Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Column Buckling
Column Buckling
Uploaded by
AbdullahMofarrah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pages123
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document123
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesColumn Buckling
Column Buckling
Uploaded by
AbdullahMofarrah123
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
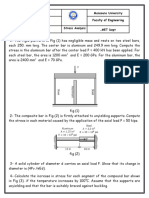
Buckling of columns
Columns fail by buckling when their critical load is reached. Long columns can be analysed with
the Euler column formula
F = n 2 E I / L2 (1)
where
F = allowable load (lb, N)
n = factor accounting for the end conditions
E = modulus of elastisity (lb/in2, Pa (N/m2))
L = length of column (in, m)
I = Moment of inertia (in4, m4)
Factor Counting for End Conditions
column pivoted in both ends : n = 1
both ends fixed : n = 4
one end fixed, the other end rounded : n = 2
one end fixed, one end free : n = 0.25
Example - A Column Fixed in both Ends
An column with length 5 m is fixed in both ends. The column is made of an Aluminium I-beam 7
x 4 1/2 x 5.80 with a Moment of Inertia iy = 5.78 in4. The Modulus of Elasticity of aluminum is 69
GPa (69 109 Pa) and the factor for a column fixed in both ends is 4.
The Moment of Inertia can be converted to metric units like
Iy = 5.78 in4 (0.0254 m/in)4
= 241 10-8 m4
The Euler buckling load can then be calculated as
F = 4 2 (241 10-8 m4) (69 109 Pa) / (5 m)2
= 262594 N
= 263 kN
You might also like
- Preliminary Structural DesignDocument8 pagesPreliminary Structural Designaikaless100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Electric MotorsDocument40 pagesFundamentals of Electric Motorscallsandhya100% (5)
- StormmgmtDocument22 pagesStormmgmtAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 COLUMNSDocument9 pagesChapter 7 COLUMNSPraveen Kumar RNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- 14 The Principle of Lever (TM)Document4 pages14 The Principle of Lever (TM)Ranjith S WarrierNo ratings yet
- Applications of Differential Equations in Engineering CivilDocument5 pagesApplications of Differential Equations in Engineering CivilWilliam jairo sanchez100% (1)
- Lect05 - Buckling of ColumnsDocument18 pagesLect05 - Buckling of Columnsabdiaziz100% (1)
- Buckling of Strut ReportDocument19 pagesBuckling of Strut ReportEsyad E-chad50% (2)
- BEAMANAL (Metric) Con Perfiles ArcelorMittalDocument81 pagesBEAMANAL (Metric) Con Perfiles ArcelorMittalNELSONHUGONo ratings yet
- Cold-Formed Steel MembersDocument19 pagesCold-Formed Steel MembersLiviu IonNo ratings yet
- Precast Concrete Box CulvertDocument1 pagePrecast Concrete Box CulvertAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Columns: Factor Counting For End ConditionsDocument3 pagesBuckling of Columns: Factor Counting For End ConditionsAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Buckling of PipeDocument3 pagesBuckling of PipeAndrew AlexNo ratings yet
- Buckling Force (Euler's Column Formula)Document2 pagesBuckling Force (Euler's Column Formula)iskandarNo ratings yet
- Start Download: Euler's Column FormulaDocument2 pagesStart Download: Euler's Column FormulaTrushar GhosalkarNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering, ISM Dhanbad Structural Analysis-I Practical ManualDocument3 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering, ISM Dhanbad Structural Analysis-I Practical ManualanpyaaNo ratings yet
- Som Unit III 2 Mark & 8 Mark QBDocument64 pagesSom Unit III 2 Mark & 8 Mark QBkumaraguru SNo ratings yet
- A Simple Model For The Fire Resistance of Axially-Loaded Members According To Eurocode 3Document21 pagesA Simple Model For The Fire Resistance of Axially-Loaded Members According To Eurocode 3Lyes KhNo ratings yet
- Materials Selection in Mechanical Design Third Edition-A3Document2 pagesMaterials Selection in Mechanical Design Third Edition-A3Martin de la SotaNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of The Steel Coloumn: ReferencesDocument4 pagesStructural Design of The Steel Coloumn: ReferencesAsitha Chinthaka GunaratneNo ratings yet
- Som Unit IvDocument25 pagesSom Unit Ivsmg26thmayNo ratings yet
- "Beamanal" - Single-Span and Continuous-Span Beam AnalysisDocument4 pages"Beamanal" - Single-Span and Continuous-Span Beam AnalysisRonald Rusbell Madera ArnaoNo ratings yet
- Finding The Buckling Load of Non-Uniform Columns Using The Iteration Perturbation MethodDocument6 pagesFinding The Buckling Load of Non-Uniform Columns Using The Iteration Perturbation MethodAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Elastic Buckling of Single-Stepped Columns With End and Intermediate Axial LoadsDocument13 pagesElastic Buckling of Single-Stepped Columns With End and Intermediate Axial Loadsmaximo.adhavNo ratings yet
- 03 05 2014 DM CivilDocument25 pages03 05 2014 DM CivilPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Contstruction Materials TestingDocument13 pagesContstruction Materials TestingVanessa ModanzaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document47 pagesUnit 2Anbarasan Sivaraj100% (1)
- Design of Steel Beam (LRFD, Load and Resistance Factor Design)Document5 pagesDesign of Steel Beam (LRFD, Load and Resistance Factor Design)surajoffshoreNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering: Lab ManualDocument30 pagesCivil Engineering: Lab ManualSaurabh SahuNo ratings yet
- Movement, Forces, and Stresses Associated With Combination Tubing Strings Sealed in PackersDocument14 pagesMovement, Forces, and Stresses Associated With Combination Tubing Strings Sealed in PackersProsper100% (1)
- Tutorial 1Document1 pageTutorial 1Tara Chandra PanjiyarNo ratings yet
- Transformers PDFDocument30 pagesTransformers PDFMichael Williams100% (1)
- Materiaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter5Document34 pagesMateriaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter5ahmed11 engyemenNo ratings yet
- 2E4B BucklingDocument4 pages2E4B BucklingMohd Ridzuan Ahmad100% (1)
- Lecture 11Document8 pagesLecture 11hasanNo ratings yet
- Mechancs of SolidsDocument4 pagesMechancs of SolidsParthipan JayaramNo ratings yet
- Simple Model For Dynamic Analysis of Cable Supported StructuresDocument9 pagesSimple Model For Dynamic Analysis of Cable Supported StructuresOrvin RommelNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis AssignmentDocument3 pagesStructural Analysis AssignmentPalaka RahulNo ratings yet
- 3.strength of MaterialsDocument6 pages3.strength of MaterialsNandhini NallasamyNo ratings yet
- DeflectionDocument9 pagesDeflectionXet FatNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method (FEM) : Course Code: NTME 637Document19 pagesFinite Element Method (FEM) : Course Code: NTME 637Nurul FaizahNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1Document2 pagesSheet - 1Abdel Hamied EbrahemNo ratings yet
- Floating Piers Modulation To Provides Static Stability: M. Shahrabi, K. Bargi, I. SeyfipoorDocument6 pagesFloating Piers Modulation To Provides Static Stability: M. Shahrabi, K. Bargi, I. Seyfipoorapk1111985No ratings yet
- Effect of Tower Stiffness On Four-Span Suspension Bridges: Dong-Ho CHOI Sun Gil GWON Ho-Sung NADocument4 pagesEffect of Tower Stiffness On Four-Span Suspension Bridges: Dong-Ho CHOI Sun Gil GWON Ho-Sung NA정주호No ratings yet
- Regarding To Buckling of Pipelines Subject To Axial Loading - Taylor & GainDocument6 pagesRegarding To Buckling of Pipelines Subject To Axial Loading - Taylor & Gainmarciojunior1No ratings yet
- Problem Set #11 1.050 Solid Mechanics Fall 2004Document2 pagesProblem Set #11 1.050 Solid Mechanics Fall 2004Anthony HouseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document37 pagesChapter 4Arun SharmaNo ratings yet
- CE6402-Strength of Materials PDFDocument12 pagesCE6402-Strength of Materials PDFSathz FlynnNo ratings yet
- ARCHDocument25 pagesARCHLa Mere ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions-Euler's Theory For Columns: Sol. 78.5 KN, 19.62 KN, 313.94 KN, 156. 96 KNDocument2 pagesPractice Questions-Euler's Theory For Columns: Sol. 78.5 KN, 19.62 KN, 313.94 KN, 156. 96 KNPrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- 784Document67 pages784vedant hiwarkarNo ratings yet
- Farabi - Dynamicstudyofat - Dynamicstudyofat 50645235Document5 pagesFarabi - Dynamicstudyofat - Dynamicstudyofat 50645235Anonymous 80p9OVNo ratings yet
- Buckling of ColumnsDocument6 pagesBuckling of ColumnsPradeep Jayasinghe100% (1)
- Wind Loading of A Paraboloidal Antenna Dish Supported On A Telescopic Extendable Mast byDocument7 pagesWind Loading of A Paraboloidal Antenna Dish Supported On A Telescopic Extendable Mast byklomps_jrNo ratings yet
- Chapt 02 Lect06Document7 pagesChapt 02 Lect06Shanmukha SundaramNo ratings yet
- Beam AnalDocument7 pagesBeam Analgercho23No ratings yet
- Buckling and Postbuckling of A Long-Hanging Elastic Column Due To A Bottom LoadDocument4 pagesBuckling and Postbuckling of A Long-Hanging Elastic Column Due To A Bottom LoadarjunNo ratings yet
- PICTURE D.1 The Experiment of Moment Distribution CoefficientDocument9 pagesPICTURE D.1 The Experiment of Moment Distribution CoefficientRaihan Alisha NabilaNo ratings yet
- Buckling of StrutsDocument6 pagesBuckling of StrutsMohamed Zamri0% (1)
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Important Qualities of A Project Leader:: The Following Are TheDocument1 pageImportant Qualities of A Project Leader:: The Following Are TheAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Important Qualities of A Project Leader:: The Following Are TheDocument1 pageImportant Qualities of A Project Leader:: The Following Are TheAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Supplies Grade 8 Supplies Grade 9 Supplies Art SuppliesDocument1 pageGrade 7 Supplies Grade 8 Supplies Grade 9 Supplies Art SuppliesAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Home Point Creation Tool Default Layer - Select Proper Layer Type, Then Point Creation Select As BelowDocument1 pageHome Point Creation Tool Default Layer - Select Proper Layer Type, Then Point Creation Select As BelowAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Notable Case Potential Conflict of Interest Unevenly Weighted Recruitment ProcessDocument1 pageNotable Case Potential Conflict of Interest Unevenly Weighted Recruitment ProcessAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Practice Test #1Document2 pagesPractice Test #1AbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Alignment: 7.5.1 Compound CurvesDocument1 pageHorizontal Alignment: 7.5.1 Compound CurvesAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Point Extraction From SurfaceDocument1 pagePoint Extraction From SurfaceAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Alignment: 7.5.1 Compound CurvesDocument1 pageHorizontal Alignment: 7.5.1 Compound CurvesAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Alignment: 7.5.1 Compound CurvesDocument1 pageHorizontal Alignment: 7.5.1 Compound CurvesAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Stairs Design Considerations 3.1 General: Parameters Values Comments/Reference S Design LoadsDocument2 pagesOutdoor Stairs Design Considerations 3.1 General: Parameters Values Comments/Reference S Design LoadsAbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet
- Box Culvert 4'x3' Thru 12'x12' ASTM C-1433Document3 pagesBox Culvert 4'x3' Thru 12'x12' ASTM C-1433AbdullahMofarrahNo ratings yet