Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summaryof Trigonometric F N
Uploaded by
Abd El Rahman OmarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summaryof Trigonometric F N
Uploaded by
Abd El Rahman OmarCopyright:
Available Formats
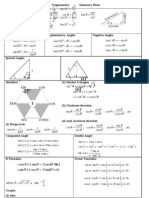
Summary of Trigonometry
Convert degrees to radians
a0 = a
180
Convert radians to degrees
180 0
a (rad ) = a
a 57.2958 0
(rad ) 0.01745a (rad )
Definition of Trigonometric Functions (Rt. )
oppositr
hypotenuse
adjacent
cos A =
hypotenuse
opposite
tan A =
adjacent
sin A =
Definition of Trigonometric Functions (Unit Circle)
hypotenuse
opposite
hypotenuse
sec A =
adjacent
adjacent
cot A =
opposite
csc A =
1
y
1
cos = x sec =
x
y
x
tan =
cot =
x
y
sin = y csc =
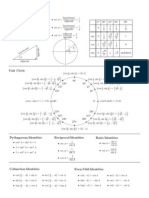
Sign of Trigonometric Functions
Special Points in Unit Circle
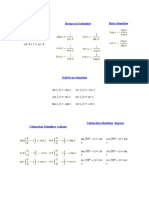
Reciprocal Identities
Pythagorean Identities
Quotient Identities
1
csc
1
cos =
sec
1
tan =
cot
sin + cos = 1
1 + tan 2 = sec 2
tan =
sin =
1
sin
1
sec =
cos
1
cot =
tan
csc =
Inverse Functions
a
b
c
Law of Sine:
=
=
sin A sin B sin C
1 + cot 2 = csc 2
sin
cos
cos
cot =
sin
a 2 = b 2 + c 2 2bc cos A
Law of Cosine: b 2 = a 2 + c 2 2ac cos B
c 2 = a 2 + b 2 2ab cos C
R = [ / 2, / 2]
y = sin 1 x
where x = sin y
D = [1, 1]
y = cos 1 x
where x = cos y
D = [1, 1]
[0, ]
y = tan 1 x
where x = tan y
D = (, )
( / 2, / 2)
y = cot 1 x
where x = cot y
D = (, )
(0, )
y = sec 1 x
where x = sec y
D = (, 1] [1, )
[0, / 2) [ ,3 / 2)
y = csc 1 x
where x = csc y
D = (, 1] [1, )
(0, / 2] ( , / 2]
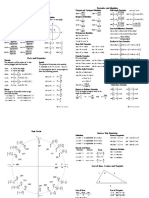
Summary of Trigonometry
Sum and Difference Identities:
sin( ) = sin cos cos sin
cos( ) = cos cos sin sin
tan tan
tan ( ) =
1 tan tan
Double-Angle Identities
sin 2 = 2 sin cos
cos 2 = cos 2 sin 2
= 1 2 sin 2
= 2 cos 2 1
2 tan
tan 2 =
1 tan 2
Weierstrass Substitution
Half-Angle Identities
sin =
sin
2 tan( / 2)
1 + tan 2 ( / 2)
1 tan ( / 2)
1 + tan 2 ( / 2)
2 tan( / 2)
tan =
1 tan 2 ( / 2)
cos =
cos
tan
1 cos
2
1 + cos
2
1 cos
sin
1 cos
=
=
1 + cos 1 + cos
sin
Product-to-Sum Identities
Sum-to-Product Identities
1
[sin( x + y) + sin( x y)]
2
1
cos x sin y = [sin( x + y ) sin( x y )]
2
1
cos x cos y = [cos( x y ) + cos( x + y )]
2
1
sin x sin y = [cos( x y ) cos( x + y )]
2
sin x + sin y = 2 sin
sin x cos y =
1 cos 2
2
1 + cos 2
cos 2 =
2
1 cos 2
tan 2 =
1 + cos 2
sin 2 =
x+ y
x y
cos
2
2
x+ y
x y
sin x sin y = 2 cos
sin
2
2
x+ y
x y
cos y + cos x = 2 cos
cos
2
2
x+ y
x y
cos y cos x = 2 sin
sin
2
2
Reduction Identities: Memory device is (Name follows ESOC, Sign depends on quadrant)
Sign sin
sin n =
2 Sign cos
Sign sin n E
sin n =
2
Sign cos n O
nE
nO
cos n =
2
cos n =
2
tan n =
2
cot n =
2
sec n =
2
csc n =
2
tan n =
2
cot n =
2
sec n =
2
csc n =
2
Summary of Trigonometry
You might also like
- Essential FormulaeDocument16 pagesEssential FormulaeMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- Calculus 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesCalculus 2 Summarydukefvr41No ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet: Formulas and IdentitiesDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet: Formulas and IdentitiesMuzamilNo ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Formula - by B B Susheel KumarDocument14 pagesFormula - by B B Susheel KumarB B Susheel KumarNo ratings yet
- Functions FormulasDocument3 pagesFunctions FormulasmrbubosNo ratings yet
- Math Resources Trigonometric FormulasDocument10 pagesMath Resources Trigonometric FormulasAnonymous j3w8EmJb8No ratings yet
- EquationsDocument17 pagesEquationshasanmt23100% (1)
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Condensed Formula SheetDocument2 pagesTrigonometry Condensed Formula SheetRiza Azari0% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trig Cheat Sheet 1.4Document2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet 1.4agentc0re0% (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Mathematics TrigonometryDocument129 pagesMathematics TrigonometryUdayveerSinghNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Chapter 5 Trigonometric Identities: Reciprocal Identities Even/Odd IdentitiesDocument2 pagesPre-Calculus Chapter 5 Trigonometric Identities: Reciprocal Identities Even/Odd IdentitiesDrew ClaryNo ratings yet
- Mathematics???Document6 pagesMathematics???DEFRON GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Opp Adj Opp Hyp Hyp Adj: Sin Sin Cos Cos Tan TanDocument3 pagesOpp Adj Opp Hyp Hyp Adj: Sin Sin Cos Cos Tan Tanchoosg100% (1)
- Trigonometry Formulas: X X X X X XDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Formulas: X X X X X XMahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- TrigonometruyDocument3 pagesTrigonometruyRitu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities and Inverse Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument6 pagesTrigonometric Identities and Inverse Trigonometric IdentitiesOlaf1234321No ratings yet
- For MuleDocument1 pageFor MuleAleksa992No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)Document4 pagesFormula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)naedkcinNo ratings yet
- sin θ cos θ 1 tan θ 1 cos θ 1 sin θ: Opp. HypDocument2 pagessin θ cos θ 1 tan θ 1 cos θ 1 sin θ: Opp. HypDavid J HarrNo ratings yet
- Ux VX : Função Derivada Da Função Fórmulas de IntegraçãoDocument2 pagesUx VX : Função Derivada Da Função Fórmulas de IntegraçãoJosierBaiottoNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument1 pageFormula RioJorge LópezNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Properties and IdentitiesDocument1 pageTrigonometric Properties and Identitiespra_zara2637No ratings yet
- Trigonometry FormulaesDocument7 pagesTrigonometry FormulaesAshutosh AnandNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet ReducedMritunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Math.lamar - Edu PDF Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesTutorial - Math.lamar - Edu PDF Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedAnonymous vyXcR9No ratings yet
- Trig No Metric FormulasDocument4 pagesTrig No Metric FormulasZee Shan100% (1)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions PDFDocument10 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions PDFJiung WeiNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0Document16 pagesIit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0ARYAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Formulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDocument8 pagesFormulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDiana Carolina DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios:: Institute of Academic ServicesDocument5 pagesTrigonometric Ratios:: Institute of Academic ServicesataaisgreatNo ratings yet
- Formula ListDocument5 pagesFormula ListAritra MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio Trig.Document1 pageFormula Rio Trig.Fredy Rivadeneira LoorNo ratings yet
- Mathematical RelationshipsDocument5 pagesMathematical RelationshipsJuan A RaposoNo ratings yet
- F C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E NtegralDocument2 pagesF C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E NtegralSergio Jimenez ZarzaNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Trigonometric Formulas and RelationshipsDocument6 pagesSolutions: Trigonometric Formulas and RelationshipsPreethiNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo Dif - IntegralDocument4 pagesFormulario Calculo Dif - IntegralRocki R SebastiánNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Identities Reciprocal Identities Ratio IdentitiesDocument3 pagesPythagorean Identities Reciprocal Identities Ratio IdentitiesAbhijeetNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Identities Reciprocal Identities Ratio IdentitiesDocument3 pagesPythagorean Identities Reciprocal Identities Ratio IdentitieskrsnagnaniNo ratings yet
- Math Formula SheetDocument2 pagesMath Formula Sheetrosepettle13No ratings yet
- Trignometric FormulaesDocument4 pagesTrignometric FormulaesanjaliNo ratings yet
- A FormulaDocument2 pagesA FormulaUmesh Rao H NNo ratings yet
- For MuleDocument3 pagesFor Mulerogi93No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document15 pagesUnit 3api-220078930No ratings yet
- Actual Formula Test #1 Test #2 FormulaDocument11 pagesActual Formula Test #1 Test #2 Formulanirakaru123No ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet