Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Globalization Effects HRM
How Globalization Effects HRM
Uploaded by
asimmatloobCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Globalization Effects HRM
How Globalization Effects HRM
Uploaded by
asimmatloobCopyright:
Available Formats
now Clobollzotloo effects nkM
The term Globalization has invaded the mind oI every successIul businessman and
the concept oI Global Village is a common issue in the modern business world.
What really the globalization is? The answer seems simple "iI a Iirm or an
organization expands its sales or production beyond the national boundaries, then it
is globalization", but it does not cover the real meaning oI the term. Globalization
actually means more, much more than that; it is realizing that there is a big world
out there, geographically, that reaches Iar beyond our small community and that
the world is getting closer to us all the time. Globalization is the realization that,
whether we like it or not, this big world is becoming an ever increasing Iactor in
our daily lives.
The concept oI globalization today has invaded the globe and the national
boundaries have been virtually eliminated. So what is the eIIect oI this? Simple,
the world today has became a small but a very very complex and dynamic
neighborhood. Today we live in a global village and this means that our activities
have crossed the national boundaries to become global.
Globalization symbolizes the structural making oI the world characterized by the
Iree Ilow oI technology and human resources across national boundaries presenting
an ever-changing and competitive business environment. A vital aspect oI
globalization is the way diverse challenges are being Iaced by nations in an
increasingly inter dependent world. No country can meaningIully progress today
without eIIiciently responding to demands and pressures generated by international
organizations and processes.
When going global, an organization has to reconsider the Iollowing Iactors:
O mployment Laws
O ulture
O Terminology
O orporate Social Responsibility
Globalization and HRM
Globalization is a process that is drawing people together Irom all nations oI the
world into a single community linked by the vast network oI communication
technologies. This aspect oI globalization has also aIIected the HRM in the
business world oI today. HR managers today not need to rely in a small limited
market to Iind the right employees needed to meet the global challenge, but today
they can recruit the employees Irom around the world. Besides that the eIIective
data based which is being used globally today also has made HRM a simple but
eIIective task. Thus due to globalization to some extent HRM has became more
eIIicient and eIIective, but relatively a simple task.
The most important Iactor that these organizations are made up oI People, and
since HRM is the set oI activities which deals with the people Iactor present in any
organization, this change has aIIected The Human Resources Management itselI a
lot. Human resources manager oI today must ensure that the appropriate mix oI
employees in terms oI knowledge, skills and culture.
Global HRM reIers to Human Resource Management practices that deal with
managing a diversity oI workIorce Irom all around the world.
The Iollowing challenges are being Iaced by HR managers in terms oI
globalization:
- Managing diversity oI workIorce.
- Managing pressures Ior more labor rights in third world countries.
- Managing Outsourcing oI employees.
- More part-time and temporary work
- Managing productivity and Quality
- Downsizing the workIorce
- oping with Ilexible working hours
Role oI HRM
The role oI the HR manager must parallel the needs oI the changing
organization. SuccessIul organizations are becoming more adaptable,
resilient, quick to change directions, and customer-centered. Within
this environment, the HR proIessional must learn how to manage
eIIectively through planning, organizing, leading and controlling the
human resource and be knowledgeable oI emerging trends in training and
employee development.
The Iuture success oI any organizations relies on the ability to
manage a diverse body oI talent that can bring innovative ideas,
perspectives and views to their work. The challenge and problems Iaced
oI workplace diversity can be turned into a strategic organizational
asset iI an organization is able to capitalize on this melting pot oI
diverse talents. With the mixture oI talents oI diverse cultural
backgrounds, genders, ages and liIestyles, an organization can respond
to business opportunities more rapidly and creatively. More importantly, iI the
organizational environment does not support diversity broadly, one
risks losing talent to competitors. This is especially true
Ior multinational companies (MNs) who have operations on a global
scale and employ people oI diIIerent countries, ethical and cultural
backgrounds.
Thus, a HR manager needs to be mindIul and may employ a
Think Global, Act Local` approach in most circumstances. The challenge
oI workplace diversity is also prevalent amongst Singapore`s Small and
Medium nterprises (SMs). With a population oI only Iour million
people and the nation`s strive towards high technology and
knowledge-based economy; Ioreign talents are lured to share their
expertise in these areas. Thus, many local HR managers have to undergo
cultural-based Human Resource Management training to Iurther their
abilities to motivate a group oI proIessional that are highly qualiIied
but culturally diverse. Furthermore, the HR proIessional must assure
the local proIessionals that these Ioreign talents are not a threat to
their career advancement. In many ways, the eIIectiveness
oI workplace diversity management is dependent on the skilIul balancing
act oI the HR manager.
Globalization and the hanging Face oI Human Resource Management
Globalization crush have had Iurther eIIects on HRM such as:
O democratization and pressures Ior more labor rights in countries where such
rights have been restricted
O more liberalization and deregulation
O competition Ior investment
O increased economic independence oI nations
O capital, inIormation and technology Ilows are on the increase
,internationalization oI enterprises and creation oI mergers and alliances
O ompetitiveness increasingly based (not on low wages or natural resources)
on knowledge/innovation, skills and productivity. The success oI global
companies is to a large extent dependent on their ability to organize (within
and between organizations) across national boundaries inIormation, money,
people and other resources.
O Moving production overseas to reduce costs and to Iacilitate sensitivity to
local and regional market requirements.
O ontracting out and out-sourcing. It is an important rationale oI out-sourcing
that it, on the one hand, enables an enterprise to concentrate on its core
competencies, and on the other hand, it makes service work more
productive.
O "Outsourcing is needed not just because oI the economics involved. It is
required equally because it gives opportunities, income and dignity to
service work and service workers."
O More part-time and temporary work (especially among women, the elderly
and students)
O Introduction oI new technology
O Pushing Ior a more deregulated and Ilexible labor market
O More emphasis on productivity and quality
O Greater employee involvement in the design and execution oI work
O ShiIting the Iocus oI collective bargaining Irom the nation/industry level to
the enterprise level.
O mployers are oI the view that issues relevant to the employment
relationship such as work re-organization, Ilexible working hours and
contractual arrangements, and pay Ior perIormance and skills, are
increasingly workplace-related, and should thereIore be addressed at the
enterprise level.
O xceptionally (in the USA) employers have reduced terms oI employment
through 'concession bargaining' when Iirms have been in Iinancial
diIIiculties.
O Downsizing the workIorce.
O One important response has been the introduction oI Ilexibility in the
employment relationship to increase the capacity oI enterprises to adapt
rapidly to market changes. This has involved measures such as Ilexible
working hours, part-time work, diIIerent types oI employment contracts to
the standard ones Iamiliar to collective IR Ilexibility in Iunctions, so that
employees who are multi-skilled are not conIined to the perIormance oI only
one task. They can cover up Ior absenteeism, and make some jobs
redundant, Ilexible pay which involves some component oI pay being
dependent on perIormance, whether oI the company, a group or the
individual.
O Globalization has, through technology diIIusion, substantially increased the
introduction oI new technology. This, as well as the need Ior Ilexible
adaptation to market changes, have led to the re-organization oI production
systems and methods oI work, such as the Iollowing:
O Reduction oI narrow job classiIications and demarcation lines between
managers and workers, accompanied by skills enhancement needed to
perIorm jobs with a broader range oI tasks.
O Increasing areas Ior worker involvement in the conception, execution and
control oI work.
O A greater Iocus on workplace relations and policies and practices conducive
to better motivation and perIormance such as inIormation-sharing and two-
way communication.
O These responses have increased the necessity Ior employers to make more
investments in skills training, to oIIer incentives to employees to improve
their skills, and Ior workers to take upon themselves some responsibility Ior
their own development.
O The competition generated by globalization and rapid technological changes
accompanied by shorter product liIe have, while destroying countless jobs in
industrialized countries, created opportunities Ior multi-skilled and easily
trainable workers, and Ior the most signiIicant group oI emerging employees
- the knowledge worker.
O nowledge and skills have become the most important determinants oI
investment, employment opportunities, productivity and quality and oI
Ilexibility.
O The impact globalization and inIormation technology have had on each other
has made work more mobile, capable oI being perIormed in diIIerent parts
oI the world without the need to actually set up physical Iacilities in other
countries.
Thus traditional HR has been challenged to accommodate diIIerent types oI
employment contracts, and diIIerent types oI pay systems to reward
perIormance and skills...Now HR is being seen as a business partner and
hence a very critical Iunction ..
In my opinion the qualities that a Human Resource Manager should have to
become the best are :
O xcellent ommunication Skills
O excellent Inter Personal Skills
O Be a Strategic Thinker
O visionary leader
O ntrepreneur Global Benchmarking
O High degree oI Initiative
O B an All Rounder
O een Researcher
O Global Networking Ability
O Technology Savvy
O Ability to cope with a Fast hanging nvironment.
The globalization is a HRM hallenge. The HRM Function has to make its
policies, procedures and processes to work on the global level. urrently, most oI
the HRM Policies is Iocused on the concrete country, but the employees have to
start to move Irom the country to another country and the HRM Processes have to
be able to support such a need in the organization. The globalization has a huge
impact on the HRM Function and the it is usually not ready to take more
responsibility in the movement oI the workIorce around the Globe.
You might also like
- Beyond The Wage - Ordinary Work in Diverse EconomiesDocument315 pagesBeyond The Wage - Ordinary Work in Diverse EconomiesPedram100% (1)
- The Role of HRM in Changing EnvironmentDocument11 pagesThe Role of HRM in Changing Environmentarcherselevators0% (2)
- Evolution of HRMDocument22 pagesEvolution of HRMShalemRajNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviourDocument4 pagesOrganizational BehaviourJasyanthriNo ratings yet
- 1009 3Document11 pages1009 3Allan KibetNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Employee and Labour RelationsDocument19 pagesCH 9 Employee and Labour RelationsMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Your Name in All Caps: Name of Most Recent College/Uni You Attended (Gpa) Name of College/UniverstiyDocument1 pageYour Name in All Caps: Name of Most Recent College/Uni You Attended (Gpa) Name of College/UniverstiyAsma toorNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesHuman Resource ManagementAngelica Sambo100% (1)
- Human Resource Management in Multinational CompaniesDocument11 pagesHuman Resource Management in Multinational CompaniesBuddhima De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Entering and Contracting Organizational DevelopmentDocument15 pagesEntering and Contracting Organizational DevelopmentMecheal ThomasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 UpdatedDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Updatedgkzuniga50% (2)
- Contemporary Issues in HRMDocument14 pagesContemporary Issues in HRMTaruntej Singh0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Constitutional Framework of Labor 1Document24 pagesChapter 1 Constitutional Framework of Labor 1Ma.Geraldine DalisayNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Manpower Management Among The Contractors Along QuirinoDocument24 pagesEffectiveness of Manpower Management Among The Contractors Along QuirinoMilenaNo ratings yet
- Social Responsibility and Good GovernanceDocument6 pagesSocial Responsibility and Good GovernanceChristian Earl Cambarihan PalasonNo ratings yet
- Ethics & Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument20 pagesEthics & Corporate Social ResponsibilityDr Kennedy Amadi.PhDNo ratings yet
- Functional Areas of ManagementDocument8 pagesFunctional Areas of ManagementIngrid VeronicaNo ratings yet
- Global HRMDocument23 pagesGlobal HRMPreeti Bhaskar100% (2)
- 3-Good Governance Code of EthicsDocument40 pages3-Good Governance Code of EthicsMark BelgaNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Training: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument38 pagesTransfer of Training: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinEwura Esi Eyram AboagyewaaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Employee Relations and Discipline - 2Document15 pagesCHAPTER 6 Employee Relations and Discipline - 2Gabriel Manuel100% (1)
- Organizational Culture: The Set Of: Shared Values NormsDocument13 pagesOrganizational Culture: The Set Of: Shared Values NormsRahul MittalNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in Human Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesRecent Trends in Human Resource ManagementHoney Rasheed MemonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Attributes, Qualities, and Characteristics of An EntrepreneurDocument11 pagesChapter 3 - Attributes, Qualities, and Characteristics of An EntrepreneurArnel De Los SantosNo ratings yet
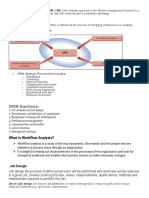
- HRM Functions:: What Is Workflow Analysis?Document3 pagesHRM Functions:: What Is Workflow Analysis?khalid bashirNo ratings yet
- COMPEN Reflective Arifah PDFDocument10 pagesCOMPEN Reflective Arifah PDFSyazwani OmarNo ratings yet
- HRM-CHAPTER 8-Industrial RelationDocument27 pagesHRM-CHAPTER 8-Industrial RelationMohd Ihsan Hakim0% (1)
- Entrepreneurial Management LessonDocument20 pagesEntrepreneurial Management LessonHANNAH FAYE VALDEZ100% (1)
- Doing Business in VietnamDocument4 pagesDoing Business in VietnamhamdardvnNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument11 pagesHRMHafsa Iqbal100% (1)
- HRM 659 - CHP 8Document30 pagesHRM 659 - CHP 8Amrezaa IskandarNo ratings yet
- Functional Areas of BusinessDocument9 pagesFunctional Areas of Businesskacem0% (1)
- Fairness and Equality - Sime DarbyDocument18 pagesFairness and Equality - Sime DarbyNoraini Raimi Sajari100% (6)
- Topic Sentence For Summary ParagraphDocument2 pagesTopic Sentence For Summary ParagraphJonathan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Keeping Up With IT Case Study 1Document2 pagesKeeping Up With IT Case Study 1Hazel Mae JumaaniNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Employee Employer RelationDocument10 pagesEthical Issues in Employee Employer Relationanimesh100% (1)
- Motivating Office EmployeesDocument16 pagesMotivating Office EmployeesAngelo ValencerinaNo ratings yet
- Cultural Diversity Can Affect The Workplace in Numerous WaysDocument5 pagesCultural Diversity Can Affect The Workplace in Numerous WaysFarhana ShahiraNo ratings yet
- 34.factors Influencing Employee Job Satisfaction A Conceptual AnalysisDocument11 pages34.factors Influencing Employee Job Satisfaction A Conceptual AnalysisJawadNo ratings yet
- Business Field EssayDocument4 pagesBusiness Field Essayapi-242023925No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Maintaining Labor Management Relations FDocument105 pagesChapter 9 Maintaining Labor Management Relations FShie Castillo ChuacoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Relations and Employee Relations in An OrganizationDocument12 pagesIndustrial Relations and Employee Relations in An OrganizationJacob Adut Mabor100% (1)
- An Understanding of Collective Agreements, Trade Disputes and Industrial ActionsDocument26 pagesAn Understanding of Collective Agreements, Trade Disputes and Industrial ActionsSalam Salam Solidarity (fauzi ibrahim)No ratings yet
- Five Functional Areas of Human Resource ManagementDocument9 pagesFive Functional Areas of Human Resource ManagementFalade Toba80% (5)
- Benefits of Workplace DiversityDocument3 pagesBenefits of Workplace DiversitykathNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Effective Communication WithinDocument2 pagesBarriers To Effective Communication WithinSuraj GaikwadNo ratings yet
- l1 - Employer and Employee RelationshipDocument22 pagesl1 - Employer and Employee RelationshipSyahirah Arif100% (1)
- Ch-4 HRM Training and DevelopmentDocument26 pagesCh-4 HRM Training and DevelopmentkarmayagnaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Organization Structure: Learning ObjectivesDocument25 pagesFoundations of Organization Structure: Learning Objectivesammarhashmi1986No ratings yet
- Ethics IntroductionDocument5 pagesEthics IntroductionpramodNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument9 pagesHuman Resource ManagementZegera MgendiNo ratings yet
- Operative Functions of HRMDocument6 pagesOperative Functions of HRMbangiapallavi100% (2)
- AbsenteeismDocument77 pagesAbsenteeismChirumadhu100% (2)
- Presentation-Recruitment and Selection ProcessDocument30 pagesPresentation-Recruitment and Selection ProcessMOHAMMED ALI CHOWDHURY64% (11)
- Trade UnionDocument30 pagesTrade UnionMatDahe MatSoto50% (2)
- Module 1 HRMDocument14 pagesModule 1 HRMrebecca lisingNo ratings yet
- Case Study TQMDocument6 pagesCase Study TQMSafwan Jamil0% (2)
- HRM EssayDocument4 pagesHRM Essayaxl16hkNo ratings yet
- Impact of Globalization of Human Resource ManagementDocument12 pagesImpact of Globalization of Human Resource ManagementnishNo ratings yet
- "People, Not Buildings, Make A Company Successful." - AnonymousDocument65 pages"People, Not Buildings, Make A Company Successful." - Anonymoussonabeta07No ratings yet
- Case Study - Module XviiiDocument20 pagesCase Study - Module XviiiShiwanthie WijesuriyaNo ratings yet
- New Trends Shaping HRMDocument20 pagesNew Trends Shaping HRMSs ArNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-1Document9 pagesQuestion Bank-1Amruta GholveNo ratings yet
- Job Order Direct LaborDocument23 pagesJob Order Direct LaborMaria Raven Joy ValmadridNo ratings yet
- Premid & MidtermDocument3 pagesPremid & MidtermMarie Carmela OclaritNo ratings yet
- Osh Profil Indonesia 18 7 2018Document66 pagesOsh Profil Indonesia 18 7 2018Erni Wiliyani ZMNo ratings yet
- Processes of Social Change in IndiaDocument12 pagesProcesses of Social Change in IndiaBushra Shaikh100% (1)
- Western India Plywoods Internship Training Project 2009Document73 pagesWestern India Plywoods Internship Training Project 2009MuhsinTpNo ratings yet
- RPMES Forms No. 2 5Document5 pagesRPMES Forms No. 2 5Edmond BautistaNo ratings yet
- 06 ABS-CBN Broadcasting Corporation V Marlyn Nazareno, Merlou Gerzon, Jennifer Deiparine, and Josephine Lerasan, G.R. No. 164156, September 26, 2006Document12 pages06 ABS-CBN Broadcasting Corporation V Marlyn Nazareno, Merlou Gerzon, Jennifer Deiparine, and Josephine Lerasan, G.R. No. 164156, September 26, 2006Alelojo, NikkoNo ratings yet
- Exam Preparatory Manual For Undergraduates - Medicine: September 2016Document9 pagesExam Preparatory Manual For Undergraduates - Medicine: September 2016indrajit sinhaNo ratings yet
- 10 FaqsDocument3 pages10 FaqsShrinal MankiwalaNo ratings yet
- RrlsDocument4 pagesRrlsElla DavidNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document10 pagesModule 5meet daftaryNo ratings yet
- Central Cities and Regional Market AnalysisDocument27 pagesCentral Cities and Regional Market Analysisminani marcNo ratings yet
- Nitto Enterprises v. NLRCDocument5 pagesNitto Enterprises v. NLRCDhang CalumbaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Letter of OfferDocument4 pagesSubject: Letter of Offersakshi negiNo ratings yet
- Chilanga Cement PLC Vs Kasote Singogo-2Document5 pagesChilanga Cement PLC Vs Kasote Singogo-2Thandiwe Deborah0% (1)
- 2019 CHAN Labor Law Table of Contents CMPDDocument19 pages2019 CHAN Labor Law Table of Contents CMPDliks5poyonganNo ratings yet
- Ipcr and DPCR BlankDocument9 pagesIpcr and DPCR BlankMeriam FernandezNo ratings yet
- Analysis: Expansion On Product OfferingDocument6 pagesAnalysis: Expansion On Product OfferingKimberly BalontongNo ratings yet
- DGD GL 001 Grants Criteria and Guidelines 2023 2024.pdf - V1Document38 pagesDGD GL 001 Grants Criteria and Guidelines 2023 2024.pdf - V1Devon Antony HeuerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - The Role of Communications in Labor-Management RelationsDocument23 pagesChapter 15 - The Role of Communications in Labor-Management RelationsANN ONYMOUSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Meaning of Division of LabourDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - Meaning of Division of LabourVaruna Sharma100% (1)
- Professional Direct Hire ReqDocument1 pageProfessional Direct Hire ReqLeigh PortillasNo ratings yet
- Labour Productivity in The Construction IndustryDocument13 pagesLabour Productivity in The Construction Industryrodop82100% (1)
- Bus498 Internship Report 1511337030Document61 pagesBus498 Internship Report 1511337030Khadija Akter 1611121630No ratings yet
- Ej Career AutobiographyDocument7 pagesEj Career Autobiographyapi-312056494No ratings yet
- Ra 8759Document6 pagesRa 8759Ian TicarNo ratings yet
- Prelims ReviewerDocument30 pagesPrelims ReviewerKrystal Grace D. PaduraNo ratings yet