Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 1 Nervous System
Uploaded by
api-2401762160 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageA stimulus is a form of energy such as electromagnetic (light), mechanical (pressure), and sound waves. B. Integration - this is the interpretation of the energy by the Central Nervous System (CNS). (Basically "thinking" about the stimulus leads to a determination of the appropriate response. C. Motor Output - takes the response out of the brain or spinal cord.
Original Description:
Original Title
7 1 nervous system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA stimulus is a form of energy such as electromagnetic (light), mechanical (pressure), and sound waves. B. Integration - this is the interpretation of the energy by the Central Nervous System (CNS). (Basically "thinking" about the stimulus leads to a determination of the appropriate response. C. Motor Output - takes the response out of the brain or spinal cord.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 page7 1 Nervous System
Uploaded by
api-240176216A stimulus is a form of energy such as electromagnetic (light), mechanical (pressure), and sound waves. B. Integration - this is the interpretation of the energy by the Central Nervous System (CNS). (Basically "thinking" about the stimulus leads to a determination of the appropriate response. C. Motor Output - takes the response out of the brain or spinal cord.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
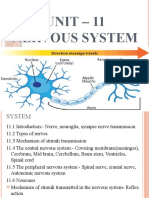
Unit 7: Human Anatomy
Content Outline: Nervous Systems (7.1)
I. Overview of the Nervous System:
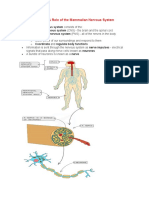
A. Sensory Input - Stimulus sent into the brain or spinal cord.
1. Sensory Receptors receive a stimulus from the environment. A stimulus is a form of
energy such as
electromagnetic (light), mechanical (pressure), and sound waves.
B. Integration
1. This is the interpretation of the energy by the Central Nervous System (CNS).
(Basically thinking about the
stimulus.)
2. This interpretation of the stimulus leads to a determination of the appropriate response.
3. Memories of events can be made during this process.
C. Motor Output - Takes the response out of the brain or spinal cord.
1. The response is carried out by Effector Cells.
a. Effectors are Muscles or Glands. (These can have an effect on your body.)
D. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1. This includes the Sensory Receptors and Motor Nerves.
III. Neuron Structure (Nerve Cell)
A. Cell Body - This takes stimuli from different dendrites and compiles the energy into one signal.
(Like a funnel.)
B. Dendrites - These collect and carry stimuli Energy in to the cell body. (They cover a large area.)
C. Axon - This one arm carries the one compiled signal away toward the next neuron or effector
cell.
D. Myelin Sheath - This is a lipid layer of insulation around the axon created by Schwann Cells. It
prevents the electrical
energy of the neuron from burning the overlying muscle tissue. (It is
analogous to the rubber covering
on electrical wires.)
F. Synapse - This is the gap between neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell.
1. Neurotransmitter - This is the chemical, produced by the neuron, used to transmit the
signal across the gap.
a. The most common neurotransmitter is Acetylcholine.
IV. Reflex Arc (The simplest neural pathway.)
A. A stimulus energy is detected by a Sensory Neuron. (Carries the energy signal to the spinal
cord.)
B. An Interneuron (of the CNS spinal cord) relays the energy back out to the motor nerve instead
of to the brain.
(Inter means go between between the sensory and motor neurons.)
C. The energy is carried out of the CNS by the Motor Neuron. It carries the energy to an effector
cell, usually a muscle.
D. This is why you do not think about a reflex, it just happens. The stimulus never made it to the
brain for integration.
You might also like
- 14.1 The Nervous SystemDocument15 pages14.1 The Nervous SystemNathan TeferaNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sys BiologyDocument6 pagesNervous Sys Biologyalviayaan807No ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument69 pagesCoordination and ResponseRegis WachenukaNo ratings yet
- Nevous System NotesDocument7 pagesNevous System NotesSchool ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Class Notes CH7 Control and CoordinationDocument4 pagesClass Notes CH7 Control and CoordinationArya tyagiNo ratings yet
- Cls 10 Control and CoordinationDocument5 pagesCls 10 Control and CoordinationpokeyballNo ratings yet
- Pre Test 1 Nervous System IntroDocument3 pagesPre Test 1 Nervous System Introsebut saja anonimNo ratings yet
- Nervous System FunctionsDocument234 pagesNervous System Functionsalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- TZ Engl363definition s20Document6 pagesTZ Engl363definition s20api-511320115No ratings yet
- Week 10 BioDocument7 pagesWeek 10 BioTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- The Neuromuscular System and ExerciseDocument20 pagesThe Neuromuscular System and ExercisenofriNo ratings yet
- Notes On THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument15 pagesNotes On THE NERVOUS SYSTEMemanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Fasil Ahmed (MSC) March 2024Document44 pagesNervous System: Fasil Ahmed (MSC) March 2024beletetewodros00No ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument22 pagesControl and CoordinationMozibor RahmanNo ratings yet
- 7 Sensitivity and CoordinationDocument19 pages7 Sensitivity and CoordinationVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Neurons & BiopsychologyDocument29 pagesAP Psych Neurons & BiopsychologyKlein ZhangNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response in Animals - 052037Document8 pagesCoordination and Response in Animals - 052037MosesNo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Document24 pagesOrganisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Mei QiiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Notes #2Document7 pagesNervous System Notes #2LeoNo ratings yet
- Class X - Control and Co-OrdinationDocument9 pagesClass X - Control and Co-OrdinationHardik SinghNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Cabil (G6)Document96 pagesNervous System - Cabil (G6)Lady Ann CabilNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of Behavior: Neural Processing and the Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesBiological Bases of Behavior: Neural Processing and the Endocrine SystemMarina QuaveNo ratings yet
- Neurology Assignment 1Document9 pagesNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7No ratings yet
- Volume 10Document26 pagesVolume 10sequeirachris24No ratings yet
- MARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesMARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue (NT) : Functions of Nerve TissueDocument14 pagesNervous Tissue (NT) : Functions of Nerve TissuekimNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous System Coordination & ReflexesDocument27 pagesHuman Nervous System Coordination & ReflexesJohn DeHans100% (2)
- Nerve Muscle PhysiologyDocument79 pagesNerve Muscle Physiologyroychanchal562100% (2)
- Human Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Nervous SystemI Kadek Adi Putra Suandana 2005No ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument4 pagesClass Notesdaniel holmesNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument71 pagesThe Nervous SystemDennis Limosnero MayorNo ratings yet
- 4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 2)Document1 page4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 2)charmainemakumbe60No ratings yet
- Discussion Notes (Anaphy)Document49 pagesDiscussion Notes (Anaphy)jade tanNo ratings yet
- Neural TissueDocument9 pagesNeural TissueJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- Ch-7, Control and Coordination in Animals. NotesDocument10 pagesCh-7, Control and Coordination in Animals. NotesHimanshi VermaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document23 pagesPresentation 2Maria KhanNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)Document52 pagesNERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)nadeemyakubu47No ratings yet
- ICSE Class X Nervous System NotesDocument20 pagesICSE Class X Nervous System Notesprogrammer.ron.akNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Document65 pagesCoordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Tashwaar TamimNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument43 pagesControl and CoordinationDukhi InsaanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System IDocument4 pagesNervous System Ijo auNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesDocument45 pagesControl and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesPriyanshu ManwaniNo ratings yet
- B10 RevisionDocument21 pagesB10 RevisionPierre BrocasNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemLouise Murphy100% (1)
- Nervous System1Document43 pagesNervous System1human anatomy100% (1)
- Botan's Cns and The Brain 2023Document115 pagesBotan's Cns and The Brain 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- PYC 1501 Basic Psychology Human Nervous System - Impulse ControlDocument10 pagesPYC 1501 Basic Psychology Human Nervous System - Impulse Controlektha_nankoomar9190% (20)
- Unit 11 Nervous SystemDocument117 pagesUnit 11 Nervous SystemChandan Shah100% (1)
- Neuronas y Musculos SternDocument18 pagesNeuronas y Musculos SternAuelillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous SystemRajesh DasariNo ratings yet
- Reflex ArcDocument1 pageReflex Arcpriyamaher2007No ratings yet
- Group 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Document24 pagesGroup 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Tara DolotaNo ratings yet
- General Psychology: The Biological Basis of Psychological FunctioningDocument62 pagesGeneral Psychology: The Biological Basis of Psychological Functioningtracy_jNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Nervous SystemUmair BasheerNo ratings yet
- Class:10 Subject:biology Chapter:control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesClass:10 Subject:biology Chapter:control and Coordinationkhushi guptaNo ratings yet
- Design Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachFrom EverandDesign Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachNo ratings yet
- Bioactivity study of modified curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticlesFrom EverandBioactivity study of modified curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticlesNo ratings yet
- Measurement 1 1 Part2Document1 pageMeasurement 1 1 Part2api-240176216No ratings yet
- Measurement (1 1) Part 1Document1 pageMeasurement (1 1) Part 1api-240176216No ratings yet
- Unit 2b VocabDocument1 pageUnit 2b Vocabapi-240176216No ratings yet
- Plant Animal CellsDocument9 pagesPlant Animal Cellsapi-240176216No ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology Exam ReviewDocument157 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology Exam ReviewJhasmin SalipotNo ratings yet
- 3.IRR of RA 8485 As Amended by RA 10631Document63 pages3.IRR of RA 8485 As Amended by RA 10631ptdwnhroNo ratings yet
- A Morphological and Anatomical Observation in Plant LeavesDocument11 pagesA Morphological and Anatomical Observation in Plant LeavesAli SulaimanNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Plant Structure and FunctionsDocument15 pages1.4 Plant Structure and Functionsaddy prairieNo ratings yet
- Environmental PsychologyDocument5 pagesEnvironmental PsychologyKarthi Keyan VeeraNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Chart Types and UsesDocument18 pagesPedigree Chart Types and UsesDrMohd IQbal SoFiNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Fishes - 2014Document482 pagesThe Physiology of Fishes - 2014Wilson Ramírez100% (1)
- Unit 1 Theoretical Perspectives of Development: StructureDocument11 pagesUnit 1 Theoretical Perspectives of Development: StructureTanyaNo ratings yet
- (Monoclonal Antibodies (Mab or Moab) ) PPDocument37 pages(Monoclonal Antibodies (Mab or Moab) ) PPMohammed R.HusseinNo ratings yet
- The Cultivation of White Oyster MushroomsDocument17 pagesThe Cultivation of White Oyster MushroomsJohn Mark NovenoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Stated and Unstated Information in A Text1Document12 pagesUnderstanding Stated and Unstated Information in A Text1Bella AzisNo ratings yet
- Biosintesis LipidDocument27 pagesBiosintesis LipidNovia EkaNo ratings yet
- The Fascia As Organ of Innerness 2015 EN ChapterDocument16 pagesThe Fascia As Organ of Innerness 2015 EN ChapterJorge Flores TorresNo ratings yet
- Teaching Practice TPTG620 ExcellentDocument43 pagesTeaching Practice TPTG620 ExcellentEngineer ZainNo ratings yet
- 101-Normal Skin MCQsDocument25 pages101-Normal Skin MCQsHybat ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Marcel Veldhuis Scientist Royal Netherland InstituteDocument30 pagesMarcel Veldhuis Scientist Royal Netherland InstituteInder MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Biographical DataDocument29 pagesBiographical DataJai - HoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Ele3103Document14 pagesAssignment Ele3103Yizhar EfendyNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics ExptsDocument13 pagesEnzyme Kinetics ExptsChemistryIndianguyNo ratings yet
- Pages From Fm3!05!70Document16 pagesPages From Fm3!05!70lawofseaNo ratings yet
- ISC Class 12 Biology Question Paper 01 (2018) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5Document5 pagesISC Class 12 Biology Question Paper 01 (2018) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5HemantNo ratings yet
- Ehedg Food Insudtry Cleaning ValidationDocument14 pagesEhedg Food Insudtry Cleaning ValidationDavid100% (2)
- CAD ch1 MCQsDocument3 pagesCAD ch1 MCQsIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Selected Participants For Poster PresentationDocument3 pagesSelected Participants For Poster PresentationraghavandcpNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2MaryWyne CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NotesDocument31 pagesAnatomy NotesDane HoldenNo ratings yet
- Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Goats in Bandar LampungDocument68 pagesSeroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Goats in Bandar LampungAfifah Marwah Al-QadrieNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument6 pagesActivity No. 4 Amino Acids and ProteinsAngel EspanolNo ratings yet
- Pupillary Pathway, Pupillary Abnormalities, RAPDDocument24 pagesPupillary Pathway, Pupillary Abnormalities, RAPD015Afeefa N ANo ratings yet
- 1 Blood Pressure Disorders in Diabetes MellitusDocument467 pages1 Blood Pressure Disorders in Diabetes MellitusPaola alvarezNo ratings yet