Professional Documents
Culture Documents
128ac5fc 446
Uploaded by
Prasanth SoundappanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
128ac5fc 446
Uploaded by
Prasanth SoundappanCopyright:
Available Formats
4 4 6 METALLOGRAPHY
The mean grain diameter d is obtained as follows:
d (mm) = {Af2 = i
(6-21)
(NAy
The ASTM grain size number G can be calculated from NA (no. of grains per
square millimeter) using the following relationship:
log NA
G = - ^ ^ - 2.95
[log 2]
or,
G = [3.322 log NA] - 2.95
(6-22)
Values for d, A, and A^ as a function of G are listed in cols. 2,6, and 8 of Table 6-5.
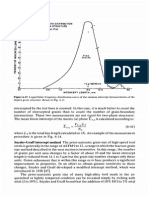
Figure 6-8 provides an example of the Jeffries procedure. In performing the grain
count, it is best to mark off the grains as they are counted in order to obtain an
accurate count. Several randomly chosen areas should be selected and measured,
and the average calculated. In most work, the grain size number is rounded to the
nearest one-half unit.
Triple-point count method Euler's Law, as described by Smith [44], can also be
used to determine grain size, although the method is used infrequently. Grainboundary triple points P within a known area are counted. If a quadruple point,
i.e., a 4-ray grain junction, is observed, it is counted as two units. The number of
grains per unit area, JY^, is given by the following relationship:
772 + 1
NA =
AT
(6-23)
where AT is the total measurement area at IX. The ASTM grain size can be
estimated by the triple-point method, as shown in Figure 6-9.
If either the Jeffries or the triple-point count method are used to estimate the
number of grains per square inch at 100X rather than the number per square
millimeter at IX, the ASTM grain size number can be calculated from the
following:
G =
+ 1
(6-24)
0.301
where NA is the number of grains per square inch at 100X. Again, the value of G is
generally rounded to the nearest one-half unit. If NA has been determined in the
traditional manner (square millimeters at IX), Eq. (6-22) is used to calculate G.
If the triple-point count technique is used at a magnification M other than
100X to determine the number of grains per square inch at the magnification of the
micrograph [substitute the area of the test grid itself for the test grid area
computed to IX, AT, in Eq. (6-23)], this value can be converted to the number per
square inch at 100X by the following relationship:
/ M\2
2
2 X
^(lOOX.in ) - NA(M, in ) (TTJ^J
(6"25)
You might also like
- 2, Is Divided by The Test Grid Area Computed at The PhotographDocument1 page2, Is Divided by The Test Grid Area Computed at The PhotographPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- C37b3eab 459Document1 pageC37b3eab 459Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Material CharacterisationDocument1 pageMaterial CharacterisationPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Figure 6-9 Example of Grain Size Determination by The Triple-Point Count Method and Comparison ToDocument1 pageFigure 6-9 Example of Grain Size Determination by The Triple-Point Count Method and Comparison ToPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 10 - Grain Size MeasurementDocument27 pages10 - Grain Size MeasurementRohib RohibNo ratings yet
- 4 6 0 Metallography: Fracture Grain Size For High-Hardness, Relatively Brittle Steels, The Prior-AusteniteDocument1 page4 6 0 Metallography: Fracture Grain Size For High-Hardness, Relatively Brittle Steels, The Prior-AustenitePrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- ECE 2306 NOTES I Jan2014Document22 pagesECE 2306 NOTES I Jan2014TinaNo ratings yet
- Steel Grain Size CalculationDocument17 pagesSteel Grain Size CalculationtechneoNo ratings yet
- Zdolnosc Maszyny Sugi-94-259 BonarDocument10 pagesZdolnosc Maszyny Sugi-94-259 BonarAndrzej JasieńskiNo ratings yet
- Algorithms in UniModBase Information System For Determine Rosin-Rammler and Gaudin-Shumann Equations of Particle Size Distribution Using Regression AnalysisDocument12 pagesAlgorithms in UniModBase Information System For Determine Rosin-Rammler and Gaudin-Shumann Equations of Particle Size Distribution Using Regression Analysissaeedullah81No ratings yet
- Earth Works ContinuationDocument23 pagesEarth Works ContinuationErasmos AffulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Areas and VolumesDocument35 pagesChapter 6 Areas and Volumesdusamouscrib2014No ratings yet
- C2005 Ukur Kejuruteraan UNIT2Document27 pagesC2005 Ukur Kejuruteraan UNIT2Jeremiah LubashNo ratings yet
- Physics Diameter ExperimentDocument4 pagesPhysics Diameter ExperimentAryana TkaNo ratings yet
- A Purposive Sampling Scheme For Precision AgricultureDocument9 pagesA Purposive Sampling Scheme For Precision AgricultureScary CreaturesNo ratings yet
- Ece2306 Surveying IIIDocument65 pagesEce2306 Surveying IIIInfinity Architectural design technologistNo ratings yet
- Jeffries Planimetric Method The Planimetric Method Developed by Jeffries HasDocument1 pageJeffries Planimetric Method The Planimetric Method Developed by Jeffries HasPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- LESSON 18 Land Leveling MethodsDocument9 pagesLESSON 18 Land Leveling MethodsMegaNo ratings yet
- Appendix A-ShapeDocument10 pagesAppendix A-ShapeAhmadMoaazNo ratings yet
- Plain & Reinforced Concrete-1: Sieve AnalysisDocument17 pagesPlain & Reinforced Concrete-1: Sieve AnalysishzwchNo ratings yet
- Metallography Experiment ReportDocument8 pagesMetallography Experiment ReportAMINANo ratings yet
- Activity 2 #1Document2 pagesActivity 2 #1Jireh RiveraNo ratings yet
- The D2star Table Exposed - GruskaDocument6 pagesThe D2star Table Exposed - Gruskatehky63No ratings yet
- CuboDocument14 pagesCuboapi-397491176No ratings yet
- CH Simple InferenceDocument15 pagesCH Simple InferenceSoohyung LeeNo ratings yet
- Intro To Stereo Logy Grain SizeDocument64 pagesIntro To Stereo Logy Grain SizeRaistlin1No ratings yet
- Quantitative Microscopy 4 6 7Document1 pageQuantitative Microscopy 4 6 7Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Paper2 Scheme Physics Form4 SBP 2007 Mid YearDocument7 pagesPaper2 Scheme Physics Form4 SBP 2007 Mid YearruslawatiNo ratings yet
- Determination of YoungDocument4 pagesDetermination of Youngkhats8465683No ratings yet
- sm8 116Document2 pagessm8 116Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- GMH 02 NoRestrictionDocument5 pagesGMH 02 NoRestrictionKarma Pema DorjeNo ratings yet
- Java 1Document18 pagesJava 1Sasa LeungNo ratings yet
- Time Saving DesignDocument22 pagesTime Saving DesignViswanadh OngoluNo ratings yet
- Strassen AlgorithmDocument4 pagesStrassen AlgorithmMahesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Problems: Centroids and Distributed LoadsDocument5 pagesProblems: Centroids and Distributed LoadsTommyVercettiNo ratings yet
- ChangesDocument22 pagesChangesslobakrajinaNo ratings yet
- W.B Fundamentals of SurveyingV 1Document92 pagesW.B Fundamentals of SurveyingV 1jicelaNo ratings yet
- Offsets at Irregular IntervalsDocument16 pagesOffsets at Irregular IntervalsRenjith S AnandNo ratings yet
- Radiative Heat Transfer Evaluation in Complex Enclosure Using Zonal MethodDocument7 pagesRadiative Heat Transfer Evaluation in Complex Enclosure Using Zonal MethodStacy WilsonNo ratings yet
- Grain Size Determination: 1. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesGrain Size Determination: 1. ObjectiveAMINANo ratings yet
- Project 3 - MathemagicianDocument3 pagesProject 3 - MathemagicianWaka WakaNo ratings yet
- Pub 1440Document8 pagesPub 1440kapilnandwanaNo ratings yet
- Stat 512 Homework 6 SolutionDocument6 pagesStat 512 Homework 6 SolutionaverysloaneNo ratings yet
- Matrix Square Root Computation AlgorithmDocument12 pagesMatrix Square Root Computation AlgorithmdoraemonminiNo ratings yet
- Ray TracingDocument5 pagesRay TracinglaptopbagNo ratings yet
- Surveying m5Document23 pagesSurveying m5Er Anoop SinghNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Prelim 1Document57 pagesEngineering Drawing Prelim 1chienikolaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Work BengDocument20 pagesEarth Work BengAlemi HerbertNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Estimation of α from the sample range. The sample range, usually denoted by w, is theDocument1 page8.3 Estimation of α from the sample range. The sample range, usually denoted by w, is theRanniBps-ErlNo ratings yet
- Fast Mean Filtering Technique (FMFT) : S. Rakshit, A. Ghosh, B. Uma ShankarDocument8 pagesFast Mean Filtering Technique (FMFT) : S. Rakshit, A. Ghosh, B. Uma ShankarNavdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- An Example of Application of The Geostatistics Approach Using The GS+ SoftwareDocument17 pagesAn Example of Application of The Geostatistics Approach Using The GS+ SoftwareRossana CairaNo ratings yet
- TraverseMercator-RedFearns (GeoToGrid)Document5 pagesTraverseMercator-RedFearns (GeoToGrid)ihwan n hNo ratings yet
- Astm 112Document45 pagesAstm 112Vajid Madathil100% (1)
- C3 MEI A-Level Maths CourseworkDocument18 pagesC3 MEI A-Level Maths CourseworkMaurice Yap100% (1)
- PE 14 VariabilityDocument6 pagesPE 14 VariabilityAhmed Abdullah NoorNo ratings yet
- Land Grading Survey and Design: Figure 4.1: Grid Pattern Used For Staking A Field Which Is To Be Graded (A.M. Michael)Document5 pagesLand Grading Survey and Design: Figure 4.1: Grid Pattern Used For Staking A Field Which Is To Be Graded (A.M. Michael)tizazuNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering & Technology Peshawar: Name Reg No: Depat: Semseter: Quiz: Subject: TeacherDocument10 pagesUniversity of Engineering & Technology Peshawar: Name Reg No: Depat: Semseter: Quiz: Subject: TeacherATIF KHANNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Statistical Inference: A Computational ApproachFrom EverandFundamental Statistical Inference: A Computational ApproachNo ratings yet
- Building Material Estimates and Rates Build Up: Second EditionFrom EverandBuilding Material Estimates and Rates Build Up: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Jeffries Planimetric Method The Planimetric Method Developed by Jeffries HasDocument1 pageJeffries Planimetric Method The Planimetric Method Developed by Jeffries HasPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Table 6-8 Grain Size Analysis by The Saltykov Area Method:, D, and S (D) - All Methods Produced Higher NDocument1 pageTable 6-8 Grain Size Analysis by The Saltykov Area Method:, D, and S (D) - All Methods Produced Higher NPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 19c2ccd0 462Document1 page19c2ccd0 462Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 128ac5fc 446Document1 page128ac5fc 446Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Microscopy 4 4 1Document1 pageQuantitative Microscopy 4 4 1Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 6-7.4 Summary: Grain Size Analysrs Saltykov Area MethodDocument1 page6-7.4 Summary: Grain Size Analysrs Saltykov Area MethodPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 1f346bb9 472Document1 page1f346bb9 472Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Microscopy 4 6 7Document1 pageQuantitative Microscopy 4 6 7Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Nonequiaxed Grains When The Grain Shape Is Noticeably Distorted, Grain SizeDocument1 pageNonequiaxed Grains When The Grain Shape Is Noticeably Distorted, Grain SizePrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 468 Metallography: Table 6-7 Basic Information For The Saltykov Area MethodDocument1 page468 Metallography: Table 6-7 Basic Information For The Saltykov Area MethodPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 6-6.6 Summary: Quantitative Microscopy 4 3 5Document1 page6-6.6 Summary: Quantitative Microscopy 4 3 5Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Max X: Quantitative Microscopy 4 6 9Document1 pageMax X: Quantitative Microscopy 4 6 9Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 4 6 0 Metallography: Fracture Grain Size For High-Hardness, Relatively Brittle Steels, The Prior-AusteniteDocument1 page4 6 0 Metallography: Fracture Grain Size For High-Hardness, Relatively Brittle Steels, The Prior-AustenitePrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 670c8c2c 463Document1 page670c8c2c 463Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- RM-H-R: Intercept Length Distribution-Duplex Grain StructureDocument1 pageRM-H-R: Intercept Length Distribution-Duplex Grain StructurePrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Snyder-Graff Intercept Method The Prior-Austenite Grain Size of High-Speed ToolDocument1 pageSnyder-Graff Intercept Method The Prior-Austenite Grain Size of High-Speed ToolPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Figure 6-11 Example of A Well-Dispersed Duplex Grain Structure in A Low-Carbon Steel (150 X, EtchedDocument1 pageFigure 6-11 Example of A Well-Dispersed Duplex Grain Structure in A Low-Carbon Steel (150 X, EtchedPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Duplex Grain Structures It Is Not Uncommon To Observe Duplex Grain Structures inDocument1 pageDuplex Grain Structures It Is Not Uncommon To Observe Duplex Grain Structures inPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Sodium Picrate - Boiling 2% Nital: Quantitative Microscopy 4 3 9Document1 pageAlkaline Sodium Picrate - Boiling 2% Nital: Quantitative Microscopy 4 3 9Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 29709e37 449Document1 page29709e37 449Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- c6c7b65f 461Document1 pagec6c7b65f 461Prasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Standard Chart Methods The 1930 Revision of ASTM Specification E2 ContainedDocument1 pageStandard Chart Methods The 1930 Revision of ASTM Specification E2 ContainedPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- 6-7.2 Grain Size Measurement: 4 3 6 MetallographyDocument1 page6-7.2 Grain Size Measurement: 4 3 6 MetallographyPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet
- Delineation of Grain Boundaries Methods To Reveal Austenite Grain Structures inDocument1 pageDelineation of Grain Boundaries Methods To Reveal Austenite Grain Structures inPrasanth SoundappanNo ratings yet