Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Knowledge Ddeficit
Uploaded by
novagary0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesKnowledge Ddeficit
Uploaded by
novagaryCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
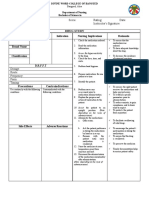
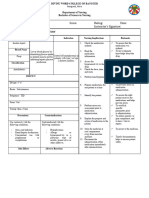
Assessment Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Nursing History: Knowledge deficit After an hour of Independent: After an hour of
r/t condition nurse-patient 1. Provides knowledge base from nurse-patient
A case of Ms. J.M, 16 year prognosis, treatment, interaction the 1. Review disease which patient can make interaction the
old, complained of self care and risk patient will process/prognosis. Discuss informed choices. Effective patient was able to
persistent severe factors for peptic verbalize hospitalization and communication and support at verbalize
abdominal pain. ulcer. understanding of prospective treatment as this time can diminish anxiety understanding of
disease indicated. and promote healing. disease
process, prognosis, Encourage questions, process, prognosis,
Subj. cue: and potential expression of concern. 2. Changing position worsens the and potential
complications. 2. Teach the patient to change pain, so the person often tries to complications.
“ mubalik pa kha ni ako positions slowly
lie very still.
sakit? As verbalized by 3. Teach the patient about the
3. Bland diets may help reduce
patient. appropriate foods to eat when
acid, Restrict or avoid those
nauseated and those to avoid
foods that may cause irritation
4. Teach the patient the
to the digestive system.
Obj. cue: importance of maintaining
4. The body, for its well-being and
fluid intake
to enable it performs mentally
Frequently asking 5. Teach the patient that they
and physically, requires a
question about his need to contact the doctor if
balanced fluid intake.
condition, vomiting persists for more
5. Even if your symptoms are mild,
treatment and diet than 24 hours
you may have peptic ulcers. You
With worried gaze should see your doctor to talk
about your symptoms. Peptic
Lab: ulcers can get worse if they
None aren’t treated.
NURSING CARE PLAN
Name of Pt. ________MS. J.M_______________ Date: _______________________
You might also like
- Intuitive Eating in Treatment of Eating Disorders by Evelyn Tribole, MS, RDDocument5 pagesIntuitive Eating in Treatment of Eating Disorders by Evelyn Tribole, MS, RDEvelyn Tribole, MS, RD100% (1)
- Tibia and Fibula Fracture PhysiotherapyDocument31 pagesTibia and Fibula Fracture Physiotherapyunknown unknown100% (1)
- Performance Appraisal FormDocument3 pagesPerformance Appraisal FormGautam Dutta100% (1)
- NCP of Patient With GastritisDocument4 pagesNCP of Patient With GastritisBer AnneNo ratings yet
- Silverstein L, Kurtzman G y Shatz P. (2009) Suturing For Optimal Soft Tissue Manament. Journal of Oral Implantology Vol. 35 (2), 82-90 PDFDocument9 pagesSilverstein L, Kurtzman G y Shatz P. (2009) Suturing For Optimal Soft Tissue Manament. Journal of Oral Implantology Vol. 35 (2), 82-90 PDFamilesco0% (1)
- NEW - Hormone Balancing DrinkDocument9 pagesNEW - Hormone Balancing DrinkTAE'S POTATONo ratings yet
- Etched Cast RestorationsDocument41 pagesEtched Cast Restorationssharanya chekkarrajNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For AbortionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For AbortionCarson Birth100% (2)
- NCP For Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument5 pagesNCP For Hyperemesis Gravidarumclaire parkNo ratings yet
- NCP On Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than A Body Requirements R/T Inability To Ingest FoodDocument1 pageNCP On Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than A Body Requirements R/T Inability To Ingest FoodErle Gray CadangenNo ratings yet
- "Nagsusuka Ang Anak Ko.": Nursing Care ProcessDocument2 pages"Nagsusuka Ang Anak Ko.": Nursing Care Processgeorgia50% (2)
- Afinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesAfinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - CancerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - CancerChristineAla0% (1)
- GERDDocument5 pagesGERDSteve Randolph67% (3)
- NCP2 CunananDocument2 pagesNCP2 CunananAbbyNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning: By: Chin V. UlamDocument2 pagesDischarge Planning: By: Chin V. UlamChin Villanueva UlamNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPJo Chiko FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Cough NCPDocument2 pagesCough NCPMYLENE GRACE ELARCOSANo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - SLHDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan - SLHheartyprincess54No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Independent: MedicationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Independent: MedicationWinsel Therese CAMARI�ASNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument4 pagesJaundicepamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarivic Yuson MalagarNo ratings yet
- Sample TCP - GraceGuitguitenDocument4 pagesSample TCP - GraceGuitguitenLauren JalandoniNo ratings yet
- KUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE ConstipationDocument2 pagesKUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE Constipationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- NCP For MIDocument5 pagesNCP For MIjaira magbanuaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationRainier Rhett ConchaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermLorie May GuillangNo ratings yet
- Forro Intestinal Obstruction-2Document4 pagesForro Intestinal Obstruction-2Shiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageGestational Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanASIS, MARK ANTHONY M.No ratings yet
- CancerDocument3 pagesCancerShaira De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (AGE)Document2 pagesDiarrhea (AGE)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Stroke Care Plan PDFDocument1 pageStroke Care Plan PDFJot grewalNo ratings yet
- University of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingDocument23 pagesUniversity of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingReina RamonesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NCP Template 2Document2 pagesDrug Study NCP Template 2Janico Lanz BernalNo ratings yet
- Name: Babu Kaji Maharjan: Patient's IdentificationDocument6 pagesName: Babu Kaji Maharjan: Patient's IdentificationAlisha MaharjanNo ratings yet
- SLU Nursing Care Plan for Gastric MassDocument3 pagesSLU Nursing Care Plan for Gastric MassSoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- Name: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralDocument2 pagesName: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Nursing DignosisDocument5 pagesNursing DignosisvishnukulakkadaNo ratings yet
- Forro Intestinal ObstructionDocument3 pagesForro Intestinal ObstructionShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument3 pagesAssessmentJemma GandaNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 NCPDocument5 pagesActivity 5 NCPAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis Nursing Care PlanVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- HealthDocument6 pagesHealthBernadette_Ort_4336No ratings yet
- NSG Man BulimiaDocument21 pagesNSG Man BulimiaMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation for GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation for GastroenteritisgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- University of The Philippines ManilaDocument6 pagesUniversity of The Philippines ManilaTessa Lisbury SteakNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDan MandigNo ratings yet
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: O V A ADocument16 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: O V A AKym RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Chapoco Week 10Document4 pagesChapoco Week 10sofia yapNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia: Monitoring and Maintaining Serum Potassium LevelsDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia: Monitoring and Maintaining Serum Potassium LevelsDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- 2 PlanDocument8 pages2 PlanAyobami AdeleyeNo ratings yet
- Name: de Guzman, Cameron Josh B. Section: 2Bsn-ADocument3 pagesName: de Guzman, Cameron Josh B. Section: 2Bsn-ACameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NCP For SchizoDocument6 pagesNCP For SchizoGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- OB - NCP (Episiotomy)Document3 pagesOB - NCP (Episiotomy)eosNo ratings yet
- NCP 1. Molar PregnancyDocument2 pagesNCP 1. Molar PregnancyMaria Eliza AgustinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-1: Medical Diagnoses: Colorectal CancerDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan-1: Medical Diagnoses: Colorectal CancerBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Liver DiseaseDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Liver DiseaseTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Insulin AspartDocument2 pagesInsulin AspartCrissah LacernaNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer & Metabolic SyndromeDocument9 pagesPeptic Ulcer & Metabolic SyndromeApril Mae Magos LabradorNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Perineal Laceration Pain ManagementDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Perineal Laceration Pain ManagementAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Dilatation and CurettageDocument2 pagesDilatation and CurettageBheru Lal50% (2)
- Clien With CMLDocument4 pagesClien With CMLAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge Deficit FINALDocument8 pagesNCP Knowledge Deficit FINALJOSHUA JOSE TERCEnONo ratings yet
- UPSC Prelims 2021 Geography Revision: High Probable Topics Part 2Document86 pagesUPSC Prelims 2021 Geography Revision: High Probable Topics Part 2PreethiNo ratings yet
- Face Eyes Nose Programme 2019Document13 pagesFace Eyes Nose Programme 2019Renato GoodfellowNo ratings yet
- Section 16: Additional Information: Health Hazard 3 Fire Hazard 1Document1 pageSection 16: Additional Information: Health Hazard 3 Fire Hazard 1johnNo ratings yet
- Bionic Final PDFDocument4 pagesBionic Final PDFJasmine RaoNo ratings yet
- Noncompliance Unilateral Maxillary Molar DistalizationDocument6 pagesNoncompliance Unilateral Maxillary Molar Distalizationaa bbNo ratings yet
- Madre de Cacao With Lemon Scent As Hand Sanitizer: By: Johnro P. LustadoDocument20 pagesMadre de Cacao With Lemon Scent As Hand Sanitizer: By: Johnro P. LustadoJamailla MelendrezNo ratings yet
- Broselow Pediatric Emergency TapeDocument13 pagesBroselow Pediatric Emergency TapePaulo KaleNo ratings yet
- Rare Homeopathic Remedies for Specific ConditionsDocument8 pagesRare Homeopathic Remedies for Specific ConditionsIndhumathiNo ratings yet
- Infection Control: Tel: SnleprometricDocument14 pagesInfection Control: Tel: SnleprometricSami MdNo ratings yet
- Sub-Adventitial Divestment Technique For Resecting Artery-Involved Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort StudyDocument11 pagesSub-Adventitial Divestment Technique For Resecting Artery-Involved Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort StudyMatias Jurado ChaconNo ratings yet
- Turkey's Growing Healthcare Sector Driven by Private ProvidersDocument69 pagesTurkey's Growing Healthcare Sector Driven by Private ProviderssbulenterisNo ratings yet
- Sociological Theories of Deviance: Definitions & ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesSociological Theories of Deviance: Definitions & ConsiderationsP TejeswariNo ratings yet
- Hospital Business ModelsDocument8 pagesHospital Business ModelsPOLOKO MHUSIWANo ratings yet
- Bilateral Congenitally Missing Second Premolars in A Growing Female PatientDocument5 pagesBilateral Congenitally Missing Second Premolars in A Growing Female PatientIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Time Out: GrammarDocument8 pagesTime Out: GrammarNguyễnVũHoàngTấnNo ratings yet
- Misrak FeyissaDocument41 pagesMisrak FeyissaN SNo ratings yet
- ANA MAPEH S2017 Ans KeyDocument15 pagesANA MAPEH S2017 Ans KeyVan Errl Nicolai SantosNo ratings yet
- Legalize ItDocument2 pagesLegalize Itaisar aisarNo ratings yet
- B NursingDocument10 pagesB NursingAyeshia OliverNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeDocument13 pagesTherapeutic Communication: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeJor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Zimmer Cemented CPTDocument20 pagesZimmer Cemented CPTJayjeet BhoiteNo ratings yet
- Reading 3Document3 pagesReading 3Astri R SitumorangNo ratings yet
- Stiletto - Spring 2015Document24 pagesStiletto - Spring 2015TGI Justice ProjectNo ratings yet
- CrossFit®-Injury Prevalence and Main Risk Factors (Curiosidade)Document5 pagesCrossFit®-Injury Prevalence and Main Risk Factors (Curiosidade)TUTOR PAULO EDUARDO REDKVANo ratings yet
- Ecological Systems Theory by Bronfenbrenner: Prepared By: Karen B. Reginaldo Jung PuertoDocument20 pagesEcological Systems Theory by Bronfenbrenner: Prepared By: Karen B. Reginaldo Jung Puertochristian ferrerNo ratings yet