1.
Machine
hronous machine
(1)
ent probe (1)
ine-to-line), 32,
rough a neutral,
equence A-B-C)
2) Have the instructor check you machine and meter connections before proceeding.
3) Record in the Table 1: the voltage
and real power P
total
(3P
AN
).
b) Negative-Sequence Impedance
1) Connect the synchronous machine to operate as a 173 V, 32
winding) synchronous motor, grounded through a neutral, with the field winding
short-circuited, and negative sequence voltages (sequence A
stator windings as shown in Fig. 2.
2) Have the instructor check you
3) Record in the Table 1: the voltage
and real power P
total
(3P
AN
).
eck you machine and meter connections before proceeding.
: the voltage V
A
at the stator terminal A (L1), stator current
edance
us machine to operate as a 173 V, 32, Y-connected (armature
motor, grounded through a neutral, with the field winding
egative sequence voltages (sequence A-C-B) are applied to the
wn in Fig. 2.
eck your machine and meter connections before proceeding.
: the voltage V
A
at the stator terminal A (L1), stator current
.
proceeding.
stator current I
A
,
nected (armature
he field winding
re applied to the
e proceeding.
stator current I
A
,
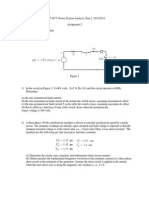
c) Zero-Sequence Impedance
1) Connect the synchronous machine to operate as
winding) synchronous motor, grounded through neutral, with the field winding
short-circuited, and single phase
(connected in parallel) as shown in Fig. 3.
2) Have the instructor check you
2) Record in the Table 1: the voltage
power P
L1-
! "ote that three phase windings are connected in parallel)
Positive #e$uence
egative #e$uence
%ero #e$uence
4. REPORT AND QUESTIONS
a) Calculate the positive (Z
using the measured voltages and currents.
b) Draw the positive, negative and zero sequence circuits and label the parameters.
ce
ous machine to operate as 25V, 12, Y-connected (armature
motor, grounded through neutral, with the field winding
e phase 25 V AC source is applied to the three stator windings
hown in Fig. 3.
ck your &achine and &eter connections be'ore proceeding!
the voltage V at the stator ter&inal () stator current
three phase windings are connected in parallel)
* +
Table 1
TIONS
Z
+
), negative (Z
-
) and zero (Z
0
) sequence impedances (R + j X)
s and currents.
ive and zero sequence circuits and label the parameters.
nected (armature
field winding
e stator windings
e proceeding!
urrent I) and real
el)
P
total
dances (R + j X)
rameters.
You might also like
- Experiment 8 Synchronous Generator Line SynchronizationDocument10 pagesExperiment 8 Synchronous Generator Line SynchronizationMd Rodi Bidin100% (1)
- Synchronous Motor Test TestDocument5 pagesSynchronous Motor Test TestChidamparam PalaniyappanNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine Parameter Measurement and TestingDocument8 pagesSynchronous Machine Parameter Measurement and TestingryankuoNo ratings yet
- Synchronizing a Synchronous GeneratorDocument9 pagesSynchronizing a Synchronous GeneratorGeniusAtwork2021No ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Synchronous Motor V-CurvesDocument12 pagesExperiment 7 Synchronous Motor V-Curvesshukla_shrishNo ratings yet
- BEKP 3673 - Assignment 2Document4 pagesBEKP 3673 - Assignment 2Shaiful Ashwat ShukorNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Lab ManualDocument34 pagesPower Systems Lab ManualPrashant Ramesh BurhadeNo ratings yet
- 6 +ok+MEASURE+MENT+OF+SEQUENCE+REACTANCES+OF+SALIENT+POLE+SYNCHRONOUS+MACHINEDocument3 pages6 +ok+MEASURE+MENT+OF+SEQUENCE+REACTANCES+OF+SALIENT+POLE+SYNCHRONOUS+MACHINEaissmsNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine Lab BookDocument5 pagesSynchronous Machine Lab BookMarko PetkovićNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical ComponentsDocument36 pagesSymmetrical ComponentsFaten Nabilla NordinNo ratings yet
- 9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotorDocument4 pages9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotormanishNo ratings yet
- Syncronous Machine ReactanceDocument7 pagesSyncronous Machine ReactanceSuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- IGEE 402 - Power System Analysis Final Examination - Sample Fall 2004Document28 pagesIGEE 402 - Power System Analysis Final Examination - Sample Fall 2004Akinbode Sunday OluwagbengaNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Alternator Performance AnalysisDocument11 pagesThree-Phase Alternator Performance AnalysisOnofre Algara Jr.100% (4)
- Emc711s Electrical Machines 315 Lib Assign-2 May-2017 PaperDocument3 pagesEmc711s Electrical Machines 315 Lib Assign-2 May-2017 PaperTimoNo ratings yet
- DC Shunt Motor Speed Control by Field & Armature MethodsDocument4 pagesDC Shunt Motor Speed Control by Field & Armature MethodsVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Analysis of D.C. Electric Motors: EEEE 531 - Mechatronics Experiment #2Document8 pagesAnalysis of D.C. Electric Motors: EEEE 531 - Mechatronics Experiment #2kay_rolNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: Poly Phase Ac SystemsDocument16 pagesChapter Six: Poly Phase Ac SystemsengidawabelNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generator - Synchronization of Unloaded Machine To The Grid, V-CurvesDocument4 pagesSynchronous Generator - Synchronization of Unloaded Machine To The Grid, V-CurvesRicha KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Ac Voltage ControllerDocument3 pagesThree Phase Ac Voltage ControllerShubham DixitNo ratings yet
- 02 DC Machines LabDocument8 pages02 DC Machines LabAndubekaNo ratings yet
- Psa Unit 4Document21 pagesPsa Unit 4Aish KrishNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Components OverviewDocument6 pagesSymmetrical Components OverviewezzateisNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generator I PDFDocument38 pagesSynchronous Generator I PDFjcrodriguez8350% (2)
- Cover Type B Exam: Electrical MachinesDocument14 pagesCover Type B Exam: Electrical MachinesVikri RahmatNo ratings yet
- Prosedur Percobaan Motor SinkronSinkron Generator SinkronDocument10 pagesProsedur Percobaan Motor SinkronSinkron Generator SinkronDara AmeliaNo ratings yet
- EE 340L Experiment 6 Synchronous Generator Operation GridDocument6 pagesEE 340L Experiment 6 Synchronous Generator Operation GridMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Drives Simulation Laboratory-II: Report byDocument10 pagesPower Electronics and Drives Simulation Laboratory-II: Report byAviral TiwariNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis of Three Phase Alternator Sequence Impedance: Apparatus RequiredDocument9 pagesFault Analysis of Three Phase Alternator Sequence Impedance: Apparatus RequiredMohan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report on Inducing Voltage in a Synchronous GeneratorDocument8 pagesLab Report on Inducing Voltage in a Synchronous GeneratorMalik Hassaan SangraalNo ratings yet
- GeneratorsDocument4 pagesGeneratorsCyril Ann LlavoresNo ratings yet
- Synch Alternator Exp6Document8 pagesSynch Alternator Exp6Prìyañshú GuptãNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Components & Faults CalculationsDocument26 pagesSymmetrical Components & Faults CalculationsRTNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ProblemsDocument6 pagesPower Electronics ProblemsLu'ay AlmassriNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Generator Voltage Control ExperimentDocument6 pages3-Phase Generator Voltage Control ExperimentBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab7 EnaDocument10 pagesLab7 EnaLaiba ShahzadNo ratings yet
- 11 Synchronous Generator and Motor OperationDocument29 pages11 Synchronous Generator and Motor OperationkkrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- EES Power System Dynamics and Control Test 1 QuestionsDocument4 pagesEES Power System Dynamics and Control Test 1 QuestionsRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Short Shunt (2007)Document7 pagesShort Shunt (2007)Jeffrey NambatacNo ratings yet
- ELEC4100 Complete NotesDocument150 pagesELEC4100 Complete NotesShittyUsername2013No ratings yet
- Suggested Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesSuggested Practice ProblemsSaikat MallickNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine TestsDocument10 pagesSynchronous Machine TestsItalo ChiarellaNo ratings yet
- Group3 ExperimentNo.2Document11 pagesGroup3 ExperimentNo.2odrhey hernandezNo ratings yet
- EECS 3480 Lab Manual ExperimentsDocument54 pagesEECS 3480 Lab Manual Experimentsmohammed100% (1)
- E3G6Document10 pagesE3G6NJ De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: DC Motors ObjectDocument5 pagesExperiment 8: DC Motors ObjectSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- A Single Phase To Three Phase Power Converter For Motor Drive ApDocument8 pagesA Single Phase To Three Phase Power Converter For Motor Drive Apmd naufallNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab-II 5. Regulation of Three-Phase Alternator by Synchronous Impedance MethodDocument6 pagesElectrical Machines Lab-II 5. Regulation of Three-Phase Alternator by Synchronous Impedance Methodcholleti sriramNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff ReportDocument10 pagesKirchhoff ReportGeorge RYNo ratings yet
- Ashish Singh 2K20CEEE11 Exp-6Document6 pagesAshish Singh 2K20CEEE11 Exp-6Ashish SinghNo ratings yet
- Power System Fault Analysis and Symmetrical ComponentsDocument27 pagesPower System Fault Analysis and Symmetrical Componentsግርማ ገ.No ratings yet
- Analysis Three-Phase Ac Circuit: Work Purpose: To Demonstrate 3-Phase System "Delta" and "Wye" Connections. The Study ofDocument9 pagesAnalysis Three-Phase Ac Circuit: Work Purpose: To Demonstrate 3-Phase System "Delta" and "Wye" Connections. The Study ofnikitaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab ManualDocument37 pagesElectrical Machines Lab ManualAtharv ParanjpeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsFrom EverandElectrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab ManualDocument37 pagesElectrical Machines Lab ManualAtharv ParanjpeNo ratings yet
- Sequence ImpedenceDocument4 pagesSequence ImpedenceAnonymous m65TTcfOTNo ratings yet
- Note Book ListDocument1 pageNote Book ListSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- Booklist EEEDocument2 pagesBooklist EEESelva KumarNo ratings yet
- 493 297 1Document8 pages493 297 1gkdharNo ratings yet