Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Equilibria
Equilibria
Uploaded by
Ryantyler130 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pagealevel
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentalevel
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 page Equilibria
Equilibria
Uploaded by
Ryantyler13alevel
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
2.
3 EXERCISE 1 Equilibria
1.
Consider the following exothermic reaction:
4HCl(g) + O2(g) == 2Cl2(g) + 2H2O(g)
State, with a reason, what would happen to the amounts of chlorine and hydrogen
chloride in the system if the following changes were made after equilibrium had
been established in a sealed container:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
2.
For each of the following reactions, state and explain whether a high or low
temperature and a high or low pressure should be used to maximize the yield of
product:
a)
b)
c)
d)
3.
water is removed from the system;
extra oxygen is added to the system;
the volume of the container was reduced;
the temperature of the container was increased;
a catalyst was added.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) == 2SO3(g), H = -ve
PCl5(g) == PCl3(g) + Cl2(g), H = +ve
H2(g) + I2(g) == 2HI(g), H = -ve
HCOOH(l) + CH3OH(l) == HCOOCH3(l) + H2O(l), H = 0
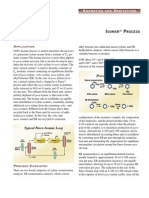
The manufacture of ammonia by the Haber process is an important example of an
industrial process which involves an equilibrium reaction:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ==2NH3(g), H = -ve
The reaction is carried out at 450 oC and 250 atm with an iron catalyst.
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
Give one reason why a higher temperature is not used.
Give one reason why a lower temperature is not used.
Give one reason why a higher pressure is not used.
Give two reasons why a lower pressure is not used.
Explain why a catalyst is used.
You might also like
- Tutorial 5 Equilibrium AnswerDocument4 pagesTutorial 5 Equilibrium AnswerNor AishahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 First LawDocument179 pagesChapter 02 First LawWen Hsiao100% (31)
- Differential Equations Mass PDFDocument27 pagesDifferential Equations Mass PDFDiana Marcela Sierra Varela100% (1)
- Topic 5 Exercise 3 - Changing The Position of EquilibriumDocument1 pageTopic 5 Exercise 3 - Changing The Position of Equilibriumzoyan570No ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Concept and Factors Affecting EquilibriumDocument4 pagesTopic 1 - Concept and Factors Affecting Equilibriumdeela decemberNo ratings yet
- WORK SHEET - Chemical EquilibriumDocument4 pagesWORK SHEET - Chemical EquilibriumAndrej ZafirovikjNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 CHM 271Document11 pagesTutorial 1 CHM 271Fatin IzzatyNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions Chapter 6: Chemical EquilibriumDocument3 pagesRevision Questions Chapter 6: Chemical EquilibriumNajiha TahirNo ratings yet
- Lech AtelierDocument2 pagesLech Atelierjackkingsman19No ratings yet
- 2021 2022 Spring General Chemistry II Study Question Set 6Document2 pages2021 2022 Spring General Chemistry II Study Question Set 6Ahmed ZakyNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium MCDocument43 pagesEquilibrium MCThaarvena Retina100% (1)
- SS 2 Chemistry Theory (2nd Term, 2024)Document2 pagesSS 2 Chemistry Theory (2nd Term, 2024)qasimyoosufNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Practice Exam (Multiple Choice) With Answers PDFDocument8 pagesEquilibrium Practice Exam (Multiple Choice) With Answers PDFJhon Carlo AgpalzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14-ChemicalEquilibriumDocument5 pagesChapter 14-ChemicalEquilibriumKhurram KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Thermochemistry and Thermodynamic - ExerciesDocument20 pagesChapter 4 - Thermochemistry and Thermodynamic - Exerciestran huyNo ratings yet
- 53 Page QuestionsDocument53 pages53 Page QuestionssezNo ratings yet
- SCH4U1 CH 7 ReviewDocument1 pageSCH4U1 CH 7 ReviewRashmi PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 WorkshopDocument3 pagesChapter 13 WorkshopjoangallagherNo ratings yet
- CHE 202 Sample MC Questions Equilibrium 1.1 2010-06-07Document5 pagesCHE 202 Sample MC Questions Equilibrium 1.1 2010-06-07Slavoj ZizekNo ratings yet
- Assignment 151Document5 pagesAssignment 151Hai Xuan DoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Equilibrium WorksheetDocument5 pagesChemistry Equilibrium WorksheetMarkNo ratings yet
- Lower 6 - Tutorial 17Document2 pagesLower 6 - Tutorial 17ronese augustusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Practice QuestionsDocument17 pagesChapter 15 Practice QuestionsKim LeeNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 1 NotesDocument8 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 1 NotesfaratrotiNo ratings yet
- ch16 CompressDocument2 pagesch16 CompressOlsa NdoshaNo ratings yet
- AP Chem CH 13 Practice QuizDocument5 pagesAP Chem CH 13 Practice QuizHasantha PereraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2018Document2 pagesWorksheet 2018joanneNo ratings yet
- 2 Topic 5 Energetics Practice QuestionsDocument14 pages2 Topic 5 Energetics Practice QuestionsLillyNo ratings yet
- Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument28 pagesChemical Thermodynamicscorey6No ratings yet
- 50 Chemistry Questions To Be Covered in Phase 2 (Master Tutors) - 2Document13 pages50 Chemistry Questions To Be Covered in Phase 2 (Master Tutors) - 2Chiluba EzronNo ratings yet
- Marasigan - Problem Set 2Document5 pagesMarasigan - Problem Set 2josephtimbol123No ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics (Or) Thermochemistry Practice PaperDocument9 pagesChemical Energetics (Or) Thermochemistry Practice PaperN. Harsha100% (1)
- LT2 ThermochemDocument3 pagesLT2 ThermochemRenzo AlvizNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document5 pagesProblem Set 2UnitedNationsAveNo ratings yet
- 2020 CHEE2001 Week 10 Tutorial SheetDocument5 pages2020 CHEE2001 Week 10 Tutorial SheetMuntaha ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Midterm 98Document7 pagesMidterm 98dr.ibrahimsalemvpNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium and K: Review Worksheet IDocument2 pagesChemical Equilibrium and K: Review Worksheet ISachinNo ratings yet
- XI Practice Paper (Unit-7)Document2 pagesXI Practice Paper (Unit-7)vapehe1792No ratings yet
- Exam 2 ChemistryDocument7 pagesExam 2 ChemistryEvelynNo ratings yet
- 5 6159233249949255946 PDFDocument5 pages5 6159233249949255946 PDFardini azmirNo ratings yet
- Practice Final Exam - CHEM102 - Spring 2023Document7 pagesPractice Final Exam - CHEM102 - Spring 2023mmmNo ratings yet
- Assessments Lesson 4 Unit 2 Thermochemical EquationsDocument2 pagesAssessments Lesson 4 Unit 2 Thermochemical EquationsCRUZ, Rochelle Joy V.No ratings yet
- 27 MARCH 2020: Assignment 5 Question PaperDocument4 pages27 MARCH 2020: Assignment 5 Question PaperShadreck SandweNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium WorksheetDocument6 pagesEquilibrium WorksheetGiselleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Thermodynamics KeyDocument5 pagesChapter 17 Thermodynamics KeyJanzelle BorbonNo ratings yet
- H For This Reaction From The Following Data: H +177.4 KJ H - 191.2 KJ H - 241.8 KJ H - 43.8 KJDocument4 pagesH For This Reaction From The Following Data: H +177.4 KJ H - 191.2 KJ H - 241.8 KJ H - 43.8 KJSaddy KhanNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry: Equilibrium Multiple Choice: (G) (G) (G) P 4Document3 pagesAP Chemistry: Equilibrium Multiple Choice: (G) (G) (G) P 4Mohammed AbdelhakeemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Level M Couse Question Document PDFDocument46 pagesChemistry Level M Couse Question Document PDFJoe ToubiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseAri Adiantari100% (1)
- HW Solutions AP Ch. 12-13Document25 pagesHW Solutions AP Ch. 12-13kleosi50% (2)
- Tutorial Module Sk025: Chemistry Semester 2 Chapter 2.0: Thermochemistry Unit 2.1: Concept of EnthalpyDocument7 pagesTutorial Module Sk025: Chemistry Semester 2 Chapter 2.0: Thermochemistry Unit 2.1: Concept of EnthalpyMUHAMMAD IMRONNo ratings yet
- Sample Quiz 3Document2 pagesSample Quiz 3elliott.rillstoneNo ratings yet
- Week 26 Homework - Equilibrium 2012Document1 pageWeek 26 Homework - Equilibrium 2012zoxen0No ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes Worksheet 234c2a8Document2 pagesEnthalpy Changes Worksheet 234c2a8spengappNo ratings yet
- ThermoChemistry ProblemsDocument4 pagesThermoChemistry ProblemsMeruert KarimNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument15 pagesChemical EquilibriumRuchi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Consider The Reaction H2 (G) + 12 O2 (G) H2O (L) Delta H - 285.84 KJmol. How Many Grams of Hydrogen Gas Are Needed To ProduceDocument1 pageConsider The Reaction H2 (G) + 12 O2 (G) H2O (L) Delta H - 285.84 KJmol. How Many Grams of Hydrogen Gas Are Needed To ProduceAntonio Hernando MañeruNo ratings yet
- U10 Packet 2022 Rates - EquilDocument9 pagesU10 Packet 2022 Rates - EquiliramtahiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 ThermochemistryDocument6 pagesChapter 9 ThermochemistryMohammad AfifNo ratings yet
- Cbse Syllabus For Class 12 Chemistry Download With Blue PrintDocument9 pagesCbse Syllabus For Class 12 Chemistry Download With Blue PrintDouglas BeachNo ratings yet
- Applied Catalysis A, General: SciencedirectDocument15 pagesApplied Catalysis A, General: Sciencedirectcholila_tamzysiNo ratings yet
- Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53 (2014) 18526 18538Document13 pagesInd. Eng. Chem. Res. 53 (2014) 18526 18538Shabih Ul HasanNo ratings yet
- 06c5 File PDFDocument3 pages06c5 File PDFMakhdum Muhardiana PutraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1004954106601341 Main PDFDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S1004954106601341 Main PDFTan EvonNo ratings yet
- FORM - C1 Council of Scientific and Industrial Research HumanDocument2 pagesFORM - C1 Council of Scientific and Industrial Research HumanvenkatathrinNo ratings yet
- Eth 41542 02Document316 pagesEth 41542 02Tetrahedro AndrésNo ratings yet
- BASF Catalyst O3-81 For N2O DecompositionDocument2 pagesBASF Catalyst O3-81 For N2O DecompositionTony ColetteNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenation of ButynediolDocument15 pagesHydrogenation of ButynediolangelofgloryNo ratings yet
- Adebajo - Methylation of Benzene With MethanolDocument8 pagesAdebajo - Methylation of Benzene With MethanolWilly DinataNo ratings yet
- Turbocharged Engines PDFDocument72 pagesTurbocharged Engines PDFVeler VelericNo ratings yet
- B e Mechanicalengineering1stto8thseDocument388 pagesB e Mechanicalengineering1stto8thseAnshuNo ratings yet
- Reduced Syllabus of JEE Main 2024 - Chemistry-1698910649896Document8 pagesReduced Syllabus of JEE Main 2024 - Chemistry-1698910649896Ryaan MansuriNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument8 pagesChemical KineticsHosam Hasan Abd ElhadyNo ratings yet
- Bullnyacadmed00592 0033Document13 pagesBullnyacadmed00592 0033stefpravlibitNo ratings yet
- 2 1 The Diagrams Show Four Different Methods of Collecting GasesDocument12 pages2 1 The Diagrams Show Four Different Methods of Collecting GasesMujeeb SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Catalytic LEL SensorsDocument9 pagesCatalytic LEL Sensorsvibhor_748408347No ratings yet
- Ozone DecompositionDocument13 pagesOzone DecompositionLad SlasNo ratings yet
- Green DieselDocument10 pagesGreen DieselJimena HdzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 6 NotesCarleyNo ratings yet
- Cjce 22656Document6 pagesCjce 22656Tua HalomoanNo ratings yet
- Reduction Research PaperDocument3 pagesReduction Research PaperUdai PratapsinghNo ratings yet
- CHM 624 Advance Organic Chemistry: ReductionsDocument29 pagesCHM 624 Advance Organic Chemistry: ReductionsJohan DaniyalNo ratings yet
- Topic - 17 - Past - Papers MarkschemeDocument10 pagesTopic - 17 - Past - Papers MarkschemeMahmoud Sameh-Abdel-LateefNo ratings yet
- Lecture IntroductionDocument9 pagesLecture IntroductionTejasv RajputNo ratings yet
- 023 Catalytic Cracking ReportDocument10 pages023 Catalytic Cracking ReportSalman HassanNo ratings yet
- METALLOBIMOLECULESDocument4 pagesMETALLOBIMOLECULESRAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics +Document22 pagesChemical Kinetics +LaraStrbacNo ratings yet
- 035 GUJARATI NIKUNJ I Green Solvent PDFDocument15 pages035 GUJARATI NIKUNJ I Green Solvent PDFkocixa9No ratings yet