Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gauges and Gauge Design PDF
Uploaded by
Joaquín Pastor ManelliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gauges and Gauge Design PDF
Uploaded by
Joaquín Pastor ManelliCopyright:
Available Formats
5/7/2011
1
IPE 381
Chapter:10
Gauges and Gauge Design
Abdullah-Al-Mamun
Lecturer, Dept. of IPE
Outline
Basics of Gauges
Classification of Gauges
Gauge Design
Screw Gauges
Adv & Disadv of Limit Gauges
Gauge Design problem
5/7/2011
2
Gauges
Gauges are inspection tool of
rigid design, without a scale,
which serves to check the
dimensions of manufacturing
parts.
Gauge do not indicate the actual
value of the inspected part of the
component.
They are used to determine
whether the part is made within
the specified limit.
Classification of Plain Gauge
Plain gauges are used for checking plain (unthreaded) holes and
shafts. Gauges are classified:
According to their type :
(a) Standard gauges- made as an exact copy of opposed(mating)
part
(b) Limit gauges- made to the limits of the dimensions
According to their purposes :
(a) Workshop Gauge: To Check Dimension after manufacture
(b) Inspection Gauge: To check part before final acceptance
(d) Purchase Inspection Gauge: To check part of other factory
(c) Reference or master gauges: To check the dimension of
Gauge
5/7/2011
3
Classification of Plain Gauge
According to the form of the tested surface :
(a) Plug gauges for checking holes.
(b) Snap and ring gauges for checking shafts.
Classification of Plain Gauge
According to their design :
(a) Single limit and double limit gauges
(b) Single ended and double ended gauges,
(c) Fixed and adjustable gauges.
5/7/2011
4
Limit Gauge
Limit gauges are made to the limits of the dimensions of the part to
be tested. There are two limit of dimensions, so we need two limit
gauge.
Go gauge should pass through or over a part while Not Go gauge
should not pass through or over the part.
Design of Limit Gauge
Allocation of Tolerance
Manufacturing Tolerance
Wear Allowance
Taylors Principle of gauge Design
Fixing of Gauge elements with handles
Taper lock design
Trilock Design
Provision of Guards
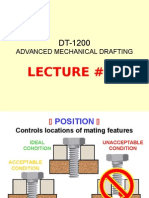
Provision of PilotCorrect Centering
Materials
Hardness and Surface finish
Rigidity
Alignment of Gauge faces
5/7/2011
5
Allocation of Tolerance
Manufacturing Tolerance
It is economically impractical to attempt to make Go and Not Go
gauges exactly to the two limits of work tolerance.
Limit gauges are made 10 times more accurate than the tolerances
they are going to control.
Allocation of Mfg Tolerance
5/7/2011
6
Allocation of Mfg Tolerance
Allocation of Tolerance
Wear Allowance
The surface of Go gauge is constantly rub
against the surface of the part in inspection and
loose their initial size
The size of plug gauge is reduced but size of
snap gauge is increased.
5% wear allowance is provided if working
tolerance is greater than 0.09 mm.
5/7/2011
7
Allocation of Wear Allowance
Taylors Principle
Go Gauge should always be so designed
that it will cover the maximum Metal
Condition(MMC) of as many dimensions
as possible in the same limit gauge,
whereas Not Go gauge to cover the
minimum metal condition of one dimension
only.
5/7/2011
8
To Check Circular Holes
Go Plug Gauge
Should Have a Full
Circular Section.
Length should be
equal to the length of
the hole.
To Check Circular Holes
Not Go Plug Gauge
should be
In the form of pin or
bar.
Should check the
upper limit of the
hole.
5/7/2011
9
To Check Circular Shaft
Ring Gauge
Should be used
as Go Gauge
Length should be
equal to the
length of the shaft
To Check Circular Shaft
Snap Gauge Should
be used as Not Go
Gauge
Should check the
low limit of shaft
For non circular
shaft, Snap gauge
will not pass through
5/7/2011
10
Fixing with Handles
Taper Lock Design
Used for diameter upto 63.5
mm.
Used for smaller size plain and
screw gauges.
Trilock Design
Used for diameter from 63.5
mm to 203mm.
Gauge is attached with handle
with three lock nuts.
Provision of Pilot
For closely toleranced parts Plug
gauge doesnt easily enter the hole so
piloting is used
5/7/2011
11
Thread or Screw Gauge
Nuts and internal threads are checked with
Plug thread gauge and screws with Ring
thread gauge.
Three types of Fit
Close Fit
Medium Fit
Free Fit
Designing a Gauge
A 25mm H8-f7 fit is to be checked.
The limit of size for H8 Hole are:
High Limit - 25.033mm.
Low Limit - 25.000mm.
The limits for the f7 shaft are:
High limit - 24.980mm.
Low limit - 24.959mm.
Taking the gauge makers tolerance to be 10% of the work tolerance,
design plug gauge and gap gauge to check the fit.
5/7/2011
12
Designing a Gauge
Find tolerance for hole an shaft
Find gauge tolerance
Basic Size for Go Plug Gauge is LL of Hole
Basic Size for Go Plug Gauge is HL of Hole
For plug gauge:
High limit of Go Plug gauge
Low limit of Go Plug gauge
High limit of Not Go Plug gauge
Low limit of Not Go Plug gauge
Repeat for Snap gauge
Draw the Diagram of Go, Not Go Plug gauge
and Go, Not Go Snap gauge
Self Study
10.7 Advantage of Limit Gauge
10.8 Disadvantage of Limit Gauge
10.9 Care of Gauges
10.10 Other types of Gauge
Thank You
You might also like
- Space Policy SWAT Future Space Strategies 13 UnclassifiedDocument189 pagesSpace Policy SWAT Future Space Strategies 13 UnclassifiedSpaceStrategosNo ratings yet
- Fanuc NCGuide PMC Simulation FunctionDocument121 pagesFanuc NCGuide PMC Simulation FunctionkenNo ratings yet
- Measurement Lab.: University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument6 pagesMeasurement Lab.: University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyKarikalan Loganathan100% (1)
- A321 DIFFERENCE GUIDE From A320Document72 pagesA321 DIFFERENCE GUIDE From A320NigelNo ratings yet
- Employee Safety Training Matrix Template ExcelDocument79 pagesEmployee Safety Training Matrix Template Excelشاز إياسNo ratings yet
- Straightness Flatness Roundness CylindricityDocument7 pagesStraightness Flatness Roundness CylindricityChristopher Plume De ChineNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mechanical DraftingDocument14 pagesAdvanced Mechanical DraftingdramiltNo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument10 pagesGD&TShahed FacebookNo ratings yet
- Machine Tools NotesDocument16 pagesMachine Tools NotesKarNo ratings yet
- Limits, Fits, ToleranceDocument51 pagesLimits, Fits, ToleranceAnthony Lopes0% (1)
- UNIT1 - Design of GaugesDocument41 pagesUNIT1 - Design of Gaugesraghav maske100% (1)
- 3-Limits Fits and TolerancesDocument22 pages3-Limits Fits and TolerancesAbhay Sharma100% (1)
- Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument4 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and TolerancingAshokNo ratings yet
- Metrology 2 Wire and 3 Wire Method Exp Manual PDFDocument9 pagesMetrology 2 Wire and 3 Wire Method Exp Manual PDFphanindra kumar100% (1)
- Mechanical Measurement LaboratoryDocument24 pagesMechanical Measurement LaboratoryMahendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Gauges and Gauge DesignDocument26 pagesGauges and Gauge DesignMurali100% (3)
- Taylor Theory of Gauging, Design and Types of Limit GaugesDocument35 pagesTaylor Theory of Gauging, Design and Types of Limit GaugesCh AdilNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Types of FixturesDocument19 pages1.1 Types of FixturesSrinivas DsNo ratings yet
- Gauge Design (Metrology)Document4 pagesGauge Design (Metrology)Lankipalli Hemanth100% (2)
- CAD-CAM Power Point PresentationDocument102 pagesCAD-CAM Power Point PresentationArgAshishGargNo ratings yet
- ComparatorsDocument54 pagesComparatorsbasanna_rvce60% (5)
- Lect - Linear and Angular Measurements PDFDocument118 pagesLect - Linear and Angular Measurements PDFEmmanuel Thomas100% (1)
- Jigs FixuresDocument36 pagesJigs FixuresThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- Methods of Mounting of Jobs and Cutting ToolsDocument19 pagesMethods of Mounting of Jobs and Cutting ToolsRaghav L NaikNo ratings yet
- LatheDocument4 pagesLatheAnees Calicut100% (1)
- Operations in TurningDocument8 pagesOperations in Turningcanavarsanayok100% (1)
- 1 Design of Machine Tool DrivesDocument23 pages1 Design of Machine Tool DrivesFurkan Ahmad100% (1)
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion BankFlorence MercyNo ratings yet
- UF6 ManualDocument24 pagesUF6 ManualPhil Ruby Tigers0% (1)
- 4th COTDocument4 pages4th COTMeljean Kalaw CastilloNo ratings yet
- Vasuanand Bba ProjectDocument66 pagesVasuanand Bba ProjectMaster PrintersNo ratings yet
- Construction ProjectsDocument13 pagesConstruction ProjectsMuhammad SafdarNo ratings yet
- Jigs and Fixture Sem III FinalDocument127 pagesJigs and Fixture Sem III Finalnikhil sidNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Day 1 GRADE 8Document2 pagesWeek 2 Day 1 GRADE 8Anonymous yElhvOhPnNo ratings yet
- Boston Consultancy Group Matrix MM101Document8 pagesBoston Consultancy Group Matrix MM101Gift Simau100% (2)
- Intoduction: Tylor's Principle For Gauge DesignDocument13 pagesIntoduction: Tylor's Principle For Gauge DesignDollar Daik100% (1)
- Surface RoughnessDocument17 pagesSurface RoughnessShanmugi VinayagamNo ratings yet
- ComparatorsDocument23 pagesComparatorsShashwat RaiNo ratings yet
- Dies and Its TypesDocument2 pagesDies and Its TypesRajat AhujaNo ratings yet
- Elementary Transmission For Transforming Rotary Into Translatory MotionDocument14 pagesElementary Transmission For Transforming Rotary Into Translatory Motionshreyas jadhavNo ratings yet
- Me 581 Machine Tool Design Section 5 Design of Spindles and Spindle SupportsDocument54 pagesMe 581 Machine Tool Design Section 5 Design of Spindles and Spindle SupportsMlhhemreNo ratings yet
- Murali - Metrology & Measurements Lab ManualDocument30 pagesMurali - Metrology & Measurements Lab ManualsubhashNo ratings yet
- Metrology 1CDocument44 pagesMetrology 1CRadhaMadhavNo ratings yet
- Types of Taper Turning Methods On Lathe Machine: Arul R Ap/MechDocument15 pagesTypes of Taper Turning Methods On Lathe Machine: Arul R Ap/MecharulsivagiriNo ratings yet
- Metrology and Computer Aided Inspection 1 ADocument68 pagesMetrology and Computer Aided Inspection 1 ATanmay SinghalNo ratings yet
- Datum Features: Functional Datum Manufacturing Datum Changing The DatumDocument29 pagesDatum Features: Functional Datum Manufacturing Datum Changing The DatumOrville SutariNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 TurningDocument12 pagesLab 2 TurningLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Metrology 2 - Slip GuagesDocument14 pagesMetrology 2 - Slip GuagesShyam VimalKumarNo ratings yet
- Clamping & Clamping DevicesDocument52 pagesClamping & Clamping DevicesTousif RezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter (5) Di Fsidl Dsidls T Design of Spindles and Spindle SupportsDocument16 pagesChapter (5) Di Fsidl Dsidls T Design of Spindles and Spindle Supportsabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter 3 Design of ClampDocument54 pages3 Chapter 3 Design of ClampKhaled HamdyNo ratings yet
- Flexible FixturingDocument24 pagesFlexible FixturingAbhishek KaushikNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slide Metrology and Inspection - PPT PDFDocument30 pagesLecture Slide Metrology and Inspection - PPT PDFEdo EdgarNo ratings yet
- KEYSDocument21 pagesKEYSAndrea Douglas100% (1)
- Gears & Gear Manufacturing Processes-2Document58 pagesGears & Gear Manufacturing Processes-2Yogesh DewangNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT (Sliding Contact Bearing) PDFDocument3 pagesASSIGNMENT (Sliding Contact Bearing) PDFRakesh Kumar Shukla KEC0% (1)
- Geometrical Tolerancing (GD&T)Document12 pagesGeometrical Tolerancing (GD&T)Kishor kumar BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Latest Report 2Document13 pagesLatest Report 2Piyush BariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Metrology Basics, Elements in Measurements & Line and End StandardsDocument80 pagesUnit 1 - Metrology Basics, Elements in Measurements & Line and End StandardsShayan ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Spur Gear: Aim of The ExperimentDocument5 pagesManufacturing of Spur Gear: Aim of The ExperimentParameshwara MeenaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Visual RealismDocument59 pagesUnit Iii Visual RealismJabin JoeNo ratings yet
- Design of Modern CNC Machines and Mechatronic ElementsDocument37 pagesDesign of Modern CNC Machines and Mechatronic Elementsnagappa talawarNo ratings yet
- Study of Sine BarDocument6 pagesStudy of Sine BarMaria Mehar100% (2)
- Question Bank Sliding Contact BearingsDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank Sliding Contact BearingsShree Prajapati100% (1)
- UNIT II System of FitsDocument30 pagesUNIT II System of FitsSunkeswaram Deva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Gauges KSRDocument38 pagesGauges KSRavutu_kunduruNo ratings yet
- 7 Gauges Wear Tolerance Slide 25Document42 pages7 Gauges Wear Tolerance Slide 25NEERAJ KISHORE PNo ratings yet
- Pakistan: Nation-State, State-Nation or Multinational State?Document12 pagesPakistan: Nation-State, State-Nation or Multinational State?Asif KhanNo ratings yet
- Control Grupos Electrogenos LobatoDocument20 pagesControl Grupos Electrogenos LobatoEdwin Santiago Villegas AuquesNo ratings yet
- SHPL Product Order Form 2021Document4 pagesSHPL Product Order Form 2021anuradha100% (3)
- Bihar-Board-Intermediate-Mathematics-Protect KeyDocument37 pagesBihar-Board-Intermediate-Mathematics-Protect Keyapi-335786032No ratings yet
- User Defined FunctionsDocument67 pagesUser Defined Functionsmohamed aliNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity ReportDocument52 pagesBiodiversity ReportAdrian HudsonNo ratings yet
- Joint Inspection Report FormatDocument2 pagesJoint Inspection Report FormatRAMAKRISHNAN RNo ratings yet
- Pride&PrejudiceDocument88 pagesPride&PrejudiceMà Ř YãmNo ratings yet
- 832Document40 pages832B. MerkurNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets Q1 - SVADocument5 pagesActivity Sheets Q1 - SVAAlma ReynaldoNo ratings yet
- Product Sheet: AutoclaveDocument2 pagesProduct Sheet: AutoclaveISHA ARORANo ratings yet
- L807268EDocument1 pageL807268EsjsshipNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportyousufNo ratings yet
- BDU-BIT-Electromechanical Engineering Curriculum (Regular Program)Document187 pagesBDU-BIT-Electromechanical Engineering Curriculum (Regular Program)beselamu75% (4)
- PointgroupsDocument13 pagesPointgroupsT alameluNo ratings yet
- Timely Hints OctoberDocument5 pagesTimely Hints OctoberDane McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Conjunction and Exposition Text-2Document19 pagesConjunction and Exposition Text-2keyshalaokkiNo ratings yet
- Excel Subhadip NandyDocument9 pagesExcel Subhadip NandyNihilisticDelusionNo ratings yet