Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
dev_ang23Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
dev_ang23Copyright:
Available Formats
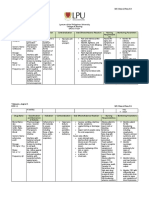
DRUG STUDY
DRUG NAME GENERAL MECHANISM OF INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
CLASSIFICATION ACTION
Ceftriaxone Cephalosporin, The cephalosporins >general >hypersensitivity >diarrhea >do not mix drug with
sodium 2 third interfere with a infections to cephalosporins >rash other antibiotics
grams IV OD generation final step in the >meningitis or related >eosinphilia >ensure for an ANST
in 90cc formation of the >gonococcal antibiotics >nausea >monitor renal or
D5Water to bacterial cell wall conjunctivitis LFTs, coagulation
run for 1 (inhibition of >preoperative studies
hour at 10 mucopeptide for prophylaxis > tell patient to report
microdrops biosynthesis), of infection in lack of response and
per minute resulting in surgery adverse side effects
unstable cell
membranes that
undergo lysis. Also,
cell division and
growth are
inhibited. The
cephalosporins are
most effective
against young,
rapidly dividing
organisms and are
considered
bactericidal
Generally, third
generation
cephalosporins
have more activity
against gram-
negative organisms
and less activity
against gram-
positive organisms
than first-
generation drugs.
Third generation
cephalosporins are
also stable against
beta-lactamases.
Cephalosporins can
be destroyed by
cephalosporinase.
Azithromyci Antibiotic, A macrolide >mild to >hypersensitivity >abdominal >obtain an ECG result
n 500 macrolide antibiotic derived moderate to azithromycin, or pain >obtain a culture and
mg/tab 1 from erythromycin. acute bacterial any macrolide discomfort sensitivity
tab OD Acts by binding to exacerbations antibiotic or >nausea and >obtain CBC, liver or
the P site of the of COPD erythromycin vomiting renal function studies
50S ribosomal >mild CAP >anorexia and cultures when
subunit and may >second line >diarrhea/lo warranted
You might also like
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Herbal Antibiotics and Antivirals: Herbal Medicine to Heal Yourself NaturallyFrom EverandHerbal Antibiotics and Antivirals: Herbal Medicine to Heal Yourself NaturallyNo ratings yet
- CephalexinDocument1 pageCephalexinnj02No ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCefuroxime Drug Studygervisrael.gonzales.twphosiNo ratings yet
- Neofloxin: (Ciprofloxacin IV Infusion)Document1 pageNeofloxin: (Ciprofloxacin IV Infusion)SharifulNo ratings yet
- Tarlac State University College of Science Department of NursingDocument2 pagesTarlac State University College of Science Department of NursingTroy MagcalasNo ratings yet
- Villamaria - Drug StudyDocument11 pagesVillamaria - Drug StudyHey LeunNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesDocument3 pagesDrug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyapi-3717941100% (6)
- Drug AnalysisDocument8 pagesDrug AnalysisDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study1Document15 pagesDrug Study1Mei MifloresNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximePriscilla ChantalNo ratings yet
- ANCEFDocument2 pagesANCEFDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- PiperacillinDocument3 pagesPiperacillinNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Leukupenia, Neutropenia, ThrombocytopeniaDocument3 pagesLeukupenia, Neutropenia, ThrombocytopeniaVANESSANo ratings yet
- Group 5 Subgroup 1: Jomarie Eve D. Enriquez Kurt Russel A. JumuadDocument25 pagesGroup 5 Subgroup 1: Jomarie Eve D. Enriquez Kurt Russel A. Jumuadrakish16No ratings yet
- 4 Cefazolin Drug StudyDocument4 pages4 Cefazolin Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics 1Document64 pagesAntibiotics 1Justin Ancog100% (1)
- Fluoroquinolones: QuinolonesDocument7 pagesFluoroquinolones: QuinolonesGhubaya CopNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocument1 pageCeftriaxone Drug StudyEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- 5drug StudyDocument7 pages5drug StudyPALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- Drug Study of OxytocinDocument4 pagesDrug Study of OxytocinNichole DancelNo ratings yet
- 5 Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument4 pages5 Cefuroxime Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Banaag Antibacterial MedsDocument5 pagesBanaag Antibacterial MedsPrince JoaquinNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument2 pagesCefuroximeJon Corpuz AggasidNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument3 pagesDrug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumPrincess Queenie OlarteNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RyDocument30 pagesDrug Study RyRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocument1 pageCeftriaxone Drug StudyEmjae Colmenares0% (1)
- DG1 CefuroximeDocument1 pageDG1 CefuroximeEkusu Yu ShunNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyyyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyyyAlleinad BarracasNo ratings yet
- Anti-Inffective AgentsDocument2 pagesAnti-Inffective AgentsJamilah BanglanNo ratings yet
- DR Ward - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDR Ward - Drug StudyLoue Jean GulfanNo ratings yet
- Cơ Chế Kháng Thuốc Gram (+) 2Document9 pagesCơ Chế Kháng Thuốc Gram (+) 2Quỳnh Nguyễn Thị NhưNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Inhibits Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis by Binding To One 1 or More of The Penicillin-Binding Proteins (PBPS) WhichDocument12 pagesCefuroxime Inhibits Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis by Binding To One 1 or More of The Penicillin-Binding Proteins (PBPS) WhichMr rawrNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument3 pagesCEFUROXIMEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- PiperacillinDocument3 pagesPiperacillinmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Emnc 4 North Drug StudyDocument12 pagesEmnc 4 North Drug StudyFrancesca Aurea MagumunNo ratings yet
- WTTH - Multidrug Resistant Urinary Tract Infection in A Dog 33066 ArticleDocument5 pagesWTTH - Multidrug Resistant Urinary Tract Infection in A Dog 33066 ArticleCabinet VeterinarNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Sana Husain & Rabia Mukaty FY-C3Document8 pagesAntibiotics: Sana Husain & Rabia Mukaty FY-C3sanNo ratings yet
- DS ObDocument7 pagesDS ObZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease - 5Document5 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease - 5fatqur28No ratings yet
- Drug Study CeftriaxioneDocument2 pagesDrug Study CeftriaxioneJulie LesmorasNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument1 pageCefuroxime Drug StudyDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.No ratings yet
- CS1 AntibioticsDocument4 pagesCS1 AntibioticsTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- CeftraixoneDocument1 pageCeftraixoneJohn HernandezNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximekrz05No ratings yet
- Basics of AntibioticsDocument42 pagesBasics of AntibioticsAsma BakheitNo ratings yet
- Quinolones: Presented by Asst. Prof Jagir Patel Dept. PharmacologyDocument37 pagesQuinolones: Presented by Asst. Prof Jagir Patel Dept. PharmacologyJagirNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefoxitinDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefoxitinShaniah DawaNo ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument4 pagesLevofloxacinWaseem HaiderNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ResumaDocument3 pagesDrug Study ResumaNicole Arriana ResumaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studymarie100% (27)
- Pharmacology AntibioticsDocument70 pagesPharmacology Antibioticsmaggie100% (1)
- Drug Study-AntibacterialDocument6 pagesDrug Study-AntibacterialKyla Marie NabongNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Sugaton - IndivDocument4 pagesDrug Study-Sugaton - IndivPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NicoleDocument6 pagesDrug Study NicoleFrancheska Nicole Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime 1Document3 pagesCefuroxime 1Gwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument66 pagesChemotherapyElias HaimanotNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care: High Risk and Low RiskDocument41 pagesAntenatal Care: High Risk and Low RiskKaneeNo ratings yet
- SZCZEPIENIA I SZCZEPIONKI - Artykuły, Dokumenty Ze StronDocument53 pagesSZCZEPIENIA I SZCZEPIONKI - Artykuły, Dokumenty Ze StronszczepieniaNo ratings yet
- Import Requirements (NEW)Document15 pagesImport Requirements (NEW)Thiago NunesNo ratings yet
- International Observership Form KansascityDocument12 pagesInternational Observership Form Kansascityসোমনাথ মহাপাত্রNo ratings yet
- Pneumococcal Vaccination in AdultsDocument23 pagesPneumococcal Vaccination in AdultsIvelisse TaverasNo ratings yet
- Infection Control and ProphylaxisDocument19 pagesInfection Control and ProphylaxisRechie RechNo ratings yet
- FINAL AddisMeetingReport 0627Document125 pagesFINAL AddisMeetingReport 0627Yusuf KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- A Lowered Probability of Pregnancy in Females in The USA Aged 25 29 Who Received A Human Papillomavirus Vaccine InjectionDocument15 pagesA Lowered Probability of Pregnancy in Females in The USA Aged 25 29 Who Received A Human Papillomavirus Vaccine InjectionChiodo72No ratings yet
- World Pneumonia Day - RYKDocument15 pagesWorld Pneumonia Day - RYKUmair AzizNo ratings yet
- Antitoxins, Antiseptics, and Disinfectants: by Vineet, Yashas and OjaswinDocument8 pagesAntitoxins, Antiseptics, and Disinfectants: by Vineet, Yashas and OjaswinOjaswin SingupurapuNo ratings yet
- Socialis Impulsum: Case BriefDocument3 pagesSocialis Impulsum: Case BriefHarsh DaveNo ratings yet
- Pregnant Women Invitation LetterDocument3 pagesPregnant Women Invitation LetterDulanjalee SachittraNo ratings yet
- 20 Soal Latihan Report Text Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pages20 Soal Latihan Report Text Dalam Bahasa InggrisDewi Lisna100% (1)
- ChickenpoxDocument4 pagesChickenpoxJen Vizcarra CaminoNo ratings yet
- Snims May 2016Document4 pagesSnims May 2016snimslibraryNo ratings yet
- Know Your Hospital - A Guide To Getting The Best CareDocument9 pagesKnow Your Hospital - A Guide To Getting The Best CareMike PosktovaNo ratings yet
- Parents' Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice On Childhood ImmunizationDocument7 pagesParents' Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice On Childhood ImmunizationUlil Amri PramadaniNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Vocabulary Review (Exercises 1)Document4 pagesTOEFL Vocabulary Review (Exercises 1)Jenny A. JamesNo ratings yet
- Final Copy of Newborn CareDocument47 pagesFinal Copy of Newborn CareSheena Claire100% (1)
- Community Health NursingDocument36 pagesCommunity Health Nursingglen100% (1)
- BP2013 IndexDocument70 pagesBP2013 IndexJeffrey AndersonNo ratings yet
- DA PAM 40-11 Preventive Medicine PDFDocument139 pagesDA PAM 40-11 Preventive Medicine PDFNicholas Henry100% (1)
- BP2012 IndexDocument68 pagesBP2012 IndexAsif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Late Presentation of Post Diphtheritic Myocarditis in A 15-Year MaleDocument3 pagesLate Presentation of Post Diphtheritic Myocarditis in A 15-Year MaleFaqih Alam RuqmanaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B and You: What You Need To KnowDocument11 pagesHepatitis B and You: What You Need To KnowMalar MuthiahNo ratings yet
- Quality AssuranceDocument43 pagesQuality Assurancekanika100% (1)
- Dengue Prevention & Control ProgramDocument13 pagesDengue Prevention & Control ProgramJuliet Echo NovemberNo ratings yet
- Citizen CharterDocument14 pagesCitizen CharterM Rajeev ReddyNo ratings yet
- 7 19 2010Document24 pages7 19 2010Durjaa BoodhooNo ratings yet
- Bacteriologia Ion DumbraveanuDocument3 pagesBacteriologia Ion DumbraveanuMihaela LitovcencoNo ratings yet