Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bernoulli Equation
Bernoulli Equation
Uploaded by
ankitkarwa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pagefluid mechanics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentfluid mechanics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageBernoulli Equation
Bernoulli Equation
Uploaded by
ankitkarwafluid mechanics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
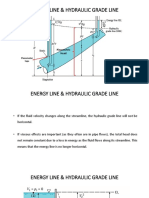
Bernoullis Equation
Work Term
Stream Line:
Kinetic Energy Term
Along a stream line, Bernoullis equation states:
2
Potential Energy Term
p
g z = Constant1
OR
p +
+
+
+ g z = Constant2
A stream line is a line which is everywhere tangent to a fluid particles velocity. By default, this
means a stream line is the path a fluid particle travels.
Stream Line
VA
Bernoullis equation can be applied between points A and B.
2
pA
VA
+
+ g zA =
A
2
Constant3 =
pB
VB
+
+ g zB
B
2
Fluid Flow Assumptions:
You should only use Bernoullis equation when ALL of the following are true:
Along a Streamline - Bernoullis equation can only be used along a streamline,
meaning only between points on the SAME streamline.
Inviscid flow - Energy loss due to viscous affects is small
Bernoullis equation can not be used through a region which is turbulent such as
mixed jets, pumps, motors, and other areas where the fluid is turbulent or mixing.
Stream lines
Mixing =
Cant Use Bernoullis Equation
Mixed Jet
Gear Pump
Stead State - The velocity of the flow,VFluid, is not a function of time.
Incompressible - Most fluid flow applications can be considered incompressible.
Incompressible means that the amount a fluid volume can be compressed is very small
compared to the initial fluid volume. Gases can generally NOT be considered
incompressible. For instance, when someone pumps up a bike tire, more and more air
is compressed into the same volume. With liquids, VERY VERY high pressures (you
are unlikely to see these as an engineer) are required to do this.
If Bernoulli's equation can be applied at points A & B on the same stream line:
This is a VERY POWERFUL TOOL for use in fluid mechanics WHEN USED CORRECTLY!!!!!
You might also like
- Bernoulli EquationDocument40 pagesBernoulli EquationHassanKM100% (2)
- Energy Equation & Its ApplicationsDocument47 pagesEnergy Equation & Its ApplicationsRopah ChihuriNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop in PipingDocument140 pagesPressure Drop in PipingTushar LanjekarNo ratings yet
- Application of The Bernoulli TheoremDocument33 pagesApplication of The Bernoulli TheoremKendra KaiserNo ratings yet
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pressure Measurement 2022-1Document38 pagesPressure Measurement 2022-1Varun VelrajNo ratings yet
- TURBOMACHINES Pumps PerformanceDocument35 pagesTURBOMACHINES Pumps PerformancejehadyamNo ratings yet
- Energy Line & Hydraulic Grade Line: Piezometric HeadDocument19 pagesEnergy Line & Hydraulic Grade Line: Piezometric HeadMaryam Arif100% (1)
- TURBOMACHINES: Pumps PerformanceDocument35 pagesTURBOMACHINES: Pumps PerformanceBaber H. ElahiNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Munson BDocument31 pagesCh3 Munson BMaryam ArifNo ratings yet
- Lec 09 CH 5Document14 pagesLec 09 CH 5Abdullah RajNo ratings yet
- 08 Lec - 8 - BERNOULLI-11639Document27 pages08 Lec - 8 - BERNOULLI-11639Mohamed AbdelrazekNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli and Energy Equations: Fluid MechanicsDocument24 pagesBernoulli and Energy Equations: Fluid MechanicsSayed ShafeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 PDFDocument71 pagesChapter4 PDFMuhammad Amirul Haziq Bin ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Lec 2Document17 pagesWeek 9 Lec 2Muhammad Bin ZubairNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument53 pagesFluid DynamicsMuaz MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Mass, Bernoulli and Energy EquationsDocument31 pagesFluid Mechanics: Mass, Bernoulli and Energy EquationsYusf ari jerjisNo ratings yet
- 03-MEC441-Finite Control Volume Analysis-Part 2Document53 pages03-MEC441-Finite Control Volume Analysis-Part 2belNo ratings yet
- 3afluiddynamics ContinuityandbernoulliequationDocument68 pages3afluiddynamics ContinuityandbernoulliequationFirzana AmiraNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Equation: Fluid Mechanics For Civil EngineeringDocument29 pagesBernoulli Equation: Fluid Mechanics For Civil Engineeringminervini markNo ratings yet
- EEEQ 221 Fluid Mechanics 3B - Notes For 12th January 2018Document37 pagesEEEQ 221 Fluid Mechanics 3B - Notes For 12th January 2018Ellie AwiNo ratings yet
- 3a Fluid Dynamics - Continuity and Bernoulli EquationDocument66 pages3a Fluid Dynamics - Continuity and Bernoulli Equation翁绍棠No ratings yet
- Lecture-07: The Bernoulli EquationDocument16 pagesLecture-07: The Bernoulli EquationabasNo ratings yet
- CHEE 305: Transport Phenomena: Chapter 7: Internal Flow Applications William M. Chirdon, PH.DDocument27 pagesCHEE 305: Transport Phenomena: Chapter 7: Internal Flow Applications William M. Chirdon, PH.DStephen AuNo ratings yet
- Venturi Orifice Meter: Flow Measuring DevicesDocument22 pagesVenturi Orifice Meter: Flow Measuring DevicesAryan ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document76 pagesChapter 2Charbel KhouryNo ratings yet
- UTP - Fluid Mechanics Course - September 2012 Semester - Chap 3 Bernoulli EquationsDocument35 pagesUTP - Fluid Mechanics Course - September 2012 Semester - Chap 3 Bernoulli EquationswhateveroilNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Fluid Dynamic: Mass, Bernoulli and Energy EquationsDocument41 pagesFluid Mechanics: Fluid Dynamic: Mass, Bernoulli and Energy EquationsJohnnie ChewNo ratings yet
- Dip. - Theory of BernoullisDocument19 pagesDip. - Theory of BernoullisDan KiswiliNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Principle: Incompressible Flow EquationDocument7 pagesBernoulli's Principle: Incompressible Flow EquationDehan FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Principle: Incompressible Flow EquationDocument3 pagesBernoulli's Principle: Incompressible Flow Equationeng_elbarbaryNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Equation (Am)Document8 pagesBernoulli's Equation (Am)Ehtisham RiazNo ratings yet
- In Fluid Mechanics Atau Momentum Transfer, We Usually Limit Our Consideration To Mechanical Forms of Energy OnlyDocument16 pagesIn Fluid Mechanics Atau Momentum Transfer, We Usually Limit Our Consideration To Mechanical Forms of Energy OnlyAuliya Ainun INo ratings yet
- Mech S of Fluids - 2231-2021Document20 pagesMech S of Fluids - 2231-2021EICQ/00154/2020 SAMUEL MWANGI RUKWARONo ratings yet
- The Bernoulli Equation: Steady Flow. There Is A Version of Bernoulli Equation ForDocument7 pagesThe Bernoulli Equation: Steady Flow. There Is A Version of Bernoulli Equation ForBhemalee Tono DimalaluanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Aerodynamics: Lecture # 1: Fundamental PrinciplesDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Aerodynamics: Lecture # 1: Fundamental PrinciplesKaySwiss11100% (1)
- Limiting Gas Ratio: Related TermsDocument14 pagesLimiting Gas Ratio: Related TermsimranunarNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics: ME-438 Spring'16 Me@DsuDocument45 pagesAerodynamics: ME-438 Spring'16 Me@DsuLuqmanNo ratings yet
- THEORY BernoulliDocument3 pagesTHEORY BernoulliEjad AdhaNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Gripper For Handling Delicate Sliced Food MaterialsDocument9 pagesBernoulli Gripper For Handling Delicate Sliced Food MaterialsKIRAN KHATRINo ratings yet
- ChE 220 Mod 4 Mass Momentum and Energy Balances 2020-2021Document61 pagesChE 220 Mod 4 Mass Momentum and Energy Balances 2020-2021May May MagluyanNo ratings yet
- Applications of The Bernoulli EquationDocument13 pagesApplications of The Bernoulli EquationSalim ChohanNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentDocument16 pagesTable of ContentElina NesNo ratings yet
- 08 Instruction Manul of Fluid Mechanics LabDocument71 pages08 Instruction Manul of Fluid Mechanics Labmichael1135100% (1)
- T227/U03/ PPP 3: Correcting UnitsDocument24 pagesT227/U03/ PPP 3: Correcting Unitsbaba maachoNo ratings yet
- Fluid AssignmentDocument9 pagesFluid AssignmentAliMubarakNo ratings yet
- NozzleDocument49 pagesNozzleShafayat AhmmedNo ratings yet
- Applications of Bernoulli's EquationDocument17 pagesApplications of Bernoulli's EquationAboo Sdam AL Mkahal100% (2)
- CH 3 AndersonDocument123 pagesCH 3 AndersonamgedNo ratings yet
- PressuremeasurementDocument35 pagesPressuremeasurementsowbarnikaganesh17No ratings yet
- Bernoulli's EquationDocument21 pagesBernoulli's Equationananthu.uNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Fluid Design ReactorDocument33 pagesFluid-Fluid Design ReactorWendell Kim Llaneta100% (1)
- Potential Flow - Chapter 6 - 3 (2012)Document6 pagesPotential Flow - Chapter 6 - 3 (2012)MARUMO_LEVYNo ratings yet
- Turbomachinery (ME-209) : Dr. Sumit Kumar Singh Guest Faculty, Mechanical Engineering Department Tezpur UniversityDocument28 pagesTurbomachinery (ME-209) : Dr. Sumit Kumar Singh Guest Faculty, Mechanical Engineering Department Tezpur UniversityR HNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli'S Principle and Its Application: Physics Project - Kevin Shijo Xi-BDocument9 pagesBernoulli'S Principle and Its Application: Physics Project - Kevin Shijo Xi-BIsaac NewtonNo ratings yet
- Bernuili EquationDocument15 pagesBernuili EquationHaitham AliNo ratings yet
- Elementary Fluid Dyp 3 - 2Document22 pagesElementary Fluid Dyp 3 - 2jojoNo ratings yet
- Rathi Bi-Fit BF PulleyDocument2 pagesRathi Bi-Fit BF PulleyVasundharaLimayeNo ratings yet
- Rathi Flexible Coupling DimensionsDocument2 pagesRathi Flexible Coupling DimensionsVasundharaLimayeNo ratings yet
- Lab 4, Problem # 7: Alarm Clock Gear TrainDocument1 pageLab 4, Problem # 7: Alarm Clock Gear TrainVasundharaLimayeNo ratings yet
- Pressure Temperature With ChartDocument1 pagePressure Temperature With ChartVasundharaLimayeNo ratings yet