Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Raghvendra
Uploaded by
Er Raghvendra Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views12 pagesppt
Original Title
raghvendra ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views12 pagesRaghvendra
Uploaded by
Er Raghvendra Singhppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
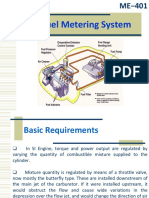
Fuel Injection in the CI Engine
For the compression ignition engine,
it is very important to promote a
means of injecting fuel into the
cylinder at the proper time in the
cycle. This is so because the injection
system starts and controls the
combustion process.
Objectives of the Injection System
The injection system of the compression ignition engine
should fulfil the following objectives consistently and
precisely:
Meter the appropriate quantity of fuel, as demanded by
the speed of, and the load on, the engine at the given
time.
Distribute the metered fuel equally among cylinders in a
multi-cylinder engine.
Inject the fuel at the correct time (with respect to crank
angle) in the cycle.
Inject the fuel at the correct rate (per unit time or crank
angle degree).
Inject the fuel with the correct spray pattern and
sufficient atomization as demanded by the design of the
combustion chamber, to provide proper penetration also.
Begin and end injection sharply without dribbling or
after injection.
To accomplish these objectives, a number of functional
elements are required. These constitute together, the fuel
injection system of the engine. These elements are as
follows.
1. Pumping elements to transfer the fuel from the tank to the
cylinder, along with the associate piping and hardware.
2. Metering elements to measure and supply the fuel at the
rate as desired by the speed and load conditions
prevailing.
3. Metering controls to adjust the rate of the metering
elements for changes in load and speed of the engine.
4. Distributing elements to divide the metered fuel equally
among the cylinders in a multi cylinder engine.
5. Timing controls to adjust the start and stop of injection.
6. Mixing elements to atomize and distribute the fuel within
the combustion chamber
Function of fuel injection equipment
The function of fuel injection equipment is to supply the
engine with fuel in qualities exactly metered in
proportion to the power required and timed with utmost
accuracy, so that the engine will deliver that power
within the limits prescribed for fuel consumption,
exhaust smoke, noise and exhaust emissions.
The fuel must be injected through suitable nozzles at
pressures high enough to cause the required degree of
atomization in the combustion chamber and to ensure
that it mixes with sufficient air for complete combustion
in the cycle time available.
In multi cylinder engines the periods of injection, the
timing and the delivered quantity must be accurately
metered to ensure an even balance between the
cylinders.
Classification Fuel Injection
Systems
FUNCTION OF DIESEL FUEL INJECTION
fuel injection pump - pressurizes fuel to high
pressure
high-pressure pipe - sends fuel to the injection
nozzle
injection nozzle - injects the fuel into the cylinder
feed pump sucks fuel from the fuel tank
fuel filter - filtrates the fuel
Functions of the system
Feeding fuel
Adjusting fuel quantity
Adjusting injection timing
Atomizing fuel
Advantages
More power is developed.
Increased fuel efficiency.
Reduced noise.
More stability.
Pollutants are reduced.
Particulates of exhaust are reduced.
Exhaust gas recirculation is enhanced.
Precise injection timing is obtained.
Pilot and post injection increase the combustion quality.
More pulverization of fuel is obtained.
A very high injection pressure can be achieved.
The powerful microcomputer makes the whole system more
perfect.
It doubles the torque at lower engine speeds.
Disadvantages
They are heavier for the same power.
Diesel fuel has low flammability.
Maintenance hazards.
Its exhaust gases causes cancer.
Technology increases the cost of the
engine
Uses and Applications
Passenger cars
Railroad rolling stock
Aircrafts
backup generators
You might also like
- Unit-4 Automobile EngineeringDocument52 pagesUnit-4 Automobile EngineeringShubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection Lec.3Document31 pagesFuel Injection Lec.3irfan khanNo ratings yet
- IC Engine and Reciprocating Machine ch-6Document20 pagesIC Engine and Reciprocating Machine ch-6heonetubeNo ratings yet
- MIXTURE Priparation CIDocument18 pagesMIXTURE Priparation CIMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 IC Engine Mixture FormationDocument29 pagesChapter 5 IC Engine Mixture FormationMulat ShityeNo ratings yet
- UnitII UpdatedDocument53 pagesUnitII UpdatedChandraSekharKondaveetiNo ratings yet
- Module - 3 Diesel Engine Fuel Injection SystemDocument30 pagesModule - 3 Diesel Engine Fuel Injection SystemIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - IceDocument30 pagesUnit 2 - IceSugumar MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Cusrow Wadia Institute of Technology,: Pune-411001Document63 pagesCusrow Wadia Institute of Technology,: Pune-411001Amit RoshanNo ratings yet
- IC Engine Chapter-7Document23 pagesIC Engine Chapter-7birhanubic23No ratings yet
- Fuel Injection System: By: Jaydeep Chauhan, 150280711005 Gourav Gupta, 150280711010 Sagar Vagadiya, 150280711016Document49 pagesFuel Injection System: By: Jaydeep Chauhan, 150280711005 Gourav Gupta, 150280711010 Sagar Vagadiya, 150280711016Raumil ManiarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Supply SystemDocument15 pagesFuel Supply SystemPraneshNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection SystemsDocument17 pagesFuel Injection Systemsअभिषेक ओझा100% (1)
- Diesel Engine Mixture Formation: 5.4. Fuel Injection SystemDocument30 pagesDiesel Engine Mixture Formation: 5.4. Fuel Injection SystemGODNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument29 pagesUntitledanilNo ratings yet
- Unit Injector: Nozzle Types, Electronic Fuel Injection System (EFI), GDI, MPFI, DTSIDocument65 pagesUnit Injector: Nozzle Types, Electronic Fuel Injection System (EFI), GDI, MPFI, DTSIMUDIT DWIVEDINo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 6 Mixture Formation in SI & CI EngineDocument12 pagesChapter 5 6 Mixture Formation in SI & CI Engineahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- MpfiDocument33 pagesMpfiKkbhuvan KkNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Electronically Controlled Fuel InjectionDocument38 pagesUnit II - Electronically Controlled Fuel InjectiondrkbalaNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines-Ii: Fuel Injection SystemDocument31 pagesInternal Combustion Engines-Ii: Fuel Injection SystemSk SajedulNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument12 pagesInternal Combustion EngineMostafa Shawky El ShenawyNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Our Title:Fuel Supply System in Ci EngineDocument19 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Our Title:Fuel Supply System in Ci EngineNebiyou KorraNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Fuel Injection SystemDocument17 pagesDiesel Engine Fuel Injection SystemKen ColeyNo ratings yet
- MPFIDocument33 pagesMPFIEr Vbhor Shrma100% (1)
- 08 Fuel Supply System 2Document122 pages08 Fuel Supply System 2ramalingeswarao annamdevulaNo ratings yet
- 2.fuel Inj Compresion IgnitionDocument19 pages2.fuel Inj Compresion IgnitionJo VialNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines-Ii: Fuel Injection SystemDocument32 pagesInternal Combustion Engines-Ii: Fuel Injection SystemPuneeth obliNo ratings yet
- ElectiveDocument30 pagesElectiveGarryson RoblesNo ratings yet
- Ci Fuel System Notes PDFDocument19 pagesCi Fuel System Notes PDFNduati JohnNo ratings yet
- Amt 224 - Aircraft Fuel Meterin SystemDocument20 pagesAmt 224 - Aircraft Fuel Meterin SystemNino AngobNo ratings yet
- 1 Gasoline Electronic Direct Injection System1Document40 pages1 Gasoline Electronic Direct Injection System1EZHILARASAN RNo ratings yet
- 6 Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection SystemsDocument34 pages6 Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection Systemsloganathanpalani100% (1)
- Fuel Supply System: Unit 1 BDocument23 pagesFuel Supply System: Unit 1 BAnubhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document78 pagesChapter 10Si Thu AungNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection SystemDocument49 pagesFuel Injection SystemRavi Teja KarumuriNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection Systems of CI EnginesDocument24 pagesFuel Injection Systems of CI EnginesShiv Kumar Singh100% (4)
- Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection SystemsDocument35 pagesGasoline Electronic Fuel Injection SystemsatulsemiloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 6 Mixture Formation in SI and CI EnginesDocument82 pagesChapter 5 6 Mixture Formation in SI and CI Enginesahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection System For Ci Engines PDFDocument6 pagesFuel Injection System For Ci Engines PDFmark mutimushiNo ratings yet
- Fuel Supply System in Petrol EnginesDocument54 pagesFuel Supply System in Petrol EnginesKLUniveristy86% (14)
- Fuel Injection in The CI EngineDocument28 pagesFuel Injection in The CI EngineNamandeep Singh OberoiNo ratings yet
- Mixture Preparation SIDocument42 pagesMixture Preparation SIMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Aemr-Unit 1-Piston EngineDocument85 pagesAemr-Unit 1-Piston Engineuthira100% (1)
- Diesel Fuel SystemDocument41 pagesDiesel Fuel SystemGetachew Tikue100% (5)
- Uice001-Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit-IV Module-IIIDocument28 pagesUice001-Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit-IV Module-IIIBoovendra VarmanNo ratings yet
- Diesel Injection SystemDocument16 pagesDiesel Injection SystemMURALIGOCAM_29070605No ratings yet
- Fuel Injection System in Automobile EnginesDocument8 pagesFuel Injection System in Automobile EnginesBrendan BrodieNo ratings yet
- CLSU ABE Review 2022 APE Chap 04 Internal Combustion EngineDocument55 pagesCLSU ABE Review 2022 APE Chap 04 Internal Combustion EngineBilly AgustinNo ratings yet
- 06 LubricationDocument22 pages06 LubricationrajishrrrNo ratings yet
- Fuel SystemDocument24 pagesFuel SystemDipranjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Report of Fuel Injection SystemDocument5 pagesReport of Fuel Injection SystemDixit ParmarNo ratings yet
- Fuel InjectionDocument93 pagesFuel InjectionCh'ng Jie HanNo ratings yet
- 7.fuel Metering SystemDocument48 pages7.fuel Metering Systemanik 01No ratings yet
- Machining ProcessingDocument20 pagesMachining ProcessingDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection PumpDocument5 pagesFuel Injection PumpanilNo ratings yet
- Galgotias College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument13 pagesGalgotias College of Engineering and TechnologyAshish YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- AE - Unit III - Lect 4Document14 pagesAE - Unit III - Lect 4Hh HhNo ratings yet
- Naval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyFrom EverandNaval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- Work Instruction. - Tensile Testing NEWDocument5 pagesWork Instruction. - Tensile Testing NEWEr Raghvendra Singh100% (1)
- Braking Systems: Past, Present & Future: Research Paper Research Paper EngineeringDocument3 pagesBraking Systems: Past, Present & Future: Research Paper Research Paper EngineeringEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Precision Tube Pipe Catalogue2016Document28 pagesPrecision Tube Pipe Catalogue2016Er Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Deepak Kumar Singh: ResumeDocument2 pagesDeepak Kumar Singh: ResumeEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Paper For Mat (ETME-2017)Document2 pagesPaper For Mat (ETME-2017)Er Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Hindalco Industries Limited: Potroom Mechanical MaintainenceDocument2 pagesHindalco Industries Limited: Potroom Mechanical MaintainenceEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Https WWW - Irctc.co - in Eticketing PrintTicketDocument2 pagesHttps WWW - Irctc.co - in Eticketing PrintTicketEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Training Report CompressoreDocument6 pagesTraining Report CompressoreEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Alumina Transfer SystemDocument3 pagesAlumina Transfer SystemEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Hindalco Industries Limited: Potroom Mechanical Maintainence Renukoot, SonebhadraDocument33 pagesHindalco Industries Limited: Potroom Mechanical Maintainence Renukoot, SonebhadraEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Full DayDocument27 pagesElectrical Engineering Full DayEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Aniil Kushwaha 13152264136277 21-Nov-2015, 07:30:00: AllahabadDocument5 pagesAniil Kushwaha 13152264136277 21-Nov-2015, 07:30:00: AllahabadEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Greater Noida Institute of Technology: 2-Stroke Petrol EngineDocument4 pagesGreater Noida Institute of Technology: 2-Stroke Petrol EngineEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Greater Noida Institute of Technology: Under-Water WeldingDocument12 pagesGreater Noida Institute of Technology: Under-Water WeldingEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Lab ManualDocument28 pagesMachine Design Lab ManualEr Raghvendra Singh100% (1)
- Greater Noida Institute of Technology: 2-Stroke Petrol EngineDocument13 pagesGreater Noida Institute of Technology: 2-Stroke Petrol EngineEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Under Water WeldingDocument23 pagesUnder Water WeldingEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Greater Noida Institute of Technology: Seminar Presentation ONDocument19 pagesGreater Noida Institute of Technology: Seminar Presentation ONEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet