Professional Documents
Culture Documents
226 6.4. Equation of A Tangent To A Curve
226 6.4. Equation of A Tangent To A Curve
Uploaded by
reacharunkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
226 6.4. Equation of A Tangent To A Curve
226 6.4. Equation of A Tangent To A Curve
Uploaded by
reacharunkCopyright:
Available Formats
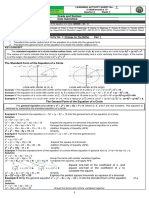
Worked example 14: Finding the equation of a tangent to a curve
QUESTION
Given g(x) = (x + 2)(2x + 1)
2
, determine the equation of the tangent to the curve at
x = 1 .
SOLUTION
Step 1: Determine the y-coordinate of the point
g(x) = (x + 2)(2x + 1)
2
g(1) = (1 + 2)[2(1) + 1]
2
= (1)(1)
2
= 1
Therefore the tangent to the curve passes through the point (1; 1).
Step 2: Expand and simplify the given function
g(x) = (x + 2)(2x + 1)
2
= (x + 2)(4x
2
+ 4x + 1)
= 4x
3
+ 4x
2
+ x + 8x
2
+ 8x + 2
= 4x
3
+ 12x
2
+ 9x + 2
Step 3: Find the derivative
g
(x) = 4(3x
2
) + 12(2x) + 9 + 0
= 12x
2
+ 24x + 9
Step 4: Calculate the gradient of the tangent
Substitute x = 1 into the equation for g
(x):
g
(1) = 12(1)
2
+ 24(1) + 9
m = 12 24 + 9
= 3
Step 5: Determine the equation of the tangent
Substitute the gradient of the tangent and the coordinates of the point into the gradient-
point form of the straight line equation.
y y
1
= m(x x
1
)
y 1 = 3 (x (1))
y = 3x 3 + 1
y = 3x 2
226 6.4. Equation of a tangent to a curve
You might also like
- Final Practice SolDocument11 pagesFinal Practice SolChris MoodyNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Composition Setting Up FunctionsDocument6 pagesWeek 3 Composition Setting Up FunctionsFor sell account Pubg newstateNo ratings yet
- HW2 SolutionDocument5 pagesHW2 Solutionaniket patelNo ratings yet
- Maths Practice QuizDocument2 pagesMaths Practice QuizPrince Aphotinel OnagwaNo ratings yet
- Cuadratura GausianaDocument2 pagesCuadratura Gausianacristina escobarNo ratings yet
- Handout - Analytic Geometry - Equation of The Circle - 045740Document8 pagesHandout - Analytic Geometry - Equation of The Circle - 045740jay ronnie pranadaNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Soal Fungsi Komposisi Dan Fungsi InversDocument54 pagesJawaban Soal Fungsi Komposisi Dan Fungsi InversSuryani SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Class Note-M101 Module-II PDFDocument24 pagesClass Note-M101 Module-II PDFprince KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Final - DERIVATIVE OF A FUNCTION HandoutDocument58 pages1 Final - DERIVATIVE OF A FUNCTION HandoutJerico MendañaNo ratings yet
- HT QPDocument121 pagesHT QPlikhithNo ratings yet
- 2233 mt1 S99sDocument5 pages2233 mt1 S99sAkoh C Josh ÜNo ratings yet
- ECE 302: Homework 1 SOLUTION: Due September 3, 2008 in ClassDocument3 pagesECE 302: Homework 1 SOLUTION: Due September 3, 2008 in ClassJack LiuNo ratings yet
- Differential EqutionDocument4 pagesDifferential EqutionthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5A: Dy DX 2 1Document11 pagesExercise 5A: Dy DX 2 1kamaldinho11No ratings yet
- Advanced Microeconomic Theory Solution Jehle 2007 EditionDocument21 pagesAdvanced Microeconomic Theory Solution Jehle 2007 EditionJamie JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Complete The Square For ExpressionsDocument5 pagesAlgebra: Complete The Square For ExpressionsTuyếnĐặngNo ratings yet
- Plates-No - 1 1-1 4Document1 pagePlates-No - 1 1-1 4MADELYN QUIMBONo ratings yet
- 4 Operation of FunctionsDocument18 pages4 Operation of FunctionsJefferson ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Calculus of Multivariable - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Document24 pagesCalculus of Multivariable - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions 2/19/7Document8 pagesAnalytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions 2/19/7Huges ApolNo ratings yet
- 7 Las m10 Week 7 Montad Nicanor Jr. S. EditedDocument4 pages7 Las m10 Week 7 Montad Nicanor Jr. S. EditedGemmhainne OrtizNo ratings yet
- Functions: If F (X) 2x - 2x + 1, Find F ( - 1) - (B) If F (T) 3t - 1, Find F (A)Document14 pagesFunctions: If F (X) 2x - 2x + 1, Find F ( - 1) - (B) If F (T) 3t - 1, Find F (A)Dinesh RajNo ratings yet
- Tailieuxanh Dap An Calculus 1 Final Test hk2 2019 2020 7797Document5 pagesTailieuxanh Dap An Calculus 1 Final Test hk2 2019 2020 7797Tâm Phạm ThànhNo ratings yet
- MAT 3310 (2009-2010, Second Term) Suggested Solution For Midterm ExaminationDocument6 pagesMAT 3310 (2009-2010, Second Term) Suggested Solution For Midterm Examinationjulianli0220No ratings yet
- Ubc Math 200 Summer Midterm 1dDocument10 pagesUbc Math 200 Summer Midterm 1dSamanthaNo ratings yet
- Sets,+relations+and+function+L5+DPP+ +11th+eliteDocument76 pagesSets,+relations+and+function+L5+DPP+ +11th+eliteSunitha ShankarNo ratings yet
- 2011-10-Elementary Approach To Modular Equations - Hypergeometric Series 2Document4 pages2011-10-Elementary Approach To Modular Equations - Hypergeometric Series 2dawson zhaoNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Tutorial 2 (Week 3) : Lecturers: Daniel Daners and James ParkinsonDocument9 pagesSolutions To Tutorial 2 (Week 3) : Lecturers: Daniel Daners and James ParkinsonTOM DAVISNo ratings yet
- Mercado, Richelle S.calculusDocument4 pagesMercado, Richelle S.calculusrichelle salesNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument19 pagesQuadratic EquationsLoh Chee WeiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cal - Week 1-2 - 1ST QRDocument7 pagesPre-Cal - Week 1-2 - 1ST QRMonica Joyce NaperiNo ratings yet
- DerivativesDocument49 pagesDerivativesCarlaNo ratings yet
- Multivariate CalculusDocument15 pagesMultivariate CalculusMartin De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- Mercado, Richelle S.calculusDocument4 pagesMercado, Richelle S.calculusrichelle salesNo ratings yet
- Sample Quiz 1Document3 pagesSample Quiz 1Yogeneswari AppalasamyNo ratings yet
- Addmath Form 4Document28 pagesAddmath Form 4Nor Hanina100% (25)
- Differential EquationDocument6 pagesDifferential Equationমে হে দীNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionDocument3 pagesQuadratic FunctionTristan Joshuel VillegasNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions PDFDocument26 pagesQuadratic Functions PDFyen 1978No ratings yet
- S S S 2 Fur Maths 1ST Term E-Note 2017Document56 pagesS S S 2 Fur Maths 1ST Term E-Note 2017palmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- Kseeb Class 12 Exam Question Paper Solutions March 2018Document29 pagesKseeb Class 12 Exam Question Paper Solutions March 2018Ravindar PurohitNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resolver Las Siguientes Ecuaciones Diferenciales LinealesDocument4 pagesEjercicios Resolver Las Siguientes Ecuaciones Diferenciales LinealesmariaNo ratings yet
- Translating Conic SectionsDocument15 pagesTranslating Conic SectionsNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument14 pagesQuadratic FunctionsMicaelahNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential Equations Segment Wise Questions From 1983 To 2011 Civil ServiceDocument6 pagesOrdinary Differential Equations Segment Wise Questions From 1983 To 2011 Civil ServiceNagendran KrishnamoorthiNo ratings yet
- Fe Tutorials Sem2Document8 pagesFe Tutorials Sem2narendasreNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT - ANALYTIC GEOMETRY - General Equation of The Circle - 045749Document7 pagesHANDOUT - ANALYTIC GEOMETRY - General Equation of The Circle - 045749jay ronnie pranadaNo ratings yet
- Geometri Analitik - Latihan Chapter 2.1Document4 pagesGeometri Analitik - Latihan Chapter 2.1Fiki Nafilah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument13 pagesQuadratic FunctionsNur AmiraNo ratings yet
- Precal - Lesson 2Document4 pagesPrecal - Lesson 2alayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Document38 pagesDifferential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Trapezoidal Rule EditedDocument3 pagesTrapezoidal Rule EditedApam BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Maths 2B Ellipse Important QuestionsDocument7 pagesMaths 2B Ellipse Important Questionssimhadri.sridharNo ratings yet
- Calculus Is Something To: P.3 Functions and Their GraphsDocument16 pagesCalculus Is Something To: P.3 Functions and Their GraphsDenmark SantosNo ratings yet
- Graphing TechniquesDocument33 pagesGraphing TechniquesCathy McKayNo ratings yet
- Cal Exam - Apr 2022 FUV - SolnsDocument3 pagesCal Exam - Apr 2022 FUV - SolnsNuong PhanNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Exercises (Differential Equation) : F HG I KJDocument3 pagesMiscellaneous Exercises (Differential Equation) : F HG I KJSarthak ChowdhuriNo ratings yet
- IntegralsDocument27 pagesIntegralssudersanaviswanathanNo ratings yet
- HolaDocument4 pagesHolaBryan RosadoNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- En (1464)Document1 pageEn (1464)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- General Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsuranceDocument19 pagesGeneral Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsurancereacharunkNo ratings yet
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 pagesProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1458)Document1 pageEn (1458)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1459)Document1 pageEn (1459)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1451)Document1 pageEn (1451)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1386)Document1 pageEn (1386)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- And Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atDocument1 pageAnd Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atreacharunkNo ratings yet
- Mate The: (Fig. - VrouldDocument1 pageMate The: (Fig. - VrouldreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1382)Document1 pageEn (1382)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- The The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesDocument1 pageThe The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesreacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1383)Document1 pageEn (1383)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1372)Document1 pageEn (1372)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1376)Document1 pageEn (1376)reacharunkNo ratings yet
- En (1374)Document1 pageEn (1374)reacharunkNo ratings yet