Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2004 OrgSeminarTestAnswer
Uploaded by
Ghadeer M HassanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2004 OrgSeminarTestAnswer
Uploaded by
Ghadeer M HassanCopyright:
Available Formats
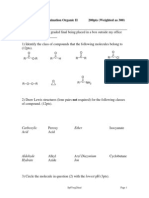
YOUR STUDENT NUMBER:
Year 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2004
Bifunctional Chemistry Test ANSWERS
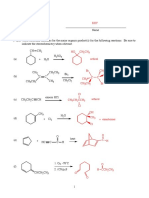
Q1
(a) Label all of the acidic hydrogen atoms on the molecules A - E shown.
H
H
H
H
O
H
H
H
H
OH
A
O
O
HH HH
H
H
D
Q1
(b)
O
H
H
H
H H H
H
H
Considering the most acidic hydrogen(s) of each molecule only, place the
molecules in order of acidity starting with the most acidic.
A (CO2H) > E (CH2) > B (CH2) > C > D
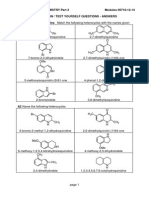
Q2
Consider the scheme below then answer the questions:
O
OEt
(a)
Br-(CH2)4-Br
ii) dilute H+ heat
Identify X and give a mechanism for its synthesis.
O
H H
i) aq. NaOH r.t.
2 eq. NaOEt
OEt
OEt
OEt
OEt
OEt
Br-CH2CH2CH2CH2-Br
O
O
O
H
OEt
OEt
O
OEt
EtO
Br
Br
resonance stablilized
intramolecular reaction faster than
intermolecular, especially if making 5-ring
Q2 continued overleaf
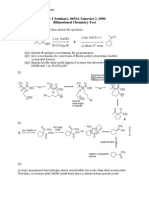
(b)
Give a mechanism for conversion of X into acetylcyclopentane (methyl
cyclopentyl ketone).
O
aq. NaOH r.t.
CH3
ONa
O
HCl (aq)
heat
CH3
OH
O
H3C
CH3
O H
O
OH
C
O
O
tautomerism
CH3
O
(c)
What would happen if acetone were allowed to react with 2 eq. NaOEt and 2 eq.
Br(CH2)4Br?
Acetone (propanone) has hydrogen atoms considerably less acidic than ethyl acetoacetate (see
Q2a). Therefore, in reaction with NaOEt (weak base) there is always ketone present in the
equilibrium mixture as well as enolate. An aldol reaction is therefore one possible side
reaction. Also the second deprotonation could take place at the same carbon as the first, or on
the other side of the C=O. Two moles of dibromide also complicates matters and so
dimers/polymers and dialkylated / and or cyclic products can form. Overall a right old
mixture would be produced!
END
You might also like
- Write Your Answers On This Sheet: N O O O O O PHDocument2 pagesWrite Your Answers On This Sheet: N O O O O O PHGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- CHEM 135 Exam 2 F15 KeyDocument7 pagesCHEM 135 Exam 2 F15 KeyMikeNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2006 Bifunctional Chemistry TestDocument2 pagesYear 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2006 Bifunctional Chemistry TestGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- CHM 1321 Assignment 1 Answers: CN H H H H HDocument10 pagesCHM 1321 Assignment 1 Answers: CN H H H H HSara YuenNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Principles and TechniquesDocument27 pagesOrganic Chemistry Principles and TechniquesAwan DubeyNo ratings yet
- 232 F 2010 Practice Midtem 3Document14 pages232 F 2010 Practice Midtem 3Chemist MeNo ratings yet
- CHEM (1st Topic)Document6 pagesCHEM (1st Topic)Lyanna VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2423 e 2Document24 pages2423 e 2Agustin KurniatiNo ratings yet
- CHM 1321 Assignment 5 Answers: 1) Name The Following CompoundsDocument15 pagesCHM 1321 Assignment 5 Answers: 1) Name The Following CompoundsSara Yuen100% (1)
- Alcohols UpdatedDocument20 pagesAlcohols Updatedkaylaboo6160No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper AnalysisDocument6 pagesSample Question Paper AnalysisarindamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 AlcoholDocument5 pagesTutorial 6 Alcoholwan arifahNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: CHEM 025, Section X, Fall 201X - Anthony DutoiDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: CHEM 025, Section X, Fall 201X - Anthony DutoiJasmin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes Organic Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEDocument477 pagesBansal Classes Organic Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEAditya Kavuluri40% (5)
- CH CH CCH C CHDocument15 pagesCH CH CCH C CHVirgilio Ebajo Jr.No ratings yet
- ANSDocument6 pagesANSIgneel CreedNo ratings yet
- RedOx Rxns PDFDocument31 pagesRedOx Rxns PDFRileShampionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Outline: Solutions, Electrolytes, Acids, Bases, and Redox ReactionsDocument13 pagesChapter 8 Outline: Solutions, Electrolytes, Acids, Bases, and Redox ReactionsNurudin ForzaNo ratings yet
- CY1101 Mid SemDocument3 pagesCY1101 Mid SemDipti Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Review Questions: Medicinal Chemistry 300550Document49 pagesReview Questions: Medicinal Chemistry 300550vanyarufusNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Assignment on Reactions & NomenclatureDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Assignment on Reactions & NomenclatureAbdullah AlteneijiNo ratings yet
- Test - 2 - Solutions and FeedbackDocument7 pagesTest - 2 - Solutions and FeedbackNondumiso MavundlaNo ratings yet
- 231 F 2010 Practice MT4 - Pp1to12Document12 pages231 F 2010 Practice MT4 - Pp1to12Chemist MeNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 31marking GuideDocument14 pagesA Level Chemistry Paper 1 Set 31marking GuidekitookebarnabasNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Chemistry Sample PracticeDocument3 pagesMcqs Chemistry Sample PracticeWajid Ali0% (1)
- Exam II: Organic Chemistry Reactions and MechanismsDocument6 pagesExam II: Organic Chemistry Reactions and MechanismsparnaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry+1+Tutor+ +vol+4+ +worksheet+23+ +Balance+Redox+Reactions+in+Neutral+Solution+ +Ion+Electron+MethodDocument26 pagesChemistry+1+Tutor+ +vol+4+ +worksheet+23+ +Balance+Redox+Reactions+in+Neutral+Solution+ +Ion+Electron+MethodziaNo ratings yet
- 1e Aldehyde & KetoneDocument48 pages1e Aldehyde & KetoneJonathan Wyatt100% (1)
- Answer Key: Chemistry 206 First Hour ExaminationDocument9 pagesAnswer Key: Chemistry 206 First Hour Examinationsudipta88No ratings yet
- Sample Test Exam One CH201Document7 pagesSample Test Exam One CH201Ashly PhilipNo ratings yet
- 2007 ADocument4 pages2007 AAmiro MayraNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Q2 D1Document31 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Q2 D1Clifford SalacNo ratings yet
- Assessing Acids, Bases, Salts and Chemical EquilibriumDocument3 pagesAssessing Acids, Bases, Salts and Chemical EquilibriumJuju ZenemijNo ratings yet
- EM Chem 2007Document8 pagesEM Chem 2007commonsensec88No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ExrecicesDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Exrecicespaulinhagraebin100% (4)
- HydrolysisH PDFDocument12 pagesHydrolysisH PDFEuwan Tyrone PriasNo ratings yet
- Oganic Cem PDFDocument2 pagesOganic Cem PDFaulaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Chemistry 30 WorksheetsDocument49 pagesElectrochemistry: Chemistry 30 Worksheetsdan anna stylesNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesClass 11 Physics Important QuestionsIshar ravaniNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Additional Problems Final Exam Part2Document6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Additional Problems Final Exam Part2John SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document30 pagesChapter 7Apichat Junsod100% (4)
- Orgsynth KeysDocument27 pagesOrgsynth KeysDebalina DassNo ratings yet
- SP 2007 Final Examination Organic II 200pts (Weighted As 300)Document21 pagesSP 2007 Final Examination Organic II 200pts (Weighted As 300)Ummi Khairani UrfaNo ratings yet
- +1 Chemistry - Some Important Questions & Answers PART 2Document12 pages+1 Chemistry - Some Important Questions & Answers PART 2ahammedkayangalkayangalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper With Answer PDFDocument5 pagesChemistry Paper With Answer PDFAnurag LaddhaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Sko3033 PDFDocument4 pagesQuiz 1 Sko3033 PDFFiona Tiwon100% (1)
- AP 02 Multiple ChoiceDocument16 pagesAP 02 Multiple ChoiceKat TomasNo ratings yet
- Hcno C H H H C H H H C H H H: Remains +1 ThroughoutDocument4 pagesHcno C H H H C H H H C H H H: Remains +1 ThroughoutpNo ratings yet
- CHEM 281 Practice Exam TitleDocument12 pagesCHEM 281 Practice Exam TitleRam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CHEM1612 Model MCQ PDFDocument11 pagesCHEM1612 Model MCQ PDFSanaullahNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument5 pagesChemical EquilibriumElixirNo ratings yet
- Chem 125 08.10.2019: Exam I Will Be Held On Thursday, October 10 at 5:00 PM, Covering CHP 1 - 3Document7 pagesChem 125 08.10.2019: Exam I Will Be Held On Thursday, October 10 at 5:00 PM, Covering CHP 1 - 3nilofar jawadiNo ratings yet
- Redox & Soln ReactionsDocument18 pagesRedox & Soln ReactionsAmey SutarNo ratings yet
- Redox ReviewDocument20 pagesRedox Reviewapi-3706290100% (1)
- OrganicDocument6 pagesOrganicTrent SwordsNo ratings yet
- CETO2B1Document13 pagesCETO2B1Ontiretse MachailweNo ratings yet
- XI Mid Term QPDocument3 pagesXI Mid Term QPtechnical SiteNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations 39Document5 pagesBalancing Equations 39Ignacio Jr. Paguyo100% (1)
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ThiopheneDocument398 pagesThiopheneAshwin MandaleNo ratings yet
- Acs سريرية نظري- د.حيدرDocument56 pagesAcs سريرية نظري- د.حيدرGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- PK Modeling Approaches for Drug DistributionDocument67 pagesPK Modeling Approaches for Drug DistributionGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Adrenocorticoids2- ادوية نظري - د.احسانDocument4 pagesAdrenocorticoids2- ادوية نظري - د.احسانGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2007 Bifunctional and Heterocyclic Chemistry TestDocument5 pagesYear 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2007 Bifunctional and Heterocyclic Chemistry TestGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Heterocyclic CompoundsDocument15 pagesChapter 12 - Heterocyclic CompoundsGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
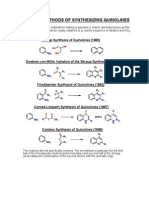
- Quinoline SynthesisDocument6 pagesQuinoline SynthesisFrancesco TutinoNo ratings yet
- Indole and Benzimidiazole NucleusDocument32 pagesIndole and Benzimidiazole NucleusSrikanth MalipatelNo ratings yet
- Heterocycles - PART 2 - Pall Knorr PyrroleDocument4 pagesHeterocycles - PART 2 - Pall Knorr PyrroleGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document39 pagesChapter 2Ghadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Cyclisations Problems 2013Document6 pagesCyclisations Problems 2013Ghadeer M Hassan100% (1)
- Cyclisations Solutions 2013Document7 pagesCyclisations Solutions 2013Ghadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Cycloadditions Problems 2013Document8 pagesCycloadditions Problems 2013Ghadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Reactivity QuinolineDocument107 pagesReactivity QuinolineIan Otto100% (1)
- Cycloadditions Solutions 2013 2Document9 pagesCycloadditions Solutions 2013 2Ghadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Heterocyclic Chemistry: There Are 9 Parts To These "Animated" Notes: 2. There Are Guidance Notes and ProblemsDocument4 pagesHeterocyclic Chemistry: There Are 9 Parts To These "Animated" Notes: 2. There Are Guidance Notes and ProblemsGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Heterocycles - PART 6 - PyrimidinesDocument3 pagesHeterocycles - PART 6 - PyrimidinesGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Heterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesDocument3 pagesHeterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
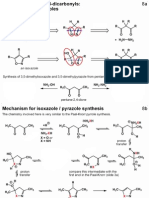
- Heterocycles - PART 5 - Isoxazoles and PyrazolesDocument4 pagesHeterocycles - PART 5 - Isoxazoles and PyrazolesGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Heterocycles - PART 5 - Isoxazoles and PyrazolesDocument4 pagesHeterocycles - PART 5 - Isoxazoles and PyrazolesGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Heterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesDocument3 pagesHeterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Heterocycles - PART 6 - PyrimidinesDocument3 pagesHeterocycles - PART 6 - PyrimidinesGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Heterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesDocument3 pagesHeterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- 2012 Hetero Model AnswerDocument3 pages2012 Hetero Model AnswerGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- 2013 Hetero Model AnswerDocument2 pages2013 Hetero Model AnswerGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- 2012 Hetero Model AnswerDocument3 pages2012 Hetero Model AnswerGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2009 Heterocyclic Chemistry TestDocument4 pagesYear 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2009 Heterocyclic Chemistry TestGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet