Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MOSFET Amplifier Basics
Uploaded by
Harsha BalamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MOSFET Amplifier Basics
Uploaded by
Harsha BalamCopyright:
Available Formats
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 1 Prof.
Liu, UC Berkeley
Lecture 18
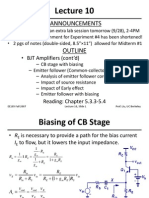
OUTLINE
Basic MOSFET amplifier
MOSFET biasing
MOSFET current sources
Common-source amplifier
Reading: Chapter 7.1-7.2
ANNOUNCEMENTS
HW#10 will be posted tonight
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 2 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
For large small-signal gain, the MOSFET should be operated
in the saturation region.
V
out
should not fall below V
in
by more than V
TH
.
Basic MOSFET Amplifier
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 3 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
MOSFET Biasing
The voltage at node X is determined by V
DD
, R
1
, and R
2
:
Also,
( )
S ox n
TH
DD
TH GS
R
L
W
C
V
V
R R
V R
V V V V V
1
where
2
1
2 1
2
1
2
1 1
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+ + =
DD X
V
R R
R
V
2 1
2
+
=
S D GS X
R I V V + =
( )
2
2
1
TH GS ox n D
V V
L
W
C I =
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 4 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
Self-Biased MOSFET Stage
Note that there is no voltage dropped across R
G
M1 is operating in the saturation region.
DD D S GS D D
V I R V R I = + +
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 5 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
MOSFETs as Current Sources
A MOSFET behaves as a current source when it is operating in
the saturation region.
An NMOSFET draws current from a point to ground (sinks
current), whereas a PMOSFET draws current from V
DD
to a
point (sources current).
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 6 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
Common-Source Stage: = 0
D out
in
D D ox n D m v
R R
R
R I
L
W
C R g A
=
=
= = 2
Amplifier circuit Small-signal analysis circuit
for determining voltage gain, A
v
Small-signal analysis circuit for
determining output resistance, R
out
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 7 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
Common-Source Stage: 0
Channel-length modulation results in reduced small-signal
voltage gain and amplifier output resistance.
( )
O D out
in
O D m v
r R R
R
r R g A
||
||
=
=
=
Small-signal analysis circuit
for determining voltage gain, A
v
Small-signal analysis circuit for
determining output resistance, R
out
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 8 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
CS Gain Variation with L
An ideal current source has infinite small-signal resistance.
The largest A
v
is achieved with a current source as the load.
Since is inversely proportional to L, A
v
increases with \L.
D
ox n
D
D ox n
o m v
I
WL C
I
I
L
W
C
r g A
2
2
= =
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 9 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
CS Stage with Current-Source Load
( )
2 1
2 1 1
||
||
O O out
O O m v
r r R
r r g A
=
=
Recall that a PMOSFET can be used as a current source from V
DD
.
Use a PMOSFET as a load of an NMOSFET CS amplifier.
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 10 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
PMOS CS Stage with NMOS Load
An NMOSFET can be used as the load for a PMOSFET CS amplifier.
2 1
2 1 2
||
) || (
O O out
O O m v
r r R
r r g A
=
=
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 11 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
CS Stage with Diode-Connected Load
A
v
is lower, but it is less dependent on process parameters
(
n
and C
ox
and drain current (I
D
).
Amplifier circuit Small-signal analysis circuit
including MOSFET output resistances
( )
( )
2
1
2
1
/
/ 1
: 0 If
L W
L W
g
g A
m
m v
= =
=
1 2
2
1 2
2
1
|| ||
1
|| ||
1
O O
m
out
O O
m
m v
r r
g
R
r r
g
g A
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
: 0 =
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 12 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
CS Stage with Diode-Connected PMOS Load
2 1
1
2 1
1
2
|| ||
1
|| ||
1
o o
m
out
o o
m
m v
r r
g
R
r r
g
g A
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
: 0 =
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 13 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
CS Stage with Degeneration
S
m
D
v
R
g
R
A
+
= =
1
: 0 If
Amplifier circuit Small-signal analysis circuit
for determining voltage gain, A
v
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 14 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
Example
A diode-connected device degenerates a CS stage.
2 1
1 1
m m
D
v
g g
R
A
+
=
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 15 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
R
out
of CS Stage with Degeneration
Degeneration boosts the output impedance:
Small-signal analysis circuit for
determining output resistance, R
out
( )
( )
S O m O S S m O
X
X
X S X S X m X O
R r g r R R g r
i
v
v R i R i g i r
+ ~ + + =
= + +
1
S X
R i v =
1
Current flowing down through r
o
is
( )
S X m X
S X m X m X
R i g i
R i g i v g i
+ =
=
1
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 16 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
Output Impedance Examples
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ ~
2
1 1
1
1
m
m O out
g
g r R
1 2 1 1 O O O m out
r r r g R + ~
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 17 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
CS Stage with Gate Resistance
For low signal frequencies, the gate conducts no current.
Gate resistance does not affect the gain or I/O impedances.
EE105 Fall 2007 Lecture 18, Slide 18 Prof. Liu, UC Berkeley
CS Core with Biasing
S
m
D
G
v
R
g
R
R R R
R R
A
+
+
=
1
||
||
2 1
2 1
D m
G
v
R g
R R R
R R
A
2 1
2 1
||
||
+
=
You might also like
- Design of A Discrete BJT Operational AmplifierDocument6 pagesDesign of A Discrete BJT Operational Amplifierjonesy5000No ratings yet
- C40 Trace Manual EnglishDocument24 pagesC40 Trace Manual EnglishBertNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20Document23 pagesLecture 20Supraja SundaresanNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Models: - The Large-Signal Model Is Used To Determine The DC Operating Point (V, V, I) of The MOSFETDocument21 pagesMOSFET Models: - The Large-Signal Model Is Used To Determine The DC Operating Point (V, V, I) of The MOSFETSoma SundarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document23 pagesLecture 13TeejayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11: Review of BJT Amplifier Design and Cascode StageDocument21 pagesLecture 11: Review of BJT Amplifier Design and Cascode StageAydin Mhysa AbetNo ratings yet
- Context: Prof J. S. SmithDocument16 pagesContext: Prof J. S. SmithЧ. ДэлгэрNo ratings yet
- FET Transistor Operation and Frequency Response in EE 359 Electronic CircuitsDocument19 pagesFET Transistor Operation and Frequency Response in EE 359 Electronic CircuitsJayashree MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Announcements: - BJT Amplifiers (Cont'd)Document24 pagesAnnouncements: - BJT Amplifiers (Cont'd)bbgirl325No ratings yet
- Lecture 14 CB Stage: Pole Frequencies: CB Stage Emitter Follower Emitter Follower Cascode StageDocument3 pagesLecture 14 CB Stage: Pole Frequencies: CB Stage Emitter Follower Emitter Follower Cascode StagetekellamerZ aka tekellamerNo ratings yet
- Announcements: - NMOSFET in ON State (Cont'd)Document19 pagesAnnouncements: - NMOSFET in ON State (Cont'd)Tanmoy RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19Document15 pagesLecture 19sureshchattuNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response: Miller Effect: Prof. NiknejadDocument21 pagesFrequency Response: Miller Effect: Prof. NiknejadPabloChiamentiBauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture17 4Document5 pagesLecture17 4tekellamerZ aka tekellamerNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Model MOSFETDocument8 pagesSmall Signal Model MOSFETRAHUL100% (1)
- 電子10Document59 pages電子10YaKuan ChuangNo ratings yet
- Mosfet OperationDocument70 pagesMosfet OperationTanmayBangaloreNo ratings yet
- FETDocument49 pagesFETPalak Agrawal100% (2)
- Tutorial 5Document10 pagesTutorial 5bayman66No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4single Stage IC Amplifier (For IT Class)Document85 pagesChapter - 4single Stage IC Amplifier (For IT Class)Rajesh BathijaNo ratings yet
- Multistage Amplifiers: Bipolar Junction Transistor: MosfetDocument16 pagesMultistage Amplifiers: Bipolar Junction Transistor: MosfetRomelDianonNo ratings yet
- AmplfierDocument7 pagesAmplfierCharuka WeerasekaraNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Lab 9 JFET AmplifiersDocument3 pagesPurpose: Lab 9 JFET AmplifiersAbhimanyu YadavNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Lab 9 JFET AmplifiersDocument3 pagesPurpose: Lab 9 JFET AmplifiersManohar PNo ratings yet
- BEE Small Signl ModelDocument13 pagesBEE Small Signl ModelalysonmicheaalaNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Circuits ExplainedDocument6 pagesOp-Amp Circuits Explainedkyope17No ratings yet
- Push Pull Ampilfier - c9Document4 pagesPush Pull Ampilfier - c9quynh04cdt1No ratings yet
- ET1006 1112S2Exam Formulae SheetsDocument4 pagesET1006 1112S2Exam Formulae SheetstestniaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument4 pagesDepartment of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & TechnologyMeowNo ratings yet
- 2018 Ee 69Document19 pages2018 Ee 69Ali MohsinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 050 - Followers: (READING: GHLM - 344-362, AH - 221-226) ObjectiveDocument7 pagesLecture 050 - Followers: (READING: GHLM - 344-362, AH - 221-226) ObjectiveArchana RkNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document3 pagesLab 7Walid Mohammed Suliman100% (1)
- Mosfet Lab 2Document11 pagesMosfet Lab 2Jaime Aguilar100% (1)
- Linear Wave Shaping: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument0 pagesLinear Wave Shaping: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringanishadandaNo ratings yet
- All About Small Signal Analysis PDFDocument12 pagesAll About Small Signal Analysis PDFSaiKanthGNo ratings yet
- Common Base Amplifier Circuit AnalysisDocument3 pagesCommon Base Amplifier Circuit AnalysisHatem DheerNo ratings yet
- Lecture21 Multistage AmplifiersDocument10 pagesLecture21 Multistage AmplifierscitraumariNo ratings yet
- Offset Cancellation OverviewDocument17 pagesOffset Cancellation OverviewMilenchoNo ratings yet
- 3 AC AmplificationDocument58 pages3 AC AmplificationAnthony BeltranNo ratings yet
- Lec2 Frequency ResponseDocument79 pagesLec2 Frequency ResponseAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Power Amplifiers Part 1 Class A: We Have Studied The Design of Small-Signal AmplifiersDocument18 pagesPower Amplifiers Part 1 Class A: We Have Studied The Design of Small-Signal AmplifiersmalamigsajpanNo ratings yet
- Multistage Amplifier AnalysisDocument25 pagesMultistage Amplifier AnalysisMahmoud AbuziadNo ratings yet
- Study CE Amplifier Gain & ImpedanceDocument3 pagesStudy CE Amplifier Gain & ImpedancesabitavabiNo ratings yet
- 365 Signal ConditioningDocument29 pages365 Signal ConditioningSunilkumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering 4 Lab 4 - MOSFET AmplifierDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering 4 Lab 4 - MOSFET AmplifierGerson SantosNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Lecture Slides For Chenming Hu Book: Modern Semiconductor Devices For ICsDocument42 pagesCh. 5 Lecture Slides For Chenming Hu Book: Modern Semiconductor Devices For ICsChenming HuNo ratings yet
- Electronics II Lab Manual 4Document5 pagesElectronics II Lab Manual 4VivekKhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 DiodesDocument11 pagesLecture 5 DiodeslongNo ratings yet
- Technical Examination LEVEL -7 Electronics and CircuitsDocument37 pagesTechnical Examination LEVEL -7 Electronics and CircuitsMadhunath YadavNo ratings yet
- Long Report Lab 7Document15 pagesLong Report Lab 7Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications QtyDocument0 pagesCommon Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications Qtyagama1188No ratings yet
- Common Source/Gate/Drain Amplifiers: Prof. NiknejadDocument28 pagesCommon Source/Gate/Drain Amplifiers: Prof. NiknejadpeterNo ratings yet
- PK Aec Lab ManualDocument26 pagesPK Aec Lab ManualkrishnagdeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Multi-Stage Amp GainDocument17 pagesMulti-Stage Amp GainJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- Announcements: - BJT (Cont'd) - BJT Amplifiers Reading: Chapter 4.6-5.1Document25 pagesAnnouncements: - BJT (Cont'd) - BJT Amplifiers Reading: Chapter 4.6-5.1sanjayr_nittNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response S-Domain Analysis Poles and ZerosDocument31 pagesFrequency Response S-Domain Analysis Poles and ZerosAbdul RajakNo ratings yet
- Notes: (No. of Printed Pages-4) ES201 Enrol. No. (ET) End Semester Examination Nov.-Dec., 2016Document6 pagesNotes: (No. of Printed Pages-4) ES201 Enrol. No. (ET) End Semester Examination Nov.-Dec., 2016Ryash ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21: Junction Field Effect Transistors. Source Follower AmplifierDocument8 pagesLecture 21: Junction Field Effect Transistors. Source Follower AmplifiercasprossNo ratings yet
- FPUDocument6 pagesFPUSatya NarayananNo ratings yet
- Algorithm 673 Dynamic Huffman Coding: 15, No. 2, June 1989, Pages 158-167Document10 pagesAlgorithm 673 Dynamic Huffman Coding: 15, No. 2, June 1989, Pages 158-167Harsha BalamNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment Report Template MS OfficeDocument30 pagesLab Assignment Report Template MS OfficeHarsha BalamNo ratings yet
- Calculas FormulasDocument2 pagesCalculas FormulasSaurabh Ray100% (1)
- 203D6Document14 pages203D6Gabo El CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Sunfire Cinema Grand Sign2 19Document20 pagesSunfire Cinema Grand Sign2 19gafesa electronicsNo ratings yet
- General and Simplified Computation of Fault Flow and Contribution of Distributed Sources in Unbalanced Distribution NetworksDocument8 pagesGeneral and Simplified Computation of Fault Flow and Contribution of Distributed Sources in Unbalanced Distribution NetworkshassanNo ratings yet
- AN7186Document7 pagesAN7186Sagar PawarNo ratings yet
- PSPICE Tutorial: The University of Texas at Arlington July 22 2010Document39 pagesPSPICE Tutorial: The University of Texas at Arlington July 22 2010ankitgdoshiNo ratings yet
- Review On Power Quality of Hybrid Renewable Energy SystemDocument7 pagesReview On Power Quality of Hybrid Renewable Energy SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Sliding Mode Controller in A Multiloop FrameworkDocument10 pagesSliding Mode Controller in A Multiloop Framework张益铭No ratings yet
- Current Sources As Active Loads - Operational AmplifiersDocument3 pagesCurrent Sources As Active Loads - Operational AmplifiersVENKATESWARLU MUVVA (PA2111004040011)No ratings yet
- Max 8729Document26 pagesMax 8729lagreta55No ratings yet
- SPHE8281DDocument35 pagesSPHE8281Ddiego-tNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument9 pagesMCQsAlbert AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- A Generic DMM Test and Calibration Strategy: Peter B. CrispDocument11 pagesA Generic DMM Test and Calibration Strategy: Peter B. CrispRangga K NegaraNo ratings yet
- LM 5116Document28 pagesLM 5116rmoscibdNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Second PartDocument34 pagesCH 4 - Second PartNasser AlmofariNo ratings yet
- IIT Kanpur ESC 201A Homework Circuit ProblemsDocument5 pagesIIT Kanpur ESC 201A Homework Circuit Problemspappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- SG6848 SGDocument13 pagesSG6848 SGjabbmfNo ratings yet
- Four-Quadrant Dynamometer/Power Supply 8960-00: Labvolt Series DatasheetDocument35 pagesFour-Quadrant Dynamometer/Power Supply 8960-00: Labvolt Series DatasheetLuis ZavalaNo ratings yet
- RTD & TC AccuracyDocument22 pagesRTD & TC AccuracyAsian InternationalNo ratings yet
- Low Current Density Anodizing Rev 0ADocument18 pagesLow Current Density Anodizing Rev 0AtootalldeanNo ratings yet
- User Manual - ICircuit - The Realtime Circuit Simulator and EditorDocument28 pagesUser Manual - ICircuit - The Realtime Circuit Simulator and EditorjancliNo ratings yet
- Nodal and Mesh Analysis - Contoh SoalDocument49 pagesNodal and Mesh Analysis - Contoh SoalPola RismaNo ratings yet
- BME (311) Electric Circuits lab Summer 2016Document140 pagesBME (311) Electric Circuits lab Summer 2016Md abdul karimNo ratings yet
- Julie Research Laboratories, Inc. v. Guildline Instruments, Inc., and Hallmark Standards, Inc., 501 F.2d 1131, 2d Cir. (1974)Document8 pagesJulie Research Laboratories, Inc. v. Guildline Instruments, Inc., and Hallmark Standards, Inc., 501 F.2d 1131, 2d Cir. (1974)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- CCS TechnicalDocument44 pagesCCS TechnicalManu Kn100% (5)
- Iso 124 PDocument19 pagesIso 124 PRobson QuinagliaNo ratings yet
- Current MirrorDocument7 pagesCurrent MirrorSatyasheel SinghNo ratings yet
- A 09-V Input Discontinuous-Conduction-Mode Boost CDocument12 pagesA 09-V Input Discontinuous-Conduction-Mode Boost CDanial RazaNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Institute of Technology: Laboratory ReportDocument7 pagesAddis Ababa Institute of Technology: Laboratory ReportAngelica WoodNo ratings yet
- Handy Circuit Analysis Techniques: Reproduction or Display. 1Document38 pagesHandy Circuit Analysis Techniques: Reproduction or Display. 1Rami WahshehNo ratings yet