Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Diffusion - Definition, Types & Examples of Diffusion
Uploaded by
carolina pintoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Diffusion - Definition, Types & Examples of Diffusion
Uploaded by
carolina pintoCopyright:
Available Formats
Login
Type your search
Biology Biology Article Biology Syllabus Biology Imp
Biology > Biology Article > Diffusion
Diffusion
Table of Contents
What is Diffusion?
Types of Diffusion
Factors affecting Diffusion
Examples of Diffusion
Causes of Diffusion
Significance of Diffusion
Diffusion Definition
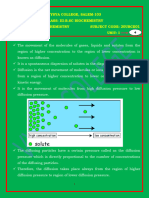
“Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of
higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
down the concentration gradient.”
Read on to explore what is diffusion and the different types of
diffusion.
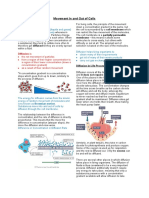
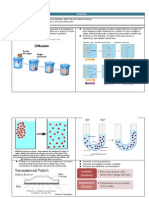
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is the process of movement of molecules under a
concentration gradient. It is an important process occurring in all
living beings. Diffusion helps in the movement of substances in and
out of the cells. The molecules move from a region of higher
concentration to a region of lower concentration until the
concentration becomes equal throughout.
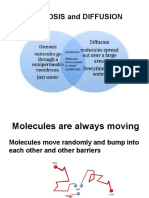
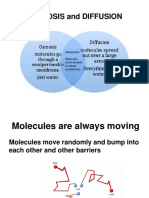
Liquid and gases undergo diffusion as the molecules are able to
move randomly.
Example:
Take water in a beaker. Add a few copper sulfate crystals in one
place and leave it as it is for some time without disturbing it. After
some time we can see that the beaker contains a uniformly
coloured solution. Here, both water and copper sulfate diffuse
independently. With this experiment, we can infer that solutes move
from a higher concentration to a lower concentration in a solution.
Also Read: Diffusion in Plants
Recommended Video:
18,870
Types of Diffusion
Diffusion is widely used in various fields such as biology, physics,
chemistry, etc. Diffusion can be classified into two main types:
Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
Simple diffusion
A process in which the substance moves through a
semipermeable membrane or in a solution without any help from
transport proteins. For example, bacteria deliver small nutrients,
water and oxygen into the cytoplasm through simple diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is a passive movement of molecules across the
cell membrane from the region of higher concentration to the
region of lower concentration by means of a carrier molecule.
Dialysis: It is the diffusion of solutes across a selectively permeable
membrane. A selectively permeable membrane is one that allows
only specific ions and molecules to pass through, while it obstructs
the movement of others.
Osmosis: It is the movement of solvent molecules from the region
of lower concentration to the region of higher concentration
through a semipermeable membrane. Since water is solvent in
every living being, biologists define osmosis as the diffusion of
water across a selectively permeable membrane. For example,
plants take water and minerals from roots with the help of osmosis.
Also Read: Facilitated Diffusion
Factors affecting Diffusion
There are a few factors that affect the process of diffusion,
which individually and collectively alters the rate and extent of
diffusion. These factors include:
Temperature.
Area of Interaction.
Size of the Particle.
The steepness of the concentration gradient.
Examples of Diffusion
A tea bag immersed in a cup of hot water will diffuse into the
water and change its colour.
A spray of perfume or room freshener will get diffused into the
air by which we can sense the odour.
Sugar gets dissolved evenly and sweetens the water without
having to stir it.
As we light the incense stick, its smoke gets diffused into the
air and spreads throughout the room.
By adding boiling water to the dried noodles, the water
diffuses causing rehydration and making dried noodles
plumper and saturated.
Causes of Diffusion
Diffusion is a natural and physical process, which happens on its
own, without stirring or shaking the solutions. Liquid and gases
undergo diffusion as the molecules are able to move randomly. The
molecules collide with each other and change their direction.
Significance of Diffusion
Diffusion is an important process, which is involved in the different
life processes. As mentioned above, it is the net movement of
particles, ions, molecules, solution, etc. In all living species, diffusion
plays an important role in the movement of the molecules during
the metabolic process in the cells.
Diffusion is important for the following reasons:
During the process of respiration, this process helps
in diffusing the carbon dioxide gas out through the cell
membrane into the blood.
Diffusion also occurs in plant cells. In all green plants, water
present in the soil diffuses into plants through their root hair
cells.
The movement of ions across the neurons that generates
electrical charge is due to diffusion.
Also Read: Difference between diffusion and osmosis
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 1. What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of higher
concentration to a region of lower concentration down the
concentration gradient.
Q2 2. List the types of diffusion.
Diffusion can be divided into two main types, namely, simple
diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
Q3 3. What is simple diffusion?
Simple diffusion is defined as the process in which a substance
moves through a semipermeable membrane or in a solution
without any help from transport proteins.
Q4 4. State an example of simple diffusion.
In a cell, water, oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules can pass
directly through the cell membrane without requiring any
energy along the concentration gradient. This is a form of
simple diffusion.
Q5 5. What is facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion can be defined as the passive movement
of molecules across the cell membrane from a region of higher
concentration to a region of lower concentration by means of
a carrier molecule.
Q6 6. Provide an example of facilitated diffusion.
In the human body, glucose molecules, sodium and potassium
ions use carrier proteins to pass through the cell membranes.
Q7 7. How does dialysis work?
Dialysis works through the diffusion of solutes across a
selectively permeable membrane. A selectively permeable
membrane is the one that allows only specific ions and
molecules to pass through while obstructing the movement of
other molecules.
Q8 8. What are the factors affecting diffusion?
Temperature, area of interaction, size of the particle and the
steepness of the concentration gradient are all factors that
affect the process of diffusion.
Q9 9. State the significance of diffusion.
Diffusion is a very important process occurring in all living
beings. All living organisms exhibit one or the other form of
diffusion, allowing the movement of the molecules during
various metabolic or cellular processes.
Learn more about diffusion, its definition, types examples, and other
related topics at BYJU’S Biology
You might also like
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceFrom EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 19031121-Abeto-Difusi Molekul Di Dalam AirDocument29 pages19031121-Abeto-Difusi Molekul Di Dalam AirZhafiraNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument9 pagesResearch PaperNifemi OlutayoNo ratings yet
- Untitled DesignDocument15 pagesUntitled DesignMarianne LopezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry ProjectGokul100% (1)
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisCharlesNo ratings yet
- B3 Movement Into and Out of Cells SlidesDocument52 pagesB3 Movement Into and Out of Cells SlidesMinh Hoàng ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Final NotesDocument16 pagesDiffusion Final NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Gene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisDocument5 pagesGene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisbodurr571No ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument11 pagesDiffusionFree LancersNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportDocument18 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Movement in and OutDocument35 pagesMovement in and OutzefanyaNo ratings yet
- Las-Q3-Wk6.1 2Document12 pagesLas-Q3-Wk6.1 2Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument4 pagesDiffusionROBERTO SHERWIN JR TANDASNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument2 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisMera FunportalNo ratings yet
- 5.7 Cell TransportDocument6 pages5.7 Cell TransportMonica B. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Laboratory Activity 2Document4 pagesBiochem Laboratory Activity 2Kristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- Laporan Physio ExDocument13 pagesLaporan Physio ExsolideoNo ratings yet
- Notes Movement in & Out of CellsDocument6 pagesNotes Movement in & Out of CellsddddddffdfdfNo ratings yet
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDocument19 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationmefunNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument30 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsEmy AnkrahNo ratings yet
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDocument19 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Diffusion - TANGDocument3 pagesAssignment 4 Diffusion - TANGJames TangNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Diffusion - TANGDocument3 pagesAssignment 4 Diffusion - TANGJames TangNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument18 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsEmy AnkrahNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport NotesDocument10 pagesCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Vs OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion Vs OsmosisK TanNo ratings yet
- Bio - 3 4 - Student EditionDocument3 pagesBio - 3 4 - Student EditionZicoNo ratings yet
- 3 - Movement in and Out of CellsDocument5 pages3 - Movement in and Out of CellsAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis and Active TransportDocument2 pagesDiffusion Osmosis and Active TransportNerminNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology: Definition:Is The Study of The Functions of Cell StructureDocument92 pagesCell Physiology: Definition:Is The Study of The Functions of Cell StructureRichard NestorNo ratings yet
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDocument19 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationLee KaiYangNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument2 pagesCell TransportOLIVEROS DESIREE L.No ratings yet
- Personal NotesDocument7 pagesPersonal NoteslayshengNo ratings yet
- Water Ang Ingon Sa Isa Ka Source: Semipermeable MembraneDocument1 pageWater Ang Ingon Sa Isa Ka Source: Semipermeable MembranemarielNo ratings yet
- Tugas Anatomi Perbedaan Osmosis Dan Anatomi: Stikes Mercu Baktijaya Padang Tahun Ajaran 2019/2020Document6 pagesTugas Anatomi Perbedaan Osmosis Dan Anatomi: Stikes Mercu Baktijaya Padang Tahun Ajaran 2019/2020Mita RiskaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion & OsmosisDocument19 pagesDiffusion & Osmosishugo roblesNo ratings yet
- Diffusion DetailedDocument7 pagesDiffusion Detailedkimberley StuartNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenDocument6 pagesCell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenSimon KnudsenNo ratings yet
- In and Out of CellsDocument3 pagesIn and Out of CellsA personNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism Simple DiffusionDocument9 pagesTransport Mechanism Simple DiffusionDhang Foods Sa BilaoNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument33 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsEmy AnkrahNo ratings yet
- Transport Across MembraneDocument5 pagesTransport Across MembraneRena Emmanuelle PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Y10 11 Diffusion ExamplesDocument23 pagesY10 11 Diffusion ExamplesDaniella AjalaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion: AND ExplanationDocument2 pagesDiffusion: AND ExplanationTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Section 1-1Document31 pagesChapter 1 Section 1-1Akar AliNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument2 pagesDiffusionAnkita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Basic Concepts in Biochemistry-HatdogDocument5 pagesAssignment 1 - Basic Concepts in Biochemistry-HatdogAllyssa Lorraine PrudencioNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument2 pagesDiffusionchrisgal21No ratings yet
- Biology-Cell MemraneDocument3 pagesBiology-Cell Memranekrbedes.pboxNo ratings yet
- 1 4 - DiffusionDocument3 pages1 4 - DiffusionsuwethajNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document15 pagesGeneral Biology 1Beejae ApalisNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion - 2nd YearDocument13 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion - 2nd YearFrancisco Samarco100% (1)
- DIFFUSIONDocument6 pagesDIFFUSIONUtsav DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveDocument10 pagesChapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveVanshika VermaNo ratings yet
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcseDocument5 pagesBIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcsesameehaNo ratings yet
- Bio - DiffusionDocument3 pagesBio - DiffusionDoreth BridgemanNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Membrane Lab ReportDocument7 pagesOsmosis Membrane Lab ReportSandra JabrooNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Centum Coaching Team Question Paper English MediumDocument5 pages11th Chemistry Centum Coaching Team Question Paper English MediumpradeepvcpNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) Process For Mild SteelDocument9 pagesOptimization of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) Process For Mild Steelzaki amNo ratings yet
- Atomic Molecular Optical Physics by Hertel C Schulz, Volume 2Document752 pagesAtomic Molecular Optical Physics by Hertel C Schulz, Volume 2anon_user-p100% (3)
- Seismic Design of Retaining WallsDocument23 pagesSeismic Design of Retaining WallsRutvik ShethNo ratings yet
- Fixed Bearing-DrawingDocument1 pageFixed Bearing-Drawingtrichandra maharjanNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Crystalline StructuresDocument71 pagesCH 3 Crystalline StructuresMusab AbdrabbuhNo ratings yet
- 2 Storeys BuildingDocument30 pages2 Storeys BuildinglavyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic LabDocument14 pagesHydraulic LabAbdallah AlhasanNo ratings yet
- From Rankine-Hugoniot Relation Fitting Procedure: Tangential Discontinuity or Intermediate/slow Shock?Document12 pagesFrom Rankine-Hugoniot Relation Fitting Procedure: Tangential Discontinuity or Intermediate/slow Shock?Rizki SuryoNo ratings yet
- New Developments of Near-UV SiPMs at FBK PDFDocument7 pagesNew Developments of Near-UV SiPMs at FBK PDFlaboratorNo ratings yet
- 4 - AltimeterDocument41 pages4 - AltimeterOmarNo ratings yet
- Proposed Pipe Pile Strain Limits For ASCE 61-19: September 2019Document13 pagesProposed Pipe Pile Strain Limits For ASCE 61-19: September 2019JOSEPH MICHAEL HERNANDEZ TAMAYONo ratings yet
- Modelling and Analysis of Guide Rail Brackets and Attaching PartsDocument10 pagesModelling and Analysis of Guide Rail Brackets and Attaching PartsMydesign mkNo ratings yet
- Gas Holdup in A Gasliquid Up Flow Bubble Column in The Presence of Double Cone Promoter PDFDocument8 pagesGas Holdup in A Gasliquid Up Flow Bubble Column in The Presence of Double Cone Promoter PDFCastañeda ValeriaNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Experiments About Light For KidsDocument7 pages9 Science Experiments About Light For KidsgaylebugayongNo ratings yet
- A Parametric Study On Shoring Structures With Multi-Row Anchors in Layered SoilDocument9 pagesA Parametric Study On Shoring Structures With Multi-Row Anchors in Layered SoilJacky LeongNo ratings yet
- Pitppt (Final)Document33 pagesPitppt (Final)Ian GaleonNo ratings yet
- 29.industrial Food-Freezing SystemsDocument17 pages29.industrial Food-Freezing Systemspratheesh100% (1)
- Rheology of The Earth's Mantle: A Historical Review: Gondwana Research July 2010Document30 pagesRheology of The Earth's Mantle: A Historical Review: Gondwana Research July 2010MarcosGouveaNo ratings yet
- 3 Elasticity PDFDocument24 pages3 Elasticity PDFniar asniar100% (1)
- 15 Gas PipingDocument2 pages15 Gas PipingedyNo ratings yet
- OFWHDocument2 pagesOFWHapi-3830954No ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Different Concentrations of Ethanol On Beetroot MembraneDocument7 pagesEffectiveness of Different Concentrations of Ethanol On Beetroot MembraneellaloftiNo ratings yet
- Particulate Processing of Metals and CeramicsDocument98 pagesParticulate Processing of Metals and CeramicsDamy Manesi0% (2)
- 6 MaxwelleqDocument7 pages6 MaxwelleqChristopher Jordan EvoniukNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Temperature Measuring DevicesDocument7 pagesCalibration of Temperature Measuring DevicesGrace N MalikNo ratings yet
- Deaerators: TEGO® AirexDocument8 pagesDeaerators: TEGO® AirexjoeNo ratings yet
- Teori Grup Dan Vibrasi-RevisiDocument204 pagesTeori Grup Dan Vibrasi-RevisiDhieka NopiharguNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Postlab ReportDocument14 pagesFluid Flow Postlab Reportgracebrewster123No ratings yet
- TERRACO WeathercoatDocument4 pagesTERRACO WeathercoatAkhilNo ratings yet