Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diffusion: AND Explanation
Uploaded by
Taimoor Qadeer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesThe process of diffusion
Original Title
Diffusion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe process of diffusion
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesDiffusion: AND Explanation
Uploaded by
Taimoor QadeerThe process of diffusion
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
DIFFUSION
INTRODUCTION AND EXPLANATION
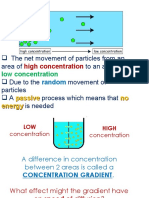
Diffusion is the chemical process when molecules from a
material move from an area of high concentration (where there
are lots of molecules) to an area of low concentration (where
there are fewer molecules). This happens through otherwise
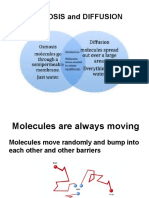
random movement. Diffusion usually happens in a gas although
it can happen in a liquid. It is possible to see diffusion happening
when two liquids are mixed in a transparent container. It
describes the constant movement of particles in all liquids and
gases. These particles move in all directions bumping into each
other. Diffusion can only work with gases and liquids. Here are
some examples of diffusion:
A sugar cube is left in a beaker of water for a while.
The smell of ammonia spread from the front of the
classroom to the back of the room.
Fumes of perfume rise from the bottle when the top is
removed.
Food coloring dropped on the beaker causing to spread
out.
Adding of sugar in water
One of the most important things about diffusion is that
molecules tend to move from places of high concentration to
places of low concentration, just by moving randomly. Therefore,
this is not the most effective way of moving in and out of cells,
however there are many examples where diffusion takes place
but is adapted so it is efficient. For example, there is more
oxygen in a lung than there is oxygen in the blood so oxygen
molecules will tend to move into the blood. Similarly, there is
more carbon dioxide molecules in the blood than in the lung so
carbon dioxide molecules will tend to move into the lung.
Diffusion can be considered to arise from probability alone areas of high density are, due to the random movement of fluid
molecules, likely to spread out within their boundary until they
can do so no longer. Diffusion is also connected to Entropy.
Entropy is a law of nature in which everything slowly goes into
disorder.
You might also like
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument2 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisMera FunportalNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument9 pagesResearch PaperNifemi OlutayoNo ratings yet
- Science SpeechDocument2 pagesScience SpeechzaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Diffusion - TANGDocument3 pagesAssignment 4 Diffusion - TANGJames TangNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Diffusion - TANGDocument3 pagesAssignment 4 Diffusion - TANGJames TangNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument2 pagesDiffusionAnkita SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is Diffusion - Definition, Types & Examples of DiffusionDocument1 pageWhat Is Diffusion - Definition, Types & Examples of Diffusioncarolina pintoNo ratings yet
- 19031121-Abeto-Difusi Molekul Di Dalam AirDocument29 pages19031121-Abeto-Difusi Molekul Di Dalam AirZhafiraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry ProjectGokul100% (1)
- Diffusion Definition: Concentration GradientDocument7 pagesDiffusion Definition: Concentration GradientDeb MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Y10 11 Diffusion ExamplesDocument23 pagesY10 11 Diffusion ExamplesDaniella AjalaNo ratings yet
- Water Ang Ingon Sa Isa Ka Source: Semipermeable MembraneDocument1 pageWater Ang Ingon Sa Isa Ka Source: Semipermeable MembranemarielNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportDocument18 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- (Original Size) Movement in and Out of CellsDocument8 pages(Original Size) Movement in and Out of CellshridanshhirparaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Final NotesDocument16 pagesDiffusion Final NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport NotesDocument10 pagesCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesDiffusion Across The Cell Membranetoro toroNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled Documenttoro toroNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Vs OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion Vs OsmosisK TanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum CodingDocument1 pageLaporan Praktikum CodingHafifah SariNo ratings yet
- B3 Movement Into and Out of Cells SlidesDocument52 pagesB3 Movement Into and Out of Cells SlidesMinh Hoàng ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Body Systems With ExamplesDocument29 pagesDiffusion and Body Systems With Examplestamilore.ishola.101No ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument4 pagesDiffusionROBERTO SHERWIN JR TANDASNo ratings yet
- Passive TransportDocument1 pagePassive TransportMariela SanotaNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument13 pagesDiffusionImen KsibiNo ratings yet
- Class Notes (1) CHP 3 Movement Into and Out of The CellDocument8 pagesClass Notes (1) CHP 3 Movement Into and Out of The CellRahil ShahNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis ExperimentDocument1 pageDiffusion and Osmosis ExperimentJodeth C. CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework: AIM: To Study of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidDocument3 pagesHoliday Homework: AIM: To Study of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidAnonymous JMcaZtNo ratings yet
- Biochem Laboratory Activity 2Document4 pagesBiochem Laboratory Activity 2Kristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion and Osmosisshaniah100% (1)
- Biology Diffusion: Examples of Diffusion in The BodyDocument2 pagesBiology Diffusion: Examples of Diffusion in The BodydonNo ratings yet
- High ConcentrationDocument23 pagesHigh ConcentrationGlprasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Diffusion DetailedDocument7 pagesDiffusion Detailedkimberley StuartNo ratings yet
- Principles of Osmosis and DiffusionDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Osmosis and Diffusionallanlopez_2009No ratings yet
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDocument19 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis Active TransportDocument1 pageDiffusion Osmosis Active Transportbubble26449No ratings yet
- Diffusion & OsmosisDocument19 pagesDiffusion & Osmosishugo roblesNo ratings yet
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDocument19 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationmefunNo ratings yet
- Lesson Note 3 - Investigating Diffusion-Unit 6.3Document6 pagesLesson Note 3 - Investigating Diffusion-Unit 6.3navidu dasisNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis and Active TransportDocument18 pagesDiffusion Osmosis and Active TransportThompson Ta Ta JevonNo ratings yet
- B1.6 DiffusionDocument3 pagesB1.6 DiffusionYevonNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenDocument6 pagesCell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenSimon KnudsenNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisCharlesNo ratings yet
- Movement in and OutDocument35 pagesMovement in and OutzefanyaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of Diffusion.Document2 pagesFactors Affecting The Rate of Diffusion.Abdul Samad50% (2)
- Transport Across MembraneDocument5 pagesTransport Across MembraneRena Emmanuelle PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Membrane Lab ReportDocument7 pagesOsmosis Membrane Lab ReportSandra JabrooNo ratings yet
- 1.0 States of Matter NotesDocument5 pages1.0 States of Matter NotesRajiv BudhooramNo ratings yet
- Diffusion BiologyDocument2 pagesDiffusion BiologyrubeenelbashaNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument11 pagesDiffusionFree LancersNo ratings yet
- Notes Movement in & Out of CellsDocument6 pagesNotes Movement in & Out of CellsddddddffdfdfNo ratings yet
- In and Out of CellsDocument3 pagesIn and Out of CellsA personNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcseDocument5 pagesBIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcsesameehaNo ratings yet
- 2 Diffusion Powerpoint 2Document17 pages2 Diffusion Powerpoint 2aisah isnaeniNo ratings yet
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- Section 2cDocument9 pagesSection 2cdrsohaireNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Lab1Document10 pagesAP Bio Lab1Eva DesireeNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis and Active TransportDocument40 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis and Active TransportCryus LipidNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandRespiratory System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Histolgy Diagrams Year2Document74 pagesHistolgy Diagrams Year2Taimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Applied Aspects 3rd Substage Head and NeckDocument4 pagesApplied Aspects 3rd Substage Head and NeckTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Applied Aspects 5th SubstageDocument10 pagesApplied Aspects 5th SubstageTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Applied Aspects of HeadDocument7 pagesApplied Aspects of HeadTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- CVS SharjeelDocument12 pagesCVS SharjeelTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Orbital Fractures:: Orbit Applied AspectsDocument4 pagesOrbital Fractures:: Orbit Applied AspectsTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- 2ND Year Histology QUICK RECAPDocument12 pages2ND Year Histology QUICK RECAPMarya Safdar100% (2)
- Abdomen and Pelvis GuidelinesDocument10 pagesAbdomen and Pelvis GuidelinesTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Sleep & EpilepsyDocument99 pagesSleep & EpilepsyTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Physiology 2ndyear Guideline by Medicos Studying SkillsDocument25 pagesPhysiology 2ndyear Guideline by Medicos Studying SkillsTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia by DR - SHAHID IQBALDocument9 pagesKingdom Animalia by DR - SHAHID IQBALTaimoor Qadeer100% (1)
- Past UHS MCQsDocument109 pagesPast UHS MCQsTaimoor Qadeer100% (1)
- Plant Diversity PDFDocument37 pagesPlant Diversity PDFTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: Made By: Muzzamil Ali Taimoor Qadeer Submitted To: Teacher MisbahDocument18 pagesAgriculture: Made By: Muzzamil Ali Taimoor Qadeer Submitted To: Teacher MisbahTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- British RajDocument18 pagesBritish RajTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Diffusion: AND ExplanationDocument2 pagesDiffusion: AND ExplanationTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Allah's Predestination and DecreeDocument1 pageAllah's Predestination and DecreeTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet