Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Safety Briefing For September 2011
Uploaded by
emmanuel_nyirendaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety Briefing For September 2011
Uploaded by
emmanuel_nyirendaCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety Briefing for September 2011
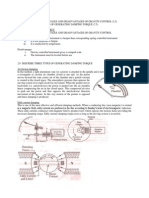
Topic: SPACE & VISIBILITY - Professional Driver HABITS Five-Point System (Part 1 of 2)
Introduction: Most people believe that crashes are random, unpredictable occurrences. In truth many crashes
are the result of poor driving habits. Fostering good driving habits is at the heart of Space and Visibility
Professional Driver habits. The Five-Point System (part 1 in this 2 part series) is based on a very simple
premise; you need two things to drive any vehicle safely; 1) space for the vehicle and 2) visibility for the driver.
What must an employee know: When reviewing the following habits that are check-marked below, you
should ask, How do you do it? and What does it do for you? And also understand the key phrase.
AIM HIGH IN STEERING
1. How do you do it? Imagine a target well ahead of you.
Example: When you throw a baseball, you dont look at the baseball; you look at the target which you
are throwing to. The same rule applies to throwing darts at a dart board.
2. What does it do for you? Imagining a target well ahead of you centers your vehicle in your lane of
traffic and also assures a smooth and safe path on turns.
3. Key Phrase: Find a safe path well ahead. Notes: Become a high aim steerer; look as far ahead as
you can. Dont look only directly in front of your vehicle while driving.
GET THE BIG PICTURE
1. How do you do it? Do not follow so closely that it prevents you from seeing the big picture ahead.
Stay away from moving billboards such as the rear of a tracker trailer.
2. What does it do for you? Not following so closely keeps you away from moving billboards
which block your vision, allows for smooth stops and turns, and buys reaction time.
3. Key Phrase: Stay back and see it all. Notes: Dont rush up behind a line of traffic making you
vulnerable to be part of an accident if something was to happen. For example, like a beautiful painting,
dont get so close that youre not able to see the whole thing, stay back and be able to take it all in.
KEEP YOUR EYES MOVING
1.How do you do it? To avoid fixating on any one object you should keep your eyes moving. Make
sure that you look to your rear every 5 to 8 seconds.
2. What does it do for you? Continually moving your eyes maintains your sense of awareness in all
driving conditions.
3. Key Phrase: Scan, dont stare. Notes: Keep eyes moving all around your vehicle; front, rear, sides.
Scan from building to building, tree-line to tree-line.
LEAVE YOURSELF AN OUT
1. How do you do it? To leave yourself an out of a possible hazardous situation you should imagine
an escape route depending on your current position. Be able to recognize the path of least resistance.
2. What does it do for you? Leaving you an out creates space on all four sides, but especially in
front of you.
3. Key Phrase: Be prepared, have a plan, expect the unexpected. Notes: Leave space between you
and the vehicle in front of you when stopped at traffic lights or stop signs in case of breakdown/stall.
MAKE SURE THEY SEE YOU
1. How do you do it? To make sure other drivers see you, you should communicate in traffic by using
your horn, lights, and signals.
2. What does it do for you? Making sure that they see you through communicating in traffic
establishes eye-to-eye contact.
3. Key Phrase: Dont gamble; use your horn, lights, and signals. Notes: Establishing eye contact
confirms that others see you. Be sure to use horn in a courteous manner to avoid creating a hostile
environment.
$afety Pay$
SAFETY MEETING AGENDA
COMPANY NAME: ____________________________________
DATE:___________
Open Meeting & Present safety topic: Space and Viibility
Employees present:
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
MEETING CHAIRED BY:_______________________________
Safety Briefing for August 2011
Topic: Workplace Fire Safety
Introduction: I BET YOU DIDNT KNOW according to National Safety Council, losses due to workplace fires
in one recent year totaled $3.1 billion. Of the more than 5,000 persons who lost their lives, an estimated 360
were workplace deaths associated with fires.
Background: There is a long and tragic history of workplace fires in this country. One of the most notable was
in Hamlet, North Carolina, where 25 workers died in a fire in a poultry processing plant. Locked fire exits and
inadequate fire extinguishing systems were the determining factors.
What must an employee know: Employees should conduct workplace fire inspections for compliance with
standards for fire safety. OSHA standards require employers to provide proper exits, fire fighting equipment,
emergency plans, and employee training to prevent fire deaths and injuries in the workplace.
Some of the areas that should be addressed:
Fire Exits:
Each workplace building must have at least two means of escape for fire emergency. Fire doors must
not be blocked or locked to prevent emergency use by employees.
Exit routes from buildings must be clear and free of obstructions and properly marked with signs
designating exits from the building.
Portable Fire Extinguishers
Each workplace building must have the proper type of fire extinguisher(s) for the fire hazards present.
Only approved fire extinguishers are permitted in workplaces, and they must be kept in good operating
condition. Proper maintenance and inspection of this equipment is required of each employer.
Emergency Evacuation Planning
A written emergency action plan must include evacuation routes used and procedures to be followed by
employees. Procedures for accounting for all evacuated employees must be part of the plan. The
written plan must be available for employee review.
An employee alarm system must be available for emergency alerting for evacuation. The alarm system
may be voice communication or sound signals such as bells, whistles or horns.
Fire Prevention Plan
A written fire prevention plan that details the area(s) of concern to guard against fires.
Procedures for storage and cleanup of flammable materials waste must be included in the plan.
Procedures for controlling workplace ignition sources must be addressed in the plan.
Include gathering points for roll call if an incident occurs.
Post telephone numbers for easy reporting.
$AFETY PAY$
SAFETY MEETING AGENDA
COMPANY NAME: ____________________________________
DATE:___________
Open Meeting & Present safety topic: Workplace Fire Safety
Employees present:
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
MEETING CHAIRED BY:_______________________________
SAFETY MEETING FOR JULY 2011
TOPIC: SAFETY WHILE WORKING ON STORM DAMAGED TIMBER
Introduction: Woods under tension from the twisting winds present a life-threatening risk. If you arrive at a
site shortly after a storm, there may still be some settling going on. Also, lodged trees, broken tops,
difficult ground conditions, walking through the jack-strawed limbs and debris is particularly hazardous, and
even more so if you are carrying a chain saw, and pose specific threats in a storm-damaged area.
OVER-HEAD HAZARDS
Catastrophic injury and death are the result of this ever present risk on our jobs. To fight this risk we must
be aware and LOOK UP!!
Proper head PPE is mandatory on the logging job.
Look Up and Out! Identify possible risk from above.
Dont place your body under anything that could fall, this includes equipment.
Maintain at least two tree lengths from any felling operation.
Be visible!!! Wear high visible clothing.
Use proper felling techniques.
MAINTAIN PROPER WORKING DISTANCES
Ground personnel and moving logging equipment can create extreme risk.
Awareness is the key for avoiding a too close incident.
High visibility clothing is essential.
Maintain at least two tree lengths from any felling operation.
Maintain proper distance from skidding activities and toppers should use shield trees when possible.
Machine operators should never enter a safe zone provided for ground personnel.
All employees must be aware of blind spots on the logging equipment.
Be especially cautious in and around the deck area, its a busy place!
SLIPS/TRIPS/FALLS
Very serious injuries occur frequently in and around a logging operation and risk is intensified with storm
damage timber strewn all over.
Be alert and aware. Be focused! Keep your mind on the business at hand!
Always use the 3-point of contact technique while mounting and dismounting equipment.
Keep platforms, steps and handles free from grease, oil and other foreign material.
Maintain a firm grip while entering or exiting a machine.
Proper footwear with good ankle support is mandatory. (No sneakers)
Avoid climbing or walking on felled trees or limbs.
Stay on the uphill side of felled timber and limbs.
When not cutting, make sure the chain brake is engaged.
Never put ground personnel at risk when the mechanical option is available.
Fully enclosed equipment and rotational felling heads not only greatly reduce risk levels but also
adds to the efficiency of the operation.
Pull-through and stroke delimbers, as well as other mechanical processing equipment increase
safety and productivity on the modern logging job.
$afety Pay$
SAFETY MEETING AGENDA
COMPANY NAME: ____________________________________
DATE:___________
Open Meeting & Present safety topic: Safety While Working On Storm Damaged Timber
Employees present:
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
MEETING PRENTED BY:_______________________________
Safety Meeting for June 2011
Topic: Slip, Trip, and Fall Hazards
Introduction: I BET YOU DIDNT KNOW that according to research from a leading university, slip,
trip, and fall accidents are second only to automobile accidents in causing personal injury. Falls on
stairways alone result in over 1 million disabling injuries each year. Most alarming to our industry is
that industrial falls cause over 1000 deaths each year.
What must an employ know: Slips occur when there is too little friction between a person's feet and
the walking surface. Many factors can cause a slip; most notable are ice, oil, water, cleaning fluids,
and other slippery substances. Additionally, wearing inappropriate footwear has lead to many slipping
accidents. If slip-resistant soles are required for certain work areas, include the requirement in your
company safety policy. Avoid walking in areas that pose slip hazards and promptly clean up spills of
slippery substances are two sure ways to avoid slips.
Trips occur when a person's foot contacts an object and they are thrown off balance. The main cause
of tripping is obvious--anytime something is in a walkway it could cause someone to trip. Another
hazard is an object which projects into the walkway-- perhaps lumber that is improperly stacked. Poor
lighting and uneven walking surfaces also cause trip hazards. Prevention of trips is simple; remove
objects that could cause a trip, repair uneven flooring, and install proper lighting if required.
Remember that this applies to the logging site too. Lose bark, limbs, vines, and other debris can cause
slips and trips.
Slips, trips, and falls cause numerous injuries every day. But they are among the easiest hazards to
correct. Take the time to look around your workplace for these hazards and work to prevent them.
Some additional tips on preventing these hazards are:
The best way to prevent slips, trips, and falls is good housekeeping in all work areas.
Rooms, work areas, hallways and steps must be kept free of equipment and materials.
When not in use, tools and other equipment should be kept in proper storage places.
Remember there's a place for everything and everything has its place.
A spill should be cleaned up immediately to eliminate the danger of a slip hazard.
Report slip, trip, and fall hazards to your immediate supervisor so repairs can be initiated.
Do not climb on storeroom shelving. If you must reach high shelves, never substitute crates,
boxes or other objects for a stepladder.
Place electrical cords and/or telephone cables so that they do not lie in heavily traveled areas.
Safety rules for preventing slip, trip, and fall hazards really are just "common sense" rules.
Nevertheless, a look at the statistics tells us they need to be repeated to eliminate the hazards, which
are costing time, money, and a lot of pain.
$AFETY PAY$
SAFETY MEETING AGENDA
COMPANY NAME: ____________________________________
DATE:___________
Open Meeting & Present safety topic: Slip, trip and fall Hazards
Employees present:
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
MEETING CHAIRED BY:_______________________________
Safety Briefing for May 2011
Topic: Lockout Responsibility Primary responsibility for lockout of equipment and machinery belongs to the
authorized employee. However, this does not alleviate other employees and supervisors from insuring that proper
lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures are followed at all times.
Introduction: Preventing Machine Surprises
Simply unplugging the machine that you are working on is not enough. Before maintenance, repairs or machine
setup, proper "LOTO" guarantees all energy sources are controlled. Many serious accidents have happened when
someone thought the energy source was turned off.
What must an employee know: Authorized employees must be certain which switch, circuit breaker, valve, or
other energy isolating devices applies to the equipment to be locked out. Properly document and enforce the use of
machine specific LOTO procedures will ensure the safety of employees.
Correct LOTO procedures ensure that a machines energy source(s) remain off and that there will not be
unexpected movement of parts. Not properly locking out energy sources such as hydraulic and air pressure have
caused many serious accidents, even death. Identifying all the machines power sources is critical. Sources can
include electrical current, stored electricity (such as in a capacitor), stored pressure (such as compressed air or
hydraulic pressure), stored mechanical energy (such as in a coiled spring) or gravity.
8 Steps of Lockout/Tagout
Think, plan and check - Think through the entire procedure. Identify all parts of your systems that need to be
shut down. Determine what switches, equipment and people will be involved. Carefully plan to ensure safe
maintenance operations.
Communicate - Notify all those who need to know that a lockout/tagout procedure is taking place.
Identify the energy source(s) - Ensure all employees involved know the energy sources associated with the
machine. Include electrical circuits, hydraulic and pneumatic systems, spring energy, gravity systems, or any
other.
Neutralize all energy source(s) - Disconnect electricity. Block movable parts. Release or block spring energy.
Drain or bleed hydraulic and pneumatic lines. Lower suspended parts to rest positions.
Lockout devices - Use only locks, hasps, and covers identified for lockout purposes. Each authorized worker
must have a singularly identified lock.
Tagout power sources - Tag machine controls, pressure lines, starter switches and suspended parts. Tags
should include your name, department, how to reach you, the date and time of tagging and the reason for the
lockout.
Verify equipment isolation - Check that all workers are clear. Ensure locking devices are securely placed.
Attempt normal start-up procedures. Return controls to the off or neutral position.
Releasing machinery from LOTO - Inspect the area and equipment. Replace machine guards. Account for all
tools and place them back into toolbox. Inform affected employees of machine start-up. Restore system
connections. Remove tags and locks. Restore machinery to original configuration. Conduct normal start-up.
Do not forget logging equipment when lockout is concerned. We have had mashed fingers and toes,
pinched pinkies and severe amputations because of improper lockout.
$AFETY PAY$
SAFETY MEETING AGENDA
COMPANY NAME: ____________________________________
DATE:___________
Open Meeting & Present safety topic: Lockout Responsibility
Employees present:
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
MEETING CHAIRED BY:_______________________________
Safety Meeting for April 2011
Topic: Overhead Hazards
Introduction: Several years ago, NCA and Forestry Mutual developed a program for loggers, timber
cruisers, and land owners that work in the woods. It was called Heads Up For Hazards. It was to
highlight the increase in injuries from snags, vines, broken limbs, or widow makers. As we go into this
new quarter of 2011, we have seen an increase in logging activity after a couple of slow years, we felt
it appropriate and timely to revisit this safety topic. As Spring time approaches and the leaves
reappear, the hazards in the trees become harder to identify.
What must an employ know: Information to avoid overhead hazards. Employees should be trained
on the following.
Follow safe operating procedures: Use well maintained, approved personal protective equipment
(PPE) for head protection.
Keep a hard hat with you and wear it. Hard hats have prevented severe injuries by deflecting
falling limbs.
Look and scan at least 50 feet ahead on your path of travel.
Look and scan at least 100 feet ahead for any overhead hazards.
Dont place your body under anything that fall or move due to gravity or the loss of hydraulic
pressure.
Maintain at least two tree lengths from all felling operations.
Be visible! Wear high visibility safety colors.
Maintain communication with others in the work zone.
Never walk into a work zone with running equipment or moving equipment until the equipment
is stopped, engine shut off and implements grounded.
In nearly every accident, it is ground personnel who are most at risk from hazards from above. As a
team, you must work together and stay focused. Take the time to look for overhead hazards, identify
the hazard, tell everyone about it, and remove it or flag it to keep personnel away. Your proper
decisions will result in a happy holiday season for all. LOOK UP!
$afety Pays
SAFETYMEETINGAGENDA
COMPANYNAME:____________________________________DATE:___________
OpenMeeting&Presentsafetytopic:OverheadHazards
Employeespresent:
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
MEETINGCHAIREDBY:_______________________________
You might also like
- Skills for Learner Drivers: A Guide for Instructional SupervisorsFrom EverandSkills for Learner Drivers: A Guide for Instructional SupervisorsNo ratings yet
- Assigment 3Document7 pagesAssigment 3PradeepNo ratings yet
- NEBOSH IGC 2 February 2022 Solved PaperDocument7 pagesNEBOSH IGC 2 February 2022 Solved PaperMuhammad Ramzan100% (1)
- Competency Based Learning Materials: SectorDocument26 pagesCompetency Based Learning Materials: Sectorgil abanador92% (13)
- Fire Training WorkbookDocument15 pagesFire Training WorkbookJames GanaNo ratings yet
- Filipino Traits CharacteristicsDocument26 pagesFilipino Traits CharacteristicsJay DexNo ratings yet
- 3 Seconds To SafetyDocument12 pages3 Seconds To SafetyJPC RADARNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Q1W4 PCO 2Document28 pagesGrade 9 - Q1W4 PCO 2Gemmy Ronald TevesNo ratings yet
- Ia-Carp Q1 W4 PDFDocument17 pagesIa-Carp Q1 W4 PDFLaurenceFabialaNo ratings yet
- Task Exposure AnalysisDocument24 pagesTask Exposure AnalysisDaren Bundalian RosalesNo ratings yet
- Toolbox Talks 2013Document28 pagesToolbox Talks 2013pakistaniNo ratings yet
- Task 03Document9 pagesTask 03Mian AdilNo ratings yet
- Safety Training Ideas Worth StealingDocument38 pagesSafety Training Ideas Worth StealingGrace Passini100% (5)
- Carpentry: Practice Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresDocument17 pagesCarpentry: Practice Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresLaurenceFabialaNo ratings yet
- Accident Incident Investigation and ControlDocument6 pagesAccident Incident Investigation and ControlEdmil PabellanoNo ratings yet
- Nebosh: Management of Health and Safety Unit Ig1Document5 pagesNebosh: Management of Health and Safety Unit Ig1asifniazi4No ratings yet
- 01 Adolphus PPT Lesson Introduction Nc2Document56 pages01 Adolphus PPT Lesson Introduction Nc2Lindyl BrionesNo ratings yet
- Local Induction by Line Manager Stockley Park CampusDocument5 pagesLocal Induction by Line Manager Stockley Park CampustesNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document48 pagesPresentation 4Emma LoreinNo ratings yet
- Grade 11-Q1 - W4-PCO-2Document28 pagesGrade 11-Q1 - W4-PCO-2Juren Andrew NievesNo ratings yet
- ColaDocument4 pagesColaJeremy Lim Choon KeatNo ratings yet
- HE BPP Module.8 Gr7-8Document23 pagesHE BPP Module.8 Gr7-8Julie Ann Carsula Cister IIINo ratings yet
- Automotive ModuleDocument21 pagesAutomotive ModuleRommel Benoza Herno100% (2)
- Emergency Evac PlanDocument16 pagesEmergency Evac Planmark100% (1)
- Tool Box TalksDocument82 pagesTool Box TalksMuhammad Asif MehmudNo ratings yet
- Obeying Traffic Laws-Tips On Making The Road A Safer PlaceDocument2 pagesObeying Traffic Laws-Tips On Making The Road A Safer PlaceGElla BarRete ReQuilloNo ratings yet
- Daffa Sayyidina - 1 LD (Safety Symbols in A Workshop)Document14 pagesDaffa Sayyidina - 1 LD (Safety Symbols in A Workshop)Daffa SayyidinaNo ratings yet
- New WordDocument22 pagesNew WordJelly Joy CampomayorNo ratings yet
- TLE-8 LAS Q2 Week4 NAIL-CAREDocument11 pagesTLE-8 LAS Q2 Week4 NAIL-CAREMint XNo ratings yet
- HFS Restoration ProjectDocument6 pagesHFS Restoration Project1mishaNo ratings yet
- Engg-411-Form-1-Planning - NMMDocument7 pagesEngg-411-Form-1-Planning - NMMNatasha Marie MallareNo ratings yet
- 11 Ways To Keep Your Construction SafeDocument14 pages11 Ways To Keep Your Construction SafegirlNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment 1 PDFDocument66 pagesHazard Identification, Risk Assessment 1 PDFHassan AliNo ratings yet
- General - Safety - Quality ControlDocument137 pagesGeneral - Safety - Quality ControlRandy PedrozaNo ratings yet
- Hazards and Risks Identification and ControlDocument4 pagesHazards and Risks Identification and ControldawnNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1 SealantDocument7 pagesInformation Sheet 1 SealantCourei-FxAlcazarNo ratings yet
- Airs-Lm 1Document21 pagesAirs-Lm 1Jumar BaldrezNo ratings yet
- 2 Feb 2022 ExamDocument15 pages2 Feb 2022 ExamRafa'eel BickooNo ratings yet
- Accident Prevention ProgramDocument4 pagesAccident Prevention ProgramVitaliy TsuzNo ratings yet
- Loss Investigation Ace UsaDocument8 pagesLoss Investigation Ace Usal_masraniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 GSMDocument20 pagesUnit 1 GSMBala SbNo ratings yet
- New Security and Safety Tips For The Yuletide SeasonDocument18 pagesNew Security and Safety Tips For The Yuletide SeasonChristopher UcheNo ratings yet
- Fleet Safety EbookDocument16 pagesFleet Safety EbookSrikanth BammhideNo ratings yet
- 20 Workplace Safety Rules and Tips To Know: SafetyinfoDocument5 pages20 Workplace Safety Rules and Tips To Know: Safetyinfogoyalvikas86No ratings yet
- Tve 11 - CSS 1ST Semester Midterm Module 2 (Davide)Document9 pagesTve 11 - CSS 1ST Semester Midterm Module 2 (Davide)winslet villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Road RisksDocument9 pagesOccupational Road RisksStephen MumbaNo ratings yet
- Contingency Plan For FireDocument5 pagesContingency Plan For FireCharisse Kharyle60% (5)
- 5 Step Risk AssessmentDocument11 pages5 Step Risk AssessmentRuppee EdwardNo ratings yet
- Eye SafetyDocument4 pagesEye Safetymnkoanyane16No ratings yet
- FME1Document1 pageFME1Angelo ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Deadly Dozen of Unsafe ConditionsDocument10 pagesThe Deadly Dozen of Unsafe ConditionsRobVajko100% (1)
- Employee Safety Manual: Apollo Retail Specialists LLCDocument23 pagesEmployee Safety Manual: Apollo Retail Specialists LLCodnoder23No ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Risk - AssessmentDocument62 pagesUNIT 5 Risk - Assessmentbabusureshdev5639No ratings yet
- Safety SecurityDocument14 pagesSafety SecuritySk BipuNo ratings yet
- Store Employee Safety Handbook: Dear Dollar General EmployeeDocument6 pagesStore Employee Safety Handbook: Dear Dollar General EmployeeLaura HugginsNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Tennis ActivatorsDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment For Tennis ActivatorsJac MacNo ratings yet
- Crowd and Crisis Management Learning ActivitiesDocument6 pagesCrowd and Crisis Management Learning ActivitiesJamaica PicoNo ratings yet
- Module 5-Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresDocument7 pagesModule 5-Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresJelie PanganNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 16Document4 pagesHuman Resource Management 16Noman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Practices in A Construction ProjectDocument60 pagesRisk Management Practices in A Construction ProjectAlimi JasmanNo ratings yet
- APM Assign2Document5 pagesAPM Assign2emmanuel_nyirendaNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 475 3501Document10 pages10 1 1 475 3501emmanuel_nyirendaNo ratings yet
- Information and Communications University School of HumanitiesDocument8 pagesInformation and Communications University School of Humanitiesemmanuel_nyirendaNo ratings yet
- 682.APM Assignment September, 2017-2Document1 page682.APM Assignment September, 2017-2emmanuel_nyirendaNo ratings yet
- CPD Me FrameworkDocument15 pagesCPD Me FrameworkRicardo FoleyNo ratings yet
- M & E TermilogiesDocument40 pagesM & E TermilogiesBobb KetterNo ratings yet
- Copper Bonded Steel Earth RodDocument9 pagesCopper Bonded Steel Earth Rodemmanuel_nyirendaNo ratings yet
- M & E TermilogiesDocument40 pagesM & E TermilogiesBobb KetterNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 EiDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 Eiemmanuel_nyirendaNo ratings yet
- Safety Briefing For September 2011Document12 pagesSafety Briefing For September 2011emmanuel_nyirendaNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument11 pagesSensors and TransducersGloriaNo ratings yet
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeFrom EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Handbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesFrom EverandHandbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Tensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesFrom EverandTensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- General Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismFrom EverandGeneral Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismNo ratings yet
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesFrom EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesNo ratings yet
- Autophagy in Health and DiseaseFrom EverandAutophagy in Health and DiseaseBeverly RothermelNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo ratings yet
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesFrom EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Hazardous Chemical PropertiesFrom EverandHandbook of Hazardous Chemical PropertiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Environmental and Health and Safety Management: A Guide to ComplianceFrom EverandEnvironmental and Health and Safety Management: A Guide to ComplianceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)