Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug 1
Uploaded by
Dexter YauderOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug 1
Uploaded by
Dexter YauderCopyright:
Available Formats
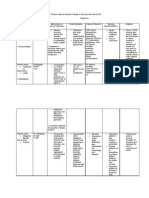
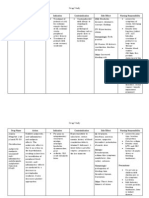
DRUG
MECHANISM OF ACTION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE EFFECT
ACTIONS
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS Assessment History: Allergy tobenazepril or other ACE inhibitors, impaired renal function, CHF, salt or volume depletion, lactation, pregnancy Physical: Skin color, lesions, turgor; T; P, BP, peripheral perfusion; mucous membranes, bowel sounds, liver evaluation; urinalysis, LFTs, renal function tests, CBC and differential Interventions WARNING: Alert surgeon:Note use of benazepril onpatient's chart; theangiotensin II formationsubsequ ent tocompensatory reninrelease during surgery willbe blocked; hypotensionmay
Generic name: Benazeprilhydrochloride Brand Name: Lotensin Pregnancy Category C (first trimester)Pregnancy Category D(second and third trimesters)
Benazepril and its metabolite benazeprilat inhibit ACE that catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, thus leading to reduce daldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex and decreased vasopressor activity.
Hypersensitivity. History of bilateral renal artery stenosis, angioedema; pregnancy
Headache, dizziness, fatigue ; cough; somnolence, nausea; hypotension, transient elevations in BUN and serum creatinine; palpitations; constipation ,gastritis; melena,rash, pruritus; musculoskeletal pain; paraesthesia, anxiety; UTI; hyperkalaemia; leucopeniaand flushing. PotentiallyFatal: Angioedema(rare)
Treatment of hypertension alone or in combination with thiazide-type diuretics
Classification: Antihypertensive ACE inhibitor DOSAGE: Oral Hypertension Adult: Initially, 10 mg oncedaily. Maintenance: 20-40mg daily as a single or in 2divided doses. Max dose: 80mg/day. Child: 6 yr: 0.2 mg/kg/day.Max dose: 40 mg/day. Renal impairment: Avoidusage in children with CrCl<30 ml/min.
be reversed withvolume expansion. Monitor patient for possibledrop in BP secondary toreduction in fluid volume(excessive perspiration anddehydration, vomiting,diarrhea) becauseexcessiv e hypotension mayoccur.
You might also like
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument70 pagesDrug Studyjahmaicao50% (2)
- Drug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationArvan SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Fosinopril SodiumDocument3 pagesFosinopril Sodiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyHannah Philene D. CalubNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug Name General Action Specific Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResDocument9 pagesDrug Name General Action Specific Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Benazepril Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBenazepril Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument58 pagesCardio DrugsMARIA ROWENA VIA J. LUCENANo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- RamiprilDocument3 pagesRamiprilapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Medication Study GuideDocument8 pagesMed Surg Medication Study Guidetina100% (1)
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRye IbarraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Drug CardsDocument32 pagesNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRenee Dwi Permata MessakaraengNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument3 pagesCaptoprilapi-3797941100% (1)
- Medication Brand Name and Generic NameDocument12 pagesMedication Brand Name and Generic Namexaliokoli127No ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMa R DyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument6 pagesDrugsMillet RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pharma Medications ListDocument35 pagesPharma Medications ListCalvin Keith YadaoNo ratings yet
- ACE InhibitorsDocument8 pagesACE InhibitorshasaɴNo ratings yet
- LisinoprilDocument3 pagesLisinoprilapi-37979410% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Drug Name Classificatio N Mechanis MOF Action Indication Contrain Dication Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classificatio N Mechanis MOF Action Indication Contrain Dication Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesPrincess TinduganNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Blood PressureDocument54 pagesDrugs Affecting Blood PressureJeremy VivitNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsDocument120 pagesPharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsDareRaymond100% (1)
- Pharmacology Drug Chart Kori JonesDocument17 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart Kori Joneskorikori33No ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: DR - SarmisthaDocument19 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: DR - SarmisthaGebby MamuayaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneDocument28 pagesAntihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneLopez JoeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyDocument24 pagesPharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyshyamkattiNo ratings yet
- Cva Smh301 (Next)Document14 pagesCva Smh301 (Next)Christine OjedaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyrocketwapNo ratings yet
- Benazepril Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesBenazepril Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- DRUG and IVF StudyDocument4 pagesDRUG and IVF StudyJohanna Camelle Insong MonteronNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument40 pagesEmergency Drugsmattheus101No ratings yet
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (O)Document26 pagesAngiotensin Receptor Blockers (O)farmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument2 pagesEnalaprilAyah PaasaNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument3 pagesCaptoprilNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- Olmesartan Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOlmesartan Drug StudydyndzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Francisco Tampos JRDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Francisco Tampos JRCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- E InquiryDocument5 pagesE InquiryDexter YauderNo ratings yet
- Rizal's First Trip AbroadDocument7 pagesRizal's First Trip AbroadDexter YauderNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Short Documentary VideoDocument3 pagesSummary of The Short Documentary VideoDexter YauderNo ratings yet
- Pre MaturityDocument3 pagesPre MaturityDexter YauderNo ratings yet
- SpellbindingDocument45 pagesSpellbindingAnuja WairagadeNo ratings yet
- MSDS Bleach PDFDocument5 pagesMSDS Bleach PDFAlfonso Alejandro Loayza RodriguezNo ratings yet
- SSB201 Group Assigment 1 - Design ThinkingDocument3 pagesSSB201 Group Assigment 1 - Design ThinkingLe CuongNo ratings yet
- Course Unit Task: Teaching PlanDocument2 pagesCourse Unit Task: Teaching PlanQueen100% (1)
- Workbook Answer KeyDocument27 pagesWorkbook Answer Keysalcedo4479% (56)
- Madeleine Leininger TFN Reporting NononoDocument33 pagesMadeleine Leininger TFN Reporting NononoWinter SonataNo ratings yet
- The Demand For, and Impact Of, Learning HIV StatusDocument36 pagesThe Demand For, and Impact Of, Learning HIV StatusWilson LancherosNo ratings yet
- FAQ Mid Day MealsDocument7 pagesFAQ Mid Day Mealsvikramhegde87No ratings yet
- Amber Sewell: Professional SummaryDocument4 pagesAmber Sewell: Professional Summaryapi-383979726No ratings yet
- Impact of Digital Media On Sleep Pattern Disturbance in Medical and Nursing StudentsDocument10 pagesImpact of Digital Media On Sleep Pattern Disturbance in Medical and Nursing StudentsValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Test Cls 12 SNDocument1 pageTest Cls 12 SNAntonia AntoNo ratings yet
- Wiri 08 - Zambia Trip Application FormDocument11 pagesWiri 08 - Zambia Trip Application Forminfo@zcfcanada.orgNo ratings yet
- ADHD and The Endocannabinoid SystemDocument11 pagesADHD and The Endocannabinoid Systempn100% (1)
- Coron School of FisheriesDocument3 pagesCoron School of FisheriesRafael DacullaNo ratings yet
- First Dispensary RegistrationDocument2 pagesFirst Dispensary RegistrationWBURNo ratings yet
- Rimso 50Document1 pageRimso 50monloviNo ratings yet
- Kangaroo Mother Care Rooming in UpdatedDocument44 pagesKangaroo Mother Care Rooming in UpdatedStar DustNo ratings yet
- Advert MBCHB Bds 2014 Applicants3Document9 pagesAdvert MBCHB Bds 2014 Applicants3psiziba6702No ratings yet
- Soares - Como Escolher Um Anestesico Local - 2005 PDFDocument9 pagesSoares - Como Escolher Um Anestesico Local - 2005 PDFjvb sobralNo ratings yet
- Takaful MaybankDocument4 pagesTakaful MaybankSHANo ratings yet
- MAPEH NasDocument7 pagesMAPEH Nasnoronisa talusobNo ratings yet
- Sports NutritionDocument254 pagesSports NutritionrodriguezdiazNo ratings yet
- Pinnacle Tecnica Quirurgica 2Document49 pagesPinnacle Tecnica Quirurgica 2Saenz Guzman LauraNo ratings yet
- Aldinga Bay's Coastal Views April 2014Document48 pagesAldinga Bay's Coastal Views April 2014Aldinga BayNo ratings yet
- Reszon Pi - Typhidot Rapid Igm 2011-01Document2 pagesReszon Pi - Typhidot Rapid Igm 2011-01Harnadi WonogiriNo ratings yet
- Villa La Paws Operations Manual-Detail 03-26-2014Document167 pagesVilla La Paws Operations Manual-Detail 03-26-2014Anonymous JKqvy986U100% (1)
- Top Brain Health FoodsDocument13 pagesTop Brain Health FoodsTudor Vieru100% (1)
- Raw Milk or Packaged Milk?Document2 pagesRaw Milk or Packaged Milk?Marriam TariqNo ratings yet
- Post Test 30 Items OBDocument5 pagesPost Test 30 Items OBJohnasse Sebastian NavalNo ratings yet