Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Frequency Modulation: DT T M K T F
Uploaded by
himeshemraanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Frequency Modulation: DT T M K T F
Uploaded by
himeshemraanCopyright:
Available Formats
www.jntuworld.
com
www.jwjobs.net
Analog Communications
Unit 4
Lecture Notes 28
Frequency Modulation
Frequency modulation is that form of angle modulation in which the instantaneous
frequency fi(t) is varied linearly with the message signal m(t) as shown by
fi(t) = fc + kf m(t)
(1)
the term fc represents the frequency of the unmodulated carrier , and the constant kf
represents the frequency sensitivity of the modulator expressed in hertz per volt .This
assumes that m(t) is a voltage waveform.
Integrating eq.1 with respect to time and multiplying the result by 2 ,we
get
(t)= 2f c t + 2k f
m(t )dt
t
(2)
The frequency modulated wave is therefore described in time domain as
s1 (t ) = Ac cos 2f c t + 2k f
m(t )dt
t
(3)
Where
(2)
k f = nk1
FM can be generated by first integrating m(t) and then using the result as the input to the
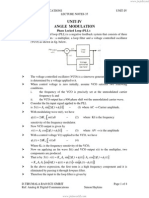
phase modulator as shown in fig.1
Fig 1 Generation of FM Wave using Phase Modulator
T. Kalpana,ECE,GMRIT
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net
Analog Communications
Unit 4
Lecture Notes 28
Fig 1 a)Modulating wave b)Frequency modulated wave c)Derivative of m(t)
d)Phase modulated wave
Fig.1a shows a sinusoidal modulating wave m(t) with 2 full cycles and FM wave
produced by this modulating wave is shown in fig.1b.fig.1c shows the derivative
dm(t)/dt,which consists of original sinusoidal modulating wave shifted in phase by 900
and the desired PM plot is shown in fig.1d.
T. Kalpana,ECE,GMRIT
www.jntuworld.com
You might also like
- Angle ModulationDocument34 pagesAngle ModulationSanjana PulapaNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation Tutorial 1Document23 pagesAngle Modulation Tutorial 1Haider Al RikabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document23 pagesChapter 5Anil RaiNo ratings yet
- Mar 8 THDocument4 pagesMar 8 THEce SudhagarNo ratings yet
- Reference: Communication Systems-Simon Haykin (2001)Document33 pagesReference: Communication Systems-Simon Haykin (2001)Mariella Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation NotesDocument88 pagesAngle Modulation Notesareebarajpoot0453879100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Frequency ModulationDocument88 pagesChapter 4 Frequency ModulationtestNo ratings yet
- Angle ModulationDocument19 pagesAngle Modulationkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document3 pagesHW 3Zero ChengNo ratings yet
- Angle ModulationDocument52 pagesAngle ModulationkshitijNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Angle ModulationDocument2 pagesUnit-Iv Angle ModulationhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Woldia University: Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Chapter ThreeDocument29 pagesWoldia University: Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Chapter ThreemulusewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document60 pagesChapter 4pramit palNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: FM Modulation: Modulation in Which The Angle of The Carrier Wave Is Varied According To The Base-BandDocument33 pagesChapter 3: FM Modulation: Modulation in Which The Angle of The Carrier Wave Is Varied According To The Base-Bandtadepeace23No ratings yet
- PCS LabDocument8 pagesPCS LabSaadat KhanNo ratings yet
- Handout 7: Phase and Frequency ModulationDocument7 pagesHandout 7: Phase and Frequency ModulationRajurajiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Angle ModulationDocument26 pagesModule 4 - Angle ModulationKala Praveen BagadiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Communication Theory - 1 (EC5.203 - Spring 2021) February 7, 2021Document2 pagesAssignment 3: Communication Theory - 1 (EC5.203 - Spring 2021) February 7, 2021Aravind NarayananNo ratings yet
- Angle ModulationDocument22 pagesAngle ModulationManish kumawatNo ratings yet
- Silicon Labs FM TutorialDocument12 pagesSilicon Labs FM TutorialAbbas Bagherifar100% (1)
- 3 Frequency Modulation: High Amplitude High FrequencyDocument25 pages3 Frequency Modulation: High Amplitude High Frequencyram_786No ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-28 Single - Tone ModulationDocument1 pageUnit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-28 Single - Tone ModulationhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation and DemodulationDocument49 pagesAngle Modulation and DemodulationAbdulaziz Al-ShammariNo ratings yet
- Questoes AMDocument7 pagesQuestoes AMDaniel Costa AraújoNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2022-23 BECE304L TH VL2022230500835 ReferenceMaterialI ThuFeb0900 00 00IST2023 AnglemodulationDocument23 pagesWINSEM2022-23 BECE304L TH VL2022230500835 ReferenceMaterialI ThuFeb0900 00 00IST2023 AnglemodulationYaganti pavan saiNo ratings yet
- Angle ModulationDocument12 pagesAngle ModulationMompati LetsweletseNo ratings yet
- 1 8Document97 pages1 8omar9aNo ratings yet
- Generation of FM Waves Indirectly and DirectlyDocument3 pagesGeneration of FM Waves Indirectly and DirectlyhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- 10 Angle ModulationDocument23 pages10 Angle ModulationMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 390gat - 23 Chapter 6Document25 pages390gat - 23 Chapter 6Avinash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- FM Modulation SpectrumDocument13 pagesFM Modulation SpectrumUrmatan MarvinNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2022-23 BECE304L TH VL2022230500822 ReferenceMaterialI ThuFeb0200 00 00IST2023 Module4-AngleModulationDocument24 pagesWINSEM2022-23 BECE304L TH VL2022230500822 ReferenceMaterialI ThuFeb0200 00 00IST2023 Module4-AngleModulationYaganti pavan saiNo ratings yet
- ECE 3202 ch2Document34 pagesECE 3202 ch2fikaduNo ratings yet
- s (t) =A t +2 π k m (t) dt)Document2 pagess (t) =A t +2 π k m (t) dt)Gopolang Jerome TaeyeleNo ratings yet
- Notes 08Document16 pagesNotes 08balkyderNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Frequency Modulation: T) Is Varied Proportionally ToDocument6 pagesExperiment 5: Frequency Modulation: T) Is Varied Proportionally ToRashmi SamantNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Systems IDocument64 pagesAnalog Communication Systems Itadepeace23No ratings yet
- Quiz 0429to0505 SolutionDocument4 pagesQuiz 0429to0505 SolutionDr-Eng Imad A. ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Course Notes AM Ch4Document34 pagesCourse Notes AM Ch4Damien MirindiNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation: Angle Modulation Is Defined As A Process in Which The AngleDocument10 pagesAngle Modulation: Angle Modulation Is Defined As A Process in Which The AngleahasanNo ratings yet
- Freqency Modulation - 3rd P&M - 2019-2020Document7 pagesFreqency Modulation - 3rd P&M - 2019-2020حسن علي جاسمNo ratings yet
- EE1 and ISE1 Communications I: Pier Luigi Dragotti Lecture TwelveDocument11 pagesEE1 and ISE1 Communications I: Pier Luigi Dragotti Lecture TwelveashokkumarNo ratings yet
- Analog Modulation: Part Ii: Angle ModulationDocument76 pagesAnalog Modulation: Part Ii: Angle ModulationkNo ratings yet
- c (t) =100 cos2 π f t .The modulation index is 6Document9 pagesc (t) =100 cos2 π f t .The modulation index is 6Nafeesa SalehNo ratings yet
- Phase and Frequency Modulation Explained: Key Differences and RepresentationsDocument12 pagesPhase and Frequency Modulation Explained: Key Differences and RepresentationsMark manuelNo ratings yet
- Communication System PDFDocument83 pagesCommunication System PDFDibyajyoti SahooNo ratings yet
- Pcs Module 2Document26 pagesPcs Module 2MOHAMMED ZAINNo ratings yet
- ECE 3202-ch2 (2)Document34 pagesECE 3202-ch2 (2)hayatasil19No ratings yet
- FMDocument76 pagesFMNicole Guzman100% (1)
- 6 MMMMDocument44 pages6 MMMMHusamHaskoNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation GuideDocument54 pagesAngle Modulation GuideJan Nicholas TeorimaNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation and Demodulation NotesDocument28 pagesAngle Modulation and Demodulation NotesbalkyderNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Exam Paper T2 PDFDocument7 pagesAnalog Communication Exam Paper T2 PDFvavaNo ratings yet
- EEE 107 Lecture 7 - Angle CW ModulationDocument47 pagesEEE 107 Lecture 7 - Angle CW Modulation許耕立No ratings yet
- Communication Channel ModulationDocument27 pagesCommunication Channel ModulationMd. Fasih Al ZaidNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-30 Narrow-Band FMDocument2 pagesUnit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-30 Narrow-Band FMhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- EC05032Notes 33 PDFDocument5 pagesEC05032Notes 33 PDFhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-34 Zero Crossing DetectorDocument2 pagesUnit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-34 Zero Crossing DetectorhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- AC Lab Material EC05032Notes-35 PDFDocument4 pagesAC Lab Material EC05032Notes-35 PDFhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Generation of FM Waves Indirectly and DirectlyDocument3 pagesGeneration of FM Waves Indirectly and DirectlyhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-29 Spectrum Analysis of Sinusoidal FM WaveDocument2 pagesUnit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-29 Spectrum Analysis of Sinusoidal FM WavehimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- EC05032!Notes 36 PDFDocument2 pagesEC05032!Notes 36 PDFhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Phase Locked Loop: DT T M K TDocument3 pagesPhase Locked Loop: DT T M K ThimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Angle Modulation: N0tes-32 Direct Method of FMDocument2 pagesUnit-Iv Angle Modulation: N0tes-32 Direct Method of FMhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Angle ModulationDocument2 pagesUnit-Iv Angle ModulationhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- EC05032!Notes 34 PDFDocument4 pagesEC05032!Notes 34 PDFhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-28 Single - Tone ModulationDocument1 pageUnit-Iv Angle Modulation: Notes-28 Single - Tone ModulationhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Narrow-Band FM: T NF F J A T SDocument2 pagesNarrow-Band FM: T NF F J A T ShimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- EC05032!Notes 35 PDFDocument7 pagesEC05032!Notes 35 PDFhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- EC05032!Notes 32 PDFDocument3 pagesEC05032!Notes 32 PDFhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- EC05032!Notes 35 PDFDocument7 pagesEC05032!Notes 35 PDFhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Solved Practice Question Set 2 On General Awareness For SSC Combined Graduate Level Exam 2012Document14 pagesSolved Practice Question Set 2 On General Awareness For SSC Combined Graduate Level Exam 2012Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- EC05032!Notes 33 PDFDocument5 pagesEC05032!Notes 33 PDFhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Simulation Reports For EC LabDocument6 pagesSimulation Reports For EC LabhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Series Voltage RegulatorDocument2 pagesSeries Voltage RegulatorhimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- T F T F A T S: Spectrum Analysis of Sinusoidal FM WaveDocument4 pagesT F T F A T S: Spectrum Analysis of Sinusoidal FM WavehimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Jntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 2Document8 pagesJntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 2himeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Simulate and Compare CE Amp Frequency ResponseDocument3 pagesSimulate and Compare CE Amp Frequency ResponsehimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Radar Syllabus BreakdownDocument248 pagesRadar Syllabus Breakdownhimeshemraan100% (1)
- Jntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 2Document8 pagesJntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 2himeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Jntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 4Document4 pagesJntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 4himeshemraanNo ratings yet
- RCDocument3 pagesRChimeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Jntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 3Document6 pagesJntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 3himeshemraanNo ratings yet
- Jntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 1Document15 pagesJntu Kak 2 2 Ece Emtl Set 1himeshemraanNo ratings yet