Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Questions On Thermo 1
Uploaded by
MuhammadAizatOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Questions On Thermo 1
Uploaded by
MuhammadAizatCopyright:
Available Formats
Department Of Mechanical Engineering
College Of Engineering
Universiti Tenaga Nasional
MEHB312 Thermodynamics II
Tutorial on Thermodynamics 1
1. Complete the following table for H2O:
T,oC
P, kPa
h, kJ/kg
200
0.7
140
80
Phase Description
1800
950
500
800
0.0
3161.7
2. Determine the specific volume of nitrogen gas at 10 MPa and 150 K based on (a)
the ideal-gas equation. (b) the generalized compressibility chart. Compare these
results with the experimental value of 0.002388 m3/kg, and determine the error
involved in each case.
3. A mass of 2.4 kg of air at 150 kPa and 12 oC is contained in a gas tight,
frictionless piston cylinder device. The air is now compressed to a final pressure
of 600 kPa. During the process, heat is transferred from the air such that the
temperature inside the cylinder remains constant. Calculate the work input during
this process.
4. A 0.5 m3 rigid tank contains refrigerant 134a initially at 200 kPa and 40 percent
quality. Heat is now transferred to the refrigerant until the pressure reaches 800
kPa. Determine (a) the mass of the refrigerant in the tank and (b) the amount of
heat transferred. Also, show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to
saturation lines.
5. A piston cylinder device contains 5 kg of refrigerant 134a at 800 kPa and 60 oC.
The refrigerant is now cooled at constant pressure until it exists as a liquid at
20oC. Determine the amount of heat loss and show the process on a T-v diagram
with respect to saturation lines.
6. A Carnot heat engine receives 650 kJ of heat from a source of unknown
temperature and rejects 200 kJ of it to a sink at 17 oC. Determine (a) the
temperature of the source and (b) the thermal efficiency of the heat engine.
7. A heat pump is used to heat a house and maintain it at 24 oC. On a winter day
when the outdoor air temperature is -5oC, the house is estimated to lose heat at a
rate of 80 000 kJ/h. Determine the minimum power required to operate this heat
pump.
8. A 0.5 m3 rigid tank contains refrigerant 134a initially at 200 kPa and 40 percent
quality. Heat is now transferred to the refrigerant from a source at 35oC until the
pressure rises to 400 kPa. Determine (a) the entropy change of the refrigerant, (b)
the entropy change of the heat source, and (c) the total entropy change for this
process.
9. Steam expands in a turbine steadily at a rate of 25 000 kg/h, entering at 8 MPa
and 450oC and leaving at 50 kPa as saturated vapor. If the power generated by the
turbine is 4 MW, determine the rate of entropy generation for this process.
Assume the surrounding medium is at 25oC.
You might also like
- Tutorial Sheet 6Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 6Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Taller 2 2023-1Document8 pagesTaller 2 2023-1anderson ortizNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)Document22 pagesThermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)cwidiNo ratings yet
- 16TF603 Entropy AssignmentDocument2 pages16TF603 Entropy AssignmentMd Sharique AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Worksheet AnalysisDocument13 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Worksheet Analysisroba angasuNo ratings yet
- Tutorials ThermoDocument1 pageTutorials ThermoNi ShiNo ratings yet
- Thermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With AnswersDocument21 pagesThermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With Answersmarc rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Practice Problem 1Document2 pagesBasic Engineering Practice Problem 1neva000No ratings yet
- Review UASDocument6 pagesReview UASkarenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1, Autumn 2023Document2 pagesAssignment 1, Autumn 2023cocodarshi2022No ratings yet
- Assignment-EntropyDocument2 pagesAssignment-Entropyme22b009No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Question Set ADocument4 pagesThermodynamics Question Set AVivek NegiNo ratings yet
- ME331 Thermodynamics: PS#5 SolutionsDocument12 pagesME331 Thermodynamics: PS#5 SolutionsCrimson MorangeNo ratings yet
- ETD - Question BankDocument6 pagesETD - Question BankGopinath VNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document1 pageTutorial 3B V V HANUMA GAYATHRINo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Important QuestionsMaha LakshmiNo ratings yet
- MEE 302 - Tutorial 1Document2 pagesMEE 302 - Tutorial 1acemumbiNo ratings yet
- Closed System ExercisesDocument2 pagesClosed System ExercisesMareta DanarNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Prob - Sheet.entropyDocument2 pages5.1 Prob - Sheet.entropyShrinivas Subhash HulsureNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument4 pagesThermowong zhi chengNo ratings yet
- β= T T T T E T Q Q: Tutorial Sheet 5 (Document6 pagesβ= T T T T E T Q Q: Tutorial Sheet 5 (deshrajNo ratings yet
- ME331 Thermodynamics: PS #4 Solutions: Numeric 1Document15 pagesME331 Thermodynamics: PS #4 Solutions: Numeric 1Crimson MorangeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 10Document7 pagesAssignment 10Mohamed RaafatNo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesImportant Questionstamilselvan nNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document3 pagesExercise 2mehmet candanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5Train DiskenthNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Roshan ShanmughanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 6 - ME 211TDocument2 pagesSheet 6 - ME 211TOmar AlkadyNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicscamilaskishoreNo ratings yet
- CHE 220-FALL23-Homework VDocument2 pagesCHE 220-FALL23-Homework Vsemikonino35No ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document2 pagesSheet 2Ahmed Rabie Abd Elazeem100% (1)
- T 5Document2 pagesT 5jfl2096No ratings yet
- In A Gas TurbineDocument7 pagesIn A Gas TurbineANBU RAJ ANo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics First Law Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics First Law Practice QuestionsRamis RafayNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument3 pagesThermoAmrinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet No2Document7 pagesTutorial Sheet No2عبدالله عمرNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 Dr. Gamal Nada Sheet 3 (Entropy), ContinuedDocument3 pagesThermodynamics 2 Dr. Gamal Nada Sheet 3 (Entropy), ContinuedEmptySilenceNo ratings yet
- QP 12345Document2 pagesQP 12345Siva ShankarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicR SuyaoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Review ProblemssayanNo ratings yet
- KasdkfjDocument10 pagesKasdkfjPravallika KolliparaNo ratings yet
- ETD Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesETD Important QuestionsRavi KîshôreNo ratings yet
- Test 1 With AnsDocument4 pagesTest 1 With AnsKavinesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- Me8391 Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesMe8391 Important QuestionsMohsin EngrNo ratings yet
- Assignment ProblemsDocument2 pagesAssignment ProblemsRam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sheet #7Document4 pagesSheet #7AHMED BAKRNo ratings yet
- Second Law of Thermodynamics and EntropyDocument2 pagesSecond Law of Thermodynamics and EntropybsdkNo ratings yet
- ChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Document5 pagesChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Irene Kaye AceroNo ratings yet
- Assgnment 1Document3 pagesAssgnment 1Akash Singh TanwarNo ratings yet
- First Law Applied To Flow Process and Second Law of Thermodynamics Assignment - 2Document3 pagesFirst Law Applied To Flow Process and Second Law of Thermodynamics Assignment - 2Supriyo sahuNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsbalusharma1212No ratings yet
- Course 228 FileDocument7 pagesCourse 228 FilegrfNo ratings yet
- Sheet #7Document4 pagesSheet #7Iam A gnoomNo ratings yet
- Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument21 pagesEngineering Thermodynamicsrkrajesh86No ratings yet
- Availability Analysis: Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesAvailability Analysis: Tutorial QuestionsJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 First Law 2016Document8 pagesAssignment 1 First Law 2016PabitraBadhuk0% (1)
- Corn Cob As Component For Green ConcreteDocument35 pagesCorn Cob As Component For Green ConcreteLaarni Duran100% (3)
- Semi Final Grade 7Document5 pagesSemi Final Grade 7Shielo Marie CardinesNo ratings yet
- Tornado Technologies - Velocity Purge Reducer Notes and Purge RatesDocument3 pagesTornado Technologies - Velocity Purge Reducer Notes and Purge RatesIan MannNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between Hydrology and Hydraulics?: (Continue Reading)Document7 pagesWhat's The Difference Between Hydrology and Hydraulics?: (Continue Reading)Carlo CabanusNo ratings yet
- Effects of Sun on Earth and Living ThingsDocument1 pageEffects of Sun on Earth and Living ThingsSel Vie DoraNo ratings yet
- Water-Lithium Bromide Vapor Absorption SystemDocument15 pagesWater-Lithium Bromide Vapor Absorption SystemSagar MoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Thin Film Deposition: 7. Introduction To Sputtering and DC PlasmaDocument41 pagesChapter 9 Thin Film Deposition: 7. Introduction To Sputtering and DC PlasmaRaj TokasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Spectroscopic Methods of Analysis - Part 1Document31 pagesLecture 6-Spectroscopic Methods of Analysis - Part 1Leo PisNo ratings yet
- 1.EBTKE CONEX 2013 Adjat SudradjatDocument10 pages1.EBTKE CONEX 2013 Adjat SudradjatMarbun BennyNo ratings yet
- 3 Basic Concept of HazardDocument43 pages3 Basic Concept of HazardJezrael SaetNo ratings yet
- CPO Physical Science Text Book Student TextDocument714 pagesCPO Physical Science Text Book Student TextPhanibhushan Vellala100% (1)
- Sustainable Agriculture - Mba BlogDocument3 pagesSustainable Agriculture - Mba BlogBikash DalaiNo ratings yet
- Leader Achiever Test Series (Allen Digital)Document4 pagesLeader Achiever Test Series (Allen Digital)Arpita SahuNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH PRE AARAMBH CHECKLIST BY NIMISHA MAM 25th JULY 2023Document9 pagesENGLISH PRE AARAMBH CHECKLIST BY NIMISHA MAM 25th JULY 2023Aman DeoleNo ratings yet
- Vapor Liquid Equilibria: Experiment No: 1Document8 pagesVapor Liquid Equilibria: Experiment No: 1Harsh DuttaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy Management Program in SOEM-KLDocument17 pagesSustainable Energy Management Program in SOEM-KLYusmadi J MohamadNo ratings yet
- Biology IGCSE - TEXT BOOKDocument33 pagesBiology IGCSE - TEXT BOOKArni Deora44% (9)
- Climate Change: Technical Writing CMM 140Document17 pagesClimate Change: Technical Writing CMM 140Akwinder GrewalNo ratings yet
- Project Oxhydroelectric Effect Procedure and Apparatus To Extract Electric Energy From WaterDocument11 pagesProject Oxhydroelectric Effect Procedure and Apparatus To Extract Electric Energy From WaterFrancesco Paolo TuccinardiNo ratings yet
- IIT Physics Lab Manual (Combined)Document34 pagesIIT Physics Lab Manual (Combined)Victoria Aschebrook-KealiherNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 1Document15 pagesPhysical Science Week 1veive merlinNo ratings yet
- APPLICATIONS of NUCLEAR FUSION in VARIOUS INDUSTRIESDocument5 pagesAPPLICATIONS of NUCLEAR FUSION in VARIOUS INDUSTRIESSHIELA HIDALGONo ratings yet
- Te-Metals and Non Metal Final Revisor (2022-23)Document85 pagesTe-Metals and Non Metal Final Revisor (2022-23)Gautam SharrmaNo ratings yet
- Speech OutlineDocument2 pagesSpeech OutlineFiona Tieh100% (1)
- Petroleum Engineering and Project Development: Applied Graduate StudiesDocument2 pagesPetroleum Engineering and Project Development: Applied Graduate StudiesOmeruo EmekaNo ratings yet
- HY Material EDocument4 pagesHY Material Eschumiizz2best0% (1)
- Nabcep SH Guide 8-5-13Document160 pagesNabcep SH Guide 8-5-13ZeljkoSipcicNo ratings yet
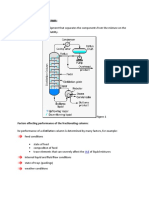
- Factors Effecting Performance of The Fractionating ColumnDocument4 pagesFactors Effecting Performance of The Fractionating ColumnHasieb Alam KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio 215 Abundance AssignmentDocument6 pagesBio 215 Abundance AssignmentKarabo Yuval TsheoleNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Sciencedirectitalo mayuber mendoza velezNo ratings yet