0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pagesSeries Convergence Tests Overview
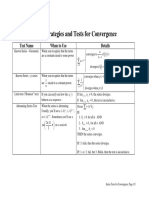
This document provides an overview of several common tests for determining if an infinite series converges or diverges, including:
1) The geometric series test, integral test, p-series test, comparison test, and limit comparison test, which can be used when terms follow specific patterns.
2) The absolute convergence test, ratio test, and alternating series test, applicable to broader classes of series.
3) Examples are given for each test to illustrate their use.
Uploaded by
Serdar BilgeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pagesSeries Convergence Tests Overview
This document provides an overview of several common tests for determining if an infinite series converges or diverges, including:
1) The geometric series test, integral test, p-series test, comparison test, and limit comparison test, which can be used when terms follow specific patterns.
2) The absolute convergence test, ratio test, and alternating series test, applicable to broader classes of series.
3) Examples are given for each test to illustrate their use.
Uploaded by
Serdar BilgeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd