Professional Documents
Culture Documents
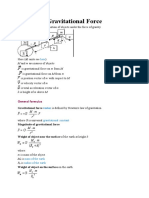
Common Physics Equations
Uploaded by
Arturo K. Cabras Jr.Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Common Physics Equations
Uploaded by
Arturo K. Cabras Jr.Copyright:
Available Formats
Common Physics Equations
CREATE VISUAL BASIC PROGRAMS FOR THE
FOLLOWING:
1. Distance traveled at constant velocity:
where v is the velocity and t is the time travelled
2. Distance traveled under acceleration:
where a is the acceleration, t is the time of acceleration, and v0 is the initial velocity
3. Velocity after acceleration:
where a is the acceleration, t is the time of acceleration, and v0 is the initial velocity
4. Force acting on an object:
where m is the mass of the object and a is the acceleration (N=kg-m/s2)
5. Force of gravity:
where G is the universal constant of gravitation, m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects, and d is the
distance between their centers of mass
G = 6.673 10 -11 m3/kgs2 (6.673E-11)
6. Kinetic energy:
where m is an objects mass and v is its velocity (Nm)
7. Potential energy (gravitational):
where m is an objects mass, g (9.807 m/s2) is the acceleration due to gravity, and y is the objects
distance above the ground (Nm)
8. Mechanical energy:
where K is an objects kinetic energy and U is its potential energy (Nm)
9. Momentum:
where m is an objects mass and v is its velocity
10. Conservation of momentum:
where p1i and p2i are the momentums of two objects before they collide, and p1f and p2f are their
momentums after the collision
11. Mass-energy equivalence:
where m is mass and c is the speed of light in a vacuum
Speed of light in a vacuum: c = 299,792,458 m/s (exact)
Microsoft Encarta 2009. 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Lifespan DevelopmentDocument295 pagesLifespan Developmentswaggerbox100% (4)
- Newton's and Einstein's Theories of Gravity: Halo A. AbdulkhalaqDocument19 pagesNewton's and Einstein's Theories of Gravity: Halo A. Abdulkhalaqbrainhub50No ratings yet
- 01 - Fundamental ConceptDocument9 pages01 - Fundamental ConceptMehul MunshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 GravitationDocument71 pagesChapter 7 GravitationWendy TangNo ratings yet
- 3786 FdocDocument3 pages3786 FdocThandanani MdakaneNo ratings yet
- Dynamics LectureDocument220 pagesDynamics LectureShiro Emiya0% (2)
- Class 9 Science: GravitationDocument11 pagesClass 9 Science: GravitationAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument11 pagesPhysics NotesnadineNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion 1Document7 pagesForce and Motion 1hannayunn990No ratings yet
- Summary of Lectures 1-5Document1 pageSummary of Lectures 1-5Junie ChannaNo ratings yet
- BSS IX, Handout Final TermDocument31 pagesBSS IX, Handout Final Termrehans.6857No ratings yet
- General Physics 1Document11 pagesGeneral Physics 1Aizeldy GuiribaNo ratings yet
- Biliran Province State UniversityDocument7 pagesBiliran Province State UniversityKyle Christian CeprezNo ratings yet
- General Science For WbcsDocument95 pagesGeneral Science For WbcsMITHUN CHATTERJEE100% (1)
- Physics of Rocket Flight: Distance, Velocity & AccelerationDocument10 pagesPhysics of Rocket Flight: Distance, Velocity & Accelerationvx800bikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Basic Principles of PhysicsDocument18 pagesChapter One: Basic Principles of Physicsm46960580No ratings yet
- Gravitational ForceDocument3 pagesGravitational ForceMuhamad Fahmi Abdul HadiNo ratings yet
- Physics SummaryDocument145 pagesPhysics SummaryAnurag PattekarNo ratings yet
- Science Notes For BestDocument6 pagesScience Notes For BestAbhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Before Newton: - GalileoDocument24 pagesForce and Motion Before Newton: - GalileotommyNo ratings yet
- Gr11-Final Exam - WorksheetDocument19 pagesGr11-Final Exam - WorksheetsoniyaspNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mechanics Revision NotesDocument5 pages1 - Mechanics Revision NotesHuaxiang HuangNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision For o Level PhysicsDocument28 pagesQuick Revision For o Level PhysicsRegie Sacil EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Keph - 10803 - Econtent 2019Document20 pagesKeph - 10803 - Econtent 2019srikanthNo ratings yet
- 7 Gravitation PHY11Document20 pages7 Gravitation PHY11mysixthidisNo ratings yet
- Universal Law of GravitationDocument17 pagesUniversal Law of GravitationScionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5&6Document24 pagesChapter 5&6Junyi JiNo ratings yet
- Overviews of StaticsDocument70 pagesOverviews of StaticsJacous WcyNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision For o Level PhysicsDocument33 pagesQuick Revision For o Level Physicsqwertymujtaba474No ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Universal GravitationDocument4 pagesNewton's Law of Universal GravitationLeon MathaiosNo ratings yet
- Bhumika Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesBhumika Physics ProjectKiran DubeyNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Test ReviewDocument21 pagesAP Physics Test ReviewAnish KalappaNo ratings yet
- 01 Mech - Introduction To Engineering MechanicsDocument13 pages01 Mech - Introduction To Engineering MechanicsCamille JarlosNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Measurement TechniquesDocument19 pagesPhysical Quantities and Measurement TechniqueslavanyagolebuissnessNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics / Unit 1/ Module 1 Introduction of MechanicsDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics / Unit 1/ Module 1 Introduction of MechanicsMangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Gravitational: Background Information For The Learners (BIL)Document32 pagesNewton's Law of Gravitational: Background Information For The Learners (BIL)Charlie CezarNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Lesson Plan Cycle 9Document6 pagesClass 9 Lesson Plan Cycle 9Vaishnavi BhandariNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS 1 Quarter 2 Activity SheetDocument26 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 1 Quarter 2 Activity SheetSeverus S Potter100% (1)
- Motion Forces and EnergyDocument13 pagesMotion Forces and EnergyAbid KhanNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Quarter 2: Module 2Document9 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Quarter 2: Module 2Maria Kriselle ApuhinNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 2Document5 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 2Normal Fan100% (1)
- HSC PHYSICS NOTES - All Topics + Quanta To QuarksDocument69 pagesHSC PHYSICS NOTES - All Topics + Quanta To QuarksAbdullaNo ratings yet
- Phy101 Quiz 1 2021 MonkeyDocument46 pagesPhy101 Quiz 1 2021 MonkeyAlishba khanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To DynamicsDocument3 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To DynamicsLvly FranciaNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics Notes: SpaceDocument12 pagesHSC Physics Notes: SpacechloeNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Physics Formula Sheets 80Document5 pagesClass 9th Physics Formula Sheets 80sanjaysonitkgNo ratings yet
- Newtonian MechanicsDocument2 pagesNewtonian MechanicsJose AdrianoNo ratings yet
- LXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 05 - Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation - 04mar2014Document2 pagesLXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 05 - Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation - 04mar2014Dito SihlanguNo ratings yet
- Chapt2 General PhysDocument61 pagesChapt2 General PhysmesayNo ratings yet
- The Laws of PhysicsDocument6 pagesThe Laws of PhysicsVelaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 SummaryDocument8 pagesPhysics 11 SummaryJ100% (5)
- 2 Force Motion Theory OKDocument20 pages2 Force Motion Theory OKSARANGMUMBAINo ratings yet
- Impulse Momentum TheoremDocument32 pagesImpulse Momentum TheoremmrdurangoNo ratings yet
- Keph - 10804-Econtent 2019Document21 pagesKeph - 10804-Econtent 2019srikanthNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 9th NotesDocument14 pagesPhysics Class 9th NotesMuhammad Iqbal75% (8)
- ForceDocument19 pagesForcePrashant sapkotaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MechanicsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To MechanicsAditya RayNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS (Level-3) Ques - 1Document2 pagesPHYSICS (Level-3) Ques - 1Theint Theint Chit HmueNo ratings yet
- Cosmos and MotionDocument13 pagesCosmos and MotionYuan Yuan ZhouNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mohsin EM Lecture 1,2Document41 pages1 - Mohsin EM Lecture 1,2UsamaNo ratings yet
- KJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLSDSDD VSCXVSRGDocument1 pageKJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLSDSDD VSCXVSRGArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Attendance OdsDocument1 pageAttendance OdsArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- KJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLDocument1 pageKJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- KJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLSDSDDDocument1 pageKJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLSDSDDArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- KJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLSDSDDocument1 pageKJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLSDSDArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Attendance OdsDocument1 pageAttendance OdsArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Mastering Mixing FundamentalsDocument82 pagesMastering Mixing FundamentalsArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- KJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLDocument1 pageKJGHGBHLBVMN, M.B VJ, JGLJLVGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG KML, NLJKH LKLMLArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- 101 Square Meals PDFDocument119 pages101 Square Meals PDFKhaye Alexa CeatrizNo ratings yet
- Dgdfgdfgdfgdsafgsdfgsfgs GG FDG DSFGDFGHDFGDF GdfgdfsgasdfvxcvxccvbxcvDocument1 pageDgdfgdfgdfgdsafgsdfgsfgs GG FDG DSFGDFGHDFGDF GdfgdfsgasdfvxcvxccvbxcvArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Date Load Type Number Load Balance Amount Paid 5/11/2014 Reload 150 33+150 183 25Document2 pagesDate Load Type Number Load Balance Amount Paid 5/11/2014 Reload 150 33+150 183 25Arturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- FestoDocument1 pageFestoArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Electrical Calculations v2.70.0.4Document1 pageElectrical Calculations v2.70.0.4Arturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- File ListDocument1 pageFile Listeverton_lcarneiroNo ratings yet
- Nokia CodesDocument2 pagesNokia CodesArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Epson l110 User ManualDocument0 pagesEpson l110 User ManualgerardoebarviaNo ratings yet
- New PrettyDocument26 pagesNew PrettyArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Electrical - SymbolDocument2 pagesElectrical - Symbolpriyanshsingh97100% (1)
- Structure of A ProgramDocument4 pagesStructure of A ProgramArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Document 1Document1 pageDocument 1Arturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Epson l110 User ManualDocument0 pagesEpson l110 User ManualgerardoebarviaNo ratings yet
- PriceDocument2 pagesPriceArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Electrical - SymbolDocument2 pagesElectrical - Symbolpriyanshsingh97100% (1)
- VSO ConvertXtoDVD v4.1.10.348 FinalDocument2 pagesVSO ConvertXtoDVD v4.1.10.348 FinalArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Gaisano Interpace Pricelist July 2013Document2 pagesGaisano Interpace Pricelist July 2013Arturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- 3d MaxDocument1 page3d MaxArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- 3d MaxDocument1 page3d MaxArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet
- Noise PollutionDocument7 pagesNoise PollutionArturo K. Cabras Jr.No ratings yet