Professional Documents
Culture Documents
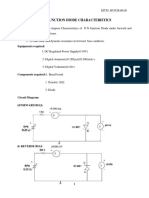
MOSFETs: Drain Voltage Effects On Channel Current
Uploaded by
parmis12120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views16 pagesThis document discusses the effects of increasing drain voltage on MOSFET channel current. Increasing drain voltage widens the depletion region and raises the barrier height between the drain and channel. This causes the current versus drain voltage curve to be non-flat due to the Early effect or channel length modulation. The current increases exponentially with drain voltage according to an exponential model, due to a phenomenon called drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL). At very high drain voltages, punchthrough can occur where the depletion regions converge.
Original Description:
MOSFETs: Drain Voltage Effects on Channel Current
Original Title
MOSFETs: Drain Voltage Effects on Channel Current
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the effects of increasing drain voltage on MOSFET channel current. Increasing drain voltage widens the depletion region and raises the barrier height between the drain and channel. This causes the current versus drain voltage curve to be non-flat due to the Early effect or channel length modulation. The current increases exponentially with drain voltage according to an exponential model, due to a phenomenon called drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL). At very high drain voltages, punchthrough can occur where the depletion regions converge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views16 pagesMOSFETs: Drain Voltage Effects On Channel Current
Uploaded by
parmis1212This document discusses the effects of increasing drain voltage on MOSFET channel current. Increasing drain voltage widens the depletion region and raises the barrier height between the drain and channel. This causes the current versus drain voltage curve to be non-flat due to the Early effect or channel length modulation. The current increases exponentially with drain voltage according to an exponential model, due to a phenomenon called drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL). At very high drain voltages, punchthrough can occur where the depletion regions converge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
MOSFETs: Drain Voltage
Effects on Channel Current
Prof. Paul Hasler
Origin of Drain Dependencies
Increasing Vd effects
the drain-to-channel
region:
increases depletion
width
increases barrier
height
Drain Characteristics
Current versus Drain Voltage
Current versus Drain Voltage
Current versus Drain Voltage
Not flat due to Early effect
(channel length modulation)
Current versus Drain Voltage
Not flat due to Early effect
(channel length modulation)
In BJTs --- Base Modulation Effects
Current versus Drain Voltage
Not flat due to Early effect
(channel length modulation)
I
d
= I
d
(sat) (1 + (V
d
/V
A
) )
or
I
d
= I
d
(sat) e
Vd/VA
In BJTs --- Base Modulation Effects
Current versus Drain Voltage
Not flat due to Early effect
(channel length modulation)
I
d
= I
d
(sat) (1 + (V
d
/V
A
) )
or
I
d
= I
d
(sat) e
Vd/VA
R
out
I
d
(sat)
GND
I
out
In BJTs --- Base Modulation Effects
Early Voltage Length Dependence
Width of depletion region
depends on doping, not L
Might expect Vo to linearly
vary with L
Full Range of Effects
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1
10
100
Punchthrough
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
n
A
)
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
n
A
)
Voltage (V)
Exp model
Slow / Exponential Increase:
Channel Modulation /
DIBL Effect
Other (faster) effects:
Punchthrough --- depletion
regions converge
Avalanche Breakdown ---
impact ionization
(Punchthrough voltage = 2 * V
A
)
V
A
= 5V
Cause of DIBL
Drain Induced Barrier Lowering
Data taken from a popular
1.2mm MOSIS process
Data taken from a popular
2.0mm MOSIS process
Different Manifestations of DIBL
Different Manifestations of DIBL
Drain Voltage Effects
Channel Length Modulation / Early Effect
Exponential Modeling
Drain Induced Barrier Lowering (DIBL):
Source of Exponential I-V dependence
Punchthrough: Highest Drain-Source
voltage available
You might also like
- Electronics Ch5Document30 pagesElectronics Ch5Santi Navarro MoralNo ratings yet
- Super Source FollowerDocument27 pagesSuper Source Followerkhlsakfn100% (2)
- Laboratory Manual: SRM UniversityDocument54 pagesLaboratory Manual: SRM UniversityreneeshczNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Mos Transistor Review: 3D Band Diagram of A Long Channel Enhancement Mode NMOS TransistorDocument14 pagesMos Transistor Review: 3D Band Diagram of A Long Channel Enhancement Mode NMOS TransistorKumar Amit VermaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- AE Lab Manual For EeeDocument53 pagesAE Lab Manual For EeeSRUJANA VNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Second Order EffectsDocument40 pagesSecond Order EffectsDhiraj Kumar100% (2)
- Electronics & Microprocessor Lab ManualDocument80 pagesElectronics & Microprocessor Lab ManualCyril Robinson Azariah John100% (5)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesFrom EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Intro To FinFetDocument19 pagesIntro To FinFetKota Sai JagadishNo ratings yet
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignFrom EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finfet: Haiying ZhaoDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Finfet: Haiying Zhaosherrysherry0% (1)
- 3.5 MOSFET Scaling and Small-Geometry EffectsDocument19 pages3.5 MOSFET Scaling and Small-Geometry Effectspraritlamba25No ratings yet
- BXE Experiment No.4Document6 pagesBXE Experiment No.4DsgawaliNo ratings yet
- Leakage Control For Deep-Submicron Circuits: Kaushik Roy, Hamid Mahmoodi-Meimand, and Saibal MukhopadhyayDocument12 pagesLeakage Control For Deep-Submicron Circuits: Kaushik Roy, Hamid Mahmoodi-Meimand, and Saibal MukhopadhyayDebbrat GhoshNo ratings yet
- PIPE STRESS ANALYSIS - FIV - AIV (Compatibility Mode)Document48 pagesPIPE STRESS ANALYSIS - FIV - AIV (Compatibility Mode)salma khalilaa putrii 6D100% (1)
- Lab New7 PDFDocument9 pagesLab New7 PDFSyeda Mahnoor BukhariNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Short Channel EffectsDocument5 pagesMOSFET Short Channel EffectsMujtaba KathjooNo ratings yet
- Principle of Electronics EnggDocument47 pagesPrinciple of Electronics EnggNilabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11 Frequency Response of CE AmplifierDocument4 pagesExperiment 11 Frequency Response of CE AmplifierShees Nadeem100% (2)
- CPINTERFERENCEAUCSCDocument34 pagesCPINTERFERENCEAUCSCaltamimzNo ratings yet
- TalkDocument27 pagesTalksonsfhsdlfhsadhNo ratings yet
- Mod1 (2) - EC464 Low Power VLSI Design-Ktustudents - inDocument40 pagesMod1 (2) - EC464 Low Power VLSI Design-Ktustudents - insurya sundarNo ratings yet
- Mod1 (2) - EC464 Low Power VLSI Design-Ktustudents - inDocument40 pagesMod1 (2) - EC464 Low Power VLSI Design-Ktustudents - insurya sundarNo ratings yet
- Mosfet 01Document56 pagesMosfet 01Edward Allan MangubatNo ratings yet
- Leakage in Nanometer Scale CMOSDocument8 pagesLeakage in Nanometer Scale CMOSJimit GadaNo ratings yet
- No 1Document4 pagesNo 1David JoneNo ratings yet
- List of Experiments: Diode Forward CharacteristicDocument22 pagesList of Experiments: Diode Forward CharacteristicrajeshNo ratings yet
- 7 DRPSK LPVD Unit-1 Subthreshold Leakage Power DissipationDocument28 pages7 DRPSK LPVD Unit-1 Subthreshold Leakage Power DissipationKarthikeyaNo ratings yet
- FETDocument91 pagesFETpawan_32No ratings yet
- Second-Order Effects On MOSFET Small-Signal ModelDocument22 pagesSecond-Order Effects On MOSFET Small-Signal Modelsasi kiranNo ratings yet
- Transistors and AmplifiersDocument285 pagesTransistors and AmplifiersCris Diane G. DatingginooNo ratings yet
- 1.270219lecture 1 Vtu Semiconductor DiodesDocument23 pages1.270219lecture 1 Vtu Semiconductor Diodeseesha sabnisNo ratings yet
- Supplement Free Span PDFDocument49 pagesSupplement Free Span PDFNovriyansi NainsaNo ratings yet
- Binary Signalling F OrmatsDocument12 pagesBinary Signalling F OrmatsAlango Jr TzNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of FETDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of FETYogesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transistors: Presented: October 23, 2001 Chris Green Carl Hanna Ancil Marshall Kwame OforiDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Transistors: Presented: October 23, 2001 Chris Green Carl Hanna Ancil Marshall Kwame OforiJobz Van- GNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument56 pagesLab ManualMy JaanNo ratings yet
- Multiplexer: Multiplex - Many Into OneDocument40 pagesMultiplexer: Multiplex - Many Into OneSamee UllahNo ratings yet
- AmplfierDocument7 pagesAmplfierCharuka WeerasekaraNo ratings yet
- Power For FFDocument63 pagesPower For FFsansureNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistors Analysis Mr. Zeeshan Ali, Asst. Professor Department: B.E. Electronic & Telecommunication Subject: Analog Electronics - I Semester: IIIDocument84 pagesField Effect Transistors Analysis Mr. Zeeshan Ali, Asst. Professor Department: B.E. Electronic & Telecommunication Subject: Analog Electronics - I Semester: IIIAqilAbbasiNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab NewDocument55 pagesBasic Electronics Lab NewSambhavNo ratings yet
- 04 - Second-Order Effects On MOSFET Small Signal ModelDocument27 pages04 - Second-Order Effects On MOSFET Small Signal ModelWinnie LahNo ratings yet
- LIC All Unit Q&ADocument22 pagesLIC All Unit Q&AG.MUNEER BABA,EEE18 Vel Tech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorDocument11 pagesField Effect TransistorAnurag YadavNo ratings yet
- Lab reportTTDocument13 pagesLab reportTTPaa Kwesi ArhinfulNo ratings yet
- Second Order Effects of MOSFETDocument17 pagesSecond Order Effects of MOSFETDileep KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 04Document10 pagesLab 0449 - 103 - Umair HossainNo ratings yet
- Inverter 2002Document54 pagesInverter 2002Sandro MoreroNo ratings yet
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture17 080213-FDocument35 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture17 080213-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finfet: Haiying ZhaoDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Finfet: Haiying ZhaoSai KishoreNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics LabDocument60 pagesBasic Electronics Labrahulsingle67% (3)
- Edc Lab Exp 1aand1bDocument10 pagesEdc Lab Exp 1aand1bJames TonyNo ratings yet
- Classical Mythology Notes - Chapter 1 & 2Document11 pagesClassical Mythology Notes - Chapter 1 & 2parmis1212No ratings yet
- Introduction To Nanoelectronics FinalDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Nanoelectronics Finalparmis1212No ratings yet
- MIT6 701S10 Notes by Marc BaldoDocument261 pagesMIT6 701S10 Notes by Marc BaldoAlfredo Rico GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Matlab Finite Element Modeling For Materials Engineers Using MATLABDocument74 pagesMatlab Finite Element Modeling For Materials Engineers Using MATLABPujara ManishNo ratings yet
- Transition Words and PhrasesDocument1 pageTransition Words and Phrasesparmis1212No ratings yet
- Characters in The Play: Oxford University Press, 2010, Hamlet Online, ISBN: 978-0-19-544009-6Document114 pagesCharacters in The Play: Oxford University Press, 2010, Hamlet Online, ISBN: 978-0-19-544009-6parmis1212No ratings yet
- Transition Words and PhrasesDocument1 pageTransition Words and Phrasesparmis1212No ratings yet
- CM812 Troubleshooting Flow Chart BDocument2 pagesCM812 Troubleshooting Flow Chart BYoSelf UbigDummyNo ratings yet
- Electronics MSC Sem 1Document29 pagesElectronics MSC Sem 1Pawan DongareNo ratings yet
- FLOWTITE GRP Pipe Systems - For Bridge - and Tunnel Drainage - enDocument24 pagesFLOWTITE GRP Pipe Systems - For Bridge - and Tunnel Drainage - enraji357No ratings yet
- LAB 4-PE-LabDocument7 pagesLAB 4-PE-LabLovely JuttNo ratings yet
- Plus Two Physics Previous Question Paper Hsslive SajuDocument47 pagesPlus Two Physics Previous Question Paper Hsslive SajuMathew Yoyakky78% (9)
- Pioneer Book 3 PVC WiringDocument32 pagesPioneer Book 3 PVC WiringirfanWPKNo ratings yet
- Yanmar XP185, P260WIR Service Manual Rev B 1-19-09Document112 pagesYanmar XP185, P260WIR Service Manual Rev B 1-19-09brahiam agudeloNo ratings yet
- ZDSO400-ER2, ZDSO400-ER4: User ManualDocument16 pagesZDSO400-ER2, ZDSO400-ER4: User ManualromancyyNo ratings yet
- Commissioning of Electrical EquipmentDocument3 pagesCommissioning of Electrical EquipmentThomas RussellNo ratings yet
- Measurement of PressureDocument23 pagesMeasurement of PressureOmar KhanNo ratings yet
- ELTE 307 - DR Mohamed Sobh-Lec - 5-1-11-2022Document28 pagesELTE 307 - DR Mohamed Sobh-Lec - 5-1-11-2022Lina ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Din A Mite RetrofitDocument69 pagesDin A Mite RetrofitLuis GutierrezNo ratings yet
- BJT NotesDocument4 pagesBJT NotesManjur AhmedNo ratings yet
- RF Switches Using Phase Change Materials: Yonghyun Shim, Gwendolyn Hummel, and Mina Rais-ZadehDocument4 pagesRF Switches Using Phase Change Materials: Yonghyun Shim, Gwendolyn Hummel, and Mina Rais-ZadehkaurVRNo ratings yet
- Hot Spot Temp. of TransformerDocument9 pagesHot Spot Temp. of TransformeraocalayNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument4 pagesLab ReportAgrobacterium Tumefaciens100% (2)
- MDP2N60/MDF2N60: N-Channel MOSFET 600V, 2.0A, 4.5Document8 pagesMDP2N60/MDF2N60: N-Channel MOSFET 600V, 2.0A, 4.5Erroz RosadiNo ratings yet
- PNPN and Other Device BoylestadDocument20 pagesPNPN and Other Device BoylestadJohn Lester Laurentino RamirezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Sem 1 20202021 BDA30703Document4 pagesAssignment 1 Sem 1 20202021 BDA30703Ammar WahabNo ratings yet
- ENHANCEMENT SCIE 8 WEEK 7 Copy Copy 2Document3 pagesENHANCEMENT SCIE 8 WEEK 7 Copy Copy 2Jorgie GeulinNo ratings yet
- Basic DMM Operation: Quick Training Guide - QT617ADocument15 pagesBasic DMM Operation: Quick Training Guide - QT617AThang TongNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument26 pagesCurrent ElectricityVasu MittalNo ratings yet
- Relaying Short LinesDocument16 pagesRelaying Short LinesrogeriojuruaiaNo ratings yet
- Earthing PracticesDocument16 pagesEarthing PracticesSubu ManiNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1037-12 ParticleBoardDocument16 pagesASTM D1037-12 ParticleBoardTOufiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument30 pagesChapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldNguyễn Ngoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Step1:: 1. With Neat Sketches Explain The NMOS and PMOS Fabrication ProcedureDocument6 pagesStep1:: 1. With Neat Sketches Explain The NMOS and PMOS Fabrication ProcedurehghgNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledSaif EzdanNo ratings yet
- Applied Material ScienceDocument9 pagesApplied Material SciencetalabizNo ratings yet
- Assertion and Reason QuestionsDocument13 pagesAssertion and Reason QuestionsGokul M PNo ratings yet