Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Forces: SI Unit Vector Quantity
Uploaded by
Sharuvindan NairOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Forces: SI Unit Vector Quantity
Uploaded by
Sharuvindan NairCopyright:
Available Formats
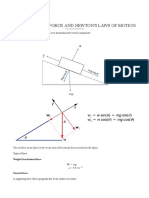
FORCES
A force can be a push or a pull. A force acting on a body tend to produce a change in
velocity or acceleration of the body.
SI unit of force is the newton (N). It is a vector quantity
Whenever we are pushing, pulling, lifting, bending, twisting, tearing, stretching or
squeezing, we are exerting a force.
Force can:
make a stationary body move
change the speed of a body
change the direction of motion of a body
Newtons 1st law of motion: If no external for is acting on it, an object will, if stationary,
remain stationary, and if moving, keep moving at a steady speed in the same straight line
Newtons 2nd law of motion: F = m a -acceleration is proportional to the force, and
inversely proportional to mass
Newtons 3rd law of motion: if object A exerts a force on object B, then object B will
exert an equal but opposite force on object A. To every action there is an equal but
opposite reaction
Question 1:
Question 2:
Question 3 :
Hookes Law
Hookes Law: springs extend in proportion to load, as long as they are under their
proportional limit.
Load (N) = spring constant (N/mm) x extension (mm)
F=kx
Limit of proportionality: point at which load and extension are no longer
proportional
Elastic limit: point at which the spring will not return to its original shape after
being stretched
Question 1:
The original length of a spring A spring is 20 cm long when a load of 10 N is hanging
from it.
Calculate the spring constant?
The length and 30 cm long when a load of 20 N is hanging from it.
TURNING EFFECTS
You might also like
- Unit-2 Force and NLMDocument6 pagesUnit-2 Force and NLMMohit ChokniwalNo ratings yet
- Assign Law of MotionDocument2 pagesAssign Law of MotionRodesa Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: 1 Grading Grade 8 "Remediation"Document6 pagesEarth Science: 1 Grading Grade 8 "Remediation"Shane Catherine BesaresNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument27 pagesBasic ConceptsowenNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of MotionDocument1 pageNewton Laws of MotionTom BombadilNo ratings yet
- Matter and Forces: Department of Education University of Mianwali, MianwaliDocument13 pagesMatter and Forces: Department of Education University of Mianwali, MianwaliSardar Safi Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Forces and Movement (Push, Pull, Fast, Slow and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Physics Books EditionFrom EverandForces and Movement (Push, Pull, Fast, Slow and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Physics Books EditionNo ratings yet
- Physics Lesson ReviewDocument4 pagesPhysics Lesson ReviewШунаси ХалиловNo ratings yet
- Physics ch-1.5 (Forces and Motion)Document3 pagesPhysics ch-1.5 (Forces and Motion)Safiul FaiyazNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Newton'S Laws of Motion: Bridge Course - Phy - I PUC - 40Document7 pages2.2 Newton'S Laws of Motion: Bridge Course - Phy - I PUC - 40Jit AggNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS MODULE 6 ReviewerDocument2 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS MODULE 6 RevieweriX ENNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Notes 1Document2 pagesDynamic Notes 1Hazmi RahmanNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsDocument12 pagesNewton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsZahra 9oNo ratings yet
- Physics Motion Object Mass Velocity State of Rest Accelerate Magnitude Direction Vector SI Unit NewtonsDocument1 pagePhysics Motion Object Mass Velocity State of Rest Accelerate Magnitude Direction Vector SI Unit NewtonshamadaniNo ratings yet
- Unit: 03 Dynamics: Miss Saniya Physics Merit Boarding & Day SchoolDocument15 pagesUnit: 03 Dynamics: Miss Saniya Physics Merit Boarding & Day SchoolUmer FarooqNo ratings yet
- 04 Newton's Laws of MotionDocument17 pages04 Newton's Laws of MotionZohaib IkramNo ratings yet
- PHY101 Lecture Note 2015 - 2016-3-1Document7 pagesPHY101 Lecture Note 2015 - 2016-3-1Kenneth SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PhysicDocument5 pagesChapter 4 PhysicWaleska MendezNo ratings yet
- Physics - Force and MotionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Force and MotionÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- Three Laws of MotionDocument22 pagesThree Laws of MotionCamille Neriza FeLicianoNo ratings yet
- Ap 1 DynamicsDocument10 pagesAp 1 DynamicsCai MingleiNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument9 pagesForceMohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-momentum and CollisionDocument73 pagesPHYSICS-momentum and CollisionJamelleNo ratings yet
- Physics: Unit 3 (Forces) Key Notes or IdeasDocument2 pagesPhysics: Unit 3 (Forces) Key Notes or IdeasRana Muhammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Fisika Dasar - Buk Fitriyanti - Kuliah 03 - GayaDocument20 pagesFisika Dasar - Buk Fitriyanti - Kuliah 03 - GayaMUHAMMAD SALAFYNo ratings yet
- 02 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovDocument16 pages02 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovKVP LyricsNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 8, Quarter 1: Force and MotionDocument3 pagesScience Grade 8, Quarter 1: Force and MotionMin Yoongi92% (12)
- Quarter 2 Part 1Document14 pagesQuarter 2 Part 1yukikyo osamuNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Force and Law of MotionDocument5 pagesClass 9 Science Force and Law of MotionVishal DeyNo ratings yet
- Newton LawsDocument3 pagesNewton LawsA BarrettNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three (3) Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesNewton's Three (3) Laws of MotionCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1. The First and Second Law of Motion STUDENTSDocument32 pagesUNIT 1. The First and Second Law of Motion STUDENTSMarcella AnnaNo ratings yet
- Law of Motion @moazzam - GuidesDocument1 pageLaw of Motion @moazzam - GuidesMoazzamNo ratings yet
- Lecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)Document14 pagesLecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)verboseNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Laws of MotionDocument66 pagesLesson 1 - Laws of MotionGianina De LeonNo ratings yet
- Benchmark 1 Study Questions SOLUTIONSDocument4 pagesBenchmark 1 Study Questions SOLUTIONSMarman Fabro Anga-Angan100% (1)
- Physics (CETs)Document9 pagesPhysics (CETs)AkiNo ratings yet
- Force PDFDocument12 pagesForce PDFSushmitha AnchanNo ratings yet
- Force.) If The Net Force Exerted On An Object Is Zero, The Acceleration of The ObjectDocument2 pagesForce.) If The Net Force Exerted On An Object Is Zero, The Acceleration of The ObjectRaja KashmiriNo ratings yet
- G8 Lesson 1Document23 pagesG8 Lesson 1Yvonne CuevasNo ratings yet
- بحث الفيزياDocument7 pagesبحث الفيزياrdcnqvv8szNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionrizki siwiNo ratings yet
- Q1Act2 Newton's Laws of MotionDocument25 pagesQ1Act2 Newton's Laws of MotionReselle AnubNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument12 pagesNewton's LawsRacine CariahNo ratings yet
- MS Point RKPSDocument12 pagesMS Point RKPSshivamkumar6203716No ratings yet
- Force and Laws of MotionDocument21 pagesForce and Laws of MotionJINCY SEBASTIANNo ratings yet
- Science 8Document39 pagesScience 8Kevin Joseph E. MarceloNo ratings yet
- Law of MotionDocument32 pagesLaw of MotionAffan WaheedNo ratings yet
- Lab 14 Study of Newton's 2nd Law of MotionDocument5 pagesLab 14 Study of Newton's 2nd Law of MotionWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- LM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1Document40 pagesLM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument21 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionharlequinlhaiNo ratings yet
- Hit TerDocument29 pagesHit TerSai-Min Thit-KoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 2Document24 pagesDynamics 2KNEWTON EducationNo ratings yet
- Newton English1Document30 pagesNewton English1Puspa LestariNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law's of MotionDocument19 pagesNewtons Law's of MotionAira YamuyamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notes - PhysicsDocument1 pageChapter 2 Notes - PhysicsliliNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument4 pagesForce and MotionSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument8 pagesForcesapi-318478101No ratings yet
- Dynamics: What Is A Force?Document13 pagesDynamics: What Is A Force?TorettoNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument7 pagesForce and MotionEreeNo ratings yet
- Additional Questions Chapter 4: Dynamics (Newton's Laws of Motion)Document1 pageAdditional Questions Chapter 4: Dynamics (Newton's Laws of Motion)Sharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS FORM 5 Waves ExerciseDocument13 pagesPHYSICS FORM 5 Waves ExerciseSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Hookes Law W Sheet AnswersDocument13 pagesHookes Law W Sheet AnswersSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- IGCSE-Hooke's Law Worksheet 1.1Document8 pagesIGCSE-Hooke's Law Worksheet 1.1Sharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 Scalars & VectorsDocument6 pages2.1.1 Scalars & Vectorsnazran68No ratings yet
- Binomial AP GP TrigoDocument1 pageBinomial AP GP TrigoSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Express NotesDocument11 pagesElectromagnetism Express NotesShah Rafidzah KhalidNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Mathematics Revision Set 1 (Matrix and Variation)Document1 pageForm 5 Mathematics Revision Set 1 (Matrix and Variation)Sharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- F MaDocument1 pageF MaWong Weng SonNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Mathematics Revision Set 3 (Transformation)Document3 pagesForm 5 Mathematics Revision Set 3 (Transformation)Sharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- 11 IndexNumbersDocument4 pages11 IndexNumbersMun TajuddinNo ratings yet
- Nota Chapter 8Document8 pagesNota Chapter 8Evelyn LeeNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Revision Set 1Document2 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Revision Set 1Sharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Hookes Law QuestionsDocument1 pageHookes Law QuestionsSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Turning Effect of Forces)Document4 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Turning Effect of Forces)Sharuvindan Nair100% (1)
- Mark Scheme Resolving Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Document5 pagesMark Scheme Resolving Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Sharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line SCDocument9 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line SCSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Ela TT Nov 2013Document1 pageEla TT Nov 2013Sharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Planning Experiment WorksheetDocument2 pagesPlanning Experiment WorksheetFikri NafuriNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Pressure)Document7 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Pressure)Sharuvindan Nair100% (1)
- 2 0 Forces and MotionDocument41 pages2 0 Forces and MotionNaveenthiran SathananthanNo ratings yet
- How Can I Overcome My ProblemDocument14 pagesHow Can I Overcome My ProblemSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- CIM Registration Form PDFDocument1 pageCIM Registration Form PDFSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Variation.: 3.1 Cell DivisionDocument16 pagesHeredity and Variation.: 3.1 Cell DivisionElly EllynaNo ratings yet
- ULTIMA Training FormDocument1 pageULTIMA Training FormSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- F5 CH 3 StudentDocument17 pagesF5 CH 3 StudentSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Physics F4Document45 pagesPhysics F4Maheswaren MahesNo ratings yet
- Revision US1,2012 Algebraic FormulaeDocument2 pagesRevision US1,2012 Algebraic Formulaeshavnair87No ratings yet