Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capacitors Tips CP
Capacitors Tips CP
Uploaded by
Moni KakatiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Capacitors Tips CP
Capacitors Tips CP
Uploaded by
Moni KakatiCopyright:
Available Formats
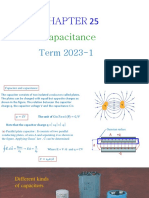
CAPACITORS
1. Electrostatics of Conductors r r a) Field inside the conductor is zero E 0 = E p . The charges reside on the surface.
b) Electric just outside the conductor is to the surface of conductor. c) Electrostatic Potential is same all throughout the charged conductor. d) Electric field near the surface of charged conductor: e) Surface Charge Density: 2. Capacitance: C =
1 r2 = 2 r1
q V C medium = KA 0 = KC vacuum d
2 0 L r log e b r a
A 0 d 4 0 (ra rb ) Spherical Capacitor: C = rb ra
Parallel Plate Capacitor: C = 3. Grouping of Capacitors: 1 = Series Grouping: Cs
Cylindrical Capacitor: C =
1
i
V = V1 + V 2
C2 V1 = C +C 2 1 C1 q1 = C +C 2 1
C1 V2 = C +C 2 1
Parallel Grouping: C p =
q = q1 + q 2
C2 q2 = C + C q 2 1 q2 1 1 4. Energy stored in Capacitor: U = CV 2 = qV = 2 2 2C U 1 = 0E2 5. Energy Density of parallel plate capacitor: u = Vol 2 6. Loss of Energy due to Sharing of Charges C V + C 2V2 C C (V V2 )2 Common Potential: V = 1 1 Energy Loss: U = 1 2 1 C1 + C 2 2(C1 + C 2 ) 7. Dielectrics 1 1 1 E p = E 0 1 p = 0 1 q p = q 0 1 K K K For Conductors: K = E = 0 , else q p q and p
Capacitance with Dielectric: C =
A 0 d t + t K
q2 2 A 0
8. Force between plates of Capacitor: F =
CAREER POINT, GUWAHATI CENTRE, G.S.ROAD, BORA SERVICE BYE LANE, GUWAHATI Ph: 0361-2466191/9864342927/9435101613
You might also like
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Capacitor 2Document31 pagesCapacitor 2Shaheer MirzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24: Capacitance and DielectricsDocument23 pagesChapter 24: Capacitance and Dielectricsccny07No ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument38 pagesCapacitorPiyush Vidyarthi100% (3)
- CapasitorsDocument30 pagesCapasitorsthinkiitNo ratings yet
- CapacitanceDocument40 pagesCapacitancerishi0% (1)
- Capacitance Theory EDocument36 pagesCapacitance Theory Ethinkiit100% (5)
- PHYSICS 2 Capacitor and CapacitanceDocument21 pagesPHYSICS 2 Capacitor and CapacitanceJohn Aaron HerreraNo ratings yet
- Note 4 PDFDocument20 pagesNote 4 PDFmarvellous muchechesiNo ratings yet
- Definitions & Examples: C C C CDocument47 pagesDefinitions & Examples: C C C CSeroKeretaMasaroWidiarNo ratings yet
- Position Vector:: C A P A C I T O RDocument41 pagesPosition Vector:: C A P A C I T O RRajeev Ranjan0% (1)
- Physics 212 Equation SheetDocument1 pagePhysics 212 Equation SheetStetson TurnerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Capacitor and Dielectrics 2016 ReviewedDocument69 pagesChapter 2 Capacitor and Dielectrics 2016 ReviewedSyaza IzzatyNo ratings yet
- CapacitanceDocument6 pagesCapacitancesenakevinNo ratings yet
- Class 07: Outline: Hour 1: Conductors & Insulators Expt. 2: Electrostatic Force Hour 2: CapacitorsDocument76 pagesClass 07: Outline: Hour 1: Conductors & Insulators Expt. 2: Electrostatic Force Hour 2: CapacitorsArrizky Putra NoordiansyahNo ratings yet
- Ch24 SSMDocument14 pagesCh24 SSMShaodong HuangNo ratings yet
- Hapter Int For XerciseDocument13 pagesHapter Int For XerciseLandau PopeNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument24 pagesUntitledanh anhNo ratings yet
- LEC - 10 Circuit 1Document67 pagesLEC - 10 Circuit 1mariamamr28624No ratings yet
- Capacitors & Energy StorageDocument44 pagesCapacitors & Energy StoragearuunrsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document10 pagesChapter 4ayunna ayunniNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitDocument23 pagesRC CircuitjanaNo ratings yet
- Capacitors - 1 PDFDocument17 pagesCapacitors - 1 PDFsriNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Solved Sheet For IITDocument8 pagesCapacitors Solved Sheet For IITSourabh DhavalaNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument26 pagesCapacitorsalman104alviNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET12Document8 pagesWORKSHEET12Anfeli JamesNo ratings yet
- Capacitancia y Dieléctricos SolDocument26 pagesCapacitancia y Dieléctricos SolYULEIMY YASMIN LUCAS ZASIGANo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument42 pagesCapacitorSujan ThapaliyaNo ratings yet
- CapacitanceDocument4 pagesCapacitancePaul Bronzon DurensNo ratings yet
- Lecture07-09 (pt2)Document63 pagesLecture07-09 (pt2)Özgür BOZANo ratings yet
- @aakashallen: QV QCVDocument21 pages@aakashallen: QV QCVAyush KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 2 CapacitanceDocument11 pages2 CapacitanceRaja Singh RNo ratings yet
- Classroom Assignment 4-1Document5 pagesClassroom Assignment 4-1Bishoy EmileNo ratings yet
- CapasitorDocument38 pagesCapasitorAhmad Arif ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- CUET Physics Chapter 7Document117 pagesCUET Physics Chapter 7arao3873No ratings yet
- CapacitanceDocument27 pagesCapacitancevenumadhavkattagoni100% (3)
- Exercise - I: Objective Problems (Jee Main)Document21 pagesExercise - I: Objective Problems (Jee Main)PranivoidNo ratings yet
- EE241: E C I: Lectric IrcuitsDocument64 pagesEE241: E C I: Lectric Ircuitss2-qx (s2.qx)No ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Capacitance and EnergyDocument27 pagesLecture 11 Capacitance and Energyvaldesc_tolNo ratings yet
- 2 Combinations of Capacitors, Energy of CapacitorsDocument11 pages2 Combinations of Capacitors, Energy of CapacitorsNauman QureshyNo ratings yet
- Chap25 10Document9 pagesChap25 10Anthony DuniganNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument27 pagesCapacitorsAr YanNo ratings yet
- CapcatiroDocument2 pagesCapcatirohumaidhtubeNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C NotesDocument23 pagesAP Physics C NotesBaba YuNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Physics Test in ElectrostaticsDocument4 pagesIIT JEE Physics Test in ElectrostaticsSanjay Kumar DokaniaNo ratings yet
- Applied Science Department (ASD) Centre For Foundation Studies and Extension Education (Fosee)Document9 pagesApplied Science Department (ASD) Centre For Foundation Studies and Extension Education (Fosee)tym101No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Capacitors (Student Copy) yDocument63 pagesUnit 2 Capacitors (Student Copy) yFazilah TawasilNo ratings yet
- Capasitor B InggrisDocument16 pagesCapasitor B InggrisSentraGintingNo ratings yet
- DPP 25 To 31 Electrostatics 7 Capacitance 15 06 2013 HOMEWORK PDFDocument32 pagesDPP 25 To 31 Electrostatics 7 Capacitance 15 06 2013 HOMEWORK PDFAmey KaleNo ratings yet
- EMF Exercise Class 6 Answers: D) X A (B CDocument3 pagesEMF Exercise Class 6 Answers: D) X A (B CRoshan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Exercise MCQ BCDocument16 pagesCapacitance Exercise MCQ BCRaaghav SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Type 1Document11 pagesCapacitance Type 1SubhashChandraMishraNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument28 pagesElectrostaticssonaliswain2345No ratings yet
- CH 25 CapacitanceDocument10 pagesCH 25 CapacitancesamiNo ratings yet
- Ch24 CapacitanceDocument23 pagesCh24 CapacitancethissisnateNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Chapter 16Document33 pagesSolucionario Chapter 16web SoftNert ChileNo ratings yet
- Exercise-01: MCQ (Single Choice Correct)Document5 pagesExercise-01: MCQ (Single Choice Correct)Shyam JhaNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and DielectricsDocument11 pagesCapacitance and DielectricsHiba SobhiNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Mechanic & DynamicsDocument1 pageMechanic & DynamicsMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- OPtics Notes IITDocument18 pagesOPtics Notes IITMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Physics, Halliday, Resnick and Walker (Chapter 31, Q.No-31)Document2 pagesFundamental of Physics, Halliday, Resnick and Walker (Chapter 31, Q.No-31)Moni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Optics TipsDocument2 pagesOptics TipsMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Waves and Sound Subjective QuestionsDocument1 pageWaves and Sound Subjective QuestionsMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Material & MagnetismDocument1 pageMagnetic Material & MagnetismMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Calculus Assignment - IIT-JEE, AIEEEDocument2 pagesCalculus Assignment - IIT-JEE, AIEEEMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE 2012 Physics QuestionsDocument8 pagesIIT-JEE 2012 Physics QuestionsmonikakatiNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument1 pageProperties of MatterMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- River Boat ConceptDocument1 pageRiver Boat ConceptMoni Kakati50% (2)
- Practical Viva QuestionsDocument1 pagePractical Viva QuestionsMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Magnetism FORMULADocument1 pageMagnetism FORMULAMoni Kakati0% (1)
- Heating & Chemical - TipsDocument1 pageHeating & Chemical - TipsMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Debrogliewaves CPDocument2 pagesDebrogliewaves CPMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- MagnetismoDocument41 pagesMagnetismoomaramunNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitsDocument24 pagesElectrical Circuitshamang khullafahNo ratings yet
- RPMT 2005 Question PaperDocument7 pagesRPMT 2005 Question PaperMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Mass Force and GravityDocument8 pagesMass Force and GravityMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Math 5Document2 pagesMath 5Moni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry: SO HCO CO NODocument3 pagesInorganic Chemistry: SO HCO CO NOMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Phy Test 9Document1 pagePhy Test 9Moni KakatiNo ratings yet