Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formulae For PDF
Formulae For PDF
Uploaded by
Vinayak MuleyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulae For PDF
Formulae For PDF
Uploaded by
Vinayak MuleyCopyright:
Available Formats
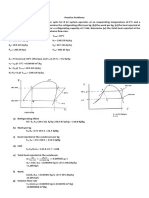
Quick reference Formulae
Temperature C or K
C = 5 9 (F - 32)
Pressure SI unit Pascal 1 Pa = 1 N/m2, too small a unit Common unit = Bar 1 Bar =105 N/m2= 0.1 Mpa
Atmospheric Pressure = 1 Bar abs at MSL Vacuum = 0 Bar abs Gauge pressure + Atmospheric pressure = Absolute pressure barg = kg/cm2g Density in kg/m3
Specific Volume = 1 / Density in m3/kg Specific Gravity = Density ratio to water Energy SI unit = 1 Joule = 1 Nm = 4.186 cal Common unit = kilocalorie 1 kcal = heat reqd to raise 1 kg water by 1C 1 kcal = 4186.8 Joules Cp = sp. heat capacity in kcal/kg C Conversions between SI and other units mWC = meters water column 1 Bar = 10 mWC 1 Bar = 14.23 PSI (Lbs/in2) 150 psi = 10.54 Kg/cm2g 50 psi = 3.5 Kg/cm2g
10 bar g = 11 bar a = 10.2 kg/cm2g = 11.2 kg/cm2a = 145 psig = 1 MPa = 106 N/m2
Where = Density(kg/m3) m = Mass (kg) V= Volume (m3) vg= Specific volume (m3/kg)
Enthalpy of saturated steam:
hg = hf + hfg Where: hg = Total enthalpy or total heat of saturated steam (kJ/kg) hf = Liquid enthalpy (Sensible heat) (kJ/kg) hfg = Enthalpy of evaporation (Latent heat) (kJ/kg)
(c) Steamline 2008
Page 10.1
Formulae
Back to top
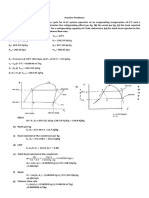
Heat Balance in Process:
Where, Primary Q = Quantity of heat energy released (in kcals) m = Mass of steam releasing the heat (in kgs) hfg = Specific enthalpy of evaporation of steam (in kcals/kg) Secondary Q = m x cp x T Where, Secondary Q = Quantity of heat energy absorbed (in kcals) m = Mass of the substance absorbing the heat (in kgs) cp = Specific heat capacity of the substance (in kcals / kg C ) T = Temperature rise of the substance (in C) Primary Q = Secondary Q Primary Q = m x hfg
Heat transfer equation:
Q = U x A x T Where: Q = Heat transferred per unit time (kcals/hr) U = Overall heat transfer coefficient (kcals/hr / mC) A = Heat transfer area (m) T = Temperature difference between the primary and secondary fluid (C)
Steam line sizing:
D = 1000 x Where, D = Line size in mm m = Mass flowrate of steam in kg/h V = Specific volume in m3/kg = a constant 3.14 c = velocity m/s 4xmxV 3600 x x c
Calculating Savings:
Boiler Heat Input = Qf x GCV where, Qf = Quantity of fuel (in kg/hr) GCV (Gross Calorific Value) =Energy contained in fuel in kcal/kg Boiler Heat Output = Qs x (Hs - Hw) where, Qs = Quantity of steam (in kg/hr) Hs = Heat contained in steam (Enthalpy of Saturated steam hg) Hw = Heat already present in the water from which steam is raised Boiler = Qs x (Hs - Hw) Qf x GCV of fuel kg/hr x kcal/kg kcal/kg kg/hr x Rs/kg
Qf =
Qs x (Hs - Hw) GCV x
Cost of solid fuel =
Qs x (Hs - Hw) x Cost of fuel GCV x Qs x (Hs - Hw) x Cost of fuel GCV x x
Page 10.2
Cost of FO / gas =
litres/hr x Rs/litre
(c) Steamline 2008
Formulae
Back to top where, Qc = Quantity of condensate (in kg/hr) Hc = Heat contained in condensate (in kcal/kg) Hw = Heat already present in the water at ambient tenmperature (in kcal/kg) GCV (Gross Calorific Value) =Energy contained in fuel in kcal/kg = Boiler efficiency = Specific gravity of liquid/gas fuel
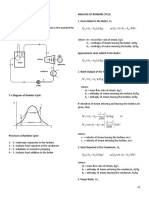
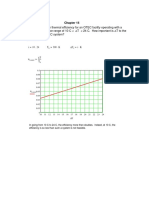
% Flash steam calculation:
% Flash steam generated = ( hf1 - hf2 ) x 100 hfg2
Where, hf1 = Enthalpy of water at the higher pressure kcal/kg hf2 = Enthalpy of water at the flashing pressure kcal/kg hfg2 = Enthalpy of evaporation at the flash steam pressure
Flash Steam Pressure
% Flash Steam Generated
Condensate Pressure (kg/cm 2 g)
Actual rating of a Boiler:
Actual Rating = F&A Rating X 540 / ( hg hfFW) where, hg = enthalpy of steam at generation pressure hfFW = Feed water enthalpy
Blowdown:
Blowdown (in kgs) = Where, F = Feedwater TDS in ppm B = Boiler water set point in ppm S = Steam generation in kg/hr. Back to top F XS B-F
(c) Steamline 2008
Page 10.3
Formulae
You might also like
- Board Problems 2Document11 pagesBoard Problems 2Josue Carubio Ricalde Jr.100% (2)
- Evap Cond F F G G Sat SatDocument17 pagesEvap Cond F F G G Sat SatAlexis CarpenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18 Solving Problem On Boiler Performance - Students - Vol 2Document68 pagesLecture 18 Solving Problem On Boiler Performance - Students - Vol 2Dr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN100% (2)
- Performance OF Boilers: Bibin ChidambaranathanDocument58 pagesPerformance OF Boilers: Bibin ChidambaranathanDr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN50% (2)
- 4single Effect Evaporators ProblemsDocument24 pages4single Effect Evaporators Problemsananth2012100% (5)
- Eto Na Lex 2 10Document10 pagesEto Na Lex 2 10Alexis CarpenaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Gambar Febri Heat PumbDocument9 pagesTugas Gambar Febri Heat PumbPONTAS ABDULLAH HASIBOEANNo ratings yet
- SteamDocument36 pagesSteamsalilm31100% (2)
- LESSON 9 Steam Generators 2Document12 pagesLESSON 9 Steam Generators 2Salt PapiNo ratings yet
- 2-21 LastDocument22 pages2-21 LastAlexis CarpenaNo ratings yet
- Formula 7Document3 pagesFormula 7Raj SakariaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5-Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesMODULE 5-Rankine CycleNigel Ceasar SilvaNo ratings yet
- Condenser Flow Rate CalculationDocument2 pagesCondenser Flow Rate Calculationjoo2585No ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant (Rankine Cycle)Document8 pagesSteam Power Plant (Rankine Cycle)Antonio BeraoNo ratings yet
- Cooling LoadDocument91 pagesCooling LoadPiyush PandeyNo ratings yet
- Blower PowerDocument8 pagesBlower PowerRaffy Luna100% (1)
- ACMV - Revision Notes - 2Document3 pagesACMV - Revision Notes - 2daniel.lim7725No ratings yet
- Boiler Capacity: Ton/hour Is The Amount of Heat (At 100C) That Can Change Water To Stream (In 1 Hour)Document23 pagesBoiler Capacity: Ton/hour Is The Amount of Heat (At 100C) That Can Change Water To Stream (In 1 Hour)S Tunkla EcharojNo ratings yet
- Gpsa - M05Document21 pagesGpsa - M05mobywicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Useful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowDocument3 pagesUseful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowAshok BaldaniyaNo ratings yet
- Useful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowDocument3 pagesUseful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowAshok BaldaniyaNo ratings yet
- Steam Main PropertiesDocument14 pagesSteam Main Propertiespoojapsharma83No ratings yet
- Edr 3 Prob 4Document7 pagesEdr 3 Prob 4Arfel Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- 15.1 250 KG/H of Air Saturated at 2°C Is Mixed With 50 KG/H of Air at 35°C and 80% RHDocument17 pages15.1 250 KG/H of Air Saturated at 2°C Is Mixed With 50 KG/H of Air at 35°C and 80% RHNathan EscobalNo ratings yet
- Week 5 & 6Document10 pagesWeek 5 & 6Mariel MirafloresNo ratings yet
- Toluene Energy 2520 BalanceDocument3 pagesToluene Energy 2520 Balanceapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Cooling Towers and Air DryersDocument21 pagesCooling Towers and Air DryersVince Harrison BalfermosoNo ratings yet
- RankineDocument12 pagesRankineMeej AustriaNo ratings yet
- New Energy BlanceDocument23 pagesNew Energy BlanceArslan SamNo ratings yet
- Coolingtowerdryer 140208204949 Phpapp02 PDFDocument22 pagesCoolingtowerdryer 140208204949 Phpapp02 PDFJel SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Boiler Efficiency CalculationDocument4 pagesBoiler Efficiency CalculationasifdcetNo ratings yet
- ClassWork CPD 2022Document20 pagesClassWork CPD 2022crazzyboy292No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document17 pagesChapter 4Thanh LâmNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 - 2Document82 pagesThermodynamics 2 - 2Collin FarNo ratings yet
- Combustion Notes (University Level)Document44 pagesCombustion Notes (University Level)Devdutt Sharma100% (1)
- 2nd Assignment Sa Ipe 2Document9 pages2nd Assignment Sa Ipe 2Pryce YurongNo ratings yet
- 7-Boiler PerformanceDocument21 pages7-Boiler PerformanceYohan ManaligodNo ratings yet
- Boiler PerformanceDocument21 pagesBoiler PerformanceLily CruzNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: By: Engr. Ejay P. MarasiganDocument49 pagesThermodynamics: By: Engr. Ejay P. MarasiganGodwill Escabel100% (1)
- Vapor Compression CycleDocument23 pagesVapor Compression CycleNiaz KilamNo ratings yet
- ch14 PDFDocument8 pagesch14 PDFAkash ThummarNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 and Data ShammaDocument4 pagesExp 4 and Data ShammaAhmed ShammaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Measurements and PropertiesDocument18 pagesBasics of Measurements and Propertiespoojapsharma83No ratings yet
- Balance de Energia de Reactor: Calculo Del Calor Del SueloDocument27 pagesBalance de Energia de Reactor: Calculo Del Calor Del SueloJana ElyNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionsDocument7 pagesFuels and CombustionsRica ArellagaNo ratings yet
- Performance PlantDocument20 pagesPerformance Plantpoojapsharma83No ratings yet
- Formulas - PipeDocument34 pagesFormulas - PipeReuben Madera DabaNo ratings yet
- Hvac Lab 3Document24 pagesHvac Lab 3Crystian Kobee EmpeynadoNo ratings yet
- 8 Steam Power Plant UpdatedDocument15 pages8 Steam Power Plant UpdatedyanyanNo ratings yet
- Reactor:: Energy BalanceDocument4 pagesReactor:: Energy BalanceSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- ch13 PDFDocument6 pagesch13 PDFAkash ThummarNo ratings yet
- HVAC Precooled AHU CalculationDocument4 pagesHVAC Precooled AHU CalculationPradeep Sukumaran100% (1)
- RefrigerationDocument34 pagesRefrigerationArshi KhanNo ratings yet
- Fuels and Lubricants PDFDocument99 pagesFuels and Lubricants PDFShamveel TaiyabNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 in PpeDocument3 pagesAssignment No. 1 in PpeJenny Mae PomedaNo ratings yet
- Pembangkitan Daya Dari PanasDocument33 pagesPembangkitan Daya Dari PanasFaiz IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Data - Sheet - 1 - Carbon Dioxide Capture From Internal Combustion Engine Exhaust Using Temperature Swing AdsorptionDocument10 pagesData - Sheet - 1 - Carbon Dioxide Capture From Internal Combustion Engine Exhaust Using Temperature Swing AdsorptionKhadija RAISSINo ratings yet
- Angricultural ProcessingDocument8 pagesAngricultural ProcessingYendis Samson100% (1)
- 477 220 Harware PDFDocument9 pages477 220 Harware PDFzoksiNo ratings yet
- To Perform The Torsion Test OnDocument8 pagesTo Perform The Torsion Test OnBurhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- TMI Tutorials - Smear Slide Analysis - Getting StartedDocument18 pagesTMI Tutorials - Smear Slide Analysis - Getting StartedwessilissaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 2 ChemistDocument5 pagesPractice Exam 2 ChemistFATIN FARHANAH BINTI HALIDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Industrial Building System in MalaysiaDocument14 pagesIntroduction of Industrial Building System in MalaysiaNurazwani AhmadNo ratings yet
- BHEL Standards For Cable TraysDocument18 pagesBHEL Standards For Cable TraysLokesh Kumar KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Foot and Leg Protectors Ð Requirements and Test Methods For Toecaps and Metal Penetration Resistant InsertsDocument19 pagesFoot and Leg Protectors Ð Requirements and Test Methods For Toecaps and Metal Penetration Resistant InsertsArif Hasnat JonyNo ratings yet
- System Bekaplast™: Plastics EngineeringDocument5 pagesSystem Bekaplast™: Plastics EngineeringMau Atenas PerezNo ratings yet
- YASHICA Crease RecoveryDocument2 pagesYASHICA Crease RecoveryYashica Gupta100% (1)
- Question 1-Open EndedDocument4 pagesQuestion 1-Open EndedAshadi HamdanNo ratings yet
- TGD 15 Spray Structural PFPDocument48 pagesTGD 15 Spray Structural PFPXian Ying LimNo ratings yet
- Skin TonesDocument15 pagesSkin Tonesanuyasane9776No ratings yet
- Chemistry Important Questions Part2Document7 pagesChemistry Important Questions Part2KARTHIK MNo ratings yet
- Maintain Training FacilitiesDocument14 pagesMaintain Training Facilitiesrodel megollasNo ratings yet
- June 2023 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CAIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument16 pagesJune 2023 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CAIE Chemistry IGCSESkylight Stxrs100% (1)
- Catalogue Generale FPD 100 Ea4Document76 pagesCatalogue Generale FPD 100 Ea4Achraf BoudayaNo ratings yet
- Clay Specification BrochureDocument8 pagesClay Specification BrochureMohammed sabatinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry June 2008 KanDocument8 pagesChemistry June 2008 KanPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- Theory of Centrifugal Casting & Effect of Thermophysical PropertyDocument16 pagesTheory of Centrifugal Casting & Effect of Thermophysical PropertynisargNo ratings yet
- Din 7603Document10 pagesDin 7603Marcin100% (1)
- ASTM D4984 CO2 en Gas NaturalDocument3 pagesASTM D4984 CO2 en Gas Naturalfamturbo0% (1)
- CHM 475 Inorganic Chemistry: (Experiment 8)Document5 pagesCHM 475 Inorganic Chemistry: (Experiment 8)FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- 8598 1934 PDFDocument8 pages8598 1934 PDFichaigirisaNo ratings yet
- On The Immersed Friction Stir Welding of Aa6061-T6 A Metallurgic and Mechanical Comparison To Friction Stir WeldingDocument5 pagesOn The Immersed Friction Stir Welding of Aa6061-T6 A Metallurgic and Mechanical Comparison To Friction Stir WeldingKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Bemol Mos2 MsdsDocument4 pagesBemol Mos2 MsdsCarlos BrachoNo ratings yet
- Sikagrout® - 200 PDFDocument2 pagesSikagrout® - 200 PDFMohamed SalahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Air PressureDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 Air PressureSanjana ShahNo ratings yet
- Foaming Capacity of Soaps (Ameen Rasool)Document18 pagesFoaming Capacity of Soaps (Ameen Rasool)Ameen RasoolNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Solution Practice Set Objective by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument1 pageMole Concept Solution Practice Set Objective by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry50% (2)
- Bibliografia Polioles DownDocument11 pagesBibliografia Polioles DownNedy Margarita Gómez SánchezNo ratings yet