Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Communications Chap.: (Transmitter) (Receiver) 1-1 in
Uploaded by
khrid3Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Communications Chap.: (Transmitter) (Receiver) 1-1 in
Uploaded by
khrid3Copyright:
Available Formats
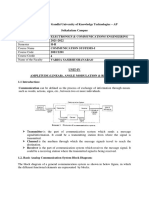
Introduction to Electronic Communications
Transmission
Source
medium
Destination
FIGURE
(receiver)
(transmitter)
it
is
Block diagram of a com-
1-1
munications system
cations,
Chap.
in its simplest
form.
necessary to superimpose a relatively low-frequency intelligence signal
onto a relatively high-frequency signal for transmission. In electronic communications
systems, the source information (intelligence signal) acts upon or modulates a single-
frequency sinusoidal signal. Modulate simply means to vary or change. Therefore, the
source information
called the modulating signal, the signal that
is
and the resultant signal
lated) is called the carrier,
essence, the source information
is
is
is
acted upon (modu-
called the modulated wave. In
transported through the system on the carrier.
With analog communications systems, modulation
is
the process of changing
some
property of an analog carrier in accordance with the original source information and
then transmitting the modulated carrier. Conversely, demodulation
is
the process of
converting the changes in the analog carrier back to the original source information.
The
total
or composite information signal that modulates the main carrier
baseband. The baseband
is
converted from
suitable for transmission through the
converted
is
at the transmitter
its
original frequency
band
to a
is
called
band more
communications system. Baseband signals are upat the receiver.
Frequency translation
band of frequencies
to another location in
and down-converted
the process of converting a frequency or
the total frequency spectrum.
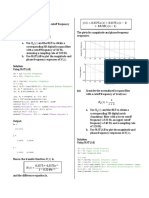
Equation 1-1
is
the general expression for a time varying sine
wave of voltage
such as an analog carrier. There are three properties of a sine wave that can be varied:
the amplitude (V), the frequency (F), or the
is
phase
(0). If the
amplitude of the carrier
varied proportional to the source information, amplitude modulation
the frequency of the carrier
modulation (FM)
(AM)
results. If
varied proportional to the source information, frequency
is
results. If the
phase of the carrier
(PM)
information, phase modulation
v(t)
is
varied proportional to the source
results.
= V
sin (litFt
(1-D
0)
where
=
V =
time-varying sine wave of voltage
v(f)
peak amplitude (Volts)
Modulated wave
Modulating
signal
(transmission
Amplifier
(information)
Demodulator
medium)
Modulator
(information
detector)
System
noise
car rier
FIGURE
1-2
Communications system block diagram.
Information
receiver
You might also like
- UNIT5 Fundamentals of Communication EngineeringDocument20 pagesUNIT5 Fundamentals of Communication EngineeringUpender Rao Sunkishala100% (4)
- Chapter 111Document3 pagesChapter 111SOMA MOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Communication SystemDocument10 pages1 Introduction To Communication SystemMOHAB MAHMOUD KAMELNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Electronic CommunicationDocument17 pagesFundamental of Electronic CommunicationLysa DeeNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems (15MT82) : (I) Information SourceDocument10 pagesCommunication Systems (15MT82) : (I) Information Sourcejeremy oswaldNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation ExplainedDocument38 pagesAmplitude Modulation ExplainedG SOMESHWAR RAONo ratings yet
- Need For Modulation: e = E sin (ω t + ϕ)Document2 pagesNeed For Modulation: e = E sin (ω t + ϕ)ptejaswini904439No ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Communication SystemDocument3 pagesBlock Diagram of Communication SystemKiranKumarNo ratings yet
- Unit Vi - Communication Systems: Elements of Communication SystemDocument18 pagesUnit Vi - Communication Systems: Elements of Communication Systemsaras_indiaNo ratings yet
- ModulationDocument4 pagesModulationshipu_ctgNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram and Components of a Communication SystemDocument3 pagesBlock Diagram and Components of a Communication SystemBlessonThomasNo ratings yet
- Communication System Unit VDocument8 pagesCommunication System Unit VTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Course EEE 431: Communication PrinciplesDocument44 pagesCourse EEE 431: Communication Principlesabdul.azeezNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Introduction To Communication SystemDocument107 pagesUnit-I: Introduction To Communication SystemSivaKumarNo ratings yet
- Communication System IntroductionDocument65 pagesCommunication System IntroductionMylavarapu SriprithamNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems 4th Edition Simon Haykin With Solutions Manual PDFDocument1,397 pagesCommunication Systems 4th Edition Simon Haykin With Solutions Manual PDFSheruNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemDheeraj RajNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Communication Systemmohd_anip9774No ratings yet
- GaddaDocument119 pagesGaddaMurthyNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation1Document44 pagesAmplitude Modulation1Dilbagh SinghNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave. For Radio Transmission We Listen To The Radio or WatchDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic Wave. For Radio Transmission We Listen To The Radio or WatchWodari Helena0% (1)
- Adc Lab Manual STUDENTDocument59 pagesAdc Lab Manual STUDENTramNo ratings yet
- Modulation: By-Sanjay Kumar 0900321088 EN-2 (A)Document17 pagesModulation: By-Sanjay Kumar 0900321088 EN-2 (A)Shikha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Modulation and DemodulationDocument2 pagesModulation and Demodulationnezar AbdoNo ratings yet
- Modulation Modulation Modulation ModulationDocument5 pagesModulation Modulation Modulation ModulationNeenu PrasannanNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument44 pagesCommunicationNilupul WijeratneNo ratings yet
- CS Assignment: 1) Week 1 SummaryDocument8 pagesCS Assignment: 1) Week 1 SummaryAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Modulation TechniquesDocument130 pagesOverview of Modulation TechniquesLalith KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 NewDocument43 pagesModule 5 NewMythri RangaswamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document5 pagesChapter 04T XombiNo ratings yet
- Bandpass Modulation & Demodulation: Engr. Ghulam ShabbirDocument114 pagesBandpass Modulation & Demodulation: Engr. Ghulam ShabbirEngr Gohar MumtazNo ratings yet
- AM Modulation: Easily Radiate Low Frequency SignalsDocument64 pagesAM Modulation: Easily Radiate Low Frequency SignalsanandNo ratings yet
- Sec 1304Document89 pagesSec 1304RAJESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Communicate Ideas Using Systems ModulationDocument2 pagesCommunicate Ideas Using Systems ModulationJohnny L. CurazaNo ratings yet
- Ec2311-Communication Engineering Introduction To Communication EngineeringDocument53 pagesEc2311-Communication Engineering Introduction To Communication EngineeringblessojchandranNo ratings yet
- Review of Multimode Techniques For Software Defined RadioDocument8 pagesReview of Multimode Techniques For Software Defined RadioTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Assignment Report Modulation: Arshdeep Singh 100905012 EIC-1Document24 pagesAssignment Report Modulation: Arshdeep Singh 100905012 EIC-1Arshdeep Singh MalhanNo ratings yet
- Conversion Techniques CCNDocument16 pagesConversion Techniques CCNHina QasimNo ratings yet
- Modulation: Encoding Information for TransmissionDocument5 pagesModulation: Encoding Information for TransmissionCandy CrUshNo ratings yet
- Transmitter and ReceiverDocument28 pagesTransmitter and ReceiverVinod NayyarNo ratings yet
- A & D Communication-III-converted 1647679245Document30 pagesA & D Communication-III-converted 1647679245Swastik BeheraNo ratings yet
- NEU EE346 Communication Systems Lecture NotesDocument61 pagesNEU EE346 Communication Systems Lecture NotessabitwebNo ratings yet
- MT1 CSDocument5 pagesMT1 CSSUDHARANI INTINo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of EcmDocument4 pagesBlock Diagram of EcmRojan JoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics Engineering 22ESC143Document21 pagesIntroduction To Electronics Engineering 22ESC143BOBAN05No ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Communication System With DetaileDocument5 pagesBlock Diagram of Communication System With Detaileravikumar rayalaNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument3 pagesDigital Modulation TechniquesrohitpowariNo ratings yet
- Analog Transmission Modulastion - Gregorio Diovani W - c11180040Document7 pagesAnalog Transmission Modulastion - Gregorio Diovani W - c11180040ye KaaNo ratings yet
- AC4 MRDocument2 pagesAC4 MRH51Dinkey BanchhorNo ratings yet
- Modulation Systems for Satellite CommunicationsDocument15 pagesModulation Systems for Satellite CommunicationsMuhammad Riaz Khan100% (1)
- HjajuDocument11 pagesHjajuaditya.bhandari2104No ratings yet
- CS-1 - Unit IvDocument41 pagesCS-1 - Unit IvSUDHARANI INTINo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation and DemodulationDocument5 pagesAmplitude Modulation and DemodulationNishantKumarNo ratings yet
- Modulation: Frequency. Recall From Previous Chapters (2, 6, 9) That We Can Write This Sinusoidal Carrier C (T) TDocument24 pagesModulation: Frequency. Recall From Previous Chapters (2, 6, 9) That We Can Write This Sinusoidal Carrier C (T) TDuong Phi ThucNo ratings yet
- FM Modulation and Demodulation Circuit Design in MatlabDocument6 pagesFM Modulation and Demodulation Circuit Design in Matlabhassna ait aliNo ratings yet
- Introduction of FSKDocument15 pagesIntroduction of FSKمهيمن الابراهيميNo ratings yet
- Modulation Is The Process of Having The Information To Be Communicated Modifies A Higher Frequency Signal Called ADocument5 pagesModulation Is The Process of Having The Information To Be Communicated Modifies A Higher Frequency Signal Called AMichael JalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemLara Jane ReyesNo ratings yet
- BandwidthDocument25 pagesBandwidthlvsaruNo ratings yet
- How to BEAT the BOARD EXAM using fx-991ES PLUSDocument21 pagesHow to BEAT the BOARD EXAM using fx-991ES PLUSRoger JayNo ratings yet
- KeypadDocument10 pagesKeypadkhrid3No ratings yet
- Adxl103 203Document16 pagesAdxl103 203herbertmgNo ratings yet
- Medium Frequency Broadcast Station in The Philippines PDFDocument45 pagesMedium Frequency Broadcast Station in The Philippines PDFGabrielBacaniNo ratings yet
- How Spot Type Photoelectric Smoke Detectors WorkDocument1 pageHow Spot Type Photoelectric Smoke Detectors Workkhrid3No ratings yet
- Acoustic Detection of Leaks in Water Pipelines UsingDocument8 pagesAcoustic Detection of Leaks in Water Pipelines Usingkhrid3No ratings yet
- Pages From Laplace - TableDocument1 pagePages From Laplace - Tablekhrid3No ratings yet
- Application Guide Fire Safety Hotel Garage A6V10430600 HQ enDocument10 pagesApplication Guide Fire Safety Hotel Garage A6V10430600 HQ enkhrid3No ratings yet
- Case Problem No 4Document2 pagesCase Problem No 4khrid3No ratings yet
- Household Water - Google Forms32Document2 pagesHousehold Water - Google Forms32khrid3No ratings yet
- Tomasi FrontDocument1 pageTomasi Frontkhrid3No ratings yet
- Front PageDocument2 pagesFront Pagekhrid3No ratings yet
- IIR Filter Design Problems and SolutionsDocument21 pagesIIR Filter Design Problems and Solutionskhrid3100% (2)
- Chapter 8 AloyDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Aloykhrid30% (1)
- Chapter 6 Matlab ProblemsDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Matlab Problemskhrid3No ratings yet
- Typical Frequency ResponseDocument1 pageTypical Frequency Responsekhrid3No ratings yet
- Pages From Tomasi-3Document1 pagePages From Tomasi-3khrid3No ratings yet
- Loaded BJT Amplifier With Capacitors That Affect The Low-Frequency Response. Determining The Effect of C On The Low - Frequency ResponseDocument1 pageLoaded BJT Amplifier With Capacitors That Affect The Low-Frequency Response. Determining The Effect of C On The Low - Frequency Responsekhrid3No ratings yet
- 7 1Document24 pages7 1khrid3No ratings yet
- BJT AC Analysis: Cursor Function for Voltage vs Time GraphsDocument1 pageBJT AC Analysis: Cursor Function for Voltage vs Time Graphskhrid3No ratings yet
- Pages From Tomasi-4Document1 pagePages From Tomasi-4khrid3No ratings yet
- 534333Document1 page534333khrid3No ratings yet
- Frequency ConsiderationsDocument1 pageFrequency Considerationskhrid3No ratings yet
- Typical Frequency ResponseDocument1 pageTypical Frequency Responsekhrid3No ratings yet
- Transmission Line Problems on Smith ChartDocument1 pageTransmission Line Problems on Smith Chartkhrid3No ratings yet
- Substituting values gives VCE as 10.16 VDocument1 pageSubstituting values gives VCE as 10.16 Vkhrid3No ratings yet
- EXAMPLE 4.27: 10R) 10 (10 K) 100 K (Satisfied) ) 3.16 VDocument1 pageEXAMPLE 4.27: 10R) 10 (10 K) 100 K (Satisfied) ) 3.16 Vkhrid3No ratings yet