Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GSM Cellular Mobile Network: By:-Pankaj Choudhary
GSM Cellular Mobile Network: By:-Pankaj Choudhary
Uploaded by
seriousreader0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesThis document provides an overview of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) cellular network standards. It describes GSM as a set of standards for narrowband digital voice transmission controlled by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute. The key objectives of GSM are to create a common cellular spectrum across countries, enable international roaming, increase network capacity, and accommodate new services through evolution of the digital network. The document then outlines the main GSM network standards, techniques used including frequency reuse and handover processes, and the architecture including base transceiver stations, mobile switching centers, home and visitor location registers.
Original Description:
Original Title
Gsm Presentation
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) cellular network standards. It describes GSM as a set of standards for narrowband digital voice transmission controlled by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute. The key objectives of GSM are to create a common cellular spectrum across countries, enable international roaming, increase network capacity, and accommodate new services through evolution of the digital network. The document then outlines the main GSM network standards, techniques used including frequency reuse and handover processes, and the architecture including base transceiver stations, mobile switching centers, home and visitor location registers.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesGSM Cellular Mobile Network: By:-Pankaj Choudhary
GSM Cellular Mobile Network: By:-Pankaj Choudhary
Uploaded by
seriousreaderThis document provides an overview of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) cellular network standards. It describes GSM as a set of standards for narrowband digital voice transmission controlled by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute. The key objectives of GSM are to create a common cellular spectrum across countries, enable international roaming, increase network capacity, and accommodate new services through evolution of the digital network. The document then outlines the main GSM network standards, techniques used including frequency reuse and handover processes, and the architecture including base transceiver stations, mobile switching centers, home and visitor location registers.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
GSM Cellular Mobile Network
By:-
Pankaj Choudhary
1 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
What is GSM?
GSM stands for “Global System for Mobile
Communications”
GSM is a set of standards for narrowband(i.e
200-KHz Bandwidth) digital voice
transmission.
Under the control of the European
Telecommunication Standards institute
(ETSI).
2 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
Aim and Objective of GSM System
Common radio spectrum in all countries.
Integrated spectrum with international
roaming.
Create large single market.
Increase available cellular radio capacity.
Better security functions.
Accommodate new services.
Compatibility with evolution of digital n/w.
3 Pankaj Choudhary2009
GSM-900 and GSM-1800 Standards
z
4 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
Techniques used in GSM
5 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
Frequency Reuse
6 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
Handover process in GSM
7 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
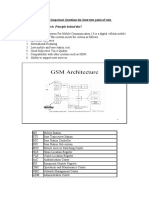
GSM System Architecture
8 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
BASE TRANSCEIVER STATION
9 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
GSM Network Entity
Mobile Service Switching Center
( MSC )
holds all the switching functions
manages the necessary radio resources,
updating the location registration
carrying out the inter-BSC and inter- MS
handover.
10 Inter-working with other networks (IWF).
Pankaj Choudhary 2010
GSM Network Entity
Home Location Register
( HLR )
Manages the mobile subscribers
database
subscriber information
part of the mobile location information
3 identities essential
the International Mobile subscriber
Identity
the Mobile station ISDN Number
the VLR address
11 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
GSM Network Entity
Visitor Location Register
( VLR )
dynamically stores subscriber information
needed to handle incoming/outgoing calls
Mobile Station Roaming Number
Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity, if
applicable
The location area in which the mobile has
been registered
Data related to supplementary service
12 parameters Pankaj Choudhary 2010
GSM Network Example
13 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
Logical Channels
Traffic TCH/F: Full-rate Traffic Channel Two-way
channels TCH/H: Half-rate Traffic Channel
(TCH)
FCCH: Frequency correction
BCH SCH: Synchronization
BCCH: Broadcast control
Base-to-
Signaling PCH: Paging mobile
CCCH
channel AGCH: Access grant
RACH: Random access
SDCCH: Stand-alone dedicated control
DCCH
SACCH: Slow associated control
Two-way
FACCH: Fast associated control
14 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
THANKS……….
15 Pankaj Choudhary 2010
You might also like
- CNT03 Basic 2G Technology Architecture PDFDocument33 pagesCNT03 Basic 2G Technology Architecture PDFSarun praNo ratings yet
- Cours Jamel HATTAY RX Mobile s1 TelecomDocument161 pagesCours Jamel HATTAY RX Mobile s1 TelecomHeba SelmiNo ratings yet
- Training Index: Mobile Network TelecommunicationsDocument16 pagesTraining Index: Mobile Network Telecommunicationsعلي عباسNo ratings yet
- Cs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersDocument11 pagesCs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersValar MathiNo ratings yet
- Cs 72 Mobile Computing 2 Mark Questions Unit I 1) What Are The Categories of Mobile Services?Document20 pagesCs 72 Mobile Computing 2 Mark Questions Unit I 1) What Are The Categories of Mobile Services?Rama SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing-Question With Answers SHORT NOTES MCDocument46 pagesMobile Computing-Question With Answers SHORT NOTES MCTauseef khan100% (2)
- Wireless and Mobile All-IP Networks: Yi-Bing Lin and Ai-Chun Pang Liny@csie - Nctu.edu - TWDocument80 pagesWireless and Mobile All-IP Networks: Yi-Bing Lin and Ai-Chun Pang Liny@csie - Nctu.edu - TWSabareesan SankaranNo ratings yet
- The Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Document32 pagesThe Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)devajeet_nerist2840No ratings yet
- GSM General Questions and Answers & Some Practical KnowledgeDocument11 pagesGSM General Questions and Answers & Some Practical KnowledgealonindNo ratings yet
- Building Bridges of UnderstandingDocument55 pagesBuilding Bridges of UnderstandingmobinilstarNo ratings yet
- Cs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersDocument11 pagesCs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersNivithaNo ratings yet
- 02 GSM FundamentalsDocument27 pages02 GSM FundamentalsWANKHAMANo ratings yet
- GSM Network Architecture: Mobile StationDocument6 pagesGSM Network Architecture: Mobile StationGurcan KavogluNo ratings yet
- Internship PPT BSNLDocument39 pagesInternship PPT BSNLDeependra SinghNo ratings yet
- Questions On GSM History of GSMDocument10 pagesQuestions On GSM History of GSMAzeemuddin KhajaNo ratings yet
- Better or Worse?: The Volte User ExperienceDocument34 pagesBetter or Worse?: The Volte User ExperiencesushiNo ratings yet
- Name: Pratyay Saha. Stream: Electronics & Communication Engineering. Year: 4 - Semester: 8 - Roll No: 08182003048. Registration No: 081820110115Document15 pagesName: Pratyay Saha. Stream: Electronics & Communication Engineering. Year: 4 - Semester: 8 - Roll No: 08182003048. Registration No: 081820110115Subir MaityNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Wireless IP Network Architectures: OutlineDocument25 pagesChapter 2: Wireless IP Network Architectures: OutlineLee TeaNo ratings yet
- GSM Basic QuestionsDocument11 pagesGSM Basic QuestionsAqęēļ ShèrGįļļNo ratings yet
- Telecom Interview Questions & AnswersDocument8 pagesTelecom Interview Questions & AnswersMd Saidur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Basic Telecom Questions and AnswersDocument20 pagesBasic Telecom Questions and AnswersMuhammad Kashif84% (25)
- Abcdefghi M NOP Rstuv: Glossary JKL Q Wxyz ADocument7 pagesAbcdefghi M NOP Rstuv: Glossary JKL Q Wxyz ASaptono GunawanNo ratings yet
- Mobile ComputingDocument17 pagesMobile ComputingPiyush SinghNo ratings yet
- It1402 Mobile Computing 2Document24 pagesIt1402 Mobile Computing 2bhrathikNo ratings yet
- GSM Global System For Mobile Communications: Telecommunication EngineeringDocument23 pagesGSM Global System For Mobile Communications: Telecommunication EngineeringAbid SagorNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions On GSMDocument18 pagesInterview Questions On GSMNikhil PandyaNo ratings yet
- GSM Concepts & RF Optimization: Presented By: Anjnay SharmaDocument32 pagesGSM Concepts & RF Optimization: Presented By: Anjnay SharmaAnjnay SharmaNo ratings yet
- GSM BasicsDocument22 pagesGSM BasicsSasanka Chamara GamageNo ratings yet
- Presentation Seminar On TelecommunicationDocument49 pagesPresentation Seminar On TelecommunicationAise HeNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Call Flow in GSM Core: Presented byDocument31 pagesA Presentation On Call Flow in GSM Core: Presented byChowkidar Amit MishraNo ratings yet
- Handoff GeneralDocument30 pagesHandoff Generaldangdoan2008No ratings yet
- Ziaullah 075 A2Document4 pagesZiaullah 075 A2Umar FarooqNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 GSMDocument181 pages1.3.1 GSMJosue FredesNo ratings yet
- GSM 2Document29 pagesGSM 2Nitesh JainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GSM: GSM Standardization and Service AspectsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To GSM: GSM Standardization and Service AspectsThiaguNo ratings yet
- GSMDocument130 pagesGSMhelpbgpNo ratings yet
- Unit-5: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication) What Is GSM?Document23 pagesUnit-5: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication) What Is GSM?AkankshaguptaNo ratings yet
- Watm Services: The Type of Data That Can Be TransferredDocument17 pagesWatm Services: The Type of Data That Can Be TransferredNeema Dev BobeenaNo ratings yet
- GSM 130921051638 Phpapp01Document23 pagesGSM 130921051638 Phpapp01andutokichoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Mobile Communication Systems PDFDocument70 pagesChapter 8. Mobile Communication Systems PDFPhan Vũ KiệtNo ratings yet
- Introduction of GSM PrincipleDocument33 pagesIntroduction of GSM PrincipleOmi OmneeNo ratings yet
- Some Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1Document23 pagesSome Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1nileshNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 2021Document26 pagesLec 2 2021Al7asanAmmarNo ratings yet
- Second Generation Mobile SystemsDocument28 pagesSecond Generation Mobile SystemsUmair KhanNo ratings yet
- 3G Communication Protocols: 4.1 UTRAN Protocol Structure: The Encryption Mechanism Is Built Into RadioDocument9 pages3G Communication Protocols: 4.1 UTRAN Protocol Structure: The Encryption Mechanism Is Built Into RadioSithija AlwisNo ratings yet
- Cellular System Infarstructure FHSSDocument79 pagesCellular System Infarstructure FHSSUmayanga MadushanNo ratings yet
- GSM NetworkDocument23 pagesGSM NetworkLidiyaa WandeNo ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture: Chapter 6: GSM System OverviewDocument48 pagesWireless and Mobile Network Architecture: Chapter 6: GSM System OverviewJesus RosalesNo ratings yet
- Channels and Identiies in GSMDocument5 pagesChannels and Identiies in GSMshashikala kotiNo ratings yet
- Mobile Node Correspondent Node Home Network Foreign Network Foreign Agent Home Agent Care - of AddressDocument3 pagesMobile Node Correspondent Node Home Network Foreign Network Foreign Agent Home Agent Care - of AddressMustafa Troy TroyNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 - Introduction To GSM and CDMADocument45 pagesLecture7 - Introduction To GSM and CDMANatnael MesheshaNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Architecture: Masood HabibDocument46 pagesGSM Network Architecture: Masood Habibdev12janNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImpcsDocument11 pagesIntroduction To ImpcskrkancinaNo ratings yet
- Core Network ReportDocument24 pagesCore Network ReportACDC TeamNo ratings yet
- Cheat 24Document3 pagesCheat 24BANGBANG 127No ratings yet
- Figure 1. General Architecture of A GSM NetworkDocument15 pagesFigure 1. General Architecture of A GSM NetworkPiyush MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Fixed/Mobile Convergence and Beyond: Unbounded Mobile CommunicationsFrom EverandFixed/Mobile Convergence and Beyond: Unbounded Mobile CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- The Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsFrom EverandThe Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- IP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureFrom EverandIP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent W-CDMA UMTS Radio Principles: Training ManualDocument188 pagesAlcatel-Lucent W-CDMA UMTS Radio Principles: Training Manualbigpack1982No ratings yet
- 100 KPI's For Mobile Telecom Operators - Consultant Value AddedDocument6 pages100 KPI's For Mobile Telecom Operators - Consultant Value Addedsuru2712No ratings yet
- Ir21 TM Colombia - v41 - 30apr2015Document21 pagesIr21 TM Colombia - v41 - 30apr2015Jesus RosalesNo ratings yet
- Second Generation Mobile Systems: Dr. Tuhina Samanta Lecturer Dept of I.TDocument16 pagesSecond Generation Mobile Systems: Dr. Tuhina Samanta Lecturer Dept of I.TnangaayissiNo ratings yet
- Mohammad Reza Pasandideh - ThesisDocument166 pagesMohammad Reza Pasandideh - ThesismickyalemuNo ratings yet
- Arm NewDocument347 pagesArm Newvenu4a1No ratings yet
- Telecommunication BasicsDocument18 pagesTelecommunication Basicsd_aroyNo ratings yet
- Intercepting and Redirecting Outgoing Calls With CAMEL Application PartDocument2 pagesIntercepting and Redirecting Outgoing Calls With CAMEL Application Partedenisn edenisnNo ratings yet
- Cellular Data AnalysisDocument100 pagesCellular Data AnalysisLeur SenacheNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent 8650 SDM R3.1 - FeatureOverview-Common Platform PDFDocument105 pagesAlcatel-Lucent 8650 SDM R3.1 - FeatureOverview-Common Platform PDFEllis OkpotiNo ratings yet
- Training Seminar ON GSM Held at BSNL: Presented By: Charli Bagga Kriti Rastogi (AEI-08)Document51 pagesTraining Seminar ON GSM Held at BSNL: Presented By: Charli Bagga Kriti Rastogi (AEI-08)Ankita BharadwajNo ratings yet
- 3G KPI Formula Ericsson NSN Huawei###Document97 pages3G KPI Formula Ericsson NSN Huawei###Wahyu KurniawanNo ratings yet
- HP Communications & Media Solutions Products and Solutions GuideDocument80 pagesHP Communications & Media Solutions Products and Solutions GuideThilina SampathNo ratings yet
- GSM Overview PresentationDocument22 pagesGSM Overview PresentationVenkata RamanaNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Call FlowDocument18 pagesWcdma Call FlowaymancNo ratings yet
- 2G Evolution, GSM Principle, Network ArchitectureDocument80 pages2G Evolution, GSM Principle, Network Architecturemanojsingh474No ratings yet
- GSM-Power Control, H-O, DTXDocument32 pagesGSM-Power Control, H-O, DTXRaju Sutradhar100% (1)
- GPRS Call Flow - v20021218Document36 pagesGPRS Call Flow - v20021218rookie.caozhongzeNo ratings yet
- MC R20 - Unit-2Document43 pagesMC R20 - Unit-2Yadavilli VinayNo ratings yet
- Mvno A4 2106Document12 pagesMvno A4 2106Ahmed SamyNo ratings yet
- SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking ServiceDocument7 pagesSMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking ServiceashariNo ratings yet
- 0IB401101 UVC System Introduction ISSUE1.00Document19 pages0IB401101 UVC System Introduction ISSUE1.00Christophe MalgogneNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 23.251Document20 pages3GPP TS 23.251santanameroNo ratings yet
- The Future of Mobile Communications: Professor Rolando Carrasco BSC (Hons), PHD, Ceng, FieeDocument47 pagesThe Future of Mobile Communications: Professor Rolando Carrasco BSC (Hons), PHD, Ceng, Fieevaibhav7492No ratings yet
- Paf-Kiet: Project ProposalDocument4 pagesPaf-Kiet: Project Proposaltalha khanNo ratings yet
- SV Interface PDFDocument16 pagesSV Interface PDFSrinath VasamNo ratings yet
- MPC - Unit 1Document60 pagesMPC - Unit 1Janarish Saju CNo ratings yet
- GSM and SS7 OverviewDocument16 pagesGSM and SS7 Overviewnkverma53No ratings yet
- GPON Mobile BackhaulDocument48 pagesGPON Mobile BackhaulWiswanto Wae100% (2)
- Cs 6304 Analog and Digital Communication 2 Marks and 16 Marks Questions and Answers 2 Marks Unit 1Document6 pagesCs 6304 Analog and Digital Communication 2 Marks and 16 Marks Questions and Answers 2 Marks Unit 1Thiru DaaNo ratings yet